(e) the fixation of carbon dioxide and the light- independent stage of photosynthesis
1/6
Earn XP
Description and Tags
To include how the products of the light-dependent stage are used in the light-independent stage (Calvin cycle) to produce triose phosphate (TP) with reference to ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP), ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase (RuBisCO) and glycerate 3-phosphate (GP) – no other biochemical detail is required.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
The light-independent stage and what does it produce
referred to as the Calvin cycle
This stage produces complex organic molecules, including (but not limited to)carbohydrates, such as:
Starch (for storage)
Sucrose (for translocation around the plant)
Cellulose (for making cell walls)
Where can the light independent stage take place?
does not require energy from light
can therefore take place in light or darkness. However, as it requires inputs of ATP and reduced NADP from the light-dependent stage,
it cannot continue indefinitely in darkness, as these inputs will run out
What are the three main steps within the Calvin cycle
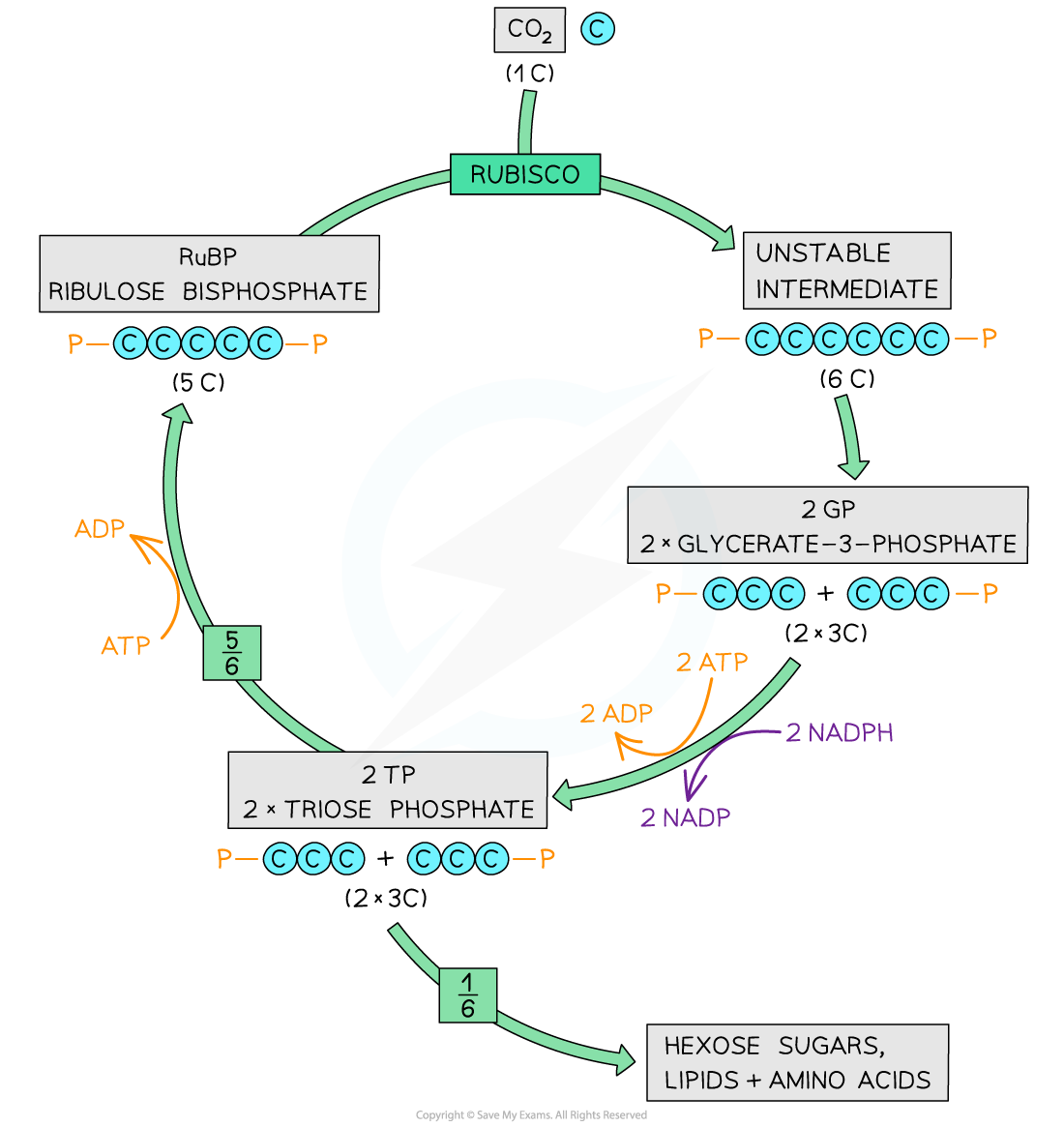
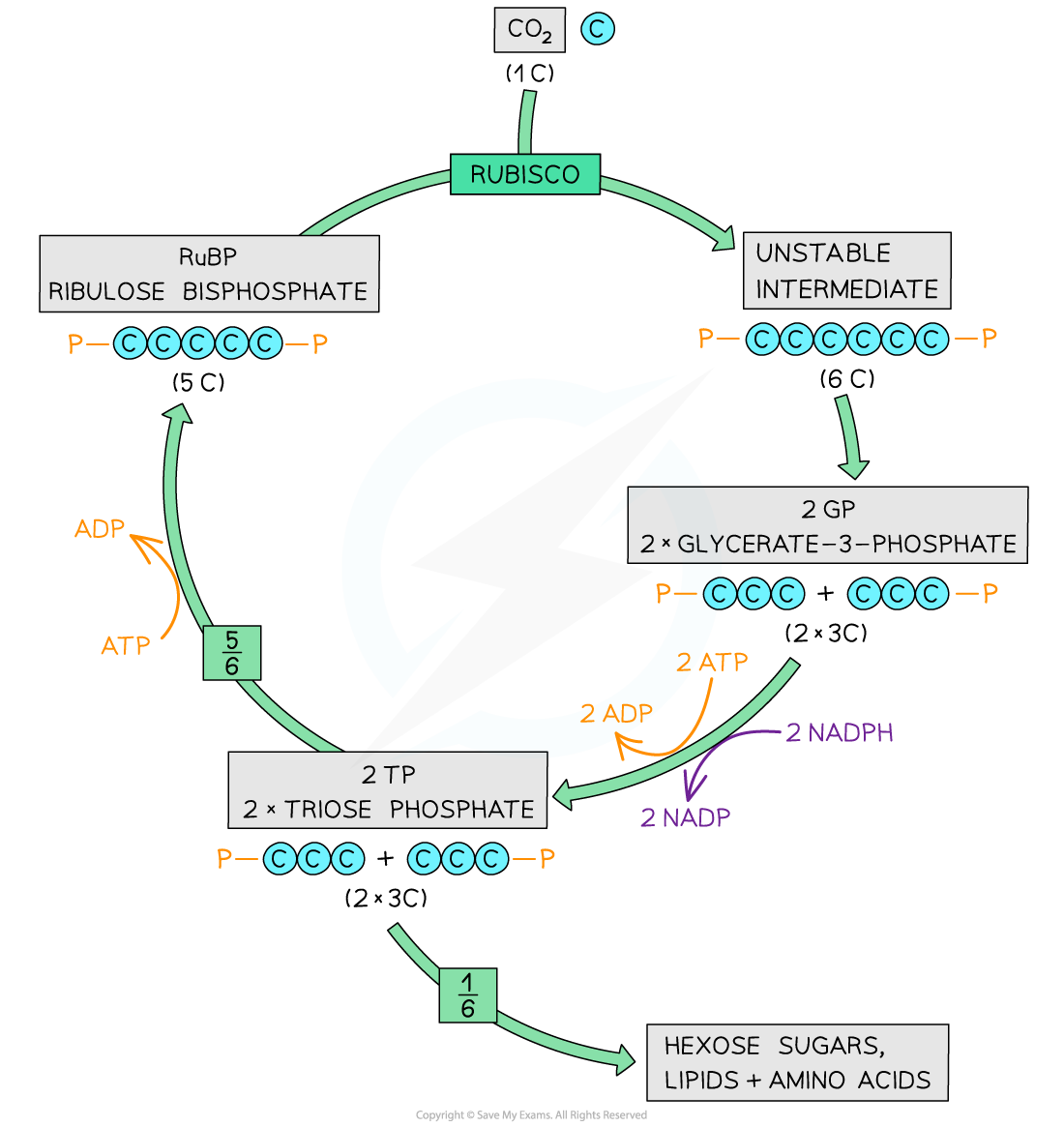
Rubisco catalyses the fixation of carbon dioxide by combination with a molecule of ribulose biphosphate (RuBP), a 5C compound to yield Two molecules of glycerate 3-phosphate (GP), a 3C compound
GP is reduced to triose phosphate (TP) in a reaction involving reduced NADP and ATP
RuBP is regenerated from TP in reactions that use ATP.
Carbon fixation
Carbon dioxide combines with a five-carbon (5C) sugar known as ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP)
An enzyme called rubisco (ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase) catalyses this reaction
The resulting six-carbon (6C) compound is unstable and splits in two
This gives two molecules of a three-carbon (3C) compound known as glycerate 3- phosphate (GP)
The carbon dioxide has been ‘fixed’ (it has been removed from the external environment and has become part of the plant cell)
Glycerate 3-phosphate (GP) is not a carbohydrate but the next step in the Calvin cycle converts it into one
Reduction of glycerate 3-phosphate
Energy from ATP and hydrogen from reduced NADP – both produced during the light-dependent stage of photosynthesis – are used to reduce glycerate 3-phosphate (GP) to a phosphorylated three-carbon (3C) sugar known as triose phosphate (TP)
One-sixth of the triose phosphate (TP) molecules are used to produce useful organic molecules needed by the plant
Regeneration of ribulose bisphosphate
Five-sixths of the triose phosphate (TP) molecules are used to regenerate ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP)
This process requires ATP