APHUG Midterm Review Notes
1/52
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
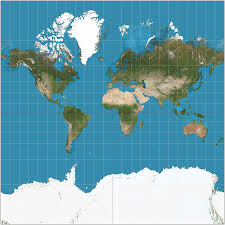
Mercator Projection
A map projection that is distorted towards the poles but useful for navigation.
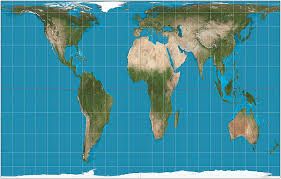
Gall-Peters Projection
A map projection that accurately represents size but distorts shape at the poles.
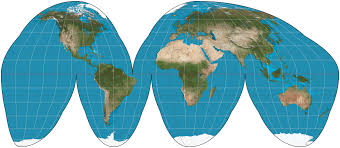
Goode Homolosine Projection
An interrupted map projection that maintains good size and shape but has poor directional accuracy.
Reference Maps
Maps that show boundaries, names, and geographic features.
Small Scale Map
A map that covers a large area with little detail.
Large Scale Map
A map that covers a small area with lots of detail.
Thematic Maps
Maps that show spatial patterns using specific data.
Choropleth Map
A thematic map where colors and shading indicate values.
Dot Density Map
A thematic map that uses dots to represent specific locations and values.
Graduated Circle Map
A thematic map that displays population-based data using circles of varying sizes.
Isoline Map
A map that groups areas according to a shared value, using lines or colors.
Cartogram
A map in which the size of areas is distorted to represent population or another variable.
Flowline Map
A map that illustrates the directionality of movement.
Absolute Direction
Cardinal directions (north, east, west, south).
Absolute Location
The exact location defined by latitude and longitude.
Relative Direction
A direction based on the surroundings (e.g., left, right).
Relative Location
A description of a place based on its features and distance from other places.
GIS
Geographic Information Systems; layered satellite images used for analysis.
Remote Sensing
The acquisition of information about an object or area from a distance, often through satellite images.
GPS
Global Positioning System; location data using latitude and longitude.
Field Observation
Firsthand data gathering through direct observation.
Secondhand Observation
Data from documents, interviews, and narratives.
Qualitative Data
Data in word form, interpretive in nature, such as opinions.
Quantitative Data
Numerical data that is replicable, such as census results.
Spatial Concepts
Ideas concerning location and relationships in space.
1st Law of Geography
The principle that relatedness decreases with distance.
Distance Decay
The diminishing interaction that occurs with increasing distance.
Time-Space Compression
The reduction of travel time that increases interaction.
Interdependence
The reliance that develops from exchanges of goods and resources.
Networks
Organized functional systems connecting nodes and flows.
Node
A central location for processes or functions.
Diffusion
The movement of items in space and over time.
Spatial Association
The relationship between objects or phenomena in a given area.
Clustered/Nucleated
A spatial pattern where objects are close together.
Dispersed
A spatial pattern where objects are spread out widely.
Sustainability
The capacity to use resources without compromising future generations.
Environmental Determinism
The theory that environment limits lifestyle choices.
Environmental Possibilism
The idea that while environmental limits exist, they can be modified with technology.
Land Use
The way land is utilized for different purposes such as agriculture, industry, and housing.
Renewable Resources
Natural resources that regenerate over time, like trees and water.
Non-renewable Resources
Finite resources that cannot be replaced easily, like oil and coal.
Scale of Analysis
The level of perspective applied to observational data, such as global, regional, or local.
Ecumene
The permanently settled areas of the Earth.
Population Density
The number of people living in a space relative to its area.
Arithmetic Density
Total population divided by land area.
Physiological Density
Total population divided by arable land area.
Pull Factor
Attributes that attract people to an area.
Push Factor
Attributes that deter people from an area.
Dependency Ratio
The ratio of dependent individuals (youth and elderly) to the working-age population.
Demographic Transition Model
A model that describes population changes over time in stages.
Overpopulation Theory
The idea that population growth outpaces food production.
Anti-Natalist Policies
Government policies aimed at decreasing birth rates.
IMR, CMR, MMR
Indicators used to assess healthcare quality: infant mortality, child mortality, and maternal mortality rates.