Cognitive Unit Vocab
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Key vocab for the cognitive Unit of IB Psychology SL
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
Schema
a mental representation of knowledge
Helps us to understand and assume how something works and what something is based on past experience
Schema Theory
states that all knowledge is organized and stored in units
when new schema is taken in, it is compared to pre-existing schemas found in memories
When these new schemas don’t match the schema we have, there is an emotional response: disappointment, confusion, frustration
based on the assumption that humans are are active processors of information
subconsciously interpret and integrate it to make sense of our experiences
if information is ever missing, the brain fills it in with schemas
limited by it not yet being clear how schemas are initially produced and their exact influence on cognitive processes as well as not accounting for why, in schema, inconsistent information is sometimes recalled
Stages of Memory
Encoding
Storage
Retrieval
Encoding
transforming sensory information into a meaningful memory
Storage
creating a biological trace of the encoded information in memory
the memory will either be retained or llost
Retrieval
using stored information and bringing it out of storage for thinking, problem-solving, and decision-making
the memory will then be rencoded but is susceptible to distortion or alteration
Assimilation
when there is no schema for something and the new and different information is categorized with old schema
may lead to inaccuracy in categorization and assumption
Accommodation
modifying the actual schema or creating an entirely new one to categorize new information
Leveling
when elements of a memory are removed or toned down
could be intentional or unintentional
Sharpening
elements of a memory are highlighted or exaggerated
could be intentional or unintentional
Script
patterns of behavior that are learned through our interaction with the environment
developed in a cultural context and is not universal
if an event doesn’t follow the script, it causes confusion or frustration
new knowledge and experience will eventually incorporate into our script
Cognitive Mental Processes
perception, thinking, decision-making, problem solving, memory, language, and attention
bottom-up processing
sensory information that comes to us from interactions with the enviornment
top-down processing
when information is processed in the mind via pre-stored memory
Cognitive Misers
states that we make the choice to not actively process information as to save time and effort
Multi-Store Memory Model
Proposed by Atkinson & Shiffrin (1971)
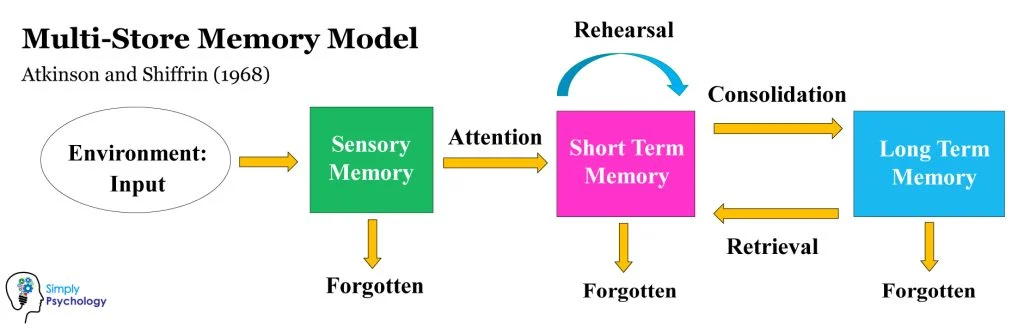
long term memory
if information is rehearsed or attached in some way, it is recorded and transferred into long term memory
has an unlimited capacity with an unknown duration
short term memory
AKA: working memory
if sensory information is recognized or considered important, it is coded and sent to short-term memory
limited capacity for 7+-2 units for 20-30 seconds
semantic memory
factual knowledge in which conscious thought calls up learned knowledge such as facts about the world
stored in prefrontal cortex and hippocampus
episodic memory
autobiographical memories in which conscious thought recalls personal experiences
stored in prefrontal cortex and hippocampus
procedural memory
memories of how to do something, similar to mussel memory and habit
implicit memory allowing action to be performed subconsciously
“how to“ knowledge
stored in the motorcortex then sent to the cerebellum
working memory model
developed by Baddeley and Hitch (1974)
believed that short term memory is not just one store, this model focuses on STM as an active space
states that LTM is a passive store that holds previously learned material for use of STM as needed
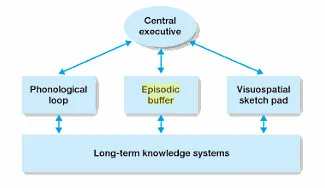
Central Executive
directs attention to tasks, general attention control
automatic level: based on habits that rely on schemas in LTM and are controlled mostly automatically by stimuli in the environment
supervisory attention: deals with planning and decision-making, creates new strategies when old ones are insufficient, active in emergency situations
handles problem-solving
limited capacity
modality-free
can process any sensory information (auditory or visual)
Phonological loop
limited capacity
handles auditory information and language (spoken and written)
any activity that requires retention of verbal sequences relies on the phonological loop
can be divided into two components
articulatory control system: the inner voice which can hold information in a verbal form
phonological store: the inner ear, holds auditory memory traces (only lasts for 1.5-2 sec if not rehearsed), can receive information directly from sensory memory in the form of auditory material from LTM
visuo-spatial sketch pad
limited capacity
“the inner eye“
stores visual and spatial information
visual: what things look like (iconic memory)
spatial: relationships between things
episodic buffer
detected to linking information across domains to form integrated units of visual, spatial, and verbal information with time sequencing
temporarily holds several sources of active information at the same time while you consider what is needed in the moment
memory
refers to the process by which information is encoded, stored, and retrieved
declarative memory
memory of facts and events and refers to memories that can be consciously recalled
this includes the episodic memory and the semantic memory
dual task technique
a procedure where participants carry out two tasks at once
verbal protocols
a process where participants think out loud as they carry out a task
dual process model
poses that we have two systems of thinking and we are always in one (system 1 & system 2)
system 1
focuses on what it seems
quick and prone to error
based decisions on past knowledge
takes heuristics (shortcuts)
operates automatically
doing things a lot can make them a system 1 process
system 2
requires concentration and effort
works with abstract concepts
works through logic
uses conscious reasoning
more reliable but slower
requires more energy
ego depletion
when there is too much on our mind to allocate energy and the cognitive load is too high
Law of easiest effort
when we experience ego depletion and there are several ways to achieve the same goal, people will choose the least demanding course of action
cognitive load
refers to the amount of working memory resources used
thoughts
occur when engaging in a cognitive process
can occur with or without emotion
the way a thought is remembered can be impacted when emotion is involved
three parts of emotion
physiological changes
subjective feelings
associated behaviors
physiological changes
physical changes in the body as a result of emotion
EX: heart racing, sweating, fight or flight
subjective feelings
Descriptors or feelings associated with particular emotions
EX: happy, sad, angry, excited
associated behaviors
actions that occur as a result of emotions
EX: smiling, running, crying
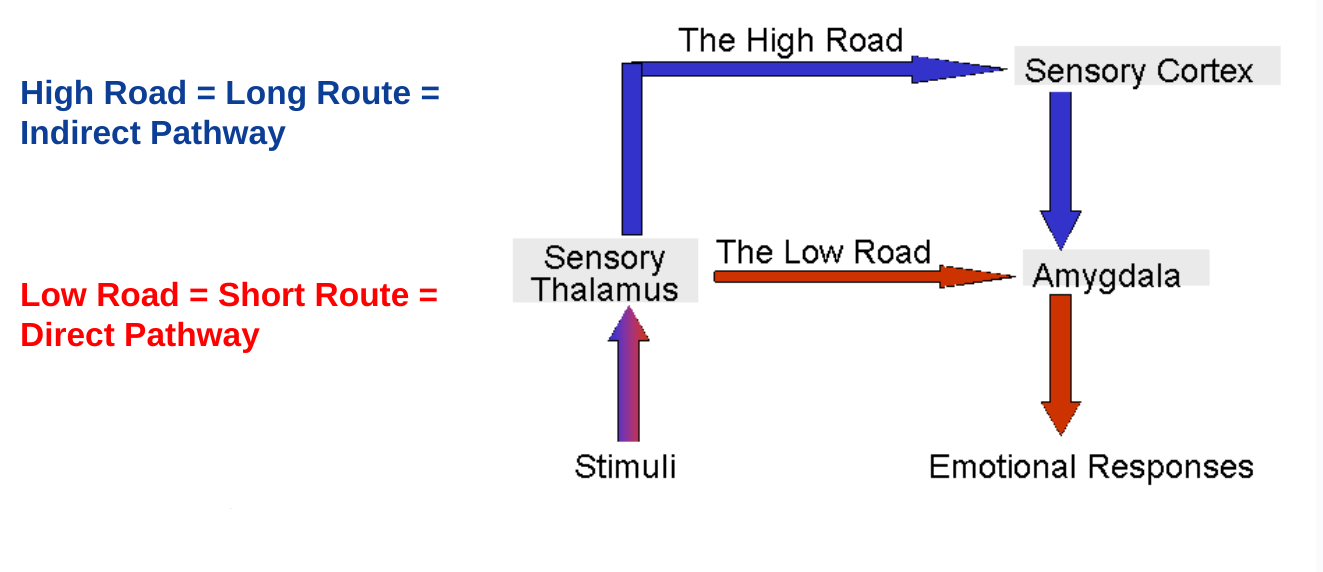
Le Doux (1999)
model of emotional pathways
having both a direct and indirect pathway enables flexibility in response which is an adaptive advantage
flashbulb memory
a unique highly emotional moment and can give rise to a clear, strong, and persistent memory
we often think these memories are more accurate, but they aren’t
proximity adds confidence to memory accuracy
characters and criteria of a flashbulb memory:
place: where they were when the event occurred or when they found out
ongoing activity: know what they were doing when the event occurred or when they found out
Informant: how they found out about the event
own effect: how the event made them feel
other effect: how the event made others feel
aftermath: what happened following the event
Thinking
the process of using knowledge and information to make plans and make Interpretations and predictions about the world
components of thinking:
problem-solving, creativity, reasoning, and decision-making
decision-making
the process of identifying and choosing alternatives based on values and pretenses of the decision maker
needed during problem-solving to reach a conclusion
problem-solving
thinking that is directed towards solving specific problems by means of a set of mental strategies
special-mechanism hypothesis
argues that for the existence of a special biological memory mechanism that, triggered by an event exceeding critical levels of surprise, creates a permanent record of the details and circumstance surrounding the experience
flashbulb memories are different to “ordinary memories“
resistant to forgetting
Importance-driven model
emphasizes that personal consequences determine the intensity of emotional reactions
commonly accepted model of a flashbulb memory
Leading questions
questions that either by the form or the content suggest to a witness which answer is desired
questions that are suggestive in some sort of way
misinformation effect
both leading questions and post-event information facilitate schema processing which may influence the accuracy of recall
post-event information
any information that you are exposed to after you have witnessed something
can come from TV/social media reports or hearing other people’s stories
Cognitive Biases
heuristics that result in patterns of thinking or decision making that are consistent and inaccurate
refers to the result of trying to fit in for self-esteem and not dependent on heuristics
Peak-end rule
a heuristic in which people judge an experience largely based on how they felt at its peak and at its end
occurs regardless of a positive or negative experience
other information is not used in reaching a decision or judgement
prospect theory
describes the way people choose between alternatives that involve risk when probabilities of outcomes are known
people evaluate these losses and gains using heuristics, EX: the framing effect
Anchoring bias
the tendency to rely too heavily on the first piece of information given when making decisions
occurs when individuals use an initial piece of information to make subsequent judgements
applied in: bargining, shopping, determining sentencing, and estimations
framing effect
people react to choices depending on how they are presented or “framed“
people prefer certain outcomes when information is framed in positive language and vice versa
when we expect success, we prefer a definitive win rather than a possible win, but when things look bad, we will gamble on an uncertain defeat rather than a definite loss
somatic marker
feelings in the body associated with emotions
EX: rapid heartbeat with anxiety
somatic marker hypothesis
suggests that good decision making depends on an ability to access appropriate emotional information linked to the situation in which the decision is being made
heuristic
a mental shortcut to allow for quick decision making
an element of system 1 processing
straight forward rules of thumb based on past experiences
availability heuristic
decisions made based on the availability of information
representative heuristic
when we assume one case is more representative than it actually is
questionnaires
any written set of questions with the goal to collect qualitative data
personal consequentiality
states that if you were closer related to the event, then there will be a stronger emotional reaction