Ruminant Nutrition Final
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
110 Terms
What are the defining characteristics of ruminants
pre gastric fermentation
herbivores
ungulates
The rumen is composed of 5 sacs. Which one is NOT considered a sac of the rumen?
Reticulum
Why should a prey species have a ruminant gastrointestinal tract?
ruminant digestive system allows for increased time in between means
ruminants can digest later on in a safe place
Volatile fatty acids are an end product of fermentation. What are the 3 most common VFA's and their total number of carbons?
Acetate C2, Propionate C3, Butyrate C4
The _______ is the main site of pre gastric fermentation, while the reticulum does this but also catches harmful objects. Most water absorption happens in the ________ which may also act as a pump regulating liquid passage. The ______ is the site gastric secretions. Absorbing nutrients within the stomach complex happens most efficiently in the ______
Rumen, Reticulum, Omasum, Abomasum, Rumen
In the abomasum, cheif cells synthesize ____.
Pepsin
Why is it important to know the evolution of the ruminant gastrointestinal tract?
The adaptation of the ruminant GI tract allows diverse species to thrive through symbiosis.
What does the microflora NOT contribute to the symbiosis relationship with a ruminant?
controls the temperature
What is an example of a chemical property that influences digestion?
heat treatment
T/F: Dry matter intake and physical characteristics of feed influence residence time, while rate of fermentation is influenced by concentration of microbes and intrinsic traits of feed.
True
What type of grazing strategy do sheep exhibit?
Intermediate feeder
What happens in the gastrointestinal tract of a browser?
Lower retention time
The prehensile action of cattle and goats differ. Generally, _______ are the least discriminate when choosing what to eat whereas _________ are the most discriminate because they use their lips and teeth to pick through plant parts easily.
Cattle, goats
Why is it not always a good idea to put sheep and cattle together when interspecies grazing?
They compete for the same resource
Typically, cattle are harvested around 80% of physiological maturity. Which of the following might result in a shift of the ideal time of harvest from 80% of physiological maturity for cattle? Select all that apply.
Change in feed price
change in value of the animal
Where is puberty defined on the composition of gain curve?
more than 50% of caloric intake contributes to adipose gain
Where do animals partition nutrients to before anything else?
Maintenance
Why is it difficult to get dairy cows pregnant during lactation?
They partition nutrients toward lactation over reproduction
Which nutrients provide energy for the body to use? Select all that apply.
Carbs, protein, lipids
The amount of energy to raise the temperature of 1 mL of water by 1 degree Celsius is a _______
calorie
What units of measure are most often used for energy among ruminant nutritionists when evaluating cattle diets?
Mcal
Having a positive retained energy means cattle have enough energy towards development, gain, or lactation. What does it mean when an animal is in a negative energy balance?
Expending more energy than they are getting from food
Immunity, Reproduction, Lactation, Muscle, etc. have a metabolic priority in the body. What happens in the bloodstream regarding delivery of nutrients?
Changes in nutrient flux depending on the metabolic priority
In the net energy system, there is ______ energy lost between gross energy and digestible energy. Net energy is differentiated from metabolizable energy due to _____ energy losses.
fecal, heat
What does TDN stand for?
Total digestible nutrients
What is the fatal flaw with the TDN calculation?
The assumption that protein and carbohydrates have the same amount of energy per gram
Animals metabolize protein to use for energy. What happens when an animal consumes more protein than it needs?
Energy is lost through urea
T/F: The energy in 1 kg of corn = the energy in 1 kg of alfalfa
False
Why is the TDN assumption of energy from protein an issue?
amount of protein consumed is dynamic
it can depend on the animals need to metabolize protein for energy
there is not always the same metabolic cost to metabolize protein from animal to animal
Energy is important when formulating cattle diets because we want to add pounds to an animal that will increase its value at market. How can we guess the final shrunk body weight of an animal we are feeding?
using frame size
using mother’s body weight at maturity
using industry averages
It is difficult to measure NEg in growing animals. Why is it much easier to measure energy used by a dairy cow?
Energy can be directly measured trough the milk
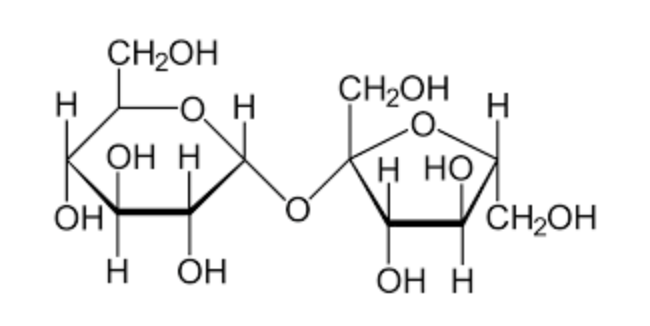
The types of glycosidic linkages between monosaccharides have major effects on energy and gain when metabolized in a growing animal. What type of glycosidic linkage does sucrose have?
alpha
Which is not a function of carbohydrates used by ruminants?
Structural components of muscles fibers
T/F carbohydrates are required for the body each day to function
False
Amylose, Amylopectin, and Glycogen are all forms of starch used by ruminants. What is the structural benefit of these molecules being branched? Select all that apply.
Branched molecules have a greater amount of anomeric carbons to increase solubility in water
braning compacts the molecule requiring less space
In aerobic fermentation, oxygen acts as the final electron acceptor. What does not act as a final electron acceptor in anaerboic fermentation?
Ca+
Ruminant ______ can breakdown starch, cellulose, and hemicellulose into glucose or fructose. Glu and Fru go through __________ to form pyruvate. Pyruvate creates _______ from fermentation that can further be metabolized and used by the animal.
microbes, glycolysis, VFAs
Microbes are beneficial when an animal does not have the ability to digest a nutrient itself. What is a cost to the ruminant with the presence of microbes?
Microbes oxidize nutrients the animal could utilize on its own
VFAs are important because they are used for many functions throughout the body. Acetate is used for ________ synthesis. _________ is used in gluconeogenisis to form glucose. Epithelial fuel sources, like _______ , are other types of energy that allow for glucose sparing by gastrointestinal tissues.
Lipid, Propionate, Butyrate
What are the benefits of altering the VFA profile to propionate?
Decreased methane production
increases circulating glucose
Feed processing increases rates of digestion and influences changes in VFA's, like greater propionate digestion. Which is not a type of feed processing?
Adding an essential oil
Ionophores, like monensin, are used in more than 90% of cattle diets. What is an effect of adding an ionophore to a ration?
Increased propionate production
Buffers are used in cattle diets to control acidity of the rumen. Typically, a weak base is used. It dissociates and creates an ion in the rumen. The greater amount of ions create a ________ environment that increases body water flow into the rumen. Essentially, flushing the __________ out of the rumen and diluting the ruminal liquid
Hydrophobic, Acid
Lactic acidosis is caused when the pH decreases and lactogenic bacteria take over due to highly fermentable carbohydrates in the diet. What are signs of lactic acidosis? Select all that apply.
Abscessed liver, poor feed intake, diarrhea, laminitis
T/F: Fiber is digested in the small intestine of ruminants
False
Associative effects can be positive or negative depending on the concentrate:forage ratio and bacteria that participate in the fermentation of those feeds for energy. What is an example of a negative associate effect?
Competition within the microflora of the rumen
Amino acids are all structured with an amine group, a carboxyl, and an R group. Which amino acids are used in protein production?
Alpha
From the diet, proteins are used for many metabolic mechanisms. What is not a function of protein?
Formation of triglycerides
The multiple stave hypothesis explains that ruminants can only synthesize as much protein according to the concentration of the limiting amino acid. What can we do to increase protein synthesis?
Increase the concentration of the limiting amino acid
Crude protein is a guess based off of the percent Nitrogen multiplied by a constant. Why do nutritionist use crude protein versus true protein? Select all that apply.
It is hard to account for microbial crude protein
nitrogen concentration is easily measurable
In ruminal fermentation of protein, there is a soluble fraction, a potentially fermentable fraction and a non-fermentable by microbes fraction. Which parts make up the equations for ruminally degradable protein and ruminally undegradable protein?
RDP= cA+dB
RUP = c+ uB
The rate of disappearance (Kd) of protein is influenced by what factors? Select all that apply.
Heat, particle size, rumen pH
The concept of asynchrony revolves around the animal rapidly fermenting carbohydrates, but not having enough protein available to the microbes. What is a consequence of this?
Decreased fermentation
Why is it less common to see protein and carbohydrate synchrony?
The urea cycle keeps high amounts of protein cycling for 3-4 days
Why does the liver resynthesize urea from ammonia (NH3) and CO2?
NH3 is a charged molecule
How much metabolizable protein is provided to the ruminant from MCP?
64%
T/F: amino acids fed to an animal are the same amino acids found in the product made from the animal.
False
Limiting amino acids prevent protein use by livestock. What can we do when feeding production animals to meet their different amino acid requirements?
Use protein complementation
What are other ways to increase protein utilization in livestock, besides protein complementation? Select all that apply.
Synthetic amino acids
ruminally protected amino acids
_____ AA are not synthesized in the body but are used for protein synthesis. _______ AA are not synthesized in adequate amounts to support an important physiological process.
essential, functional
Which vitamins can be synthesized in the rumen
Vitamin K, Vitamin B
Is water hardness an issue in terms of palatability for ruminants?
No
Calcium should be supplied at _______ % DM from _______ in cattle rations.
1, limestone
What macro mineral is important to feeding DDGS
Sulfur
In green lush pastures spring cattle may develop grass tetany. Producers can provide high _____ mineral to unlock alternative absorption pathways to alleviate mineral interactions in the spring forages.
Magnesium
Ruminants lose water in many different ways. Which one has the greatest total body water loss (>50%)?
Respiration
What factors influence water intake in ruminants?
temperature, availability, DMI, Lactation
If cattle do not seem to be eating, what is the first thing a producer should consider?
Checking the waterer
Water can be expressed as a function of body weight. On average, about how much water should cattle be consuming per day?
1 gal/100 lbs
Along the gastrointestinal tract, the epithelium consist of columnar epithelium. These epithelium have directionalitymeaning there is an apical and basolateral side.
columnar, directionality
What is this primary role of vitamins and trace minerals in the ruminant feeding industry
Aid as a vehicle whereby service fees are charged to producers
What is commonly used to protect against iodine deficiency?
Ionized salt
Where are trace minerals typically stored?
tissue
What source of trace minerals is typically the cheapest?
Inorganic
Animals do not require any nutrient as a percent. What is a reasonable estimate to establish a nutrient requirement?
DMI
All warm-blooded mammals eat to a common energy endpoint when not limited by physical fill. T/F
True
When the caloric density of the diet increases then total feed intake _____ and the energy intake _____
decreases, stays the same
What mechanism currently explains how cattle achieve satiety in short periods of time?
hepatic oxidation theory
Chemostatic regulation of intake relates to the hormones and nervous signaling that tell the brain to stop eating. What affects this? Select all that apply.
Rate of digestion, soluble nutrients, caloric density of the diet
Ruminants and nonruminants differ in the sense of metabolic fuels because nonruminants utilize ____________ while ruminants utilize propionate.
glucose F
Feed intake increases propionate that then signals satiety through what reaction
oxidation
The hormone leptin from________ decreases appetite and decreases body weight. Ghrelin is another hormone from the _______ that increases appetite and increases body weight.
adipose, stomach
Why might an animal feel hungry if they have increased body fat when leptin is supposed to decrease appetite?
Insulin has a negative feedback on leptin
The hepatic oxidation theory's function on short-term feed intake is thought to function similarly in ruminants and non-ruminants. Why then does the difference in digestion of food in ruminants result in an increased importance when feeding highly fermentable diets? Select all that apply.
High risk of acidosis, rapid fermentation means more acid production
Are predictions of dry matter intake increased, decreased, or not affected by anabolic steroids?
Increased by 6%
Propionate from rumen fermentation of CHO is used in which metabolic process to help in the formation of energy for the animal to use?
TCA cycle
Dairy x Beef crosses entering the beef system is a great example of how DMI is affected by breed type because...
Crosses eat 4% more than beef animals
What drives predictions of dry matter intake when one assumes no environmental or outside influences?
Caloric content of the diet
The presence of mud ________ intake and _________ caloric expenditure.
decreases, increases
Which ionophore contributes to reductions in daily feed intake?
Monensin
What are the end products of digestion of carbohydrates in the rumen?
VFA, MCP, CO2, CH4, H
In the digestion theory, which of these variables are (reaction rate, digesta retention time, concentration of reactants, reactor volume) positively related to digestion and which are negatively related to digestion?
reaction rate: positive
concentration of reactants: negative
reactor volume: negative
digesta retention time: positive
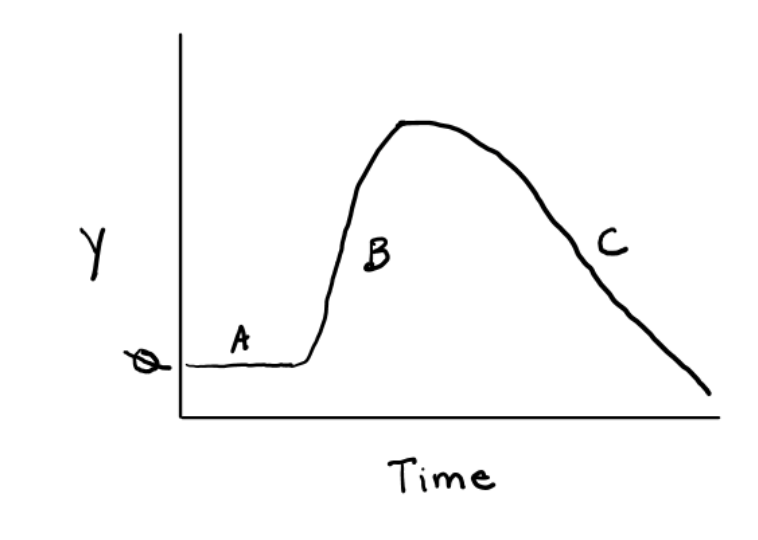
What is the y-axis is this graph illustrating retention time?
rate of appearance
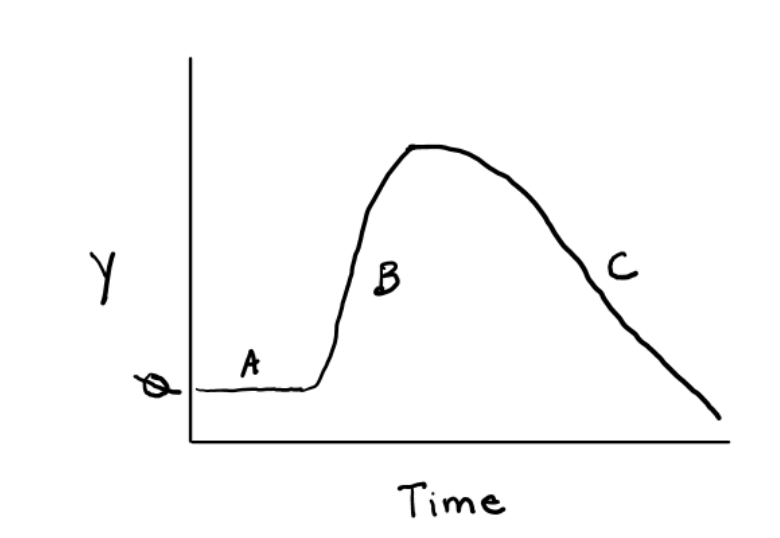
What does the letter "C" represent is this graph illustrating retention time?
K1, primary site of pooling
When estimating shrunk body weight, we use body weight x 0.96. Why do we leave 4% out of the estimation? Select all that apply.
Approximation of digesta in the GIT, cattle lose mass from stress of a trailer
T/F: Breed, sex, and physiological state affect maintenance requirements.
True
What is the most accurate way to measure maintenance requirements of an animal?
Restrict feed and measure heat loss
What are the end products of digestion of lipids, protein, and nonstructural carbohydrates in the small intestine? Select all that apply.
amino acids, fatty acids, monosaccharides
T/F: Surface area does not define heat lost from the body.
false
Digesta retention time is approximated from reactor volume and digesta flow rate, meaning feed value can differ between a larger cow and a smaller cow. Why is this?
Rumen volume is a function of body size