PSY 250 Lecture 9 Visual Pathways and Organization & Receptive Fields of Visual Neurons
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
What is the major visual information processing pathway?
The retina-geniculate-striate pathway
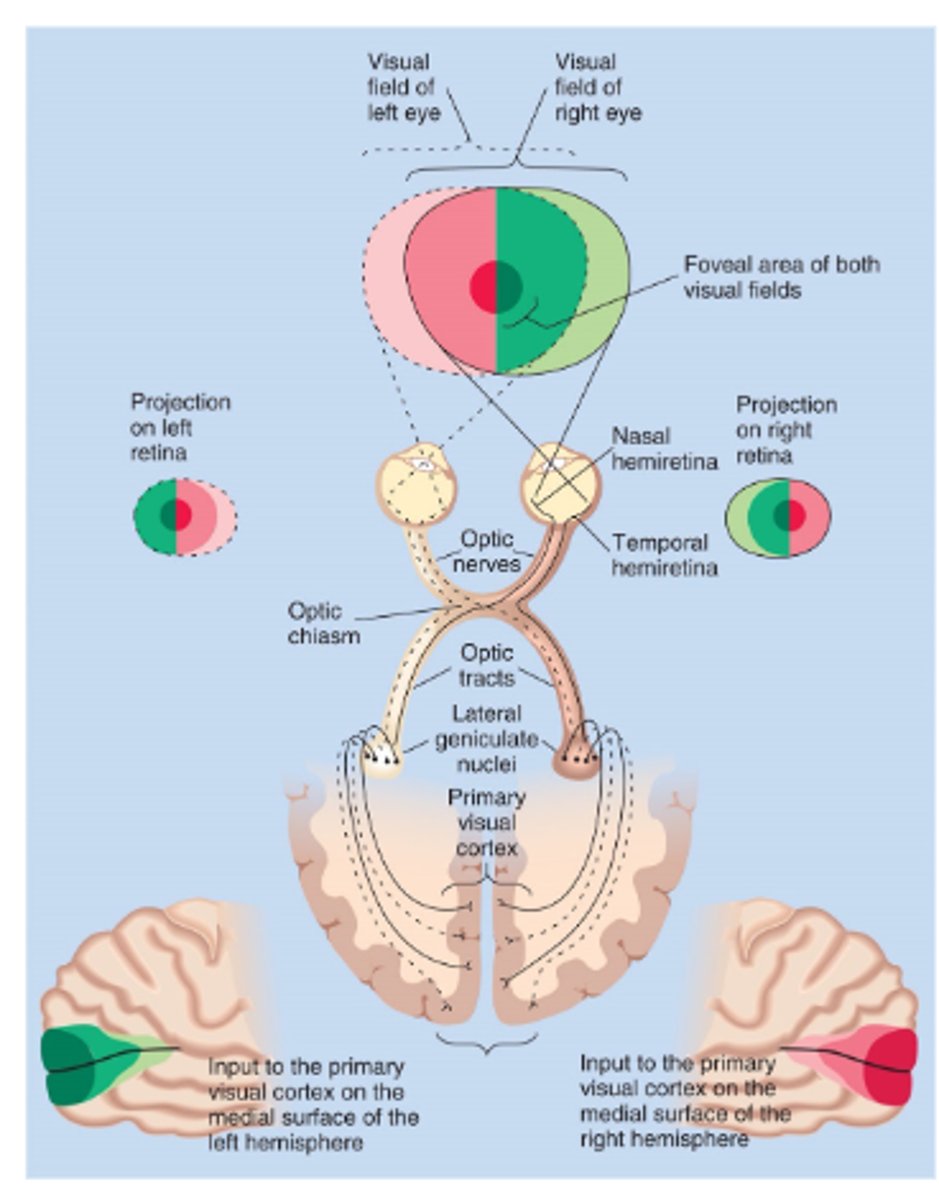
For the retina-geniculate-striate pathway, the left visual field -- _________ primary visual cortex
right
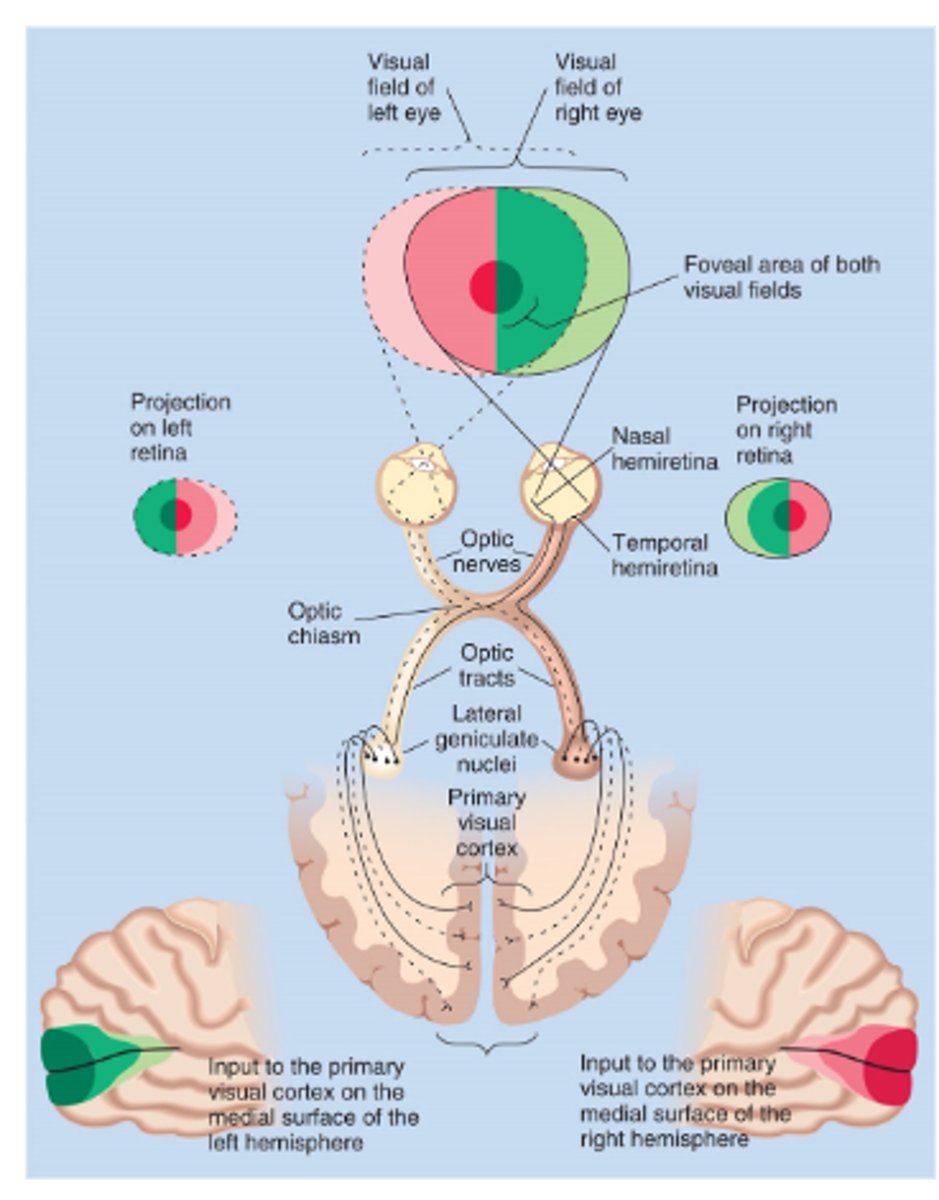
For the retina-geniculate-striate pathway, the right visual field -- _______ visual cortex
left
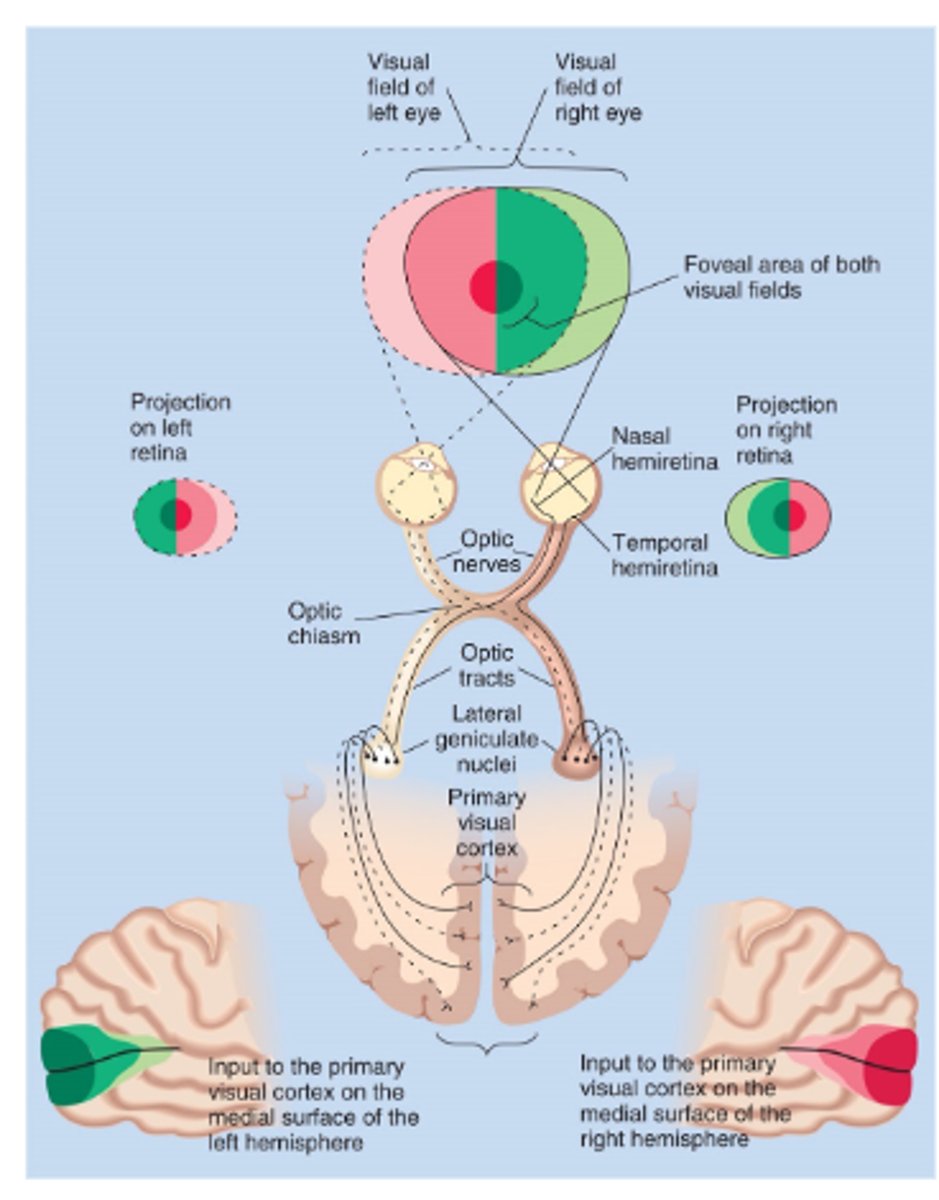
What is Hemi-retina?
Each eye has temporal and nasal portions of the retina which cover different parts of the visual field
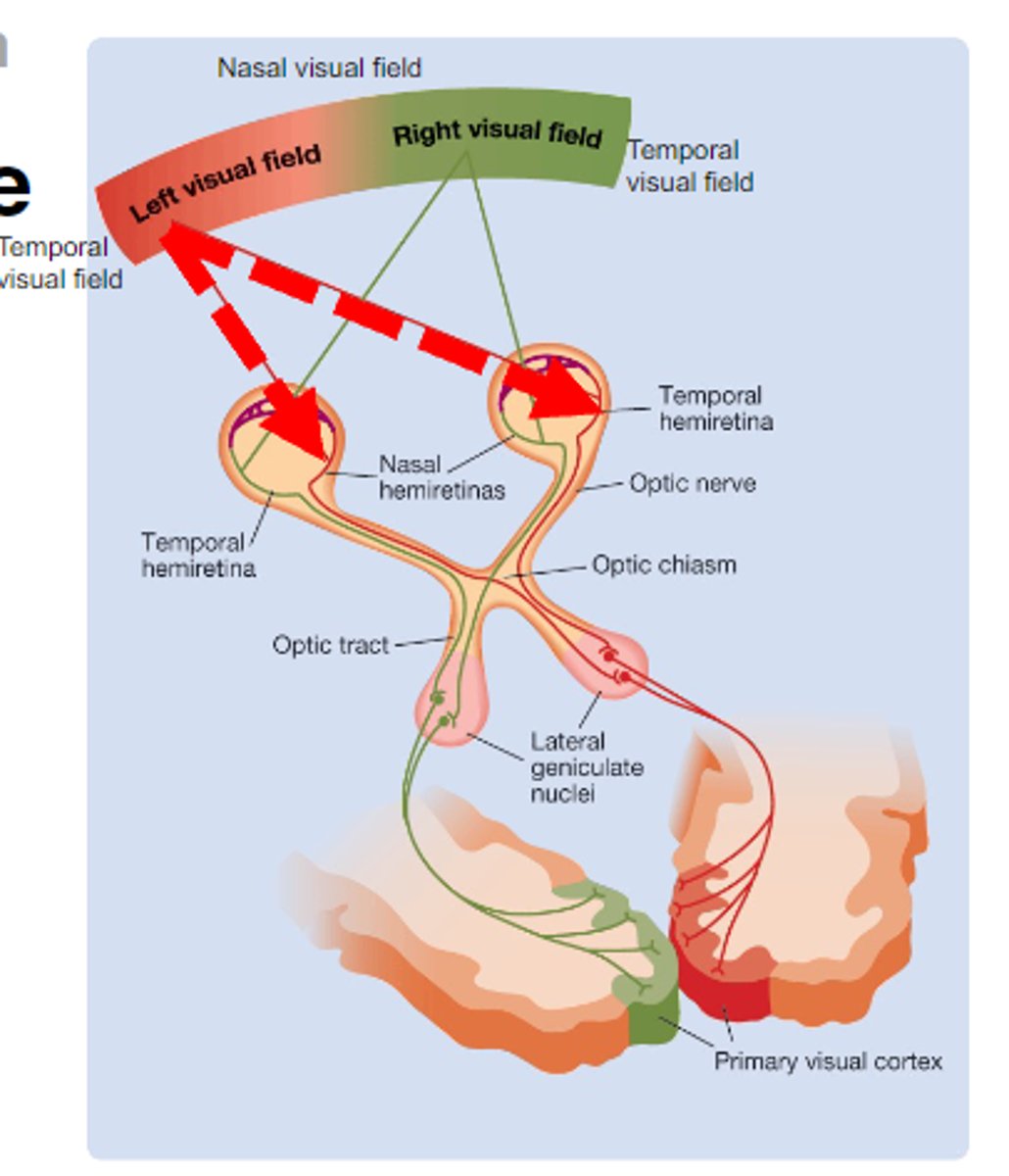
For the retina-geniculate-striate pathway, the left visual field -
• Nasal retina from left eye; crosses
• Temporal retina from right eye; does or does not cross?
does not
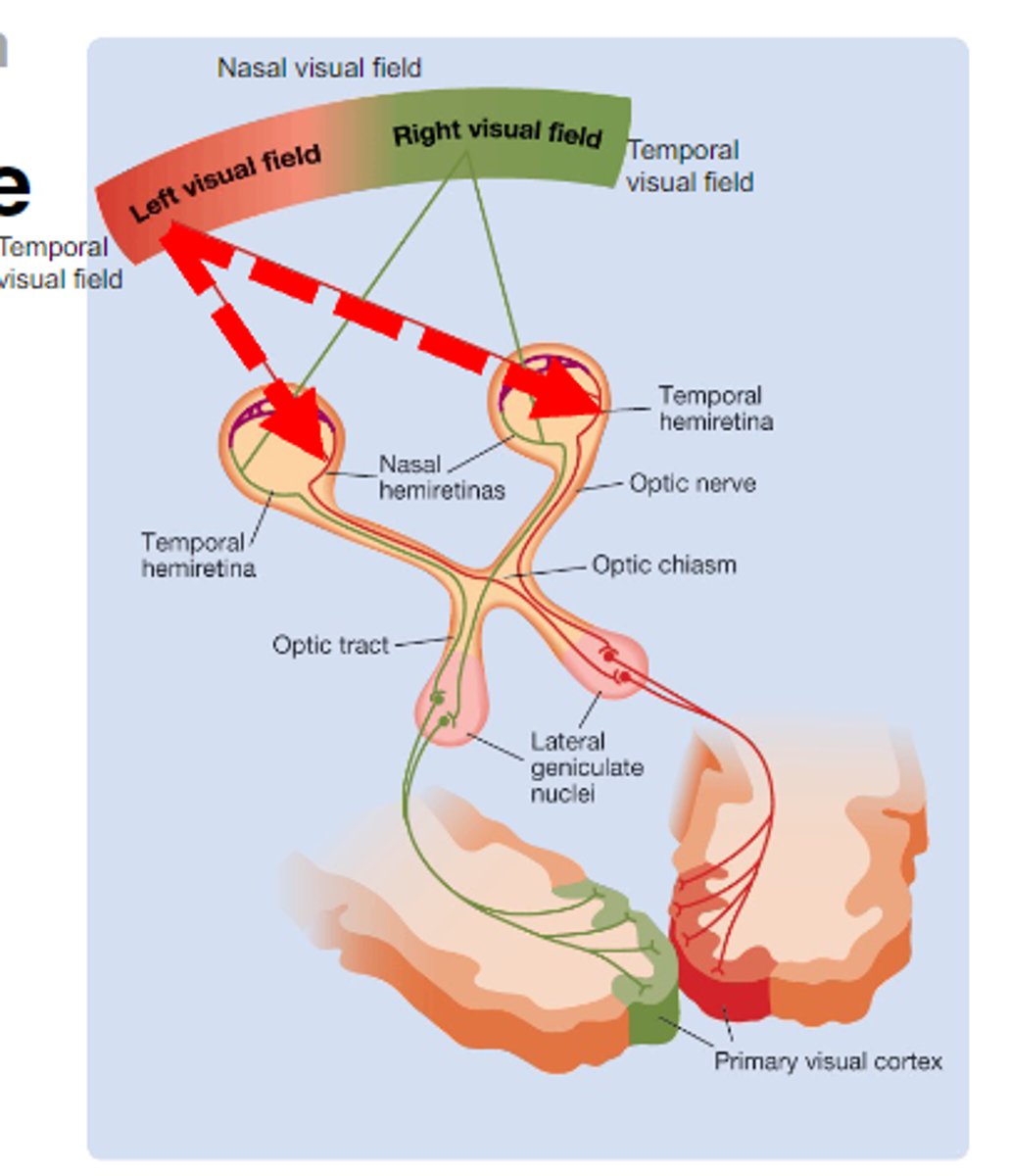
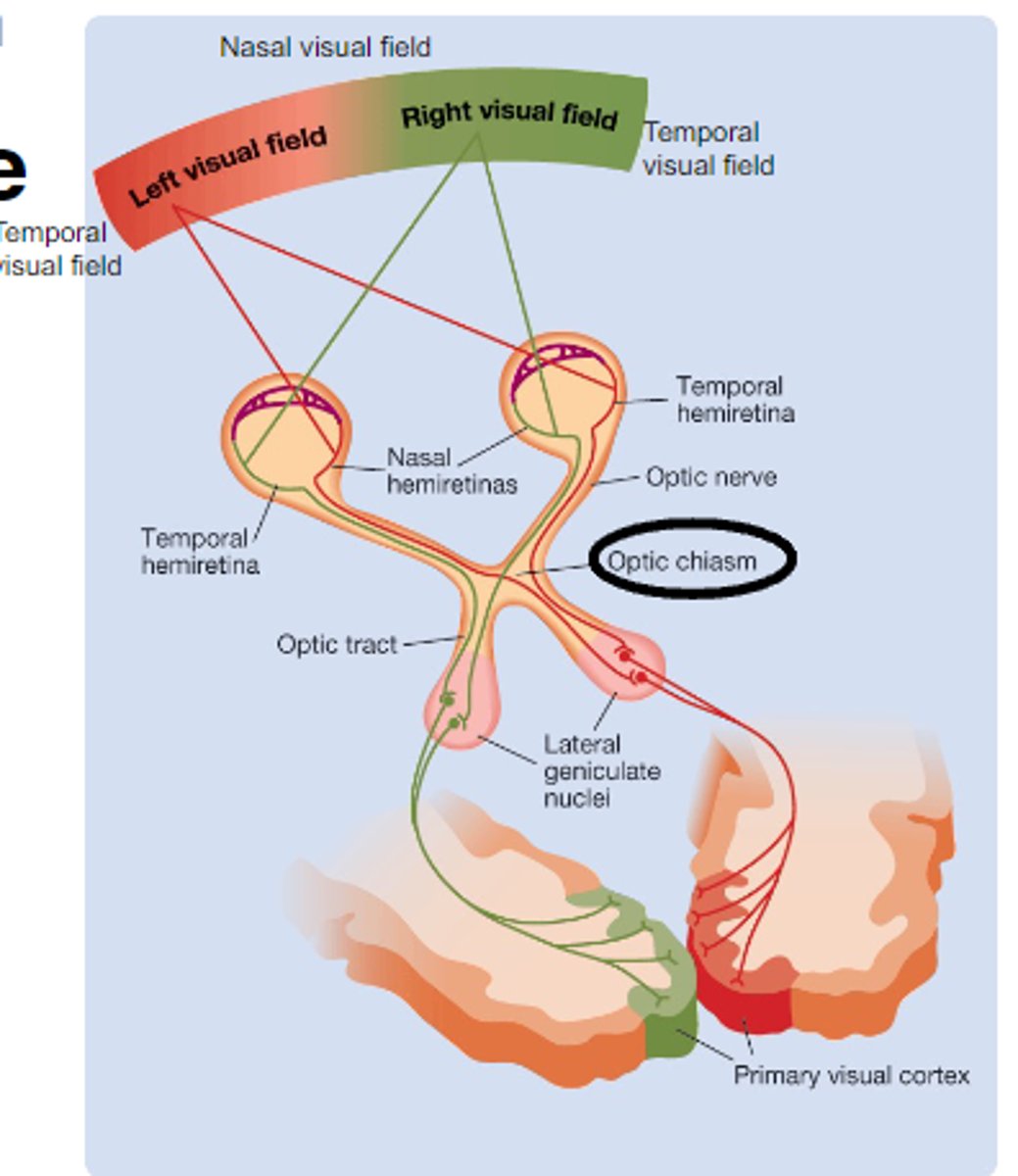
What is the Optic Chiasm?
Where axons coming from the nasal retina cross
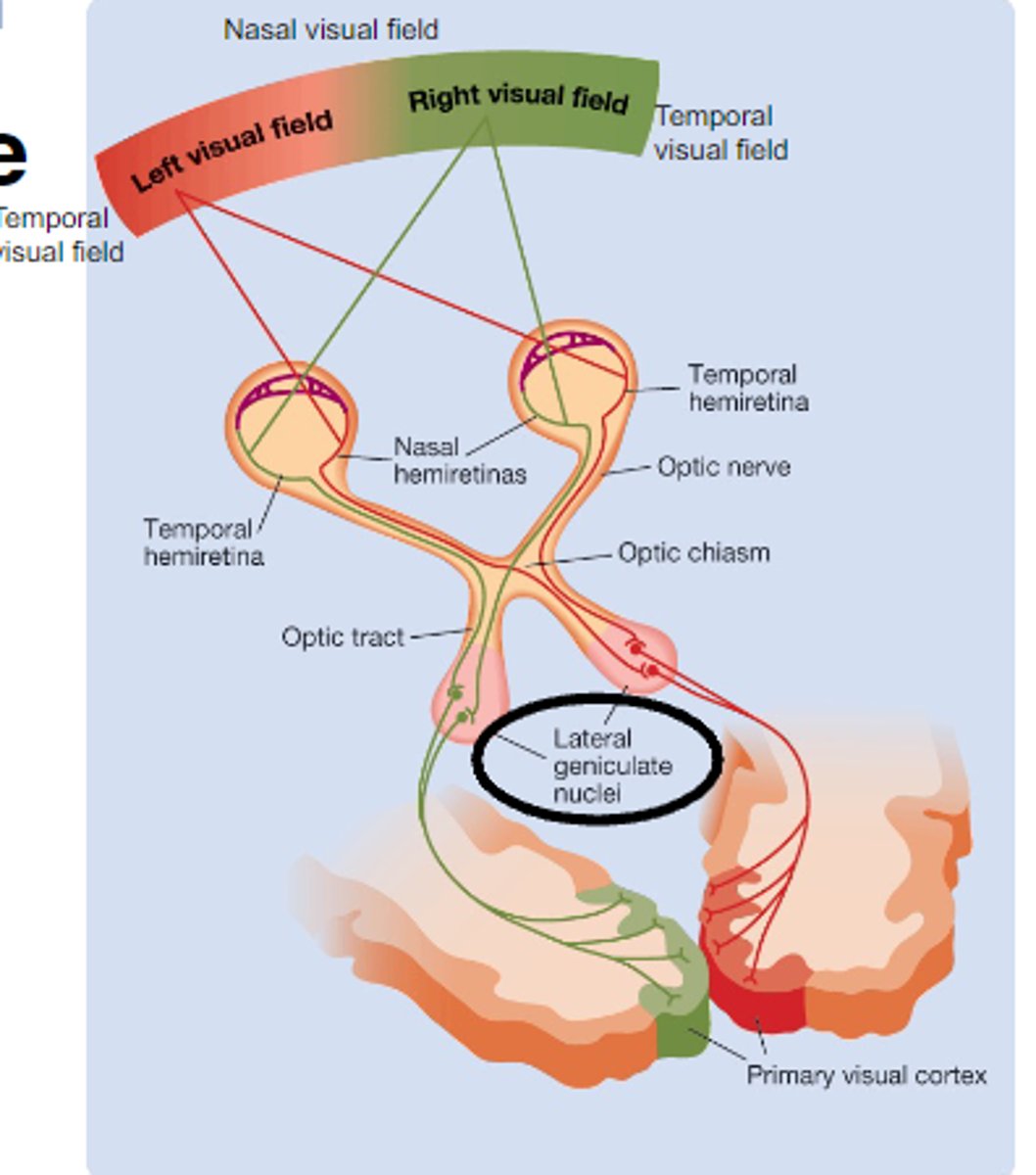
What is the Lateral Geniculate Nucleus (LGN)?
Thalamic nucleus that relays visual info from retina to the visual cortex
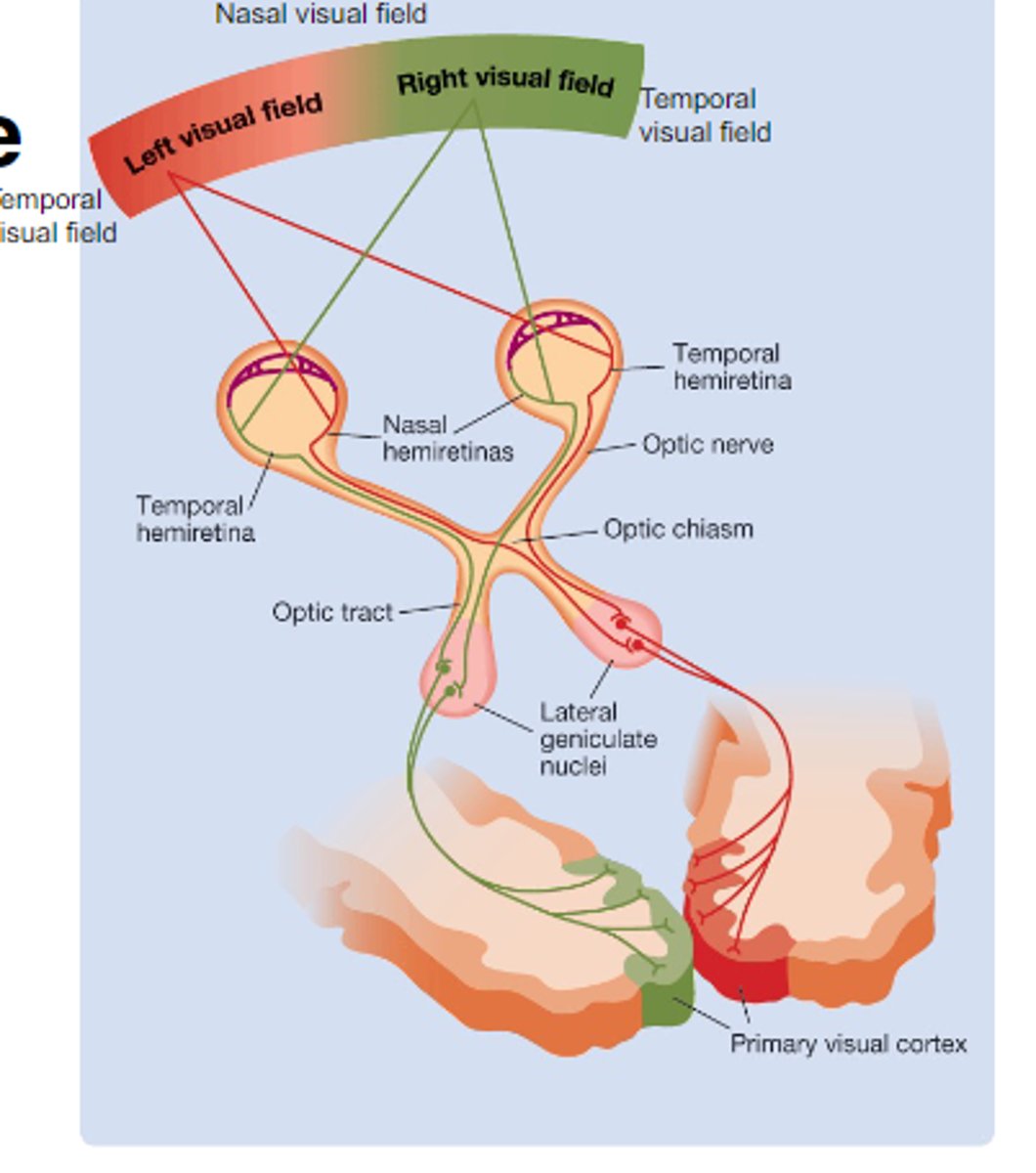
For the retina-geniculate-striate pathway, there are both....
ipsilateral and contralateral projections
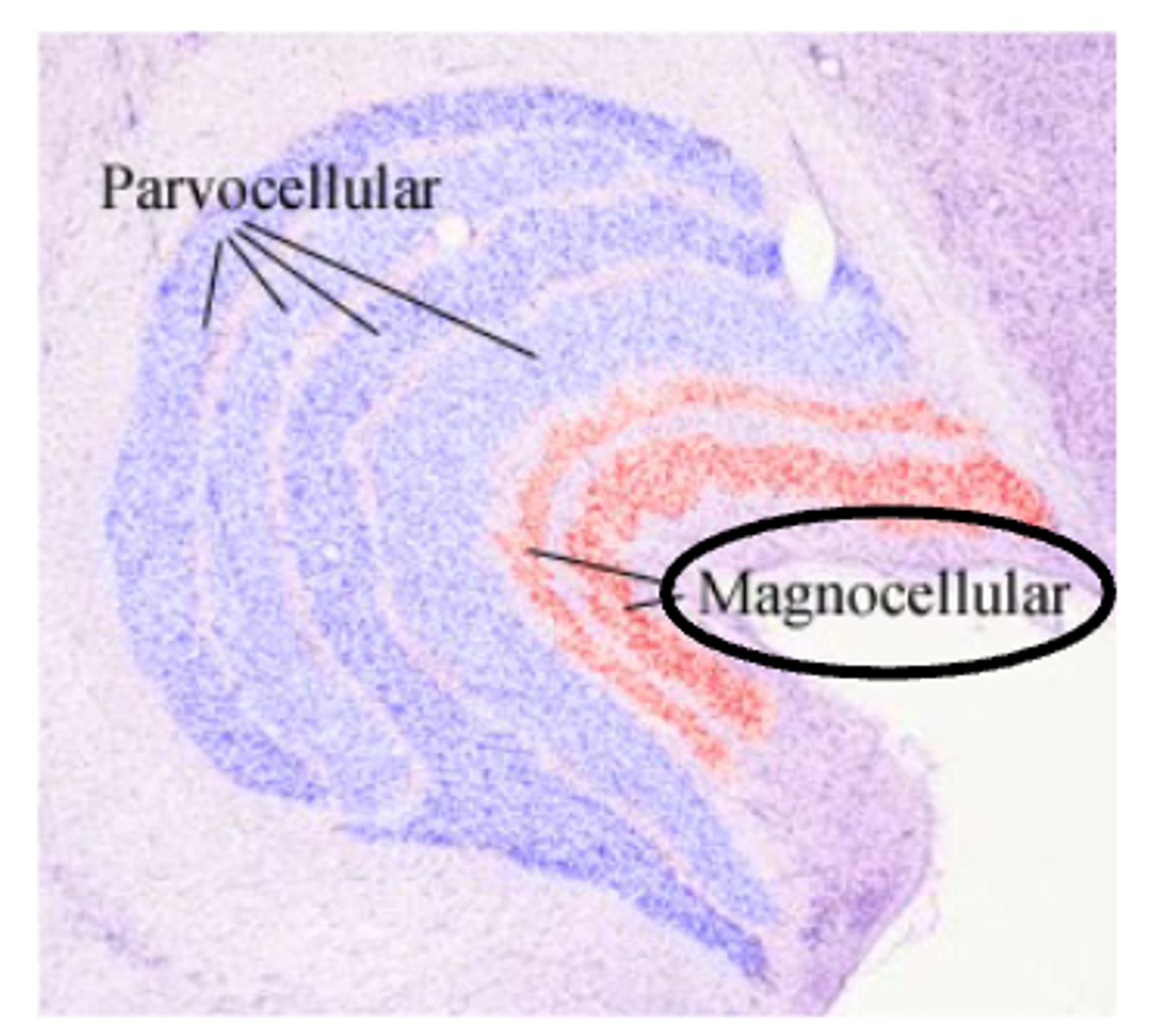
Magnocellular and Parvocellular (M and P) Channels - P channels get majority of....
input from cones, and respond to color and fine details
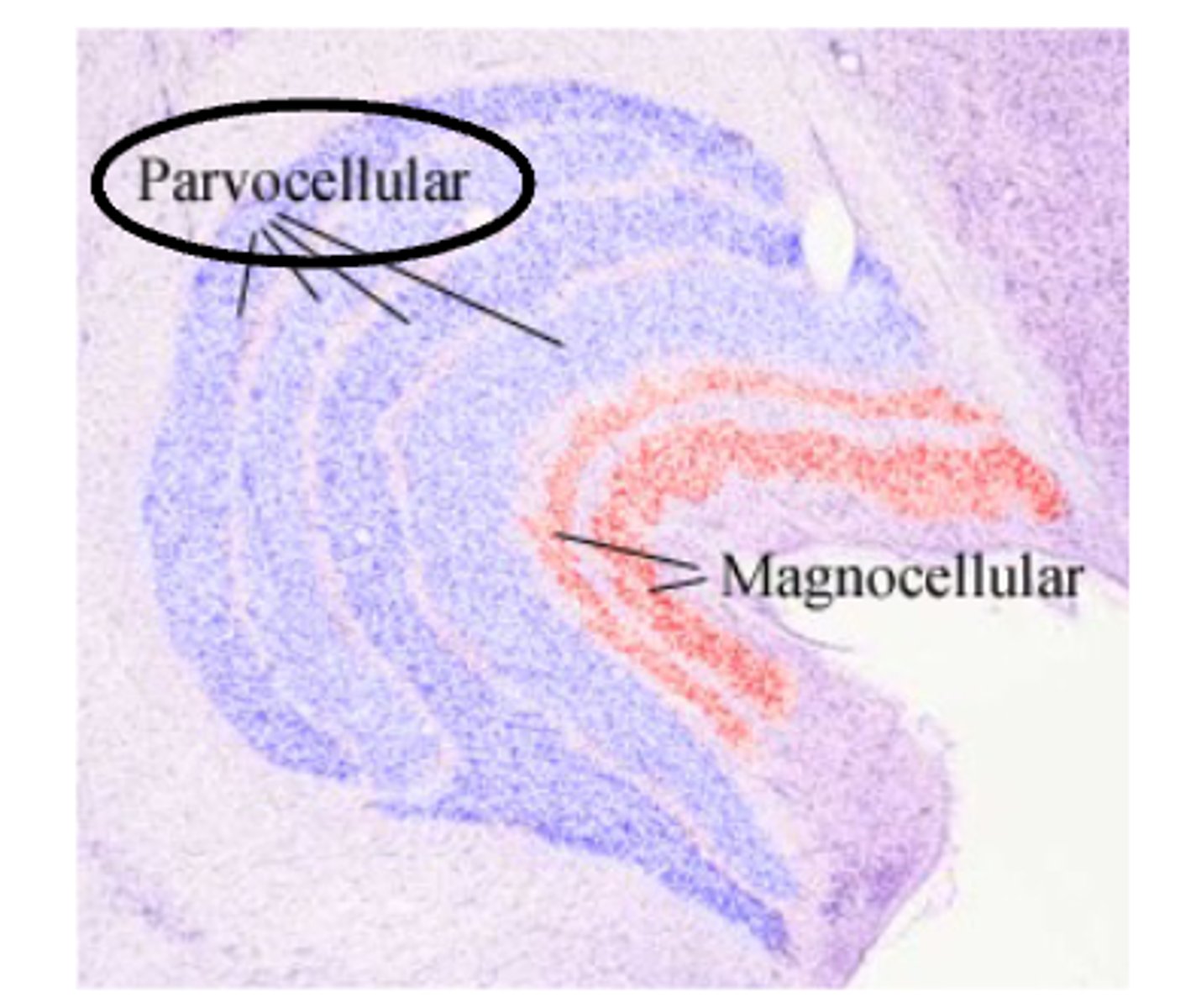
Magnocellular and Parvocellular (M and P) Channels - M channels get majority of....
input from rods, and respond to movement
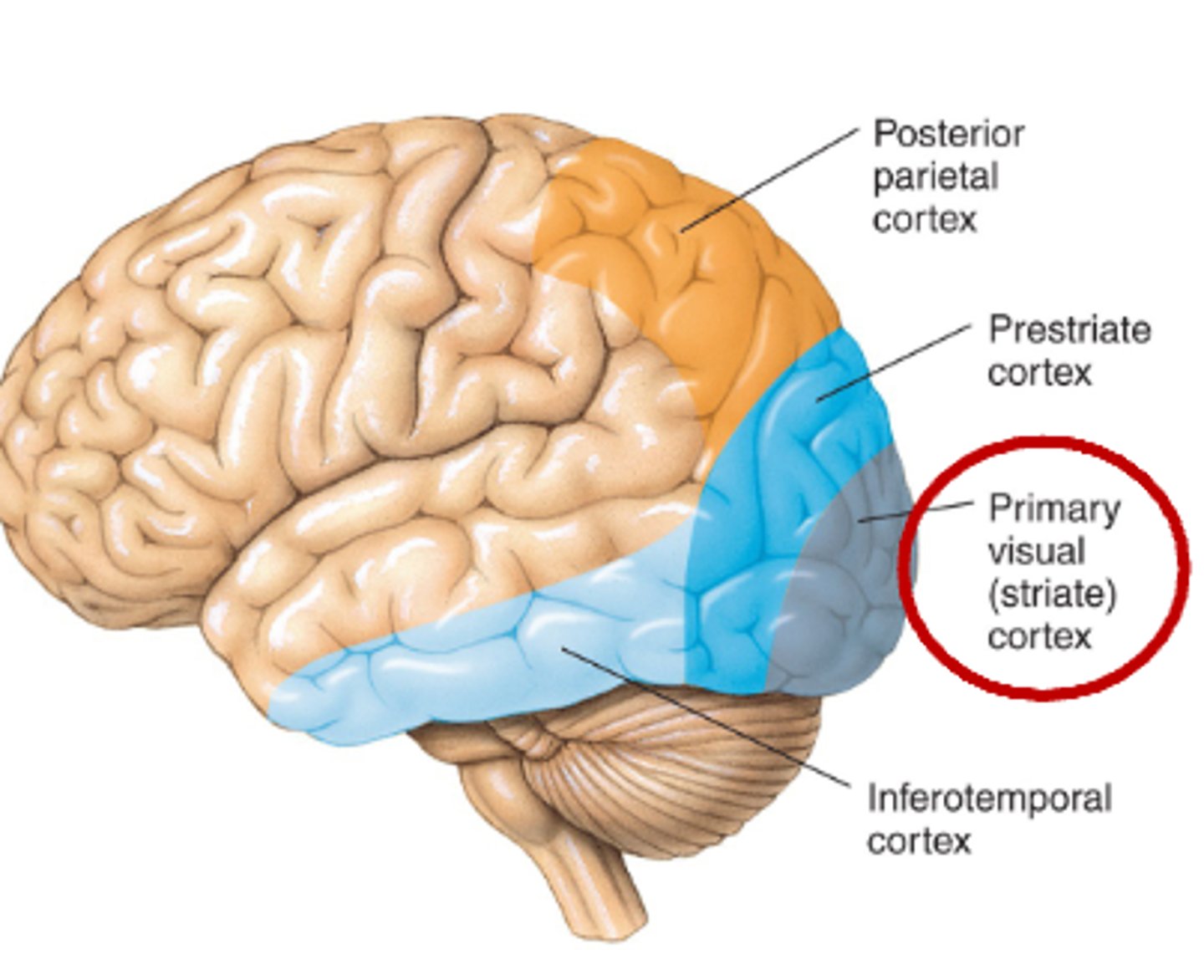
The primary visual cortex is also called...
V1 or striate cortex
Where is the primary visual cortex ?
It is deep in posterior region of the occipital lobe
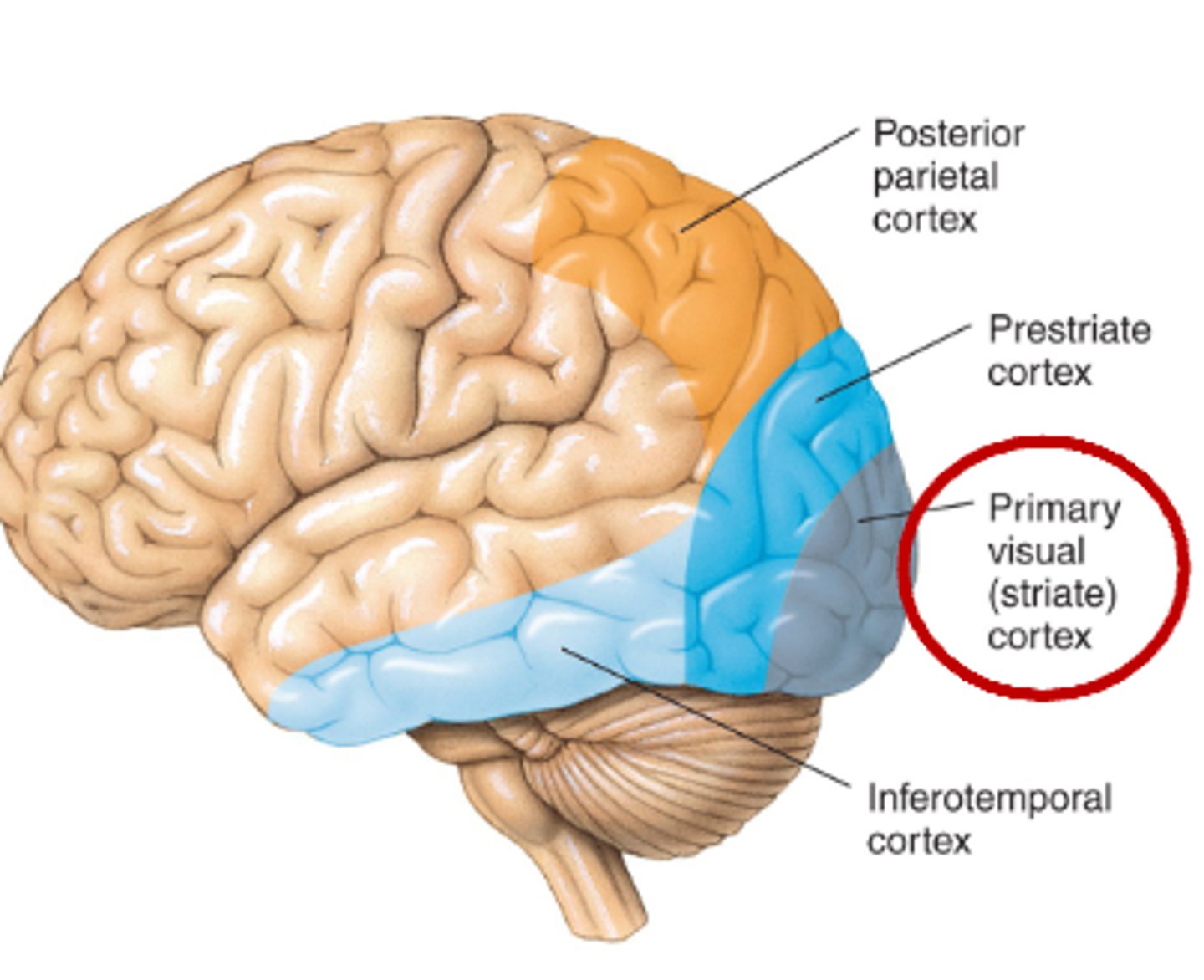
The primary visual cortex is the ______ stage of visual processing in the cerebral cortex
first
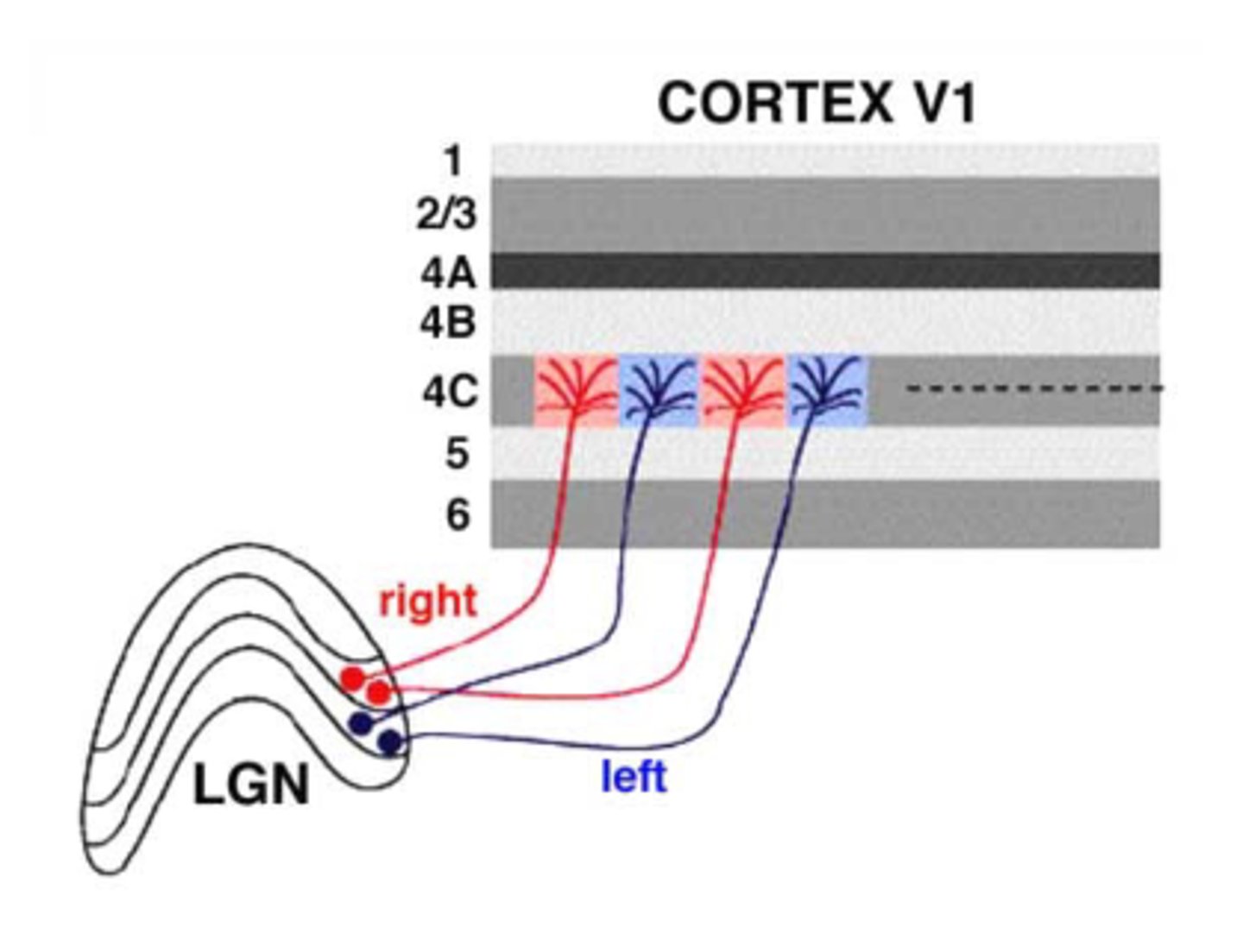
What are the V1 Properties?
- It has six layers of cells
- LGN most projection to layer 4 of V1
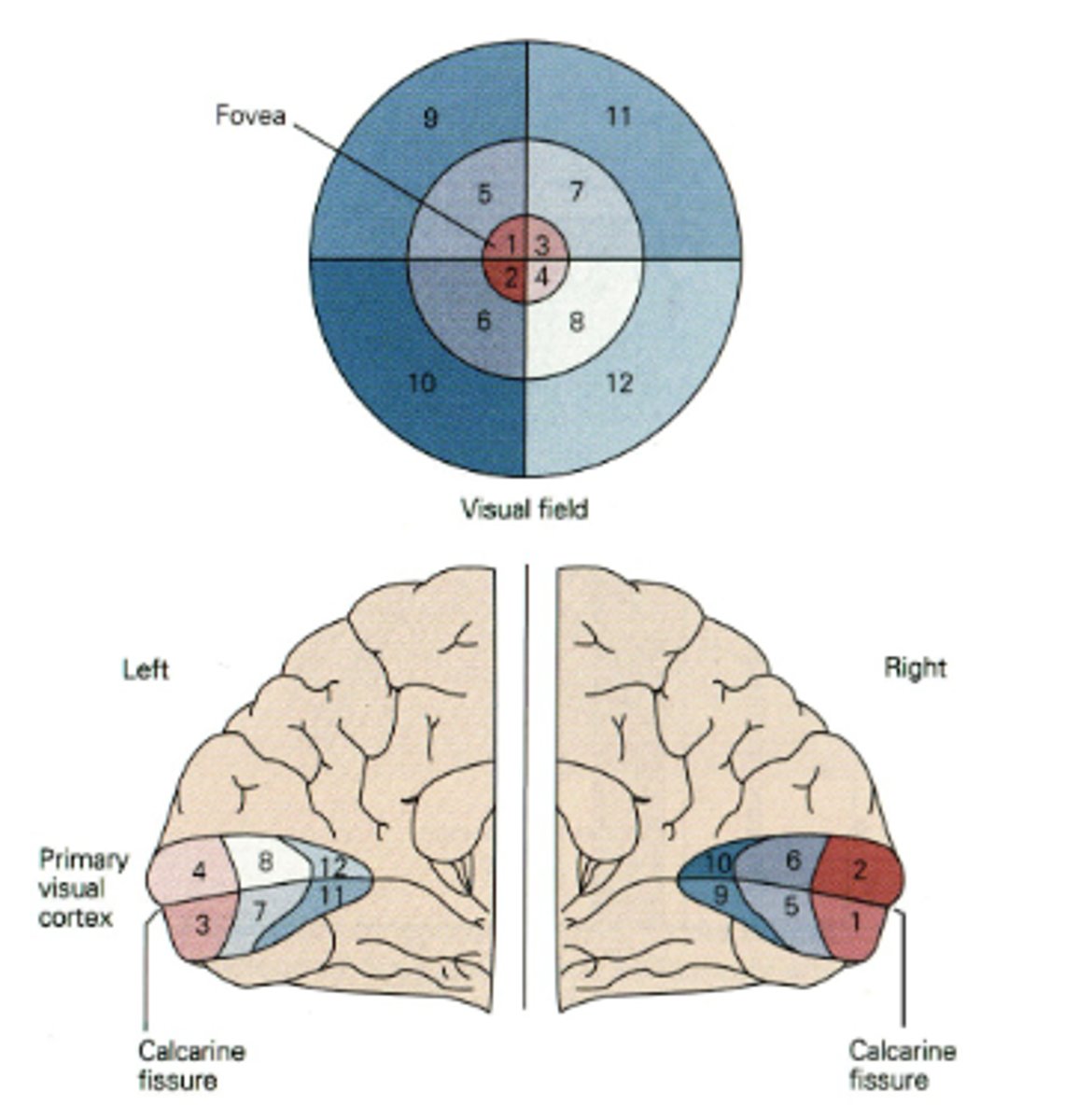
In Retinotopic Organization, it is organized like a map of the ________
retina
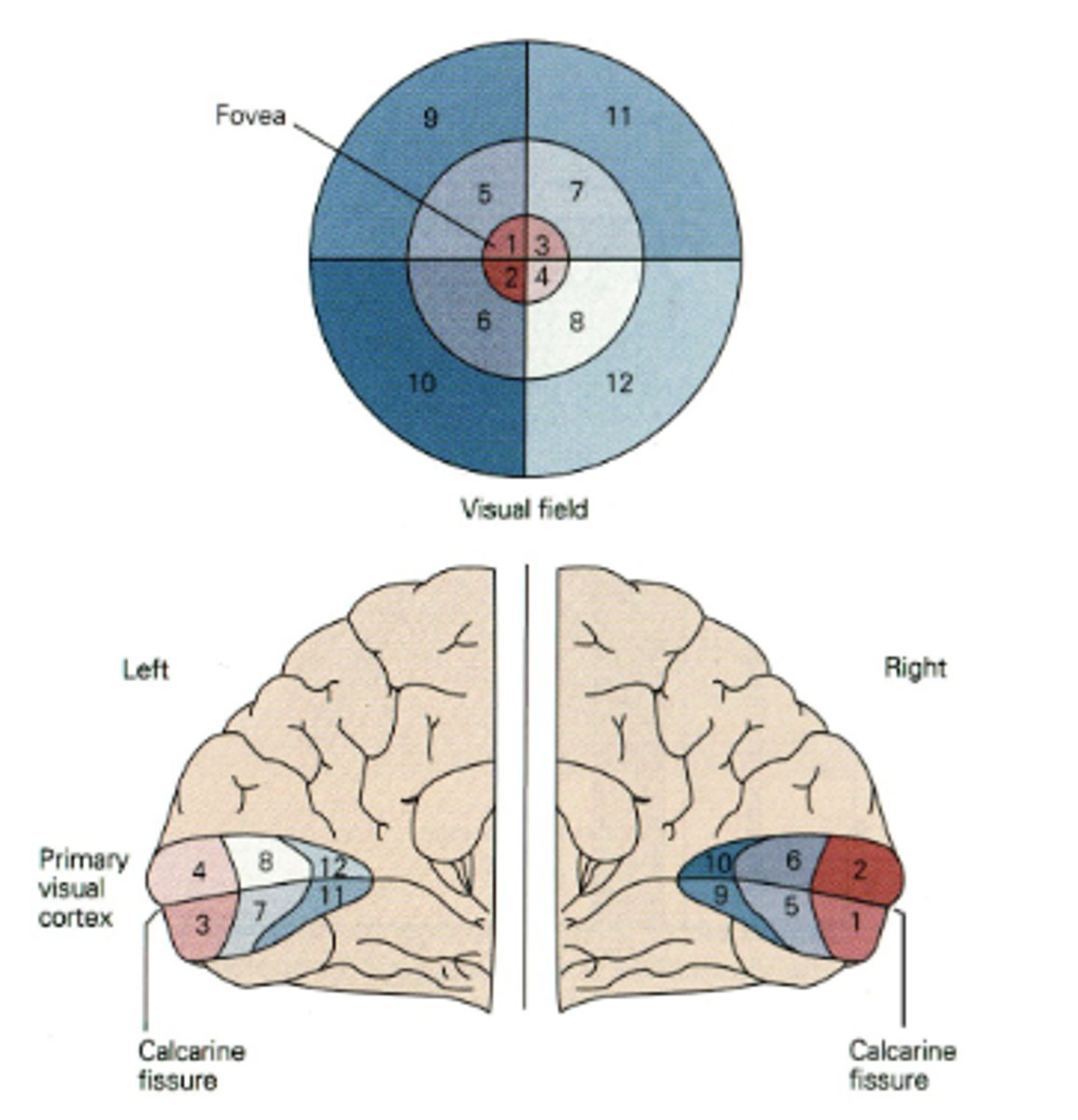
Regarding Retinotopic Organization, the fovea receives...
relatively larger representation
______________ -
• The area of the visual field within which it is possible for a visual stimulus to influence the activity of a given neuron.
• They come in different forms (i.e. circular, bar-shaped, etc)
Receptive Field
Hubel and Wiesel experiment
focus on primary visual cortex in v1; accidentally found with cat when light slide fell off screen that simple cells, though not responding to the diffuse light from screen facing them, they responded to the moving bar; simple cells have elongated center responding best to bars of light or dark (i.e. lines)
What are the four properties of receptive fields in the retina, LGN, and layer 4 in V1?
1. Receptive fields from the fovea are smaller
2. Most have circular receptive fields
3. Neurons have monocular receptive fields (only respond to stimulation in one eye)
4. Receptive fields can have both an excitatory and inhibitory area
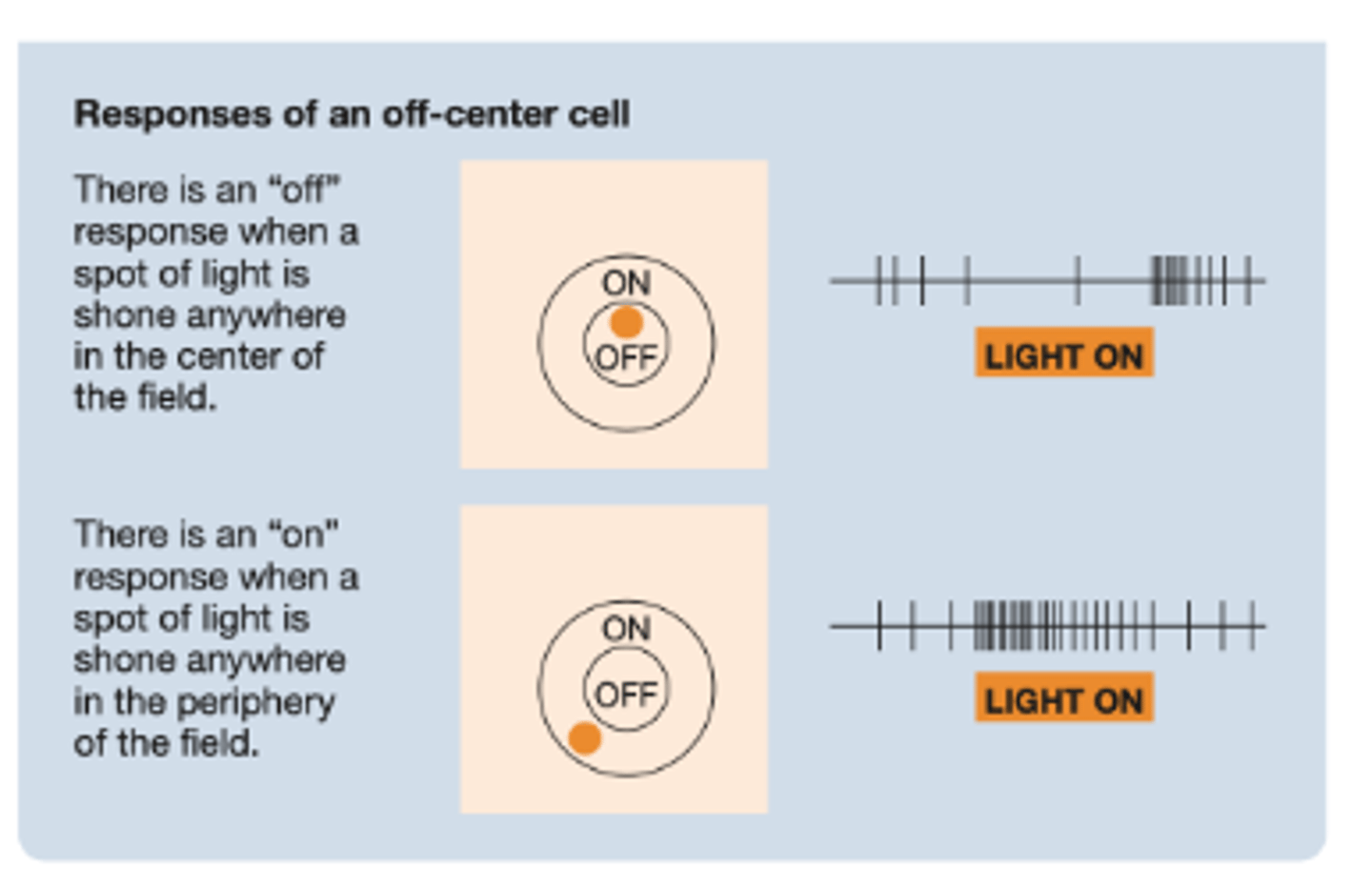
On-center or off-center cells -
Center and Surround:
• Light in center of the receptive fields causes excitatory responses, while light in surround causes inhibitory responses
• Is this on-center or off-center?
On-center
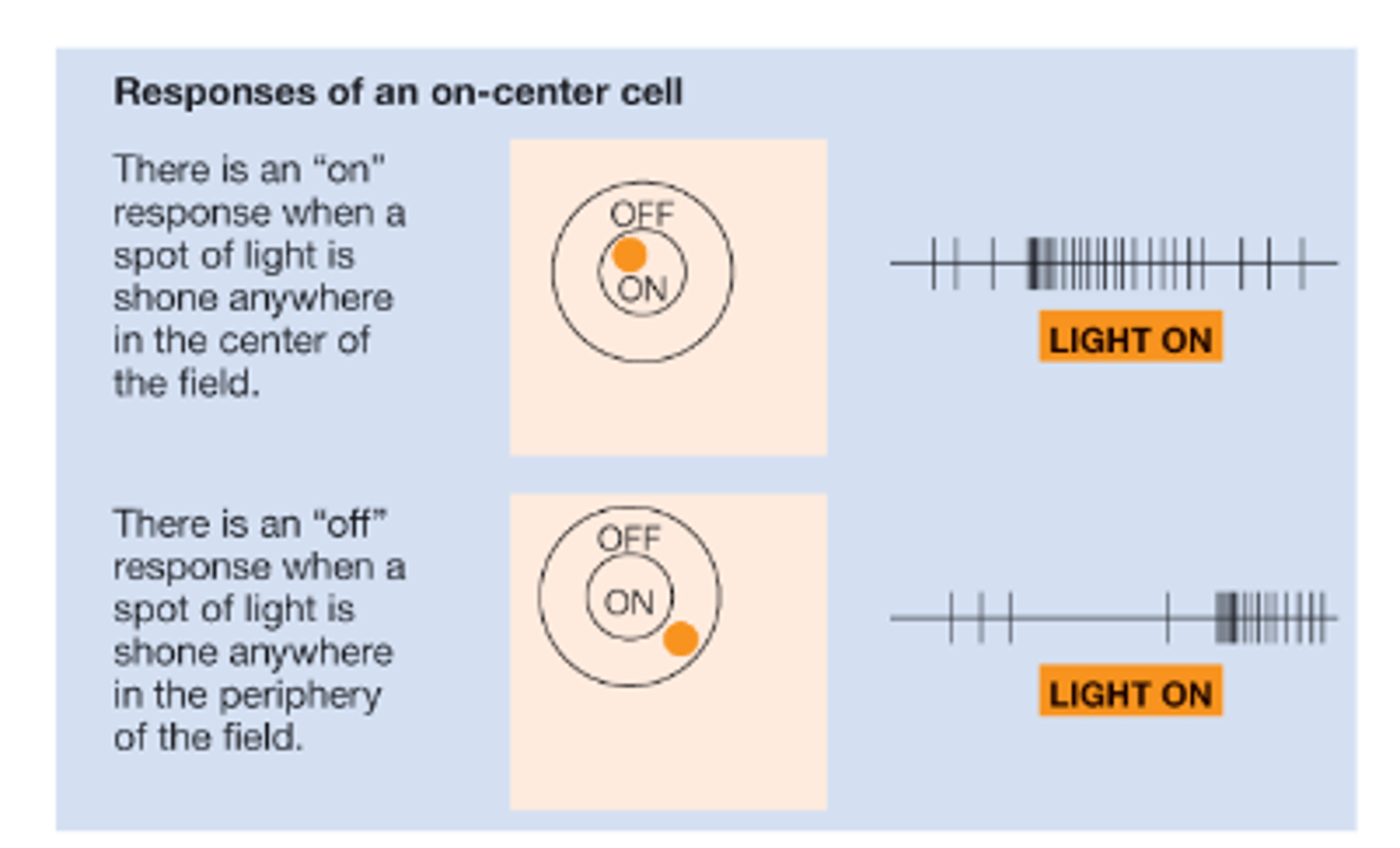
On-center or off-center cells -
Center and Surround:
• Light in center of the receptive fields causes inhibitory responses, while light in surround causes excitatory responses
• Is this on-center or off-center?
Off-center
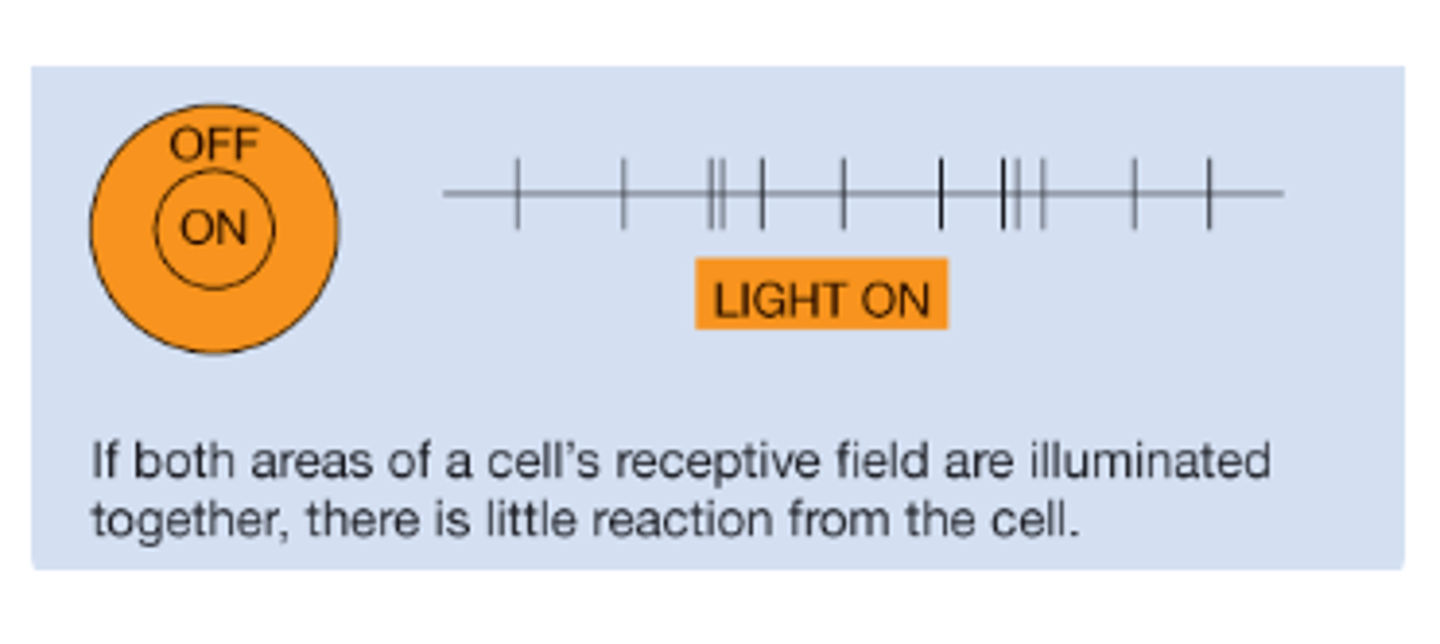
______ effect if light is simultaneously shone in both "on area" and "off area"
Null
Example of "ON-Center cell" in the Lateral Geniculate
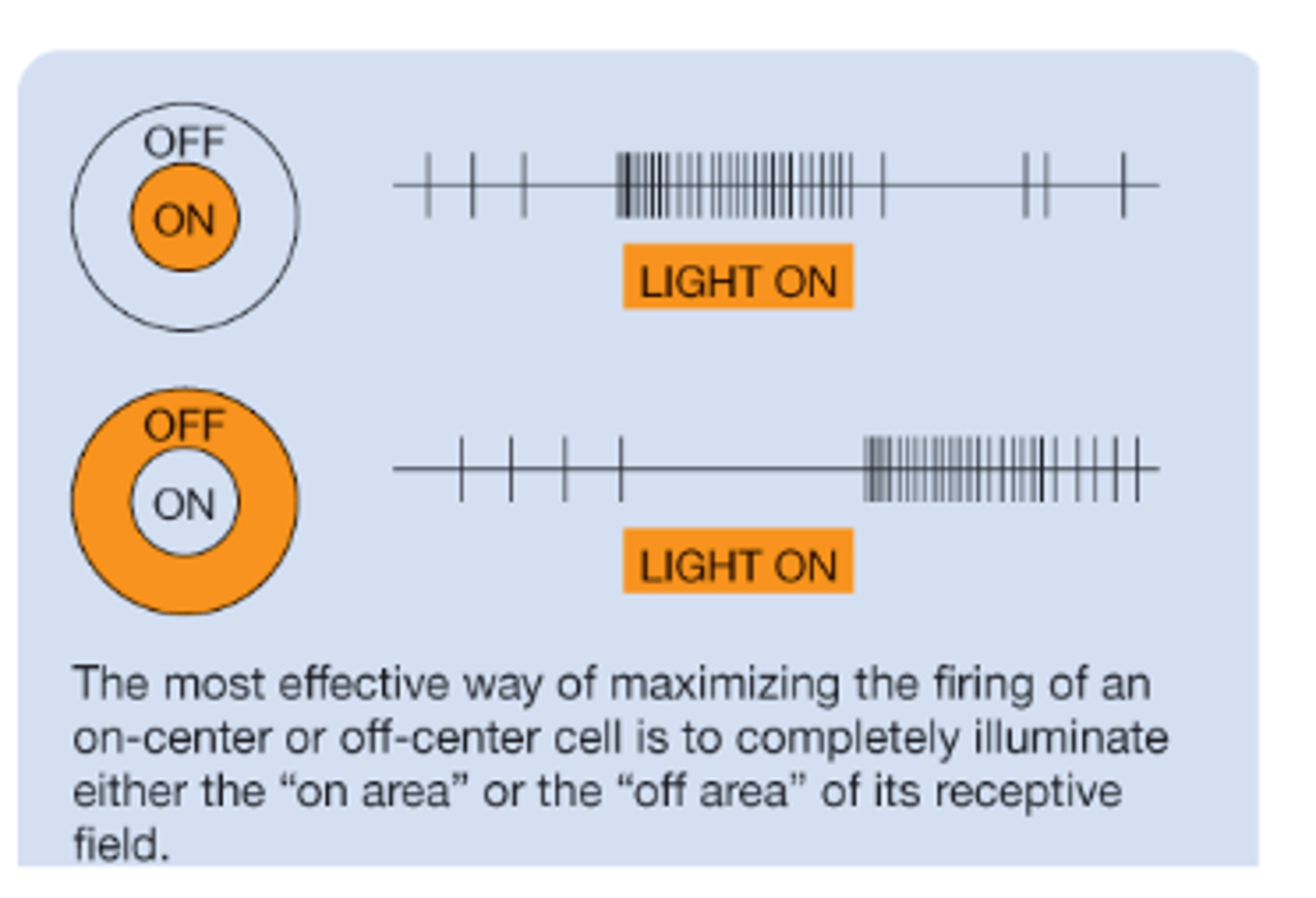
Receptive fields of neurons in V1:
• Layer 4 cells receive signals from the ______, so neurons in layer 4 of the primary visual cortex (V1) also have similar circular receptive fields
LGN
Receptive fields of neurons in V1:
• In contrast, other V1 neurons respond best to...
• They are not very responsive to small spots of light
bars of light (lines, bar, and sinewave gratings)
Two major classes of V1 neurons:
1. Simple Cells
They respond to..
lines/bars of specific orientation
Two major classes of V1 neurons:
2. _________ ______
• Also rectangular and orientation sensitive, but their receptive fields are larger than those of simple cells
• Many of them are binocular (input from both eyes)
• Usually lack on/off regions
• Example: respond to a line moving across visual field
Complex Cells