Module 8: GI System (Part 2)
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Small and Large Intestine Pains
Duodenum
Can also show symptoms of what other pathology?
Will refer to where?
What does the duodenum do?
Gastritis
Refer:
Back (Mid Thoracic Area)
OR
RUQ and R Shoulder
Finishes chemical digestion before getting into the small intestine
Duodenum:
Where is Duodenum located in the body?
Curves around what organ?
What 2 substances enter the GI tract
How many parts is the Duodenum divided ino?
Retroperitoneal
Head of the Pancreas
Bile and Pancreatic Juices
4 Parts
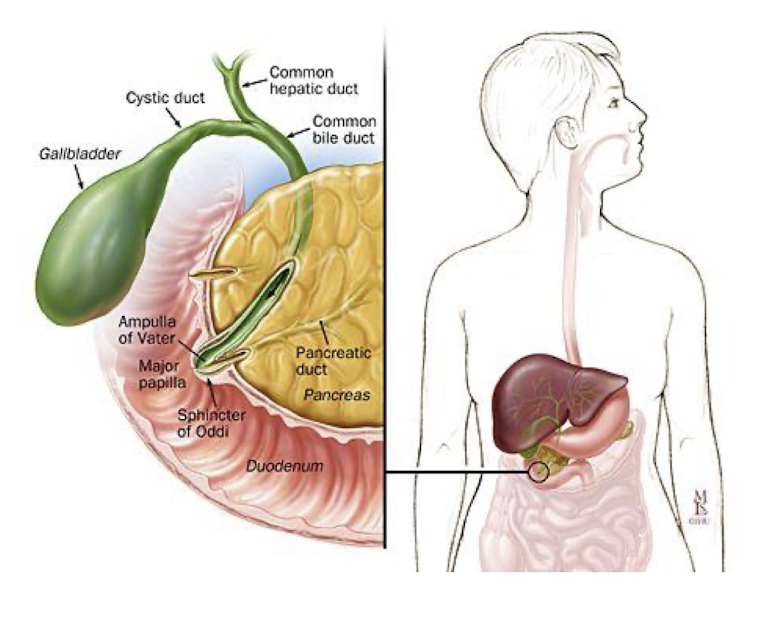
How to Palpate the Sphincter of Oddi?
Sphincter of Oddi is the size of what?
Sphincter of Oddi lines up w what spinal level?
2-3 cm up from the umbilicus on the R side
Size of a pea
L2
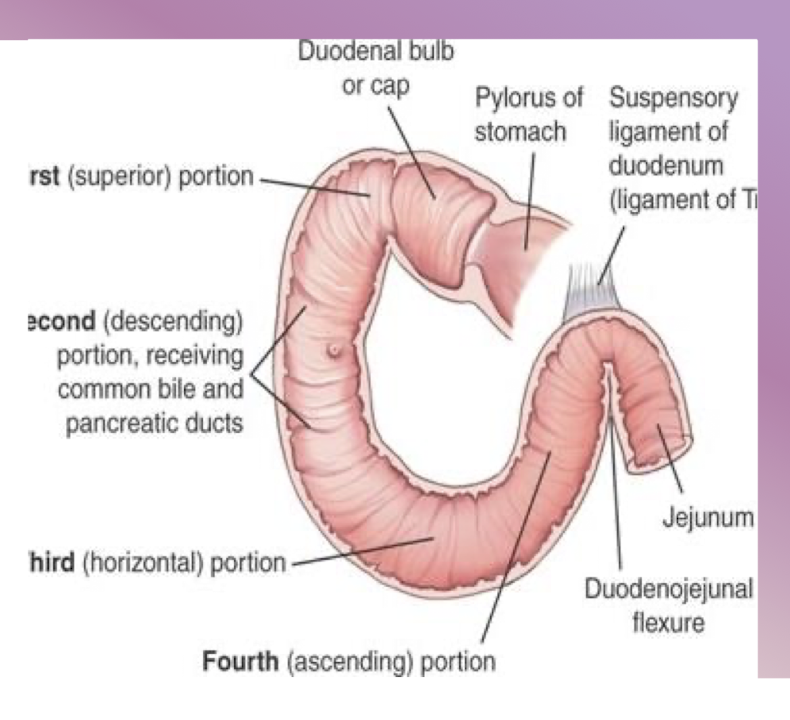
How to palpate the DJ Junction
DJ Junction is the size of what?
DJ Junction is at what spinal level?
2-3 cm abobe umbilicus on L side
Quarter
L2
Metabolic Disorders:
What is a Metabolic Disorder?
4 Examples:
Group of pathologies that contribute to reduced intestinal absorption
Celiac, Cystic Fibrosis, AIDS, Crohn’s Disease
Metabolic Disorders:
6 main S/S:
Diarrhea (MC)
Bloating
Indigestion
Anemia
Weight Loss
Abdominal Cramping
Pt considerations for Malabsorption:
What are 3 pt considerations for malabsorption?
Decreased exercise tolerance
Potentially decreased bone density
Spasms/muscle craps due to decreased electrolyte balance
IBS:
How does a physician diagnose a pt w IBS?
Recurrent symptoms of upper and lower GI system that interfere with normal functioning of the colon
Rome IV Critera
Uses Bristol Stool Scale
IBS:
When diagnosing IBS, pt will be associated with what?
IBS is AKA
What type of problem is IBS?
Recurrent abdominal pain > 1 day/wk in last 3 months
Defecation increases or decreases pain
Associate w change in stool frequency and form/apperance
Functional GI Disease
More functional than structural
IBS:
T/F: Unknown Etiology
How is IBS diagnosed?
Can IBS be identified w testes?
How is IBS usually treated?
True
Diagnosis of Exclusion
Naur
Tx:
Diet changes
Lifestyle changes
Stress management
Pharmacology (when necessary)
IBS:
Is IBS MC in men or women?
IBS co-occurs frequently w diagnoses such as: (4)
W > M
Dx:
Fibromyalgia
Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
Chronic Pelvic Pain
TMJ
IBS:
What are 4 possible pt considerations for IBS?
Stress management
Sleep habits
Diet
CNS processing
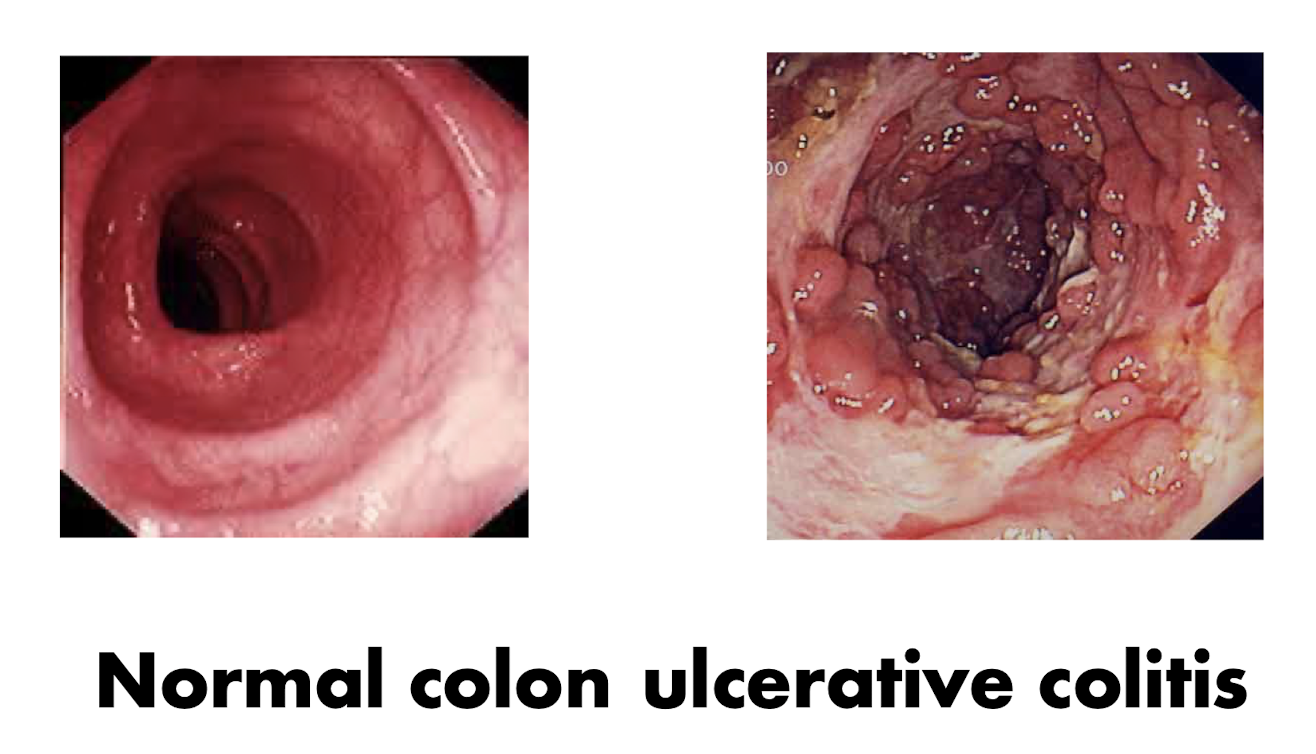
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD):
What is IBD?
2 Common IBD Diseases:
2 Inflammatory conditions of unknown cause involving genetic and immunologic influences on the GI Tract
Crohn’s Disease
Ulcerative Colitis
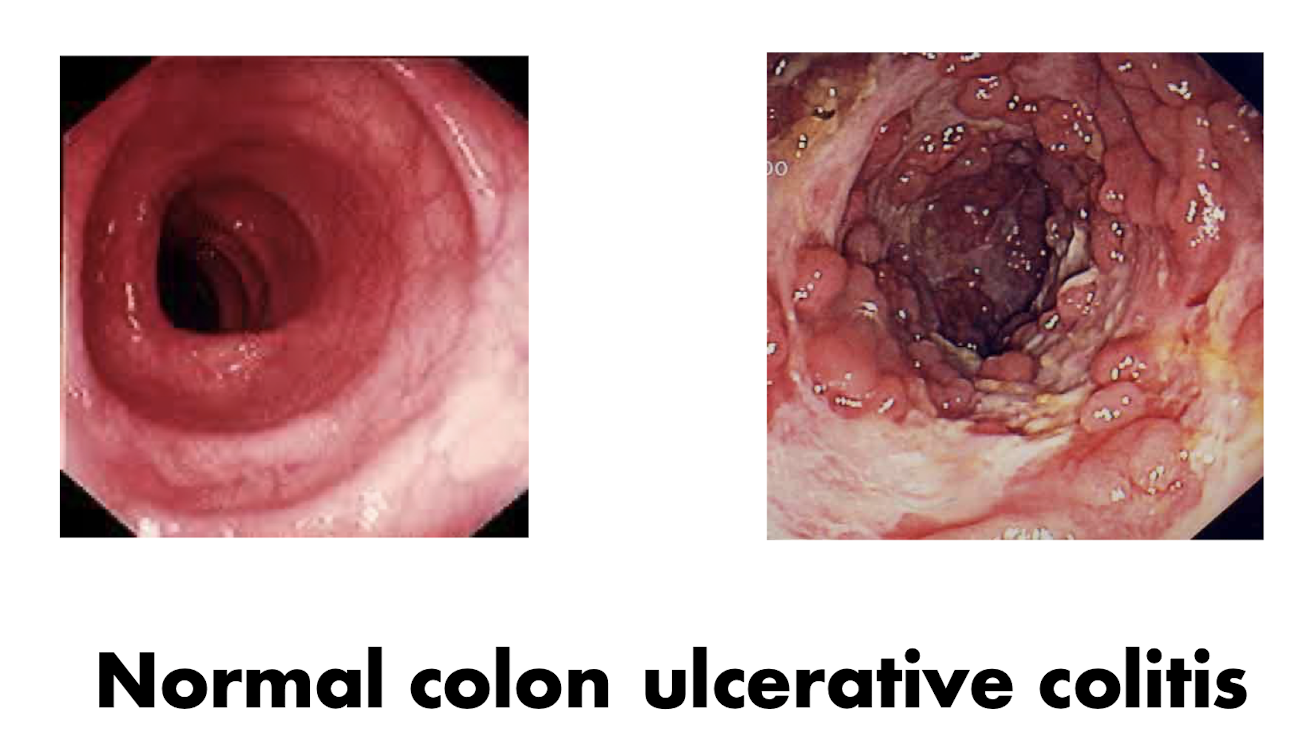
IBD:
Higher production of what?
Etiology is between what?
What is the HALLMARK sign for IBD?
Inflammatory Cytokines
Gut and Microorganisms
Bloody Diarrhea
Abdominal pn
GI Bleed
Weight Loss
IBD: Crohn’s Disease
What is Crohn’s Disease?
Where can Crohn’s Disease happen?
What is:
Inflammation of full thickness of bowel wall
Any part of digestive tract
IBD: Ulcerative Colitis
What is Ulcerative Colitis?
What does Ulcerative Colitis cause?
What body part does Ulcerative Colitis usually affect?
What is:
Inflammation of inner lining of LARGE intestine
Causes infalmmation and ulcers in lining of LARGE intestine
Colon and Rctum
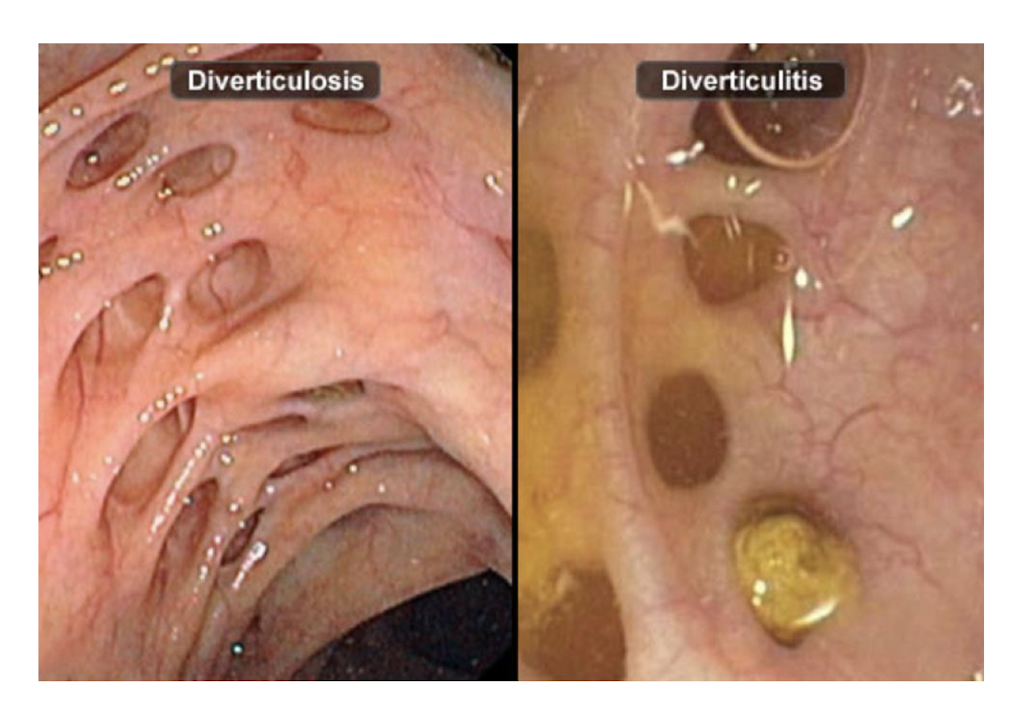
DiverticulITIS:
What is it?
Diverticulitis is a multi-factorial disease related to what?
What are the 2 types of changes that occur?
Where can Diverticulitis refer to?
What is it:
Infection or inflammation of the diverticula
Related to diet
2 Types:
Structural changes in the colonic wall
Changes in functional mobility
Low Back and Hip (L > R)
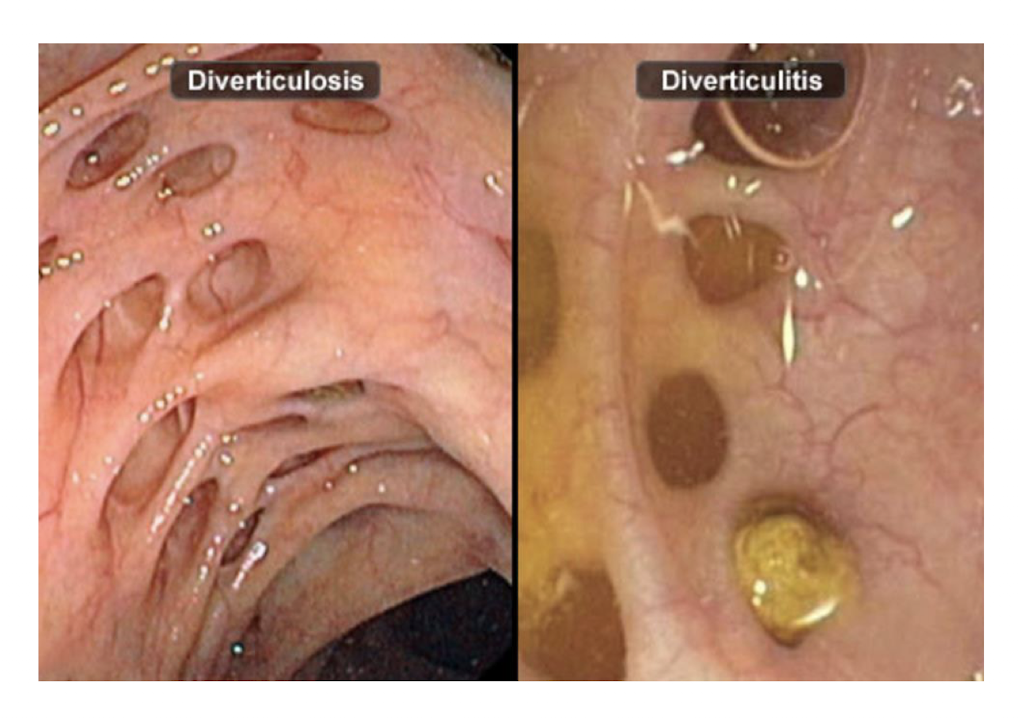
DiverticulOSIS:
What is it?
Where do the outpouchings herniate from?
More chronic form can be seen throguh where?
Presence of outpouchings in the walls of the Small Intestine OR Colon
Outpouchings from the mucosa and submucosa through the muscular layers of the colon
Imaging
What are 6 considerations for Diverticulitis?
Do NOT eat seeds
Do NOT Smoke
Eat fiber
Stay hydrated
Physical Activity improves bowel function
Breathing techniques for stress reduction
What are 4 MSK considerations for Diverticulitis?
Anterior Hip/Hip Flexor
Lumbar Spine (L4)
SIJ
Pelvic Floor (as needed)
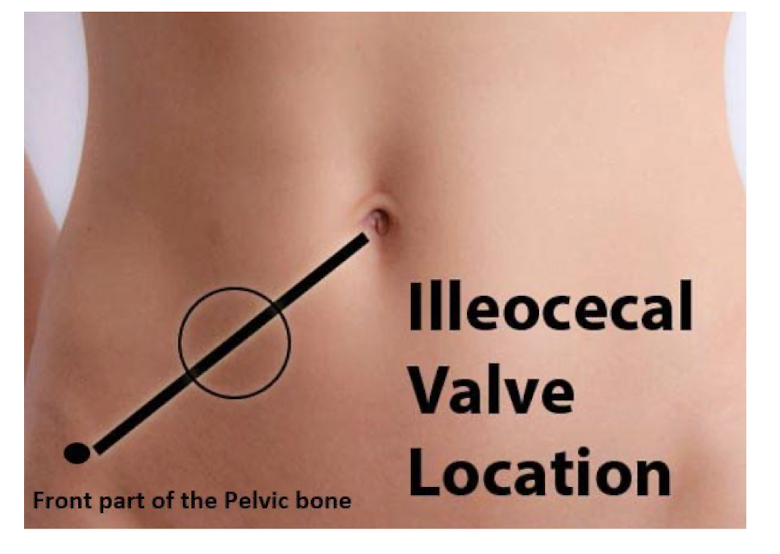
How to palpate ICV?
What size is it?
ICV aligns w what spinal level?
1/3 away from the R ASIS to Umbilicus (just above McBurney’s Point)
Dime
L5/SIJ
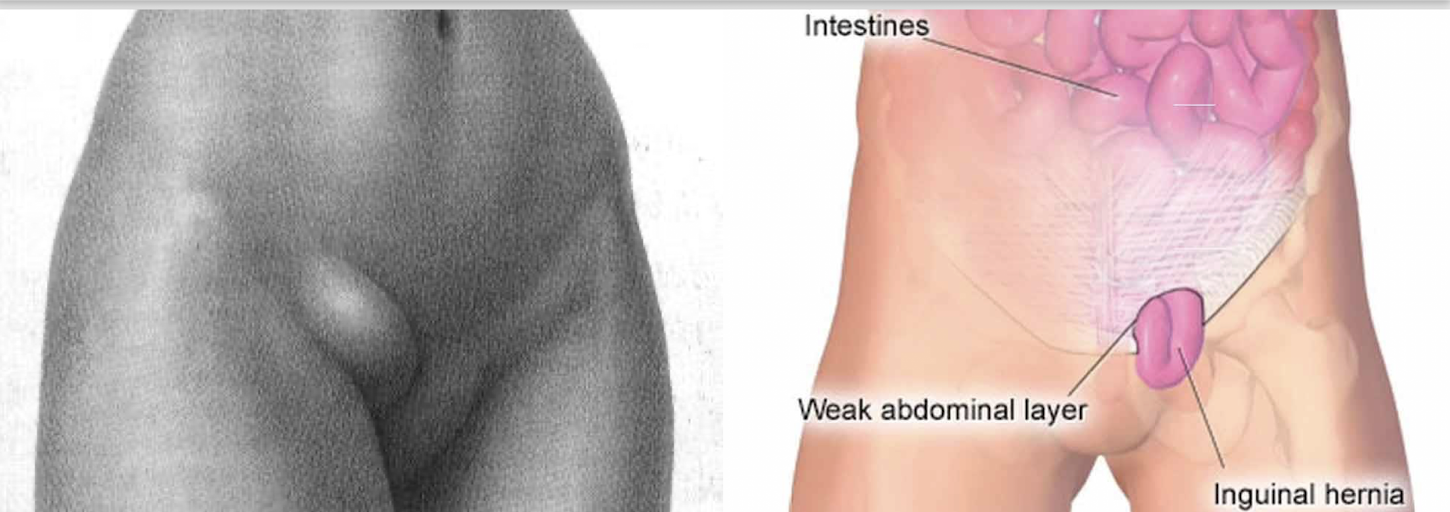
Inguinal Hernia:
What is an Inguinal Hernia?
Outpuching of abdominal contents through weak area in lower abdominal wall
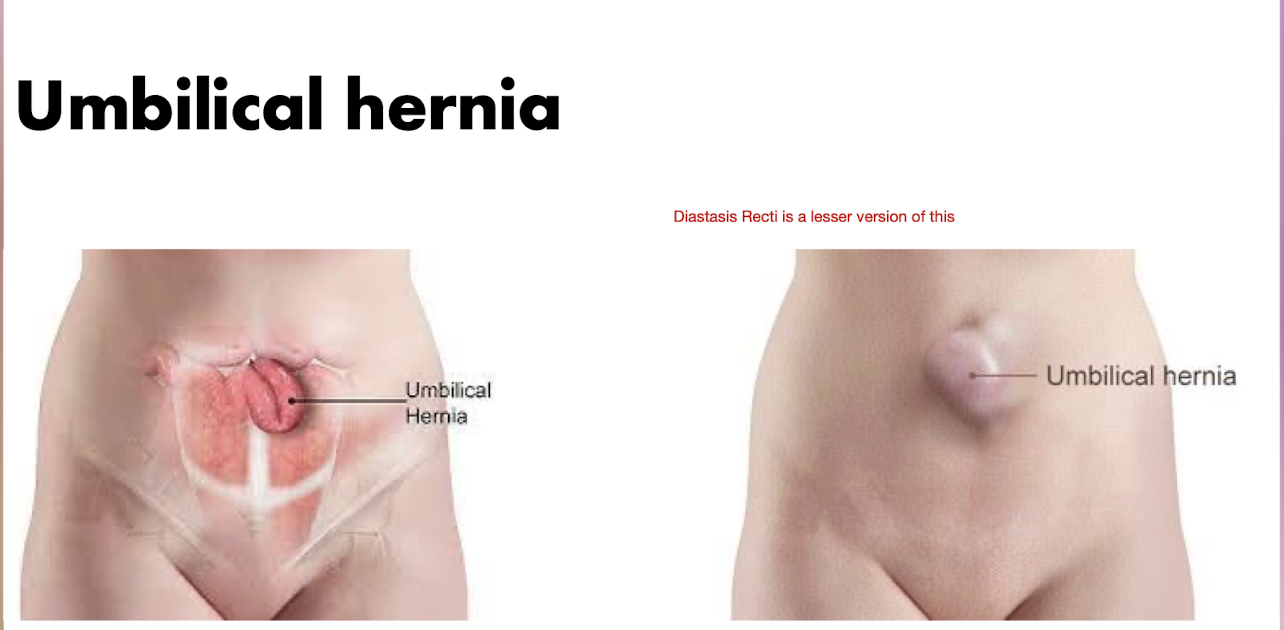
Umbilical Hernia
Apendicitis:
What is Appendicitis:
Appendix is mostly what type of tissue?
What is the cause for Appendicitis?
At least 1/3 are accompanied by what?
What is:
Inflammation of the appendix that can lead to rupture and necrosis
Lymphatic Tissue
Unknown
Obstruction and Improper Drainage
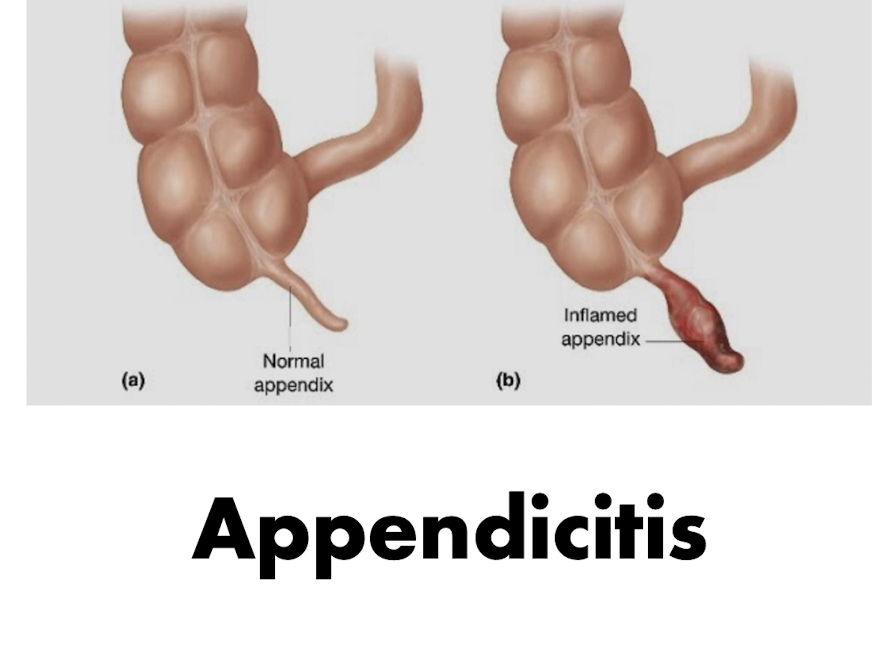
Appendicitis:
What type of referral?
What is the Tx?
Emergent Referral
Tx:
Surgical Removal
Antibiotics after sx
Bowel Function:
What are 6 subjective questions to ask for Bowel Function?
How often do they go?
Volume, Consistency?
Do u have difficulty?
Do you have excessive gas?
Are u constipated?
Do u have diarrhea?
What does an Ideal Bowel Movement look like? (5)
Medium brown, color of plain cardboard
Leave body easily w no straining or discomfort
Consistency of toothpaste and ~4-8 inches long
Should enter the water smoothy and slowly fall once reaches water
Minimal gas or odor

Bristol Poop Chart:
What is the ideal type fo poop?
Type 4
Bowel Function:
What does it mean if there is blood, pus, or blood in bowel?
Mucus can be caused by inflammation in intestines
Blood, Ulcers, Cancer
Bowel Function:
What does it mean if the stool is greasy, frothy, or foul smelling?
What is needed to break down fat?
Causes:
Frothy =
High fat content (Steatorrhea)
Lipase
Causes:
Pancreatic Insufficiency
Chronic Pancreatitis
Obstruction of Bile Duct
Bacterial Growth
Celiac Disease
Frothy = Malabsorption
Bowel Function:
What does sinking stool mean?
What color can the stool be from sitting for a while?
Can also be due to what?
Sinking Stool = Not enough fiber
Color = Dark
Infection
Bowel Function:
Constipation:
Can be due to:
Diarrhea:
Can be due to:
C:
Bowel Obstruction of carcinoma in colon
D:
Infection
Dehydration
Increased fall risk
Bowel Function:
What does dark blood indicate in the stool?
What does this stool look like?
Light stool may be due to what?
Dark Blood:
Bleed father up the GI Tract
Tarry Black Stools, Coffee Grounds
Light Blood:
Hemorrhoids
Lower GI Bleeding