Vision - chemoreceptors
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
vision
large complex sensory structure
signal transduction: light to AP
integration of info begins at level of receptor cells
information sent to brain for additional processing
photoreception
light
light
we can only see light in a tine area of wave legnth
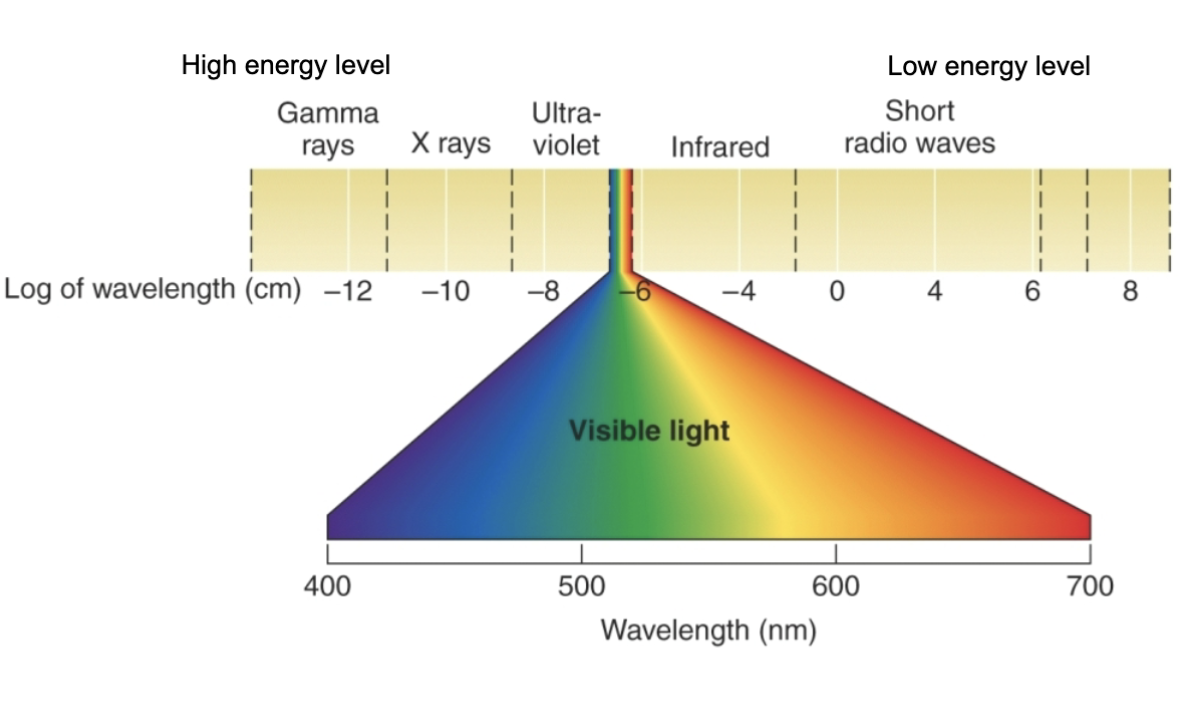
why cant we use x-rays for vision?
x-rays contain too much energy to damage rhodopsin
light outside of visable range has too much energy (damaging rhodopsine) or not enough energy to excite retinal
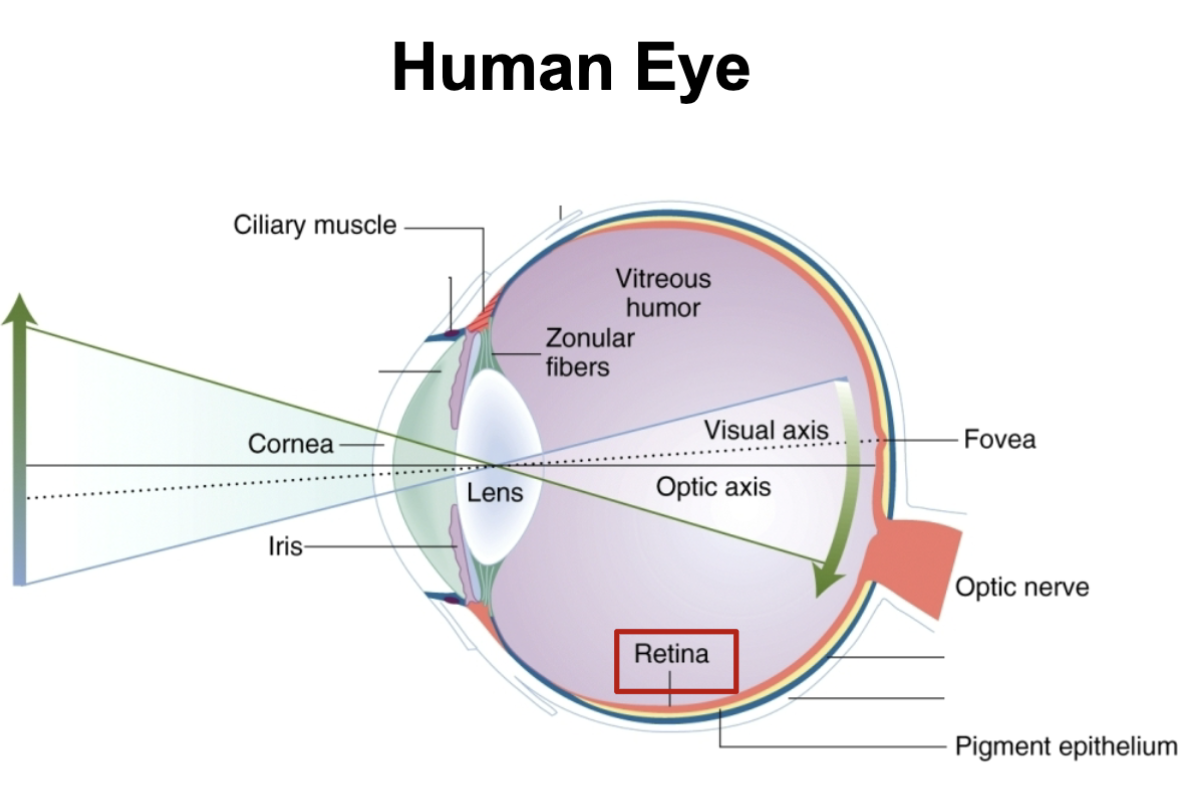
human eye
light comes in through cornea to lens to other critical parts of the eye to retina to optic nerve
the lens in your eye flips the image upside down and is sent to brain. once at the brain it flips this image back up to the way we see it now
Light passes to back of retina and the signal is then sent back to the front near the optic nerve
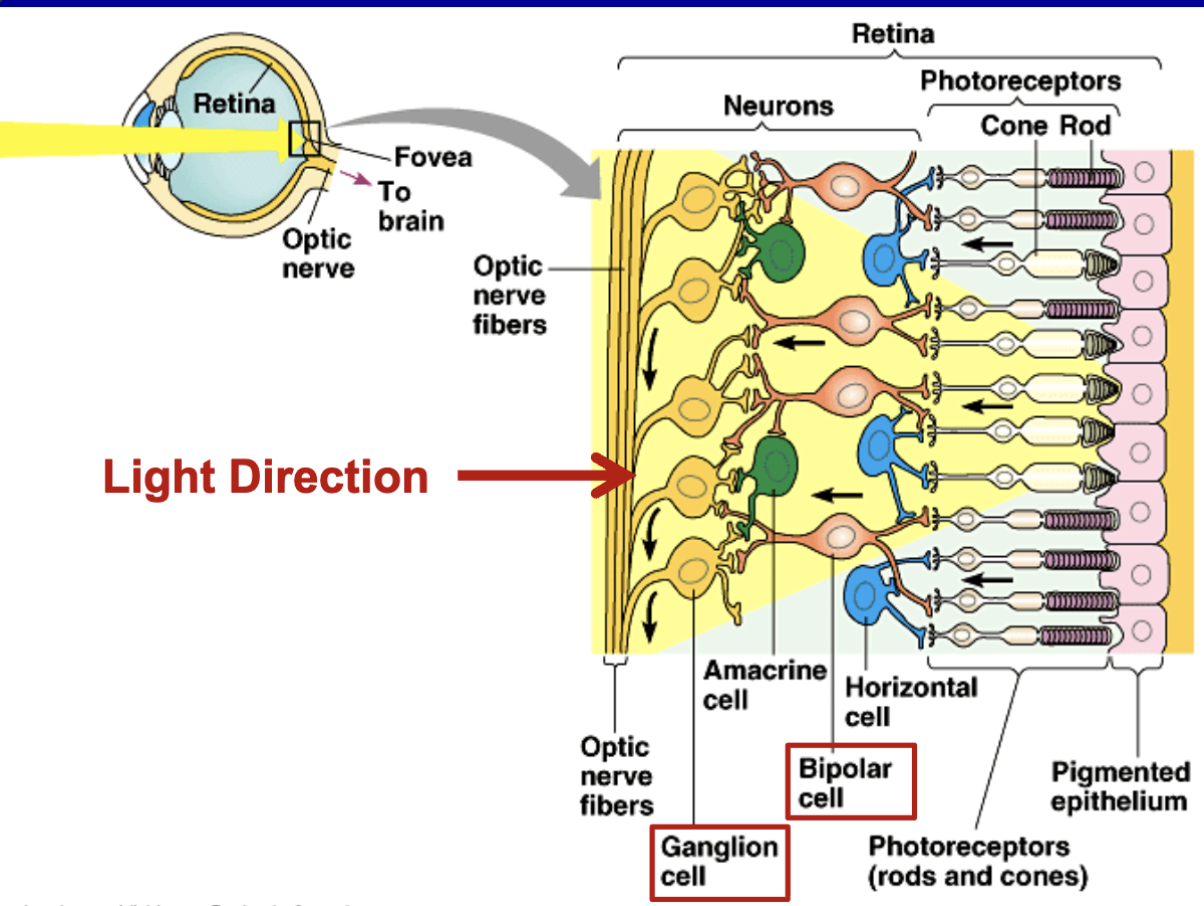
what forms the optic nerve?
ganglion cells
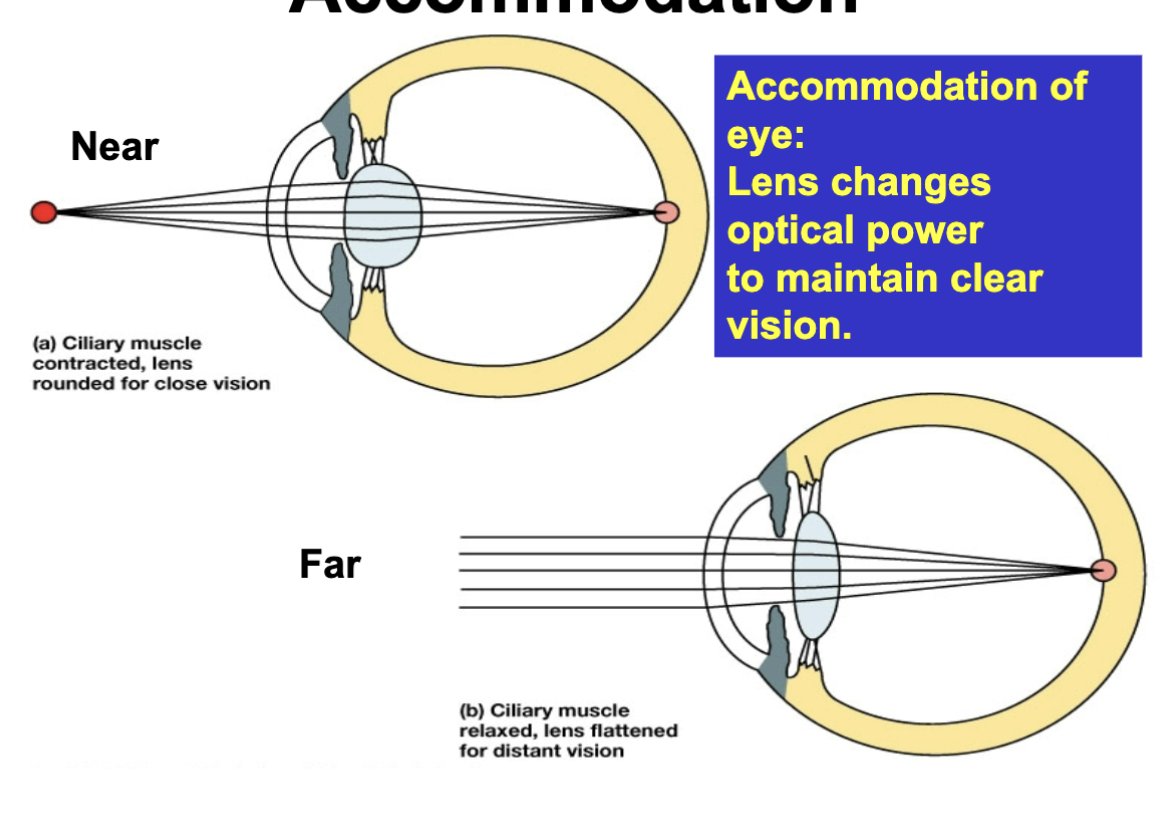
accomodation of eye
lens changes optical power to mainatin clear vision
near: cillary muscle contracted causing lens to be more rounded for close vision
far: cillary muscle relaxed causing lens to be flattened for distant vision
retina
important cells and photoreceptors
light moves through many different neurons in the retina to get to the photoreceptors
light cant go THROUGH cells in the front, these cells block the light
it has to find a way to get to the photoreceptors
Amacrine cells, bipolar cells, horizontal cells also part of processing
Bipolar cells directly connect photoreceptors to ganglion cell
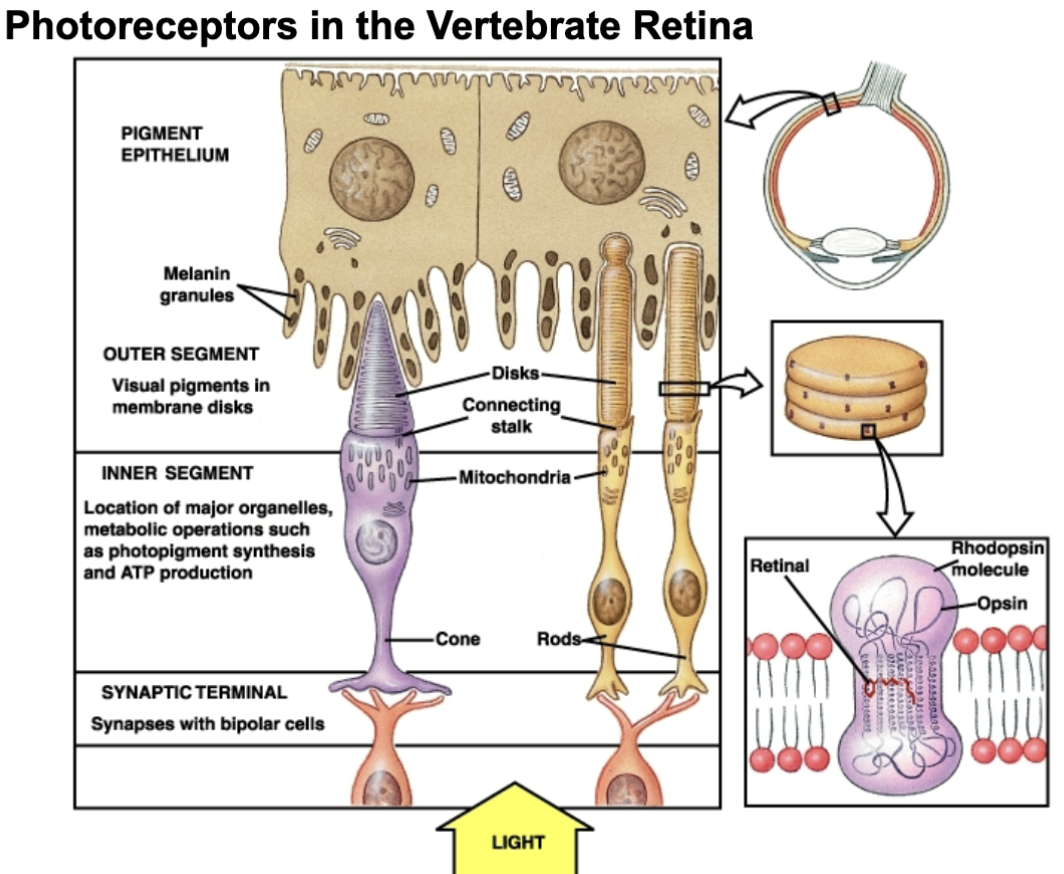
photoreceptors
cones and rod cells
send electrical signals to the brain
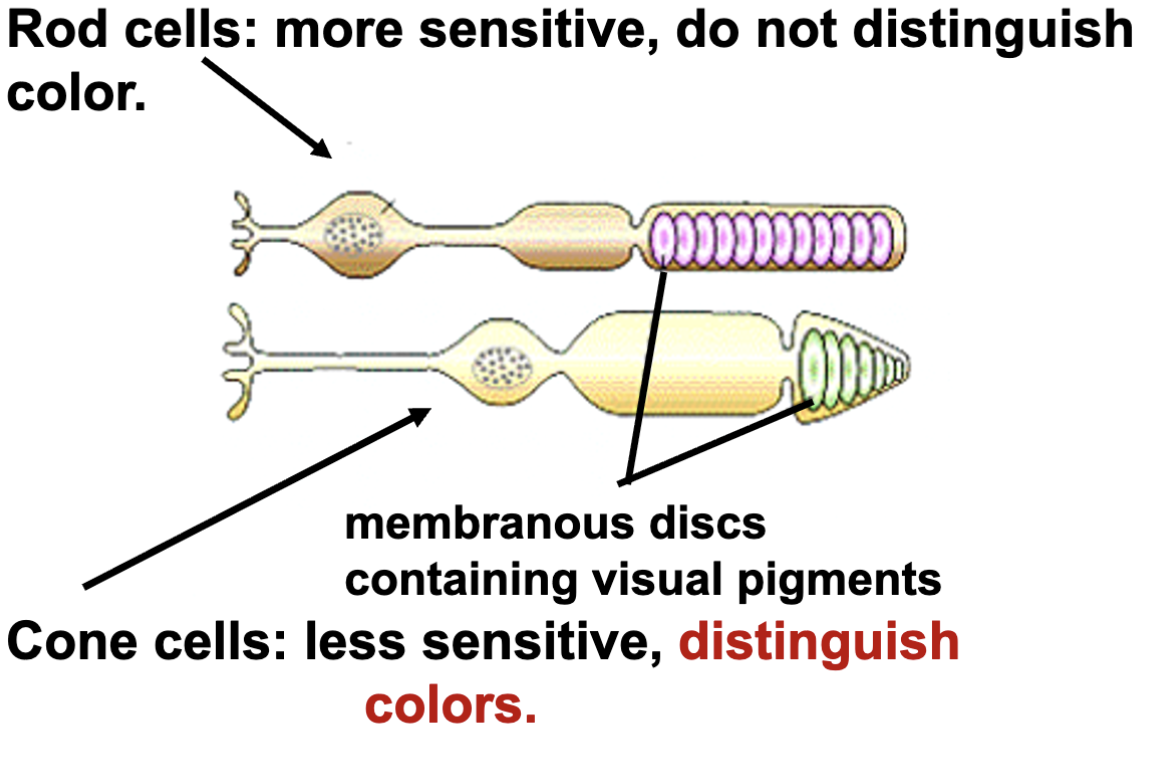
rod cells
detect absense of light (black and white)
more sensitive, dont distinguish color
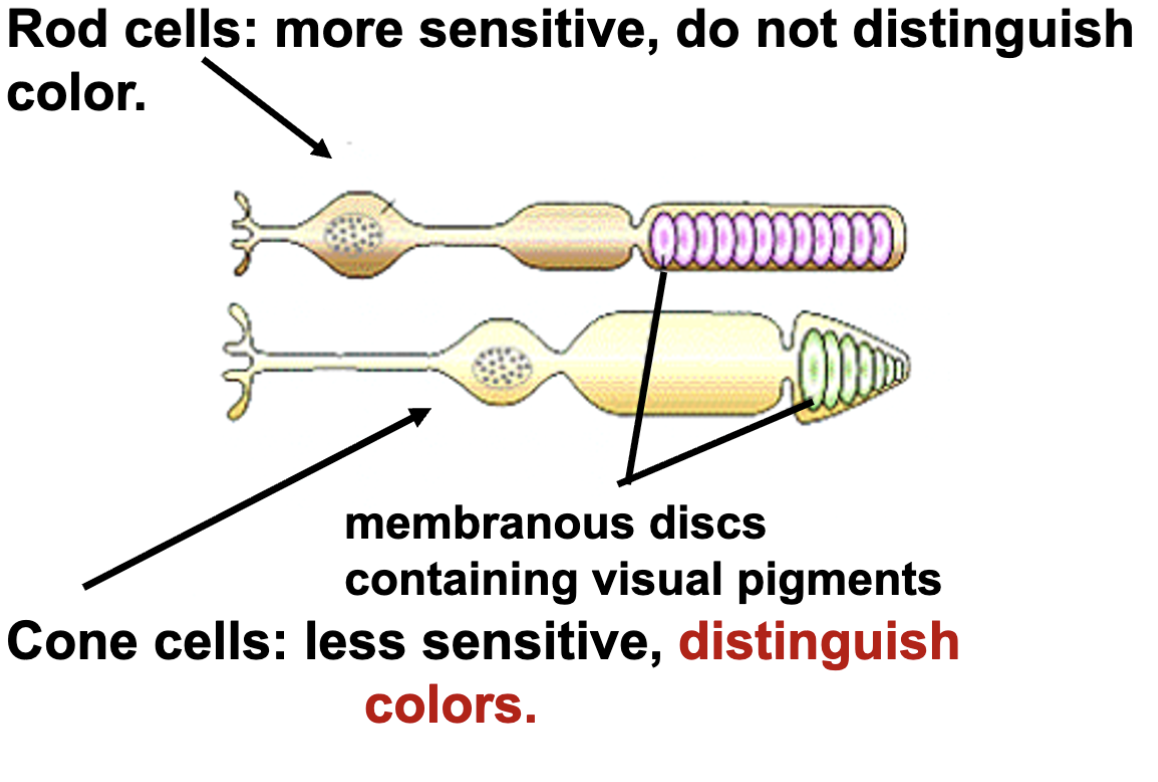
cone cells
less sensitive, distinguish color
How do we get pigment?
Retinal + Opsin protein = Rhodopsin = Photopigment
Opsin changes the amino acid sequence
Rod cells: 1 type of opsin
Black and white
Can still absorb SOME color (see photo)
Cone cells: 3 types of opsin
Red, green, blue
Light changes shape of retinal
opens ion channels
affects pigment that we see
effect of light on retinal
Retinal when light hits it it changes the shape of the rod cells
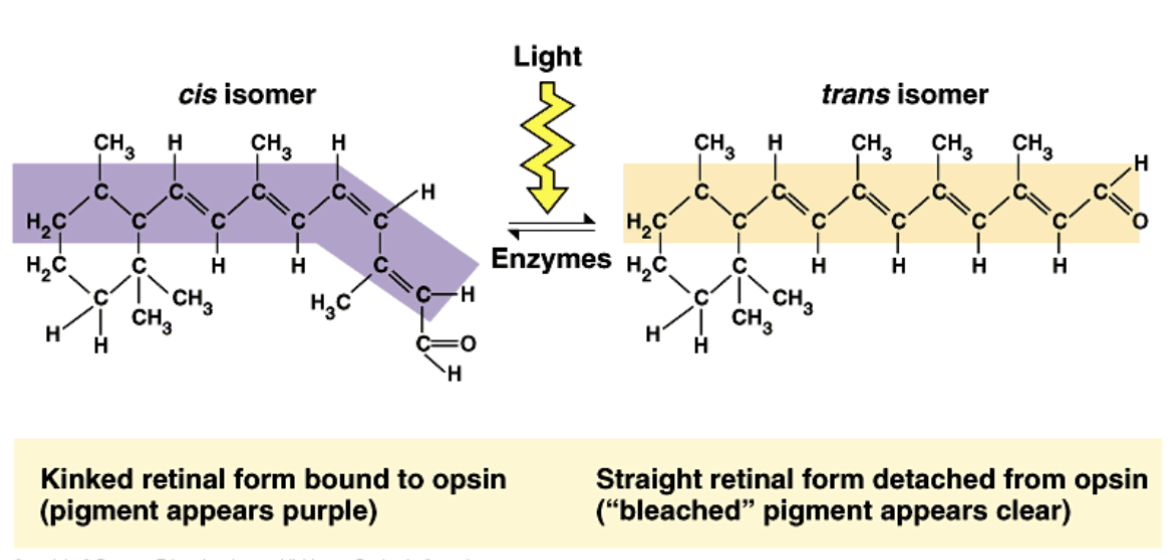
Cis vs trans this is what changes that causes an AP down the line
cis isomer: kinked retinal form bound to opsin
trans isomer: straight retinal form detached from opsin
trans recycled back to cis: this takes time
light outside of visable range has too much energy (damaging rhodopsine) or not enough energy to excite retinal
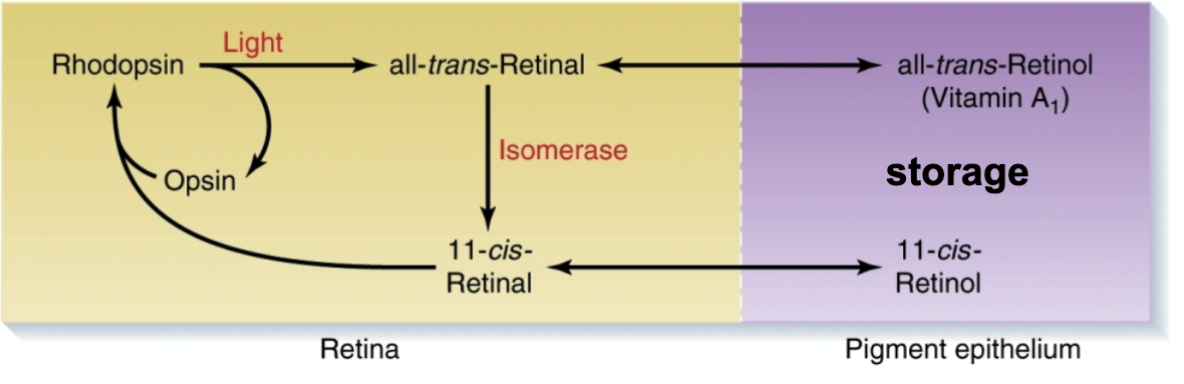
recycling of photopigment
takes time!
ex: temporary blindness after bright light
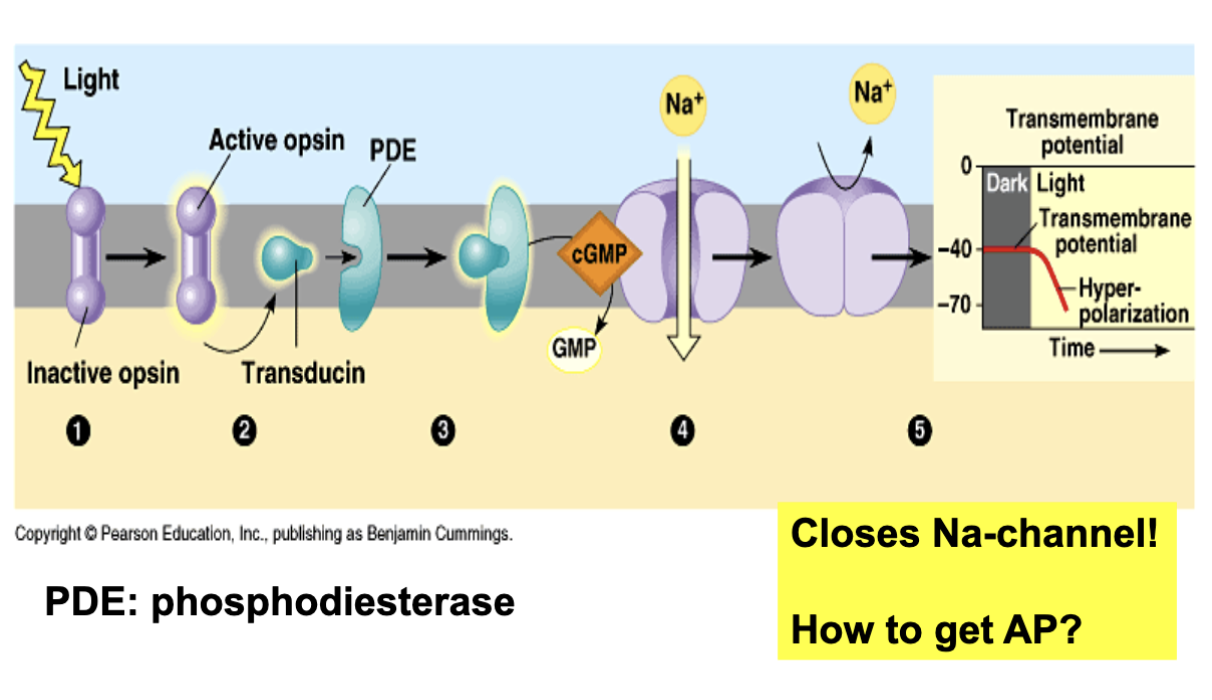
from light reception to receptor potential
Light hits rhodopsin, causing retinal to change from cis to trans shape.
This shape change is crucial for activating the phototransduction pathway.
Phosphodiesterase (PDE):
Activated by the change in retinal shape.
PDE breaks down cGMP (cyclic guanosine monophosphate).
Normally, cGMP keeps sodium channels open.
When cGMP levels drop, sodium channels close
Closing sodium channels prevents sodium ions from entering the cell.
The inside of the cell becomes more negative (hyperpolarized).
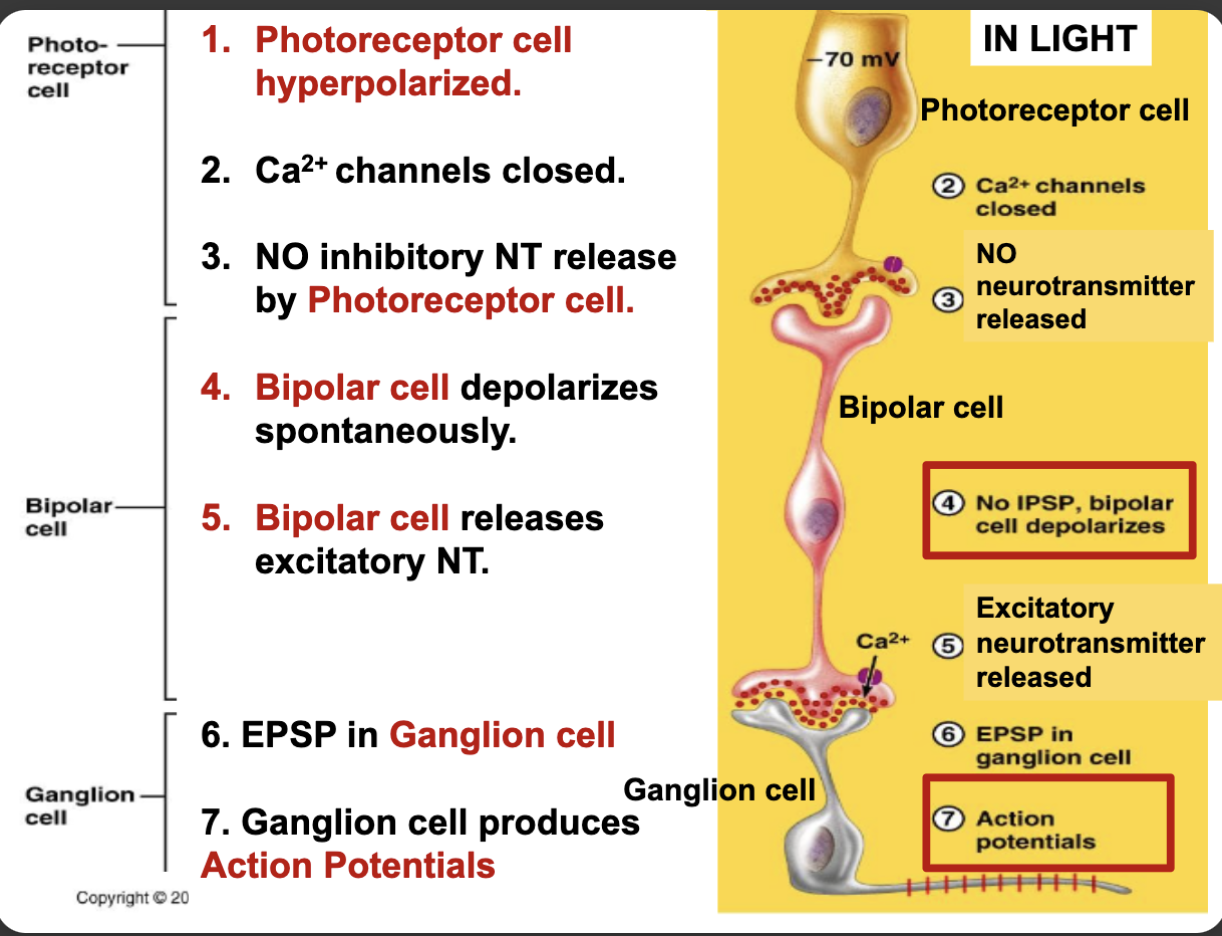
How does your vision get AP’s in light
photoreceptor cell hyperpolarized
Ca channels closed
No IPSP; bipolar cell depolarizes spontaneously
Bipolar cell releases excitatory NT
EPSP in ganglion cell
Ganglion cell produces APs
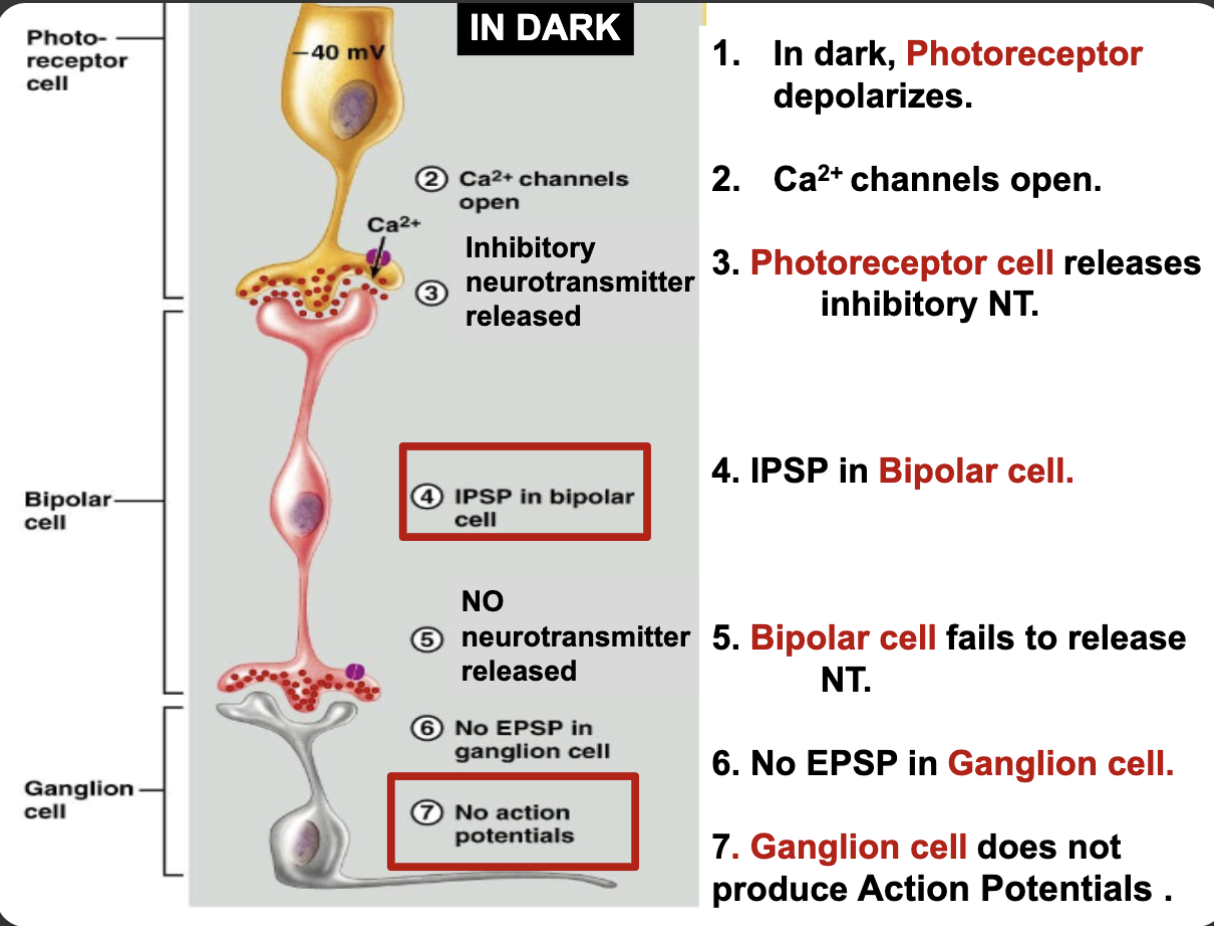
How does your vision get AP’s in dark
in dark, photoreceptor depolarizes
Ca channels open
photoreceptor cell releases inhibitory NT
IPSP in bipolar cell
Bipolar cell fails to release NT
No EPSP in ganglion cell
Ganglion cell does not produce AP’s
color mixing
primary colors: cyan, magenta, and yellow
black is the absence of light
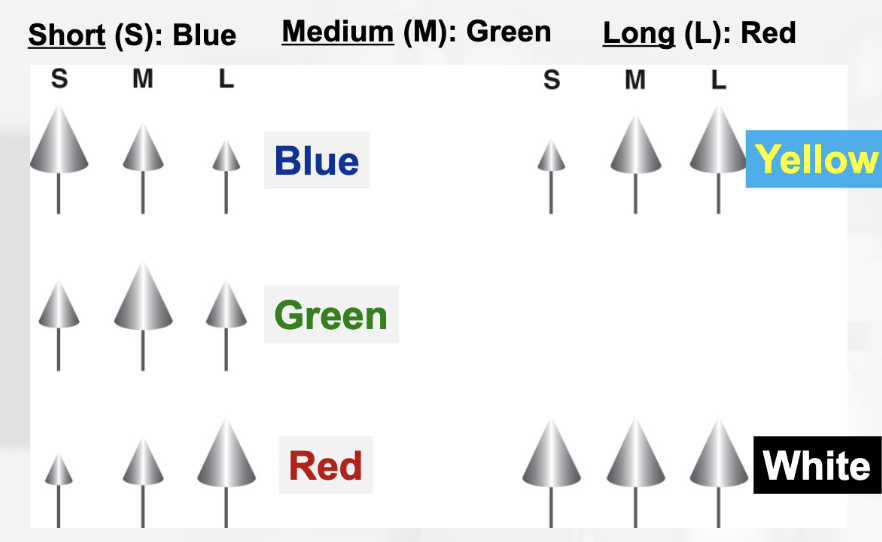
wavelegnth sensitivity of rods and 3 types of cone cells
each type of cone cell has a different opsin
patterns of firing of the 3 types of cones to diff colors. Size of cone symbolizes size of receptor response
blue: short cone has a larger response
green: medium cone has a larger response
red: large cone has a larger response
yellow: medium and large cone has a larger response
white: all cone sizes have a large response
color blindness
some people are missing certian cone colors that cause them not to be able to see certian colors
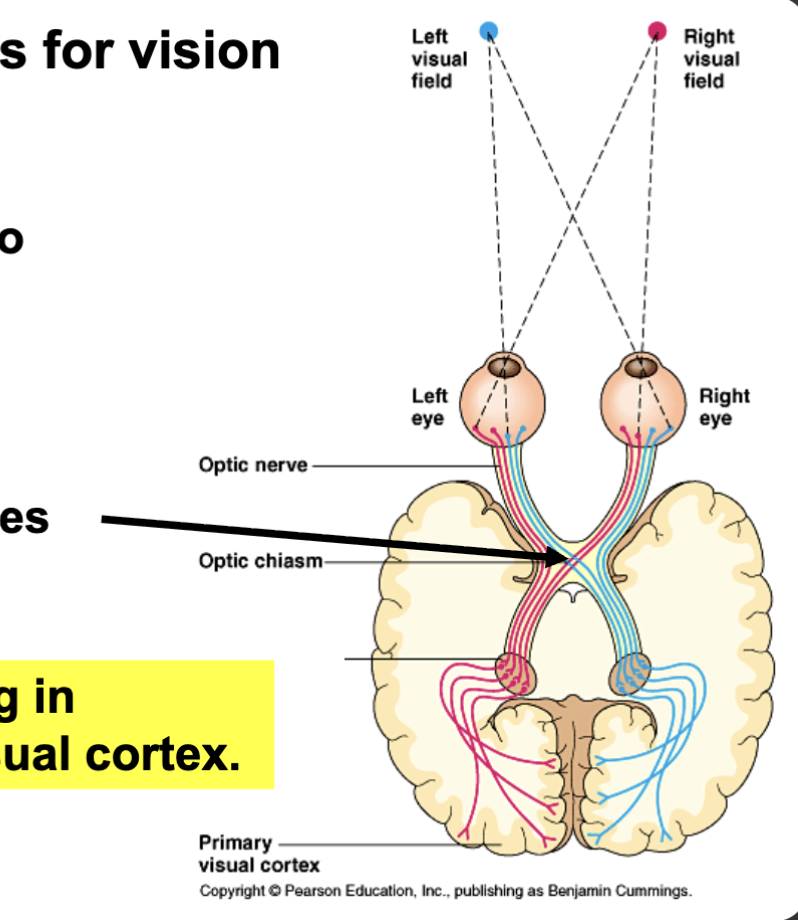
neural pathways for vision
info of object on the right visual field goes to brain on left side
same for left to right side of brain
info crosses over
visual processing in back of brain, visual cortex
ur brain can put things together and fill in info that was never there