StemUp: OCR A A level Biology 2.1.5 Biological Membranes
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
What is the name of the model for the cell membrane? (1)
The fluid mosaic model
What is the main function of the cell membrane? (1)
To control entry and exit of substances into and out of the cell
What does the 'fluid mosaic' model imply about the cell membrane? (2)
- 'Fluid' - the components of the membrane are free to move past each other
- 'Mosaic' - there are membrane proteins that are embedded in the cell membrane
Describe the structure of the cell surface membrane (2)
- A phospholipid bilayer with a hydrophobic core
- With proteins both spanning the membrane and embedded on either side
Draw and label the structure of the cell surface membrane (6)
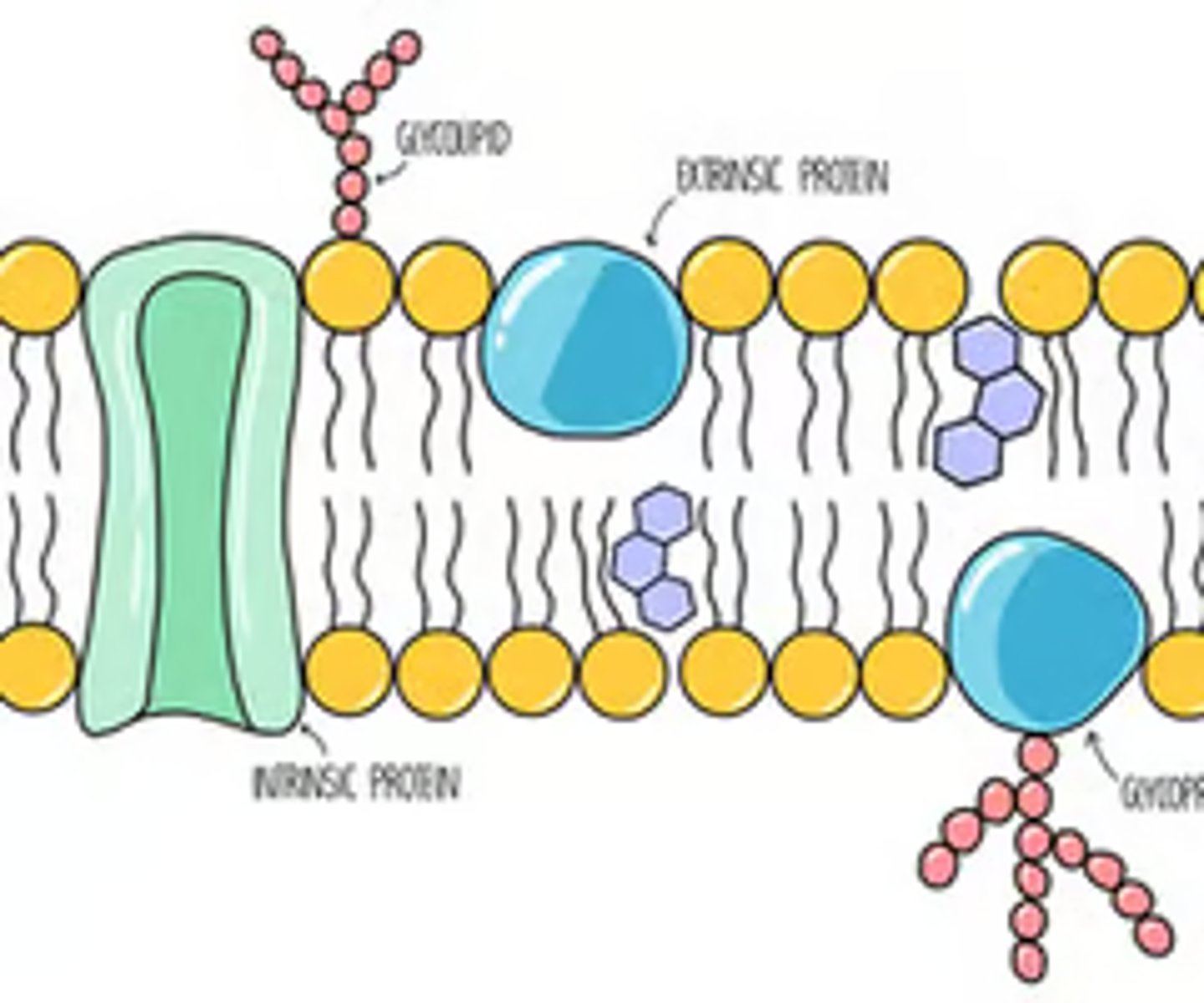
What is diffusion? (3)
- The passive movement of non polar molecules
- From an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
- Across the phospholipid bilayer
What is osmosis? (3)
- The passive movement of water molecules
- From an area of low solute concentration (high water potential) to an area of high solute concentration (low water potential)
- Across a partially permeable membrane
What is facilitated diffusion? (2)
- The passive movement of polar molecules across a membrane
- Through a channel protein
What is active transport? (2)
- The energy-requiring movement of molecules
- Against their concentration gradient
What is required for active transport? (1)
Hydrolysis of ATP
What is a carrier protein? (1)
A protein that spans the membrane and actively transports molecules across it
What is a channel protein? (1)
A hydrophilic channel that facilitates the movement of polar molecules across the membrane
What is cholesterol? (1)
A soluble lipid made in the body
How does temperature affect membrane structure and permeability? (3)
- Higher temperatures increase membrane fluidity, making it more permeable
- Very high temperatures can cause membrane proteins to denature
- Disrupting its structure and further increasing permeability.
How does solvent concentration affect membrane structure and permeability? (2)
- Organic solvents, like alcohol, dissolve lipids in the membrane
- Disrupting its structure and increasing permeability.
How does pH affect membrane structure and permeability? (2)
- Changes in pH can affect the structure of membrane proteins
- Altering the membrane's permeability.