ppt lesson 5.1 functions and organization of the skeletal system
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
what are the 4 functions of the skeletal system?
support & movement
protection
storage
manufacturing
explain how the skeleton supports as a function
supports the body, soft tissues, organs, and body walls
holds us up
tendons-
connect muscle → bone
anchorage of skeletal muscles
needed for movement
ligaments-
connect bones → bones at joints
stability of joints
explain how the skeleton protects as a function, and what 3 parts of the skeleton protects what organs
the skeleton surrounds vital organs
skull → brain
vertebrae → spinal cord
ribs → heart and lungs
what are the 2 classifications of the skeleton?
axial and appendicular
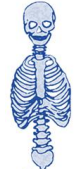
what is the axial skeleton comprised of?
makes up the central axis of the body-
skull
vertebrae
rib cage
primarily protection functions
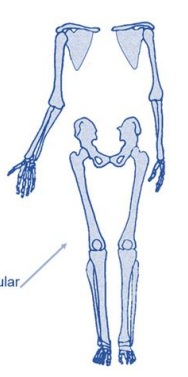
what is the appendicular skeleton comprised of, and what are the upper and lower limbs?
makes up the limbs/appendages
upper limbs-
shoulders
arms
lower limbs-
pelvis
legs
primarily support & movement functions
explain the relationships between yellow & red bone marrow to fat storage & blood cell formation
yellow marrow-
adipose tissue
fat storage
red marrow-
blood cell formation/hematopoiesis occurs
RBCs, WBCs, & platelets are produced here
explain how the skeleton stores minerals
the skeleton stores minerals, especially calcium & phosphorous
ca and p-
incorporated into bone tissue
released back into the bloodstream to maintain physiological processes levels
explain calcium homeostasis
calcium is required for muscle contraction and bone growth & remodeling
calcium homeostasis-
the skeleton maintains stable calcium levels in the blood
inadequate calcium supply-
parathyroid hormone PTH activates osteoclasts-
breaks down bone
releases calcium into the bloodstream
calcitonin activates osteoblasts that builds bones
what are the 4 classifications by shape of bones?
long
short
flat
irregular
what are long bones and examples of them?
longer than wide
ends flared for use at a joint
functions as levers, move when muscles contract
examples-
clavicle
humerus
radius
ulna
metacarpus
phalanges
femur
tibia
fibula
metarsus
what are short bones and examples of them?
cube-like and squarish shape
equal in length, width, thickness
stability, support, limited motion
examples-
wrist, ankle, knee/patella bones
which bone in the body is a sesamoid bone and why?
patella due to its shape, embedded in tendons / not directly connected to other bones
what are flat bones and examples of them?
thin, flat, curved
unique shapes to fit functions-
points of attachment for muscles
protect internal organs
examples-
cranial/skull
scapula/shoulder
sternum/breastbone
ribs
pelvis bones
what are irregular bones and examples of them?
complex and oddly shaped
structure fits function
examples-
vertebrae for spinal cord
facial bones like ones containing sinuses
what are sesamoid bones and examples of them?
small and round
embedded in tendons
function: protect tendons from compressive forces
examples-
in tendons associated with the feet, hands, knees
patella