Organic Chemistry - Rules/Basics
5.0(3)
Card Sorting
1/81
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:29 PM on 11/2/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
1
New cards
Draw: Neutral Fully Bonded Boron (2 ways)
Key - 3 Bonds

2
New cards
Draw: Neutral Fully Bonded Carbon (3 ways)
Key - 4 Bonds
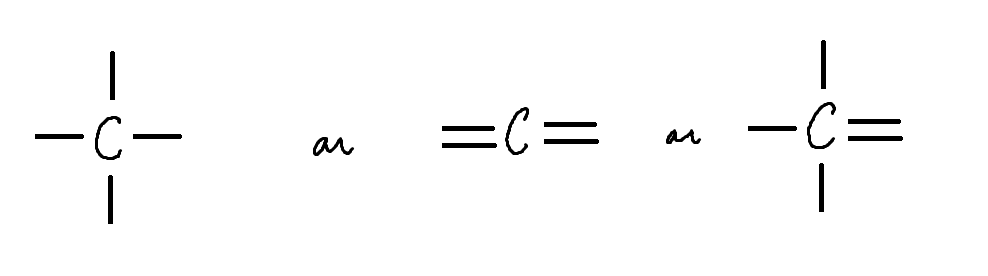
3
New cards
Draw: Neutral Fully Bonded Nitrogen (2 ways)
Key - 3 Bonds + 1 Lone Pair
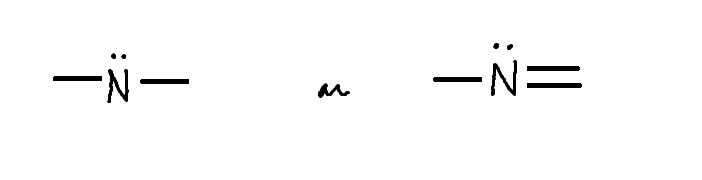
4
New cards
Draw: Neutral Fully Bonded Oxygen (2 ways)
Key - 2 Bonds + 2 Lone Pairs

5
New cards
Draw: Neutral Fully Bonded Fluorine (1 way)
Key - 1 Bond + 3 Lone Pairs
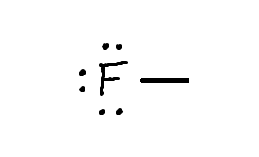
6
New cards
Identify: The Charged Atom In This Molecule
Nitrogen - Has four bonds, no lone pair, results in + charge
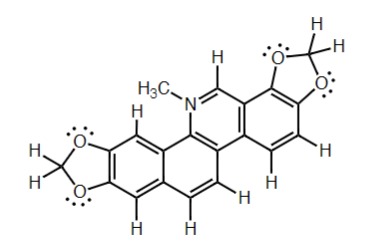
7
New cards
Identify: The Charged Atoms In This Molecule
Rightmost Oxygen - 3 lone pairs, one bond, results in - charge
3rd Right Carbon - 3 bonds, results in + charge
3rd Right Carbon - 3 bonds, results in + charge
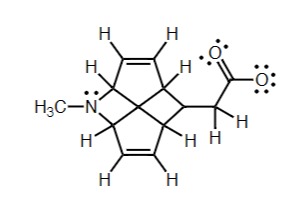
8
New cards
Which atom(s) have an oxidation state of -1 (bonded with Carbon)?
Hydrogen (H) and Boron (B)
9
New cards
Which atom(s) have an oxidation state of +1 (bonded with Carbon)?
Nitrogen (N), Oxygen (O), Sulfur (S), Halogens: Fluorine (F), Chlorine (Cl), Bromine (Br), Iodine (I)
10
New cards
Which atom(s) have an oxidation state of 0 (bonded with Carbon)?
Carbon
11
New cards
Assign oxidation states to each molecule:
Left to right: 0, +1, +2, +3, +4
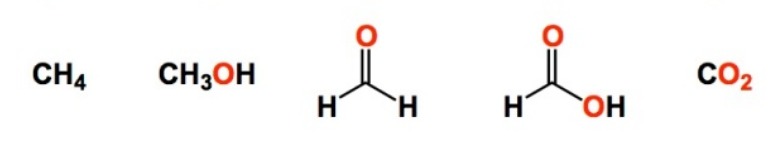
12
New cards
True or False: Molecules Rapidly Switch Between Resonance Structures
False, in truth the molecule exits in between the resonance structures
13
New cards
True or False: Curly arrows showing the making/breaking of sigma bonds are found in both reaction and resonance diagrams
False, curly arrows that make or break sigma bonds are found ONLY in reaction diagrams
14
New cards
Draw: The Trend of Electronegativity on the Periodic Table
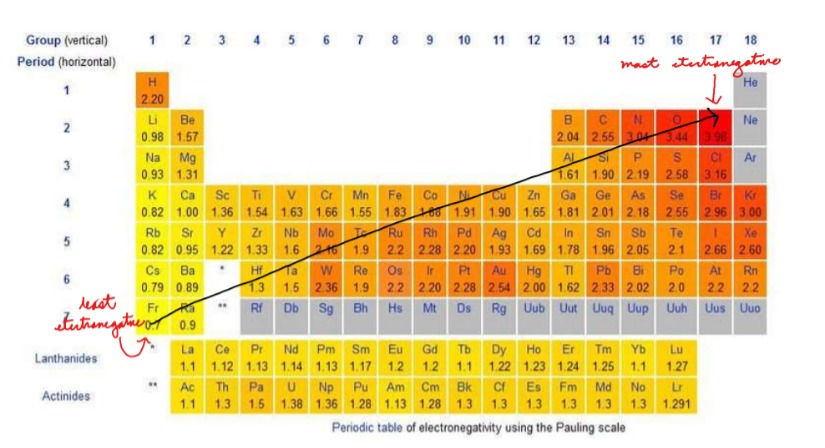
15
New cards
Draw: The Trend of Atomic Radii on the Periodic Table
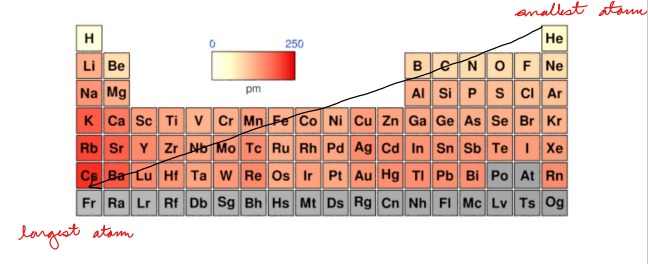
16
New cards
Rank from Most to Least Electronegative: N, B, C, F
F,N,C,B
17
New cards
Rank from Largest to Smallest: F, C, B, O
B,C,O, F
18
New cards
Rank from Smallest to Largest Difference in Electronegativity: Ionic Bonds, Polar Covalent Bonds, Covalent Bonds
Covalent, Polar Covalent, Ionic
19
New cards
True or False: Bond Length is Directly Proportional to Bond Strength. Explain your answer.
False between different elements since ionic/covalent components come into play (most ionic = strongest). True between the same elements
20
New cards
Rank from Shortest to Longest: Single Bonds, Double Bonds, Triple Bonds (between the same elements)
Triple Bonds, Double Bonds, Single Bonds
21
New cards
True or False: Triple Bonds are Stronger than Single Bonds, explain.
True, triple bonds are shorter and therefore stronger than the longer, weaker, single bonds.
22
New cards
Describe: Ionic Interactions
Interactions between ions, full +/- charges on atoms
23
New cards
Describe: Hydrogen Bonding Interactions
Bonds between Hydrogen and a more electronegative atom (O,N,S,Cl,F)
24
New cards
Describe: Dipole Interactions
A single molecule experiences charge (polarity) without the presence of another molecule (affects the orientation of molecules near each other)
25
New cards
Describe: van der Waals Interactions
Interactions between two non-polar molecules resulting in an induced dipole (the dipole is not present in individual molecules)
26
New cards
True or False: Intermolecular Forces that are More Sensitive to Distance are Stronger
False, the more sensitive a force is to distance the weaker the force is. For example, the weakest intermolecular force (van der Waals) is very sensitive to distance.
27
New cards
Which Molecule Would Have a Higher Boiling Point, CH3CH2(OH)CH3 or C9H20
Despite the presence of hydrogen bonding, and a dipole in CH3CH2(OH)CH3, the abundance of weak van der Waals forces in C9H20 result in greater overall strength in the molecule, thus resulting in a higher boiling point.
28
New cards
Would CH3F or CH3I have a higher boiling point?
While CH3F contains the most electronegative molecule (strong dipole moment), Iodine has 53 electrons, each of which acts as a van der Waals force. Strength in numbers, CH3I has a much higher boiling point
29
New cards
True or False: The Structure (Physical Shape) of a Molecule has No Effect on Boiling Point
False, molecules that are flatter (easier to stack) have higher boiling points than molecules that are "rounder" in shape, even if the number and type of molecules are the same.
30
New cards
What important features do we need to consider when determining the best resonance structure? Rank them in descending order of importance.
1. Full octets on all atoms (over is worse than under)
2. Minimum amount of charge (total number of +/- charges)
3. Charges match electronegativity
4. Minimized distance between charges
2. Minimum amount of charge (total number of +/- charges)
3. Charges match electronegativity
4. Minimized distance between charges
31
New cards
What is a rule for determining the hybridization of an atom?
Number of bonding domains (bonds + lone pairs) minus 1.
32
New cards
Are sp, sp2, or sp3 bonds shorter, why?
sp. S orbitals are held closer to the nucleus of the atom, so hybrid orbitals with more s character make shorter bonds. (stronger bonds)
33
New cards
What do hybrid orbitals make, what do p orbitals make?
Hybrid orbitals make sigma bonds or hold lone pairs
P orbitals make pi bonds or hold lone pairs
P orbitals make pi bonds or hold lone pairs
34
New cards
True or False: Every atom must have the same hybridization in every resonance structure
True
35
New cards
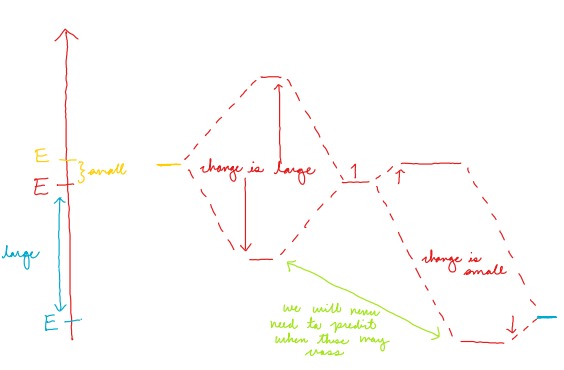
If the initial energy gap is large, how will orbital energy levels change upon mixing? What if the gap was small?
A large initial energy gap results in a small change in orbital energy levels
A small initial energy gap results in a large change in orbital energy levels
A small initial energy gap results in a large change in orbital energy levels
36
New cards
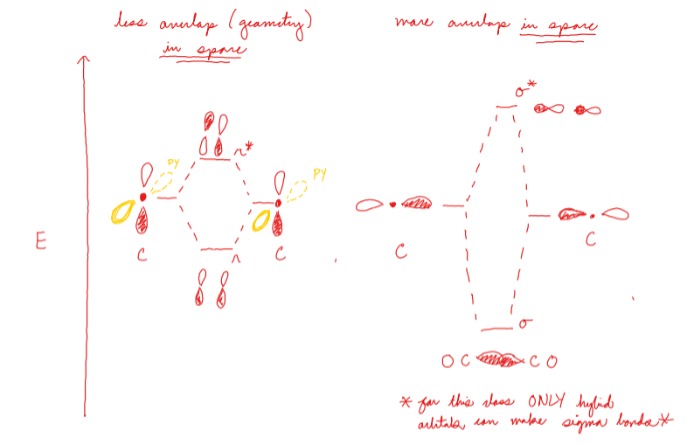
How does orbital overlap change orbital energy levels?
A greater overlap results in a large change in orbital energy levels
Less overlap results in a small change in orbital energy levels
Less overlap results in a small change in orbital energy levels
37
New cards
Define: Nucleophile
Nucleus loving, hence electron rich, electron donor, Lewis base
38
New cards
Define: Nucleophilicity
How nucleophilic a nucleophile is
39
New cards
Define: Electrophile
Electron loving, hence electron poor, electron acceptor, Lewis acid.
40
New cards
Define: Electrophilicity
How electrophilic and electrophile is
41
New cards
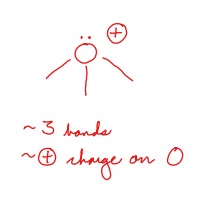
Draw an oxonium ion
A (+) oxygen with three bonds
42
New cards
What is a carbocation
A positively charged carbon with three bonds.
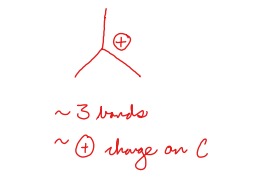
43
New cards
What is the difference between an enol and an enolate?
Enol - OH bond
Enolate - O(-)
Enolate - O(-)
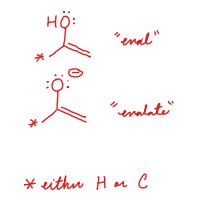
44
New cards
What factors affect acidity?
Resonance
Hybridization
Electronegativity
Polarizability
Inductive effects
Charge balance
Hybridization
Electronegativity
Polarizability
Inductive effects
Charge balance
45
New cards
How does electronegativity affect acidity?
More electronegative = more acidic
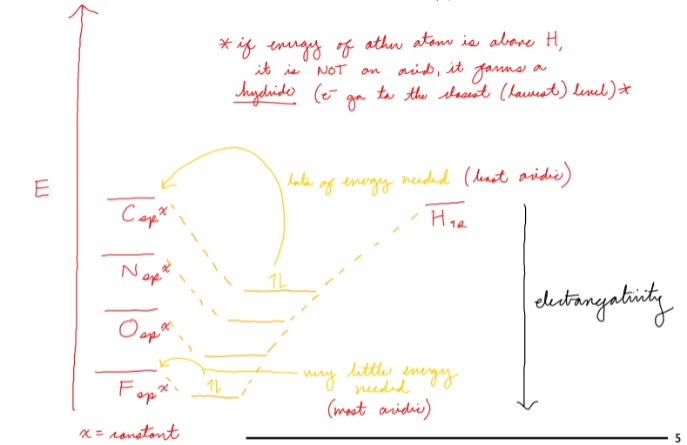
46
New cards
How does hybridization affect acidity?
sp is most acidic, sp2 is intermediate, sp3 is least acidic
From sp3 to sp2 pka changes by about 5, from sp2 to sp pka changes by about 20.
From sp3 to sp2 pka changes by about 5, from sp2 to sp pka changes by about 20.
47
New cards
How do inductive effects affect acidity?
The presence of electronegative atom/atoms not attached to the H bond in question that influences the pka of the bond.
(The electronegativity of the atom/atoms, the number of atoms, and the proximity of the atom to the bond affect the strength of inductive effects)
*Inductive effects make very minute changes*
(The electronegativity of the atom/atoms, the number of atoms, and the proximity of the atom to the bond affect the strength of inductive effects)
*Inductive effects make very minute changes*
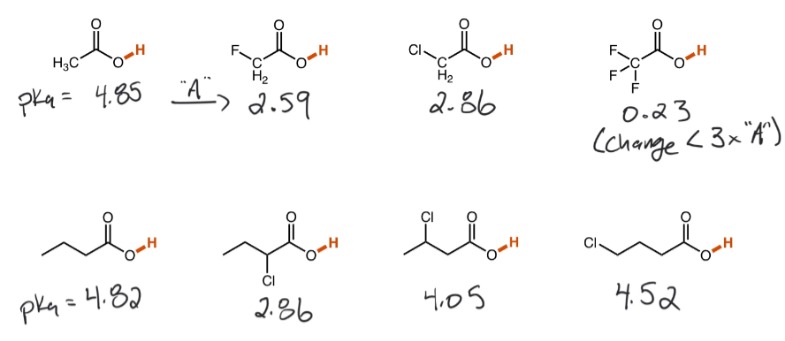
48
New cards
How does resonance affect acidity?
1. "Share the burden" if the conjugate base of an acid is capable of sharing negative charges via resonance (more stable) the acid has a lower pka (more acidic)
2. "Move charge to a new atom" if the charge can be moved to a new atom more suited to carry a charge the pka is reduced.
3. "Hybridization" resonance structures determine hybridization
2. "Move charge to a new atom" if the charge can be moved to a new atom more suited to carry a charge the pka is reduced.
3. "Hybridization" resonance structures determine hybridization
49
New cards
How does polarizability affect acidity?
Atoms with more electrons (lower in the periodic table) are easier to remove a proton from (more polarizable). More polarizable = lower pka.
50
New cards
Which side of an equilibrium equation is favoured?
The side of the equilibrium that is favoured is the one with a higher pKa
51
New cards
What are the rules for predicting bond strength?
1. Bond order wins - lower bond order = stronger bons
2. Atomic radius impacts bond length/strength (larger radii result in longer, weaker bonds)
3. Lone pairs (in the second row) repel each other resulting in weaker bonds
2. Atomic radius impacts bond length/strength (larger radii result in longer, weaker bonds)
3. Lone pairs (in the second row) repel each other resulting in weaker bonds
52
New cards
How does hybridization affect C-H bond strength?
S orbitals are held closer to the nucleus of the atom, so hybrid orbitals with more s character make stronger bonds.
53
New cards
How does substitution affect C-H bond strength?
More surrounding bonds to carbon atoms result in weaker bond strength.
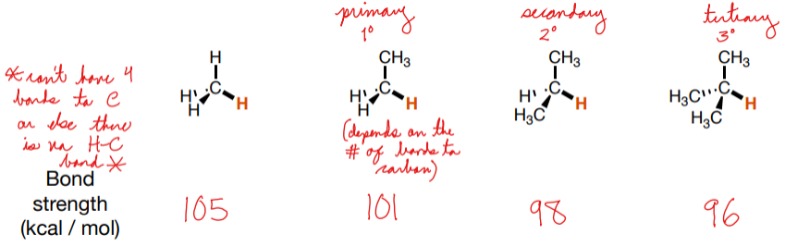
54
New cards
If a C radical is unstable, what do we know about the C-H bond it came from?
The C-H bond it came from was strong (it didn't want to break)
55
New cards
If a C radical is stable, what do we know about the C-H bond it came from?
The C-H bond it came from was weak (it was okay to break), there were more C-C bonds surrounding the C-H bond (substitution)
56
New cards
How does resonance affect bond strength?
Resonance involves delocalization of electrons over multiple bonds so they have both single and double bond character making them stronger than the single bond.
57
New cards
How do you determine the index of hydrogen deficiency?
(2x(# of carbon atoms) + 2) - (number of hydrogen atoms)
or the number of rings + the number of pi bonds
or the number of rings + the number of pi bonds
58
New cards
Rank the stability of radicals that came from primary, secondary, and tertiary C-H bonds.
1. Tertiary
2. Secondary
3. Primary
More surrounding C-C bonds make the C-H bond weaker and thus more stable as a radical
2. Secondary
3. Primary
More surrounding C-C bonds make the C-H bond weaker and thus more stable as a radical
59
New cards
What are the three names for C-H bonds near C-C single bonds? What defines each?
Primary - 1 C-C bond surrounding the center C of the C-H bond
Secondary - 2 C-C bonds surrounding the center C of the C-H bond
Tertiary - 3 C-C bonds surrounding the center C of the C-H bond
Secondary - 2 C-C bonds surrounding the center C of the C-H bond
Tertiary - 3 C-C bonds surrounding the center C of the C-H bond
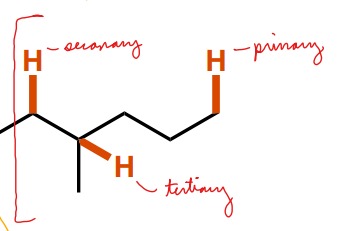
60
New cards
What are the two names for C-H bonds near C-C double bonds? What defines each?
Vinylic (connected to a C=C bond)
Allylic (beside a C=C bond)
Allylic (beside a C=C bond)
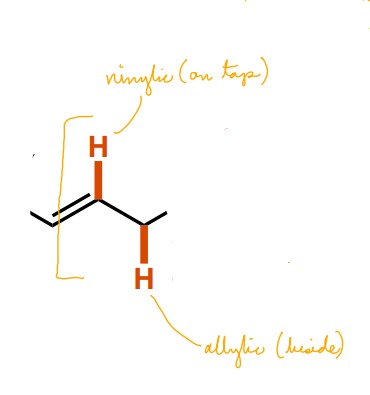
61
New cards
What are the two names for C-H bonds near C-C triple bonds? What defines each?
Acetylenic (connected to a C-C triple bond)
Propargylic (next to a C-C triple bond)
Propargylic (next to a C-C triple bond)
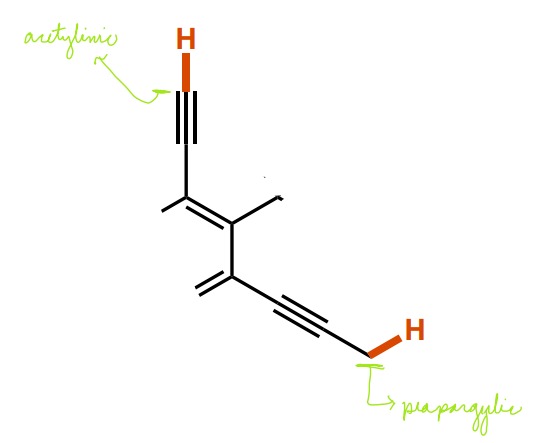
62
New cards
What are the two names for C-H bonds near benzene rings? What defines each?
Aryl (on the benzene ring(
Benzylic (next to benzene ring)
Benzylic (next to benzene ring)
63
New cards
What does a + Hf value indicate? What about a - Hf value?
A +Hf is less stable, a -Hf is more stable
64
New cards
How do branches affect stability?
More branches (number not length) create more stable molecules (in Alkanes)
65
New cards
Explain what each of these statements mean:
Hf is more positive
Hf is less negative
Hc is more negative
Hf is more positive
Hf is less negative
Hc is more negative
ALL state the same thing: the molecule being described is less stable.
66
New cards
Are trans double bonds or cis double bonds more stable?
Trans bonds are more stable because they have fewer steric interactions (non-bonding regions in close proximity). Rings are the exception since you can't have a trans ring)
67
New cards
How is stability determined in Alkenes and Alkynes?
How substituted the pi bond is (more C around the bond makes a stronger bond)
68
New cards
What are the reactivity factors of Cl for primary, secondary, and tertiary bonds?
Primary - 1
Secondary - 3.9
Tertiary - 5.2
Secondary - 3.9
Tertiary - 5.2
69
New cards
What are the reactivity factors of Br for primary, secondary, and tertiary bonds? (approx)
Primary - 1
Secondary - 80
Tertiary - 1600
Secondary - 80
Tertiary - 1600
70
New cards
What are the steps of chain reactions? What is the purpose of each?
1. Initiation (any steps that increase the number of unpaired electrons)
2. Propagation (sum together net reaction + # of radicals are conserved)
3. Termination (steps that consume unpaired electrons)
2. Propagation (sum together net reaction + # of radicals are conserved)
3. Termination (steps that consume unpaired electrons)
71
New cards
When using peroxides, what steps of a chain reaction change?
Only initiation
72
New cards
How to C-C bonds connected to a benzene ring differ from other C-C bonds?
These C-C bonds are very weak, so the C-H bonds of the C next to a benzene ring are most likely to be broken and replaced with a halogen
73
New cards
Are sp2/sp bonds involved in radical halogenation?
No, these bonds are too strong to be involved in radical halogenation. Weaker bonds are of most interest
74
New cards
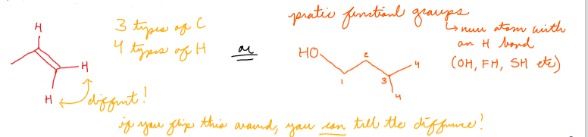
When are the # of types of C greater than the # of types of H?
When one or more C atoms have no H attached

75
New cards
When are the # of types of H greater than the # of types of C?
When there are protic functional groups (OH, NH, SH etc), or when the structure of the molecules is such that hydrogens can be identified from any direction
76
New cards
What does the range below 1500 represent on an IR spectrum?
Single bonds to carbon
77
New cards
Where are double bonds to Carbon found on the IR spectrum?
~1500-~1800
78
New cards
Which kind of bonds fall between 2000-2500 on an IR spectrum?
Triple bonds to Carbon
79
New cards
Where are bonds to hydrogen (OH, NH, CH) on an IR spectrum?
Above 2500
80
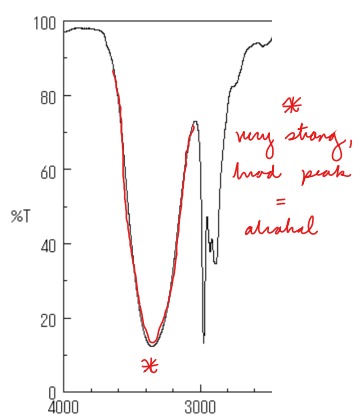
New cards
Draw an OH group on an IR spectrum
Key: Deep, wide curve
81
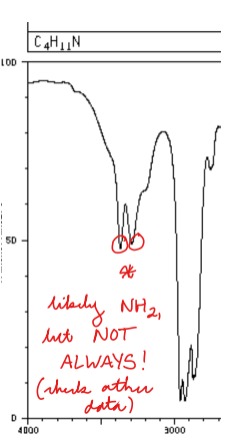
New cards
Draw a standard NH2 group on an IR spectrum
Key: Two close bumps (NOT ALWAYS NH2)
82
New cards
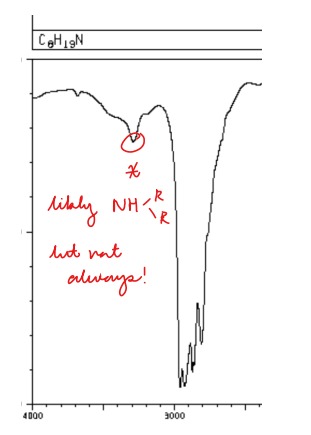
Draw a standard NH group on an IR spectrum
Key: One bump (NOT ALWAYS NH! Two NH2 bumps could be very close together!)