Materials
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering all of the materials topic for AS level AQA Physics exams.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What is a compressive force?
A force that ‘squashes’ an object (attempts to reduce its size)
What is a tensile force?
A force that stretches an object (attempts to increase its size)
Stress
σ = force/cross-sectional area of the object (units are Pa or N/m²)
σ=F/A
If tensile force, positive stress
If compressive force, negative stress
Strain
= extension/original length (ratio so no units)
ϵ=ΔL/L
If tensile force, positive strain
If compressive force, negative strain
Elastic strain energy
The same as elastic potential energy
Energy supplied to an object when an elastic object is stretched (under a tensile force)
Equal to the area under a force-extension graph
Breaking stress
force over unit area required to break a material
Ultimate tensile stress
Maximum force per unit area (tensile stress) an object can withstand.
Some materials undergo some strain beyond ultimate tensile stress before breaking.
Fractures
Occur when the material completely breaks
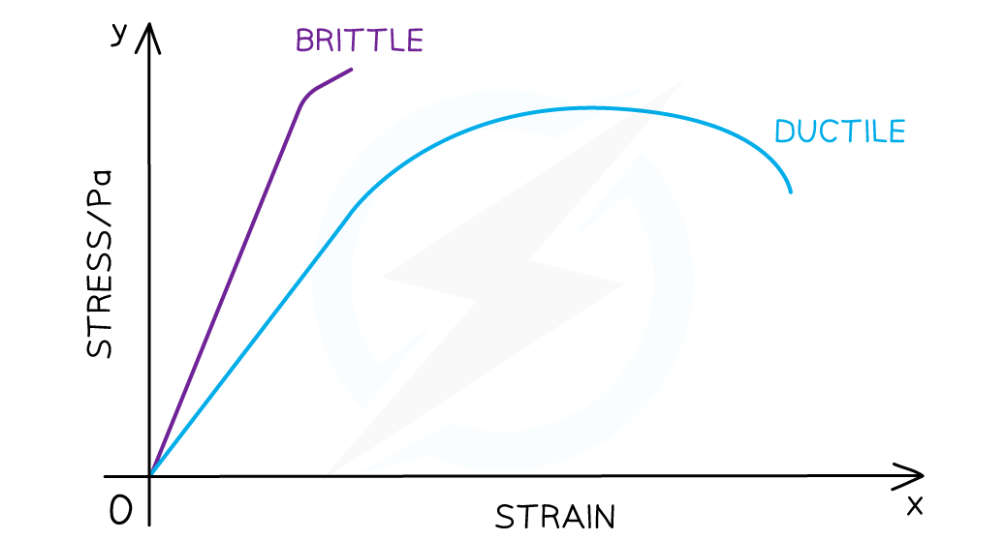
Brittle behaviour
Occurs beyond the object’s elastic limit
object extends very little. breaks suddenly and/or cracks easily
exhibits fracture behaviour
Little plastic behaviour shown
Plastic behaviour
When an object undergoes permanent deformation under stress
Occurs after the elastic limit
On a force-extension graph, look to the right of the elastic limit.
What is k in Hooke’s law
constant of proportionality/spring constant, which is a measure of the stiffness of a spring
Total energy in a spring system
The sum of all the kinetic and potential energies of an object
obeys the conservation of energy laws
total energy at all points in an oscillation is the same
Elastic potential energy
Energy stored within a material (like springs) when it is fully stretched or compressed
Equal to the area under a force-extension graph
Crumple zones (ethical transport design)
Parts of a vehicle that permanently deform
show plastic behaviour
energy from the impact is redirected towards plastically deforming the crumple zones, therefore people are not injured.
Airbags (ethical transport design)
also absorb the energy from the impact
WANNA ELABORATE?
The Young Modulus
represents the stiffness of a material
Stiff materials have a large young modulus
E = stress/strain (ratio of stress to strain)
gradient of a stress-strain graph is Young’s Modulus
Outline a method to determine the the Young Modulus of a copper wire (RQP)
xx
Elastic deformation
When the load is removed, the object will return to its original shape/length
Shown in the elastic region of the graph
Plastic deformation
The material is permanently deformed. When the load is removed, the object will not return to its original shape/length.
This is beyond the elastic limit, and is shown in the plastic region of the graph
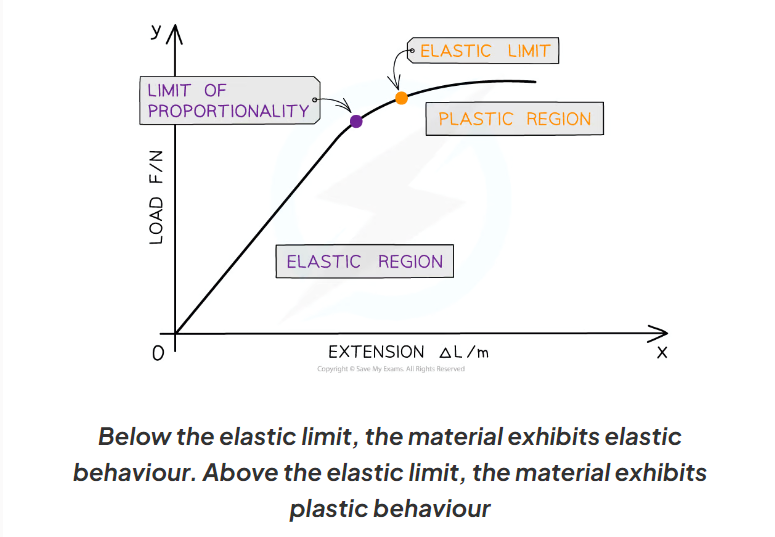
Where is the elastic region on a force-extension graph?
Where the extension is proportional to the force applied to the material (straight line)
Where is the plastic region on a graph?
Where the extension is no longer proportional to the force applied to the material (graph begins to curve). This begins at the elastic limit and ends at the point of fracture.
Where is the point of fracture on a load/extension graph?
The point at which the curve ends.
point of fracture = maximum extension of an object before it breaks.
Define ductile
materials with a larger plastic region, material stretches to a new shape/undergoes deformation before breaking.
Draw brittle line vs ductile line on a force-extension graph