anatomy 403: lymphatics 1
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
lymphatic system
lymph, lymph vessels, lymphatic organs, and red bone marrow
reticular connective tissue + lymphocytes
functions:
fluid _____ (drains excess interstitial fluid)
fat _____ (transports lipids, lipid-soluble vitamins A,D,E,K)
immune responses
balance, absorption
lymphatic system
what makes up the lymphatic system?
lymph, lymph vessels, lymphatic organs, and red bone marrow
immunity
____ immunity
non-specific
fever, inflammation
fever, pain, swelling, redness
____ immunity
specific
T-cell, B-cell, memory cells
innate, acquired
lymphocytes and acquired immunity
____ immunity: work via antibodies
B-cells → plasma ells → memory B cells
humoral
lymphocytes and acquired immunity
_____ immunity
work via cells
T-cells
T-helper cells (CD4+)
T cytotoxic cells (CD8+) → T memory cells
T regulatory cells
cellular
lymphocytes and acquired immunity
humoral immunity works via ______
B-cells → plasma cells → memory B cells
antibodies
lymphocytes and acquired immunity
cellular immunity works via _____
T-helper cells (CD4+)
T-cytotoxic cells (CD8+)
T-memory cells
T regulatory cells
cells
lymph circulation
returns excess interstitial fluid to venous return
lymphatic _____:
drain interstitial fluid
very permeable
unidirectional flow
lacteals and chyle (small intestine)
lymphatic _____:
lymph nodes
skin: follow veins
viscera: follow arteries
vessels and nodes → trunks → ducts
capillaries, vessels
edema
______ > reabsorption
at the level of capillary
many different etiologies
localized or systemic
lymphedema
filtration
HIV/AIDS
HIV
retrovirus
transmission via bodily fluids
attacks ____ (helper T) cells
these are key to acquired immunity
CD4+
HIV/AIDS
AIDS
lower Th count (<200 cells/mL)
opportunist _____
infections
lymphatic organs and tissues
____ lymphatic organs: stem cell mitosis and immunocompetence
red bone marrow
thymus
____ lymphatic organs and tissues: immune response sites
lymph nodes and nodules
spleen
primary, secondary
lymphatic organs and tissues
what organs make up the primary lymphatic organs?
red bone marrow and thymus
lymphatic organs and tissues
what organs/tissues make up the secondary lymphatics?
lymph nodes/nodules, spleen
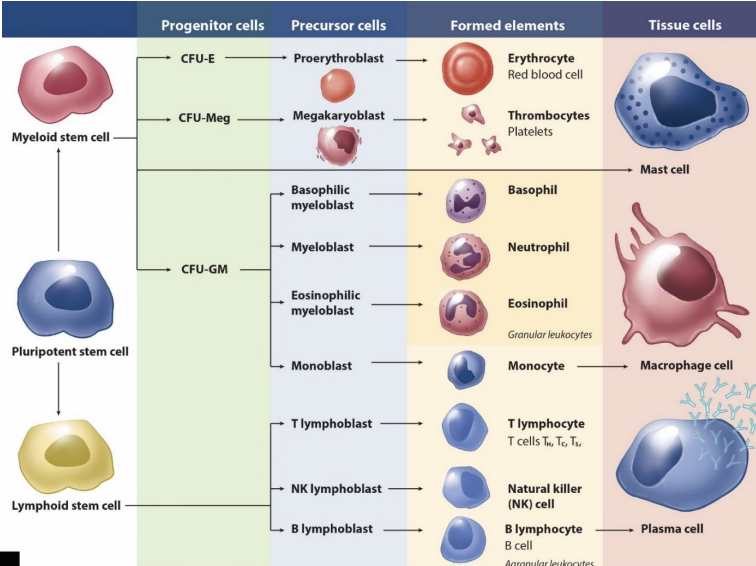
red bone marrow
hemopoietic connective tissue; _____ tissue
myeloid stem cells
erythrocutes
thrombocytes
granular leukocytes
monocytes & macrophages
lymphoid stem cells
B cells
T cells
abundant in _____ (axial skeleton) and the ends of long bones (appendicular skeleton)
myeloid, flat bones
thymus
mediastinum
bilobed, capsulated
trabeculae: lobules
____
thymocyte selection and maturation
positive and negative selection
2% survive
____
T cell release
maximum size at puberty
involution
slowly diminishes and becomes adipose
cortex, medulla
thymus
what part of the thymus does thymocyte selection and maturation?
cortex
thymus
what part of the thymus does T cell release?
medulla

what structure is this?
thymus
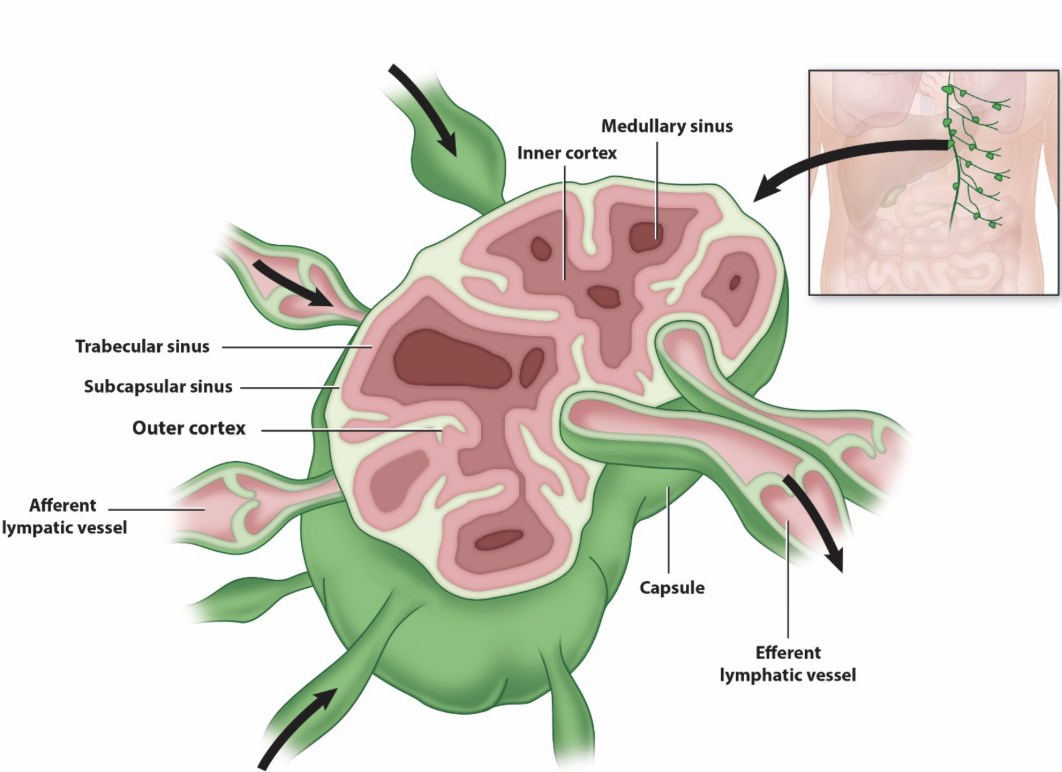
lymph nodes
bean-shaped, and typically clustered
capsule and compartments
outer cortex sinuses
lymphatic nodules (___ B cells)
inner cortex sinuses
T cells and dendritic cells
medullary sinuses
B cells, plasma cells, and macrophages
afferent vessels → sinuses → efferent vessels (hilus)
germinal
lymph nodes
what are the sinuses of the lymph nodes?
outer cortex sinus, inner cortex sinus, and medullary sinus
lymph nodes
what does the outer cortex sinus make?
lymphatic nodules (germinal B cells)
lymph nodes
what does the inner cortex sinus make?
T cells and dendritic cells
lymph nodes
what does the medullary sinus make?
B cells, plasma cells, macrophages
lymphatic nodules
_______
mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT)
lamina propria of mucous membranes
lymphocytes and antigen-presenting cells abundant
aggregated lymphoid follicles (Peyer’s patches of GALT)
diffuse or organized
waldeyer’s ring (of tonsils)
acapsular
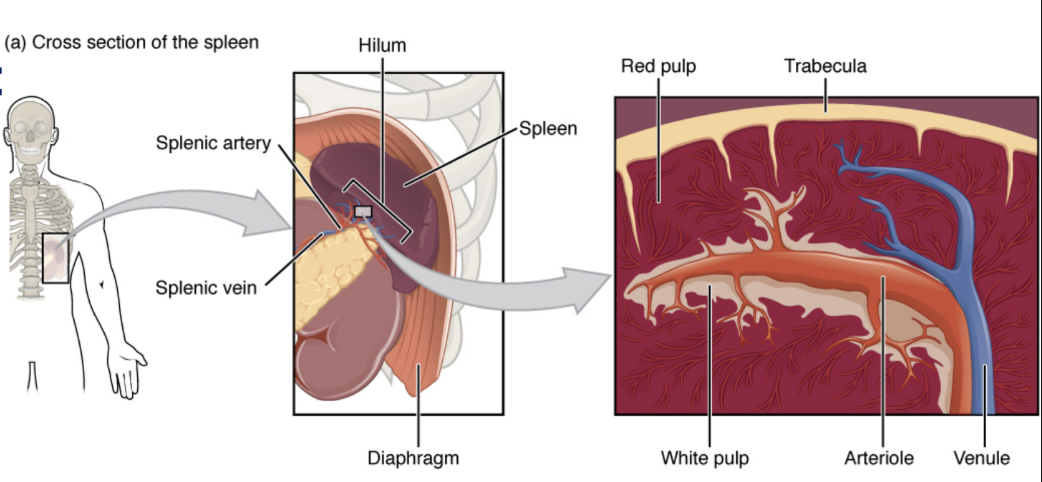
spleen: secondary organ
left hypochondriac
largest single mass of lymphoid tissue
___ pulp
lymphocyte action
___ pulp
RBC removal
platelet sequestration
hemopoiesis
white, red
tonsilitis
inflammation of the tonsils
_____ tonsils
typically viral, but can also be group A streptococcus infection
time, antibiotics
tonsillectomy
palatine
signs of infection
_____: disease of lymph nodes
very common and non-specific
abnormal size or consistenct
generalized or localized
lymphadenopathy
signs of infection
_____: enlarged, painful, inflamed
most common form of lymphadenopathy
malignancies
enlarged, often painless
lymphomas
metases
lymphadenitis
signs of infection
____: inflammation of lymph vessels
lymphangitis
metastasis
spread of a disease
_____: spread of disease along surface barrier/membranes
transcoelomic
metastasis
spread of a disease
_____: spread of disease through blood (usually venous)
sarcomas (mesenchyme) and renal carcinomas
hematogenous
metastasis
spread of a disease
_____: spread of disease via lymphatics
carcinomas (epithelial)
“firmed, fixed, and enlarged”
lymphogenous
what is metastasis?
spread of disease
what are the three types of metastasis?
transcoelomic, hematogenous, and lymphogenous
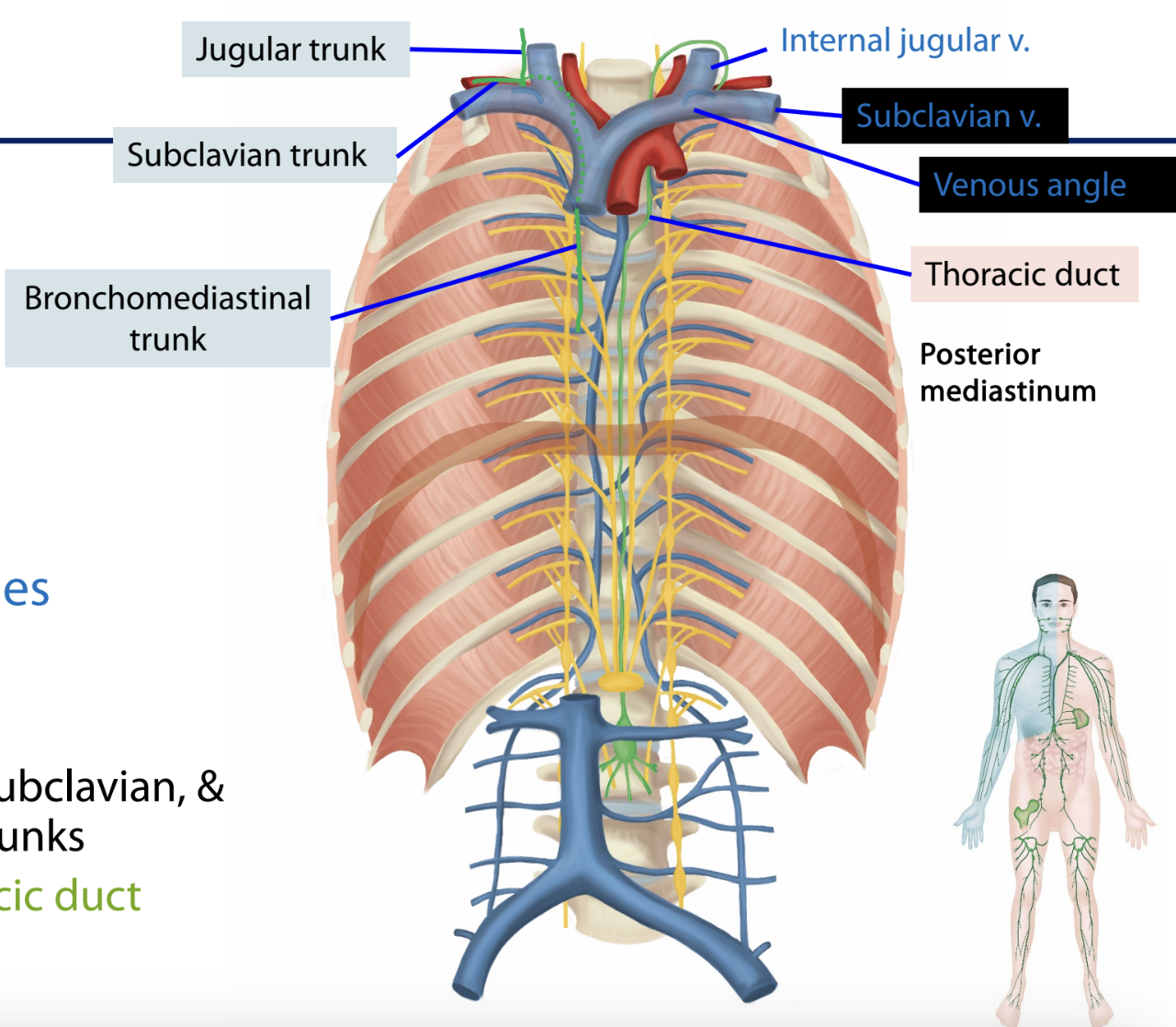
lymphatic ducts
_____
jugular
subclavian
bronchomediastinal
_____
vicinity of venous angles
right lymphatic duct
thoracic duct
receives left jugular, subclavian, and bronchomediastinal trunks
cisterna chyli → thoracic duct
trunks, ducts
lymphatic ducts
what are the trunks?
jugular, subclavian, and bronchomediastinal
lymphatic ducts
what are the ducts?
right lymphatic and thoracic ducts
lymphatic ducts
what duct receives the jugular, subclavian, and bronchomediastinal trunks?
thoracic duct
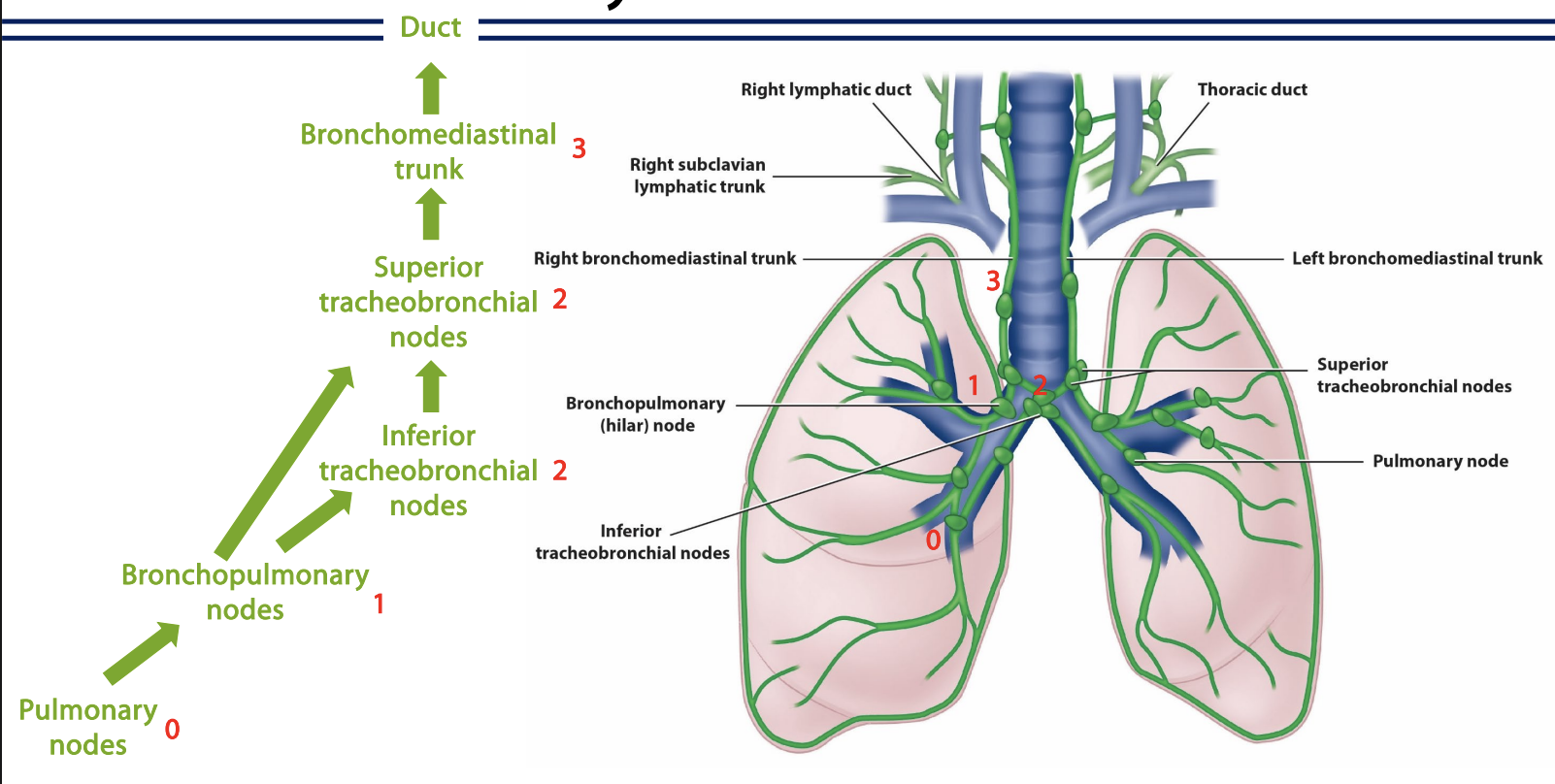
thorax: pulmonary
pulmonary nodes → bronchopulmonary nodes → inferior tracheobronchial nodes → superior tracheobrochial nodes → bronchomediastinal trunk → duct
which part does it bifurcate?
inferior tracheobronchial nodes
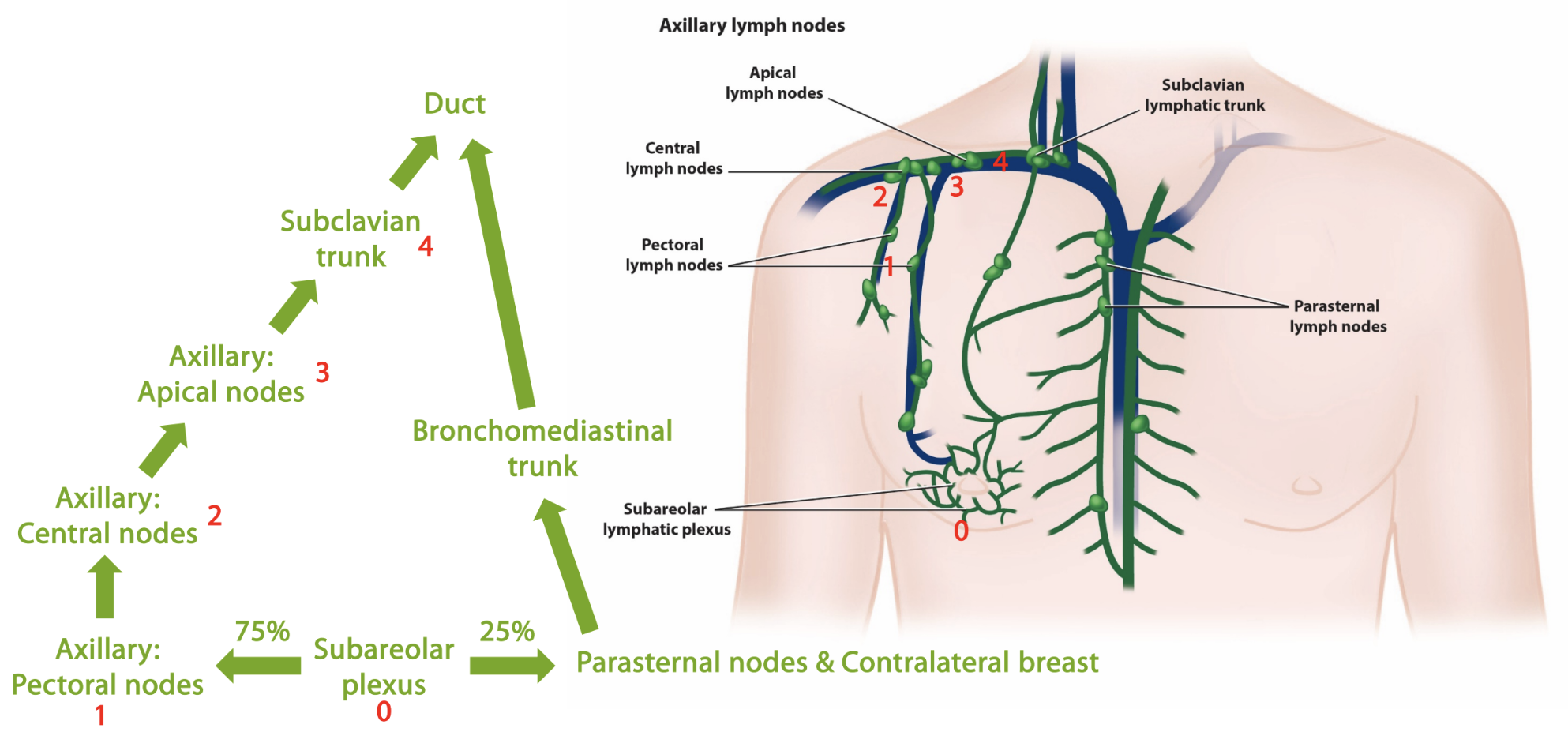
thorax: breast and axilla
subareolar plexus → 75% to ______
subareolar plexus —> 25% to ______
axillary: pectoral nodes, parasternal nodes and contralateral breast

upper limbs
deep lymphatics are _____
superficial lymphatics are ______
arteries, veins
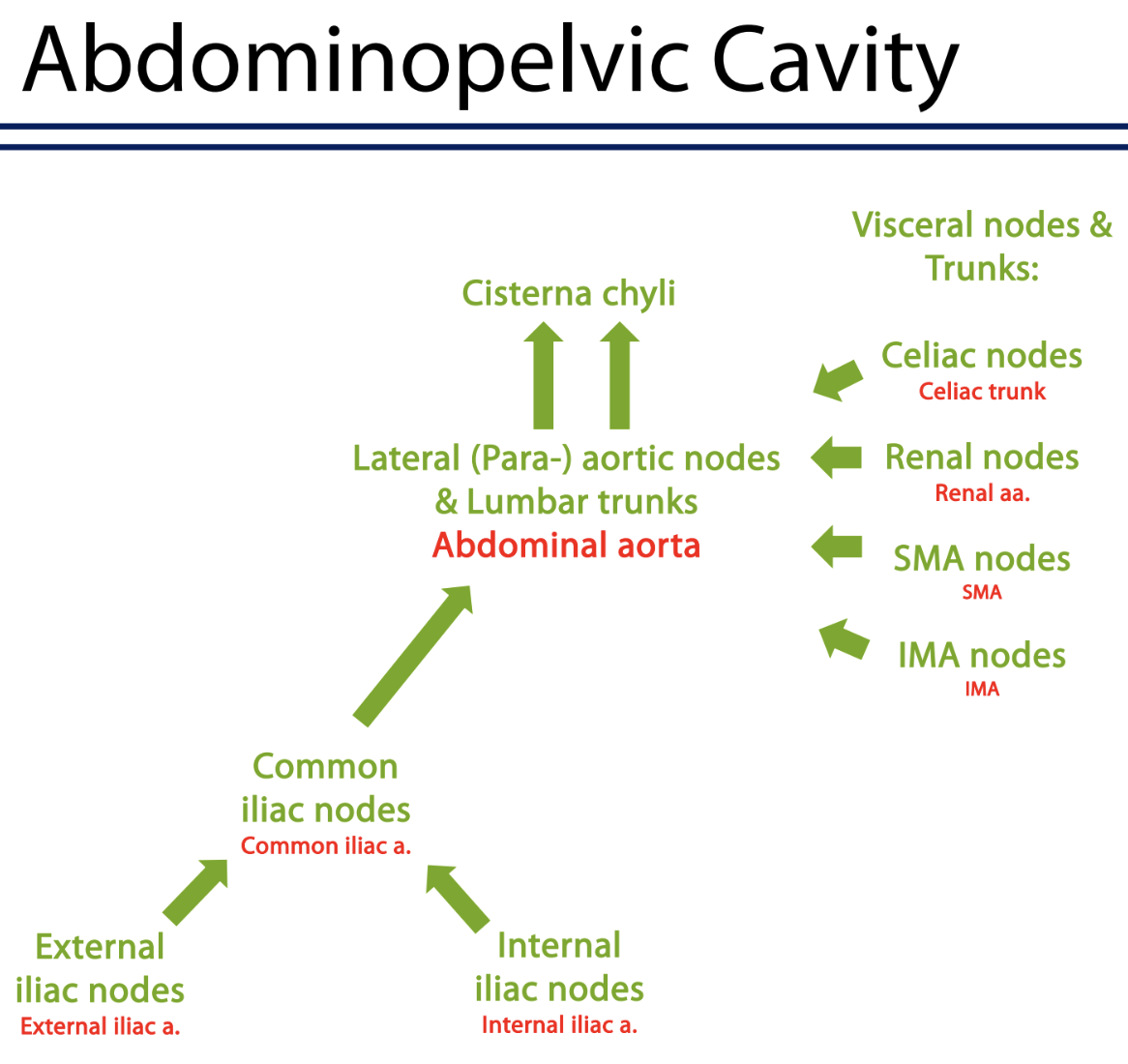
abdominopelvic cavity
everything in the abdominopelvic cavity drains into the ______
cisterna chyli
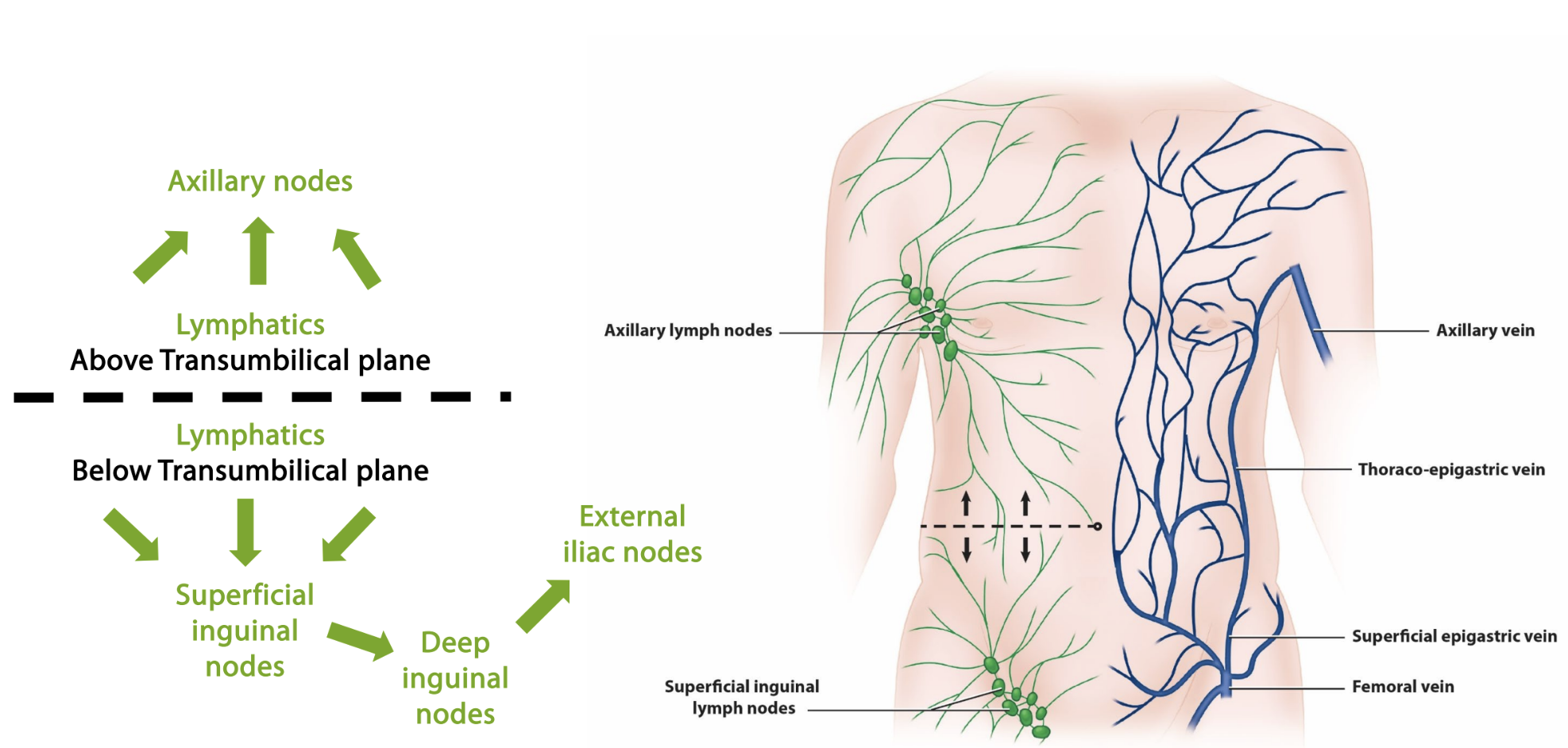
abdominal wall
lymphatics above transumbilical plane go to _____
lymphatics below transumbilical plane go to _____
axillary nodes, superficial inguinal nodes
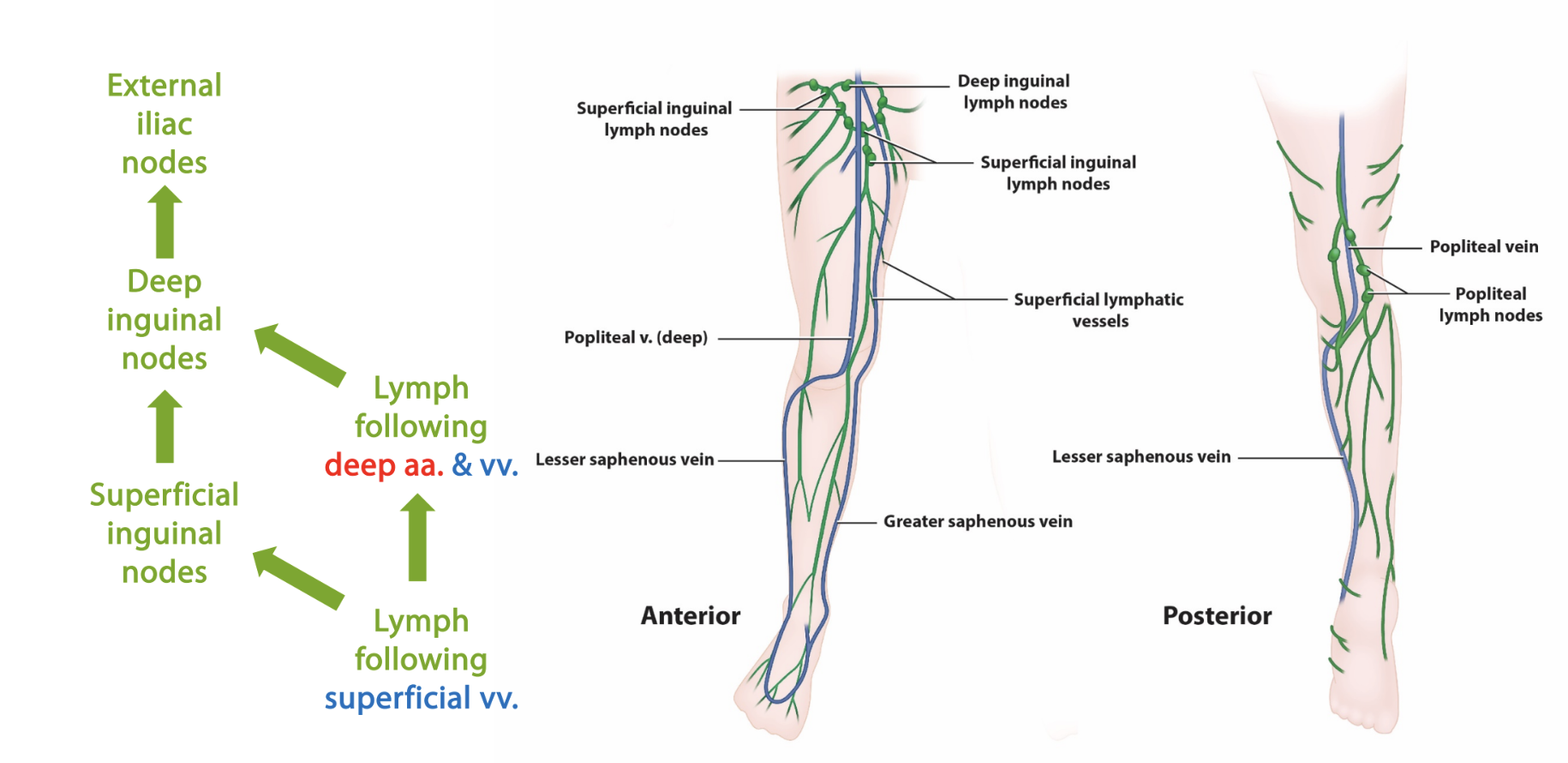
lower limb
travels along ____
veins