ap bio unit 4 cell communication and cell cycle test review
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
ligand
a chemical messenger that binds to a receptor, resulting in a transduction pathway that often ends with a transcription of a specific gene sequence
local regulators
short distance chemical signals used for autocrine or paracrine signaling
transcription factor
proteins that regulate the reading of genes to produce mRNA that will then go on to produce a protein; these proteins help RNA polymerase bind to DNA
gene
a chunk/segment of a DNA strand, ranging from a couple hundred nucleotides to a couple million nucleotide that code for specific proteins
protein kinase
an enzyme that will activate other proteins by phosphorylating them (facilitate transfer of a phosphate onto them)
g-protein coupled receptor
diverse group of membrane bound receptors that undergo conformational change to initiate a transduction pathway i
ion channel linked receptor
a ligand binds to this integral membrane protein, opening a channel to allow secondary messengers to pass through; sometimes they’re voltage gated proteins
negative feedback mechanisms
maintain homeostasis by regulating physiological processes; return system back to target set point
positive feedback mechanisms
amplify responses and processes in biological organisms; variable initiating response is moved farther away from the initial set point
amplification
(feedback loops) stimulus is further activated, initiating an additional response that produces change in the system
mitosis
type of asexual reproduction of cells in a multicellular organism that produces genetically identical daughter cells from the parental cells; distributing replicated chromosomes to daughter nuclei to initiate the formation of 2 new identical cells
how all other cells are created (except sex cells)
creates at an exponential rate
true
t/f: interphase is generally the same in mitosis and meiosis
prophase
Nuclear membrane breaks down
Chromatin condenses and chromosomes become visible
Centromeres and kinetochore proteins
Centrioles and spindle fiber microtubules appear
chromosomes— 46
chromatids— 92
how many chromosomes does the cell have during prophase? chromatids?
prophase
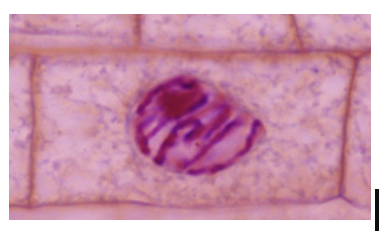
metaphase
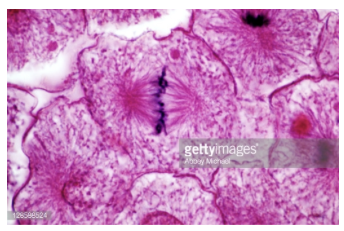
metaphase
Chromosomes line up @ equatorial line of the cell
Spindle fiber microtubules attached to centromere kinetochores of the chromosome
Helps prevent nondisjunction
anaphase
Spindle fibers are attached to the centromeres of each chromosome
Sister chromatids are pulled apart to opposite sides of the cell
Chromosomes are pulled apart
anaphase
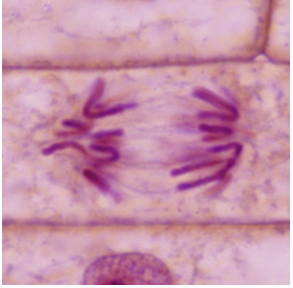
telophase
Chromosomes @ opposite sides of cells
Nuclear membrane reforming
Chromosomes untangling
Nucleolos returning
Centrioles and spindles are going away
Nucleus returning to normal
telophase
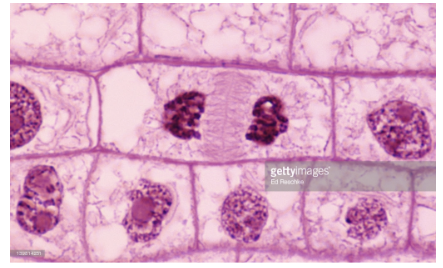
cytokinesis
Separation of cells
Cells move apart and officially form 2 daughter cells
Animal cells - a cleavage furrow forms where the cytoplasm will be pinched off
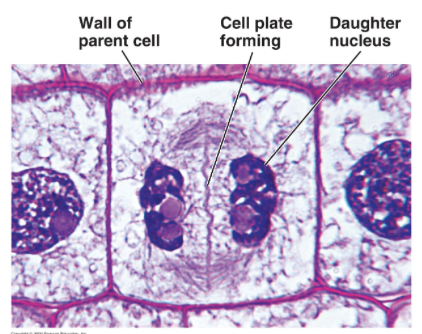
Plant cells - cell plate forms where the 2 membranes meet and the cell wall will form
cytokinesis
interphase
G0- checkpoint, opportunity for apoptosis, lag point
G1- major growth phase, creates organelles for cell function
S- DNA duplication
G2- cell creates organelles and molecules for division
the time between cell divisions when a cell is carrying out normal functions and/or preparing for mitotic division; where most of a cell’s life is spent, longest phase
**not part of mitosis
G0
checkpoint, opportunity for apoptosis, lag point; where cells wait for the right time to grow/divide, sometimes entered when something went wrong during cell division
G1
major growth phase, creates organelles for cell function
S
DNA duplication; puts cells on the trajectory to divide
G2
cell creates organelles and molecules for division
kinase
enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group from ATP to a specific molecule (phosphorylation)
cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs)
regulate transcription, mRNA processing, and differentiation of nerve cells; moves cell through G1, S, G2, and M phases
2 identical diploid daughter nuclei
Nuclei are part of somatic cells
Separation of nucleus, not the cell
Cytokinesis separates cell
what are the results of cell division and mitosis?
which proteins are in the cell
what does specialization/differentiation depend on?
differentiation
process by which during development newly formed cells become more specialized and distinct from one another as they mature
false
t/f: genomes may be different in different cells of an organism
activation of genes within a cell causes it to signal for differentiation
what causes cells to differentiate?
breaks down messengers and/or stimulatory proteins by breaking ester bonds
-esterase
PLC (phospholipase)
typically stimulated by g-proteins or tyrosine kinases, these hydrolyze lipid-based compounds to form the secondary messengers IP3 and DAG
conformational change
a change in the shape of a macromolecule, typically proteins, as induced by another molecule or environmental factors
G protein
a family of proteins tat act as molecular switches inside cells, transmitting signals from a variety of stimuli following their release from a transmembrane receptor
cAMP, IP3, Ca²+ (also DAG and NO)
secondary messengers examples
secondary messengers
stimulate proteins, leading to a response in a transduction pathway
tyrosine kinase
family of enzymes in the cell membrane that mediate multiple responses following dimerization to imitate transduction pathways pertaining to proliferation, metabolism, and apoptosis
phosphorylation cascade
a sequence of signaling pathway events where one enzyme phosphorylates others, causing a chain reaction that amplifies a signal/response
adenylyl cyclase
an enzyme that synthesizes cAMP to amplify a transduction pathway
phosphorylation
when a phosphate is couple with a larger molecule, activating or inhibiting that molecule
ubiquitin
regulatory protein that tags proteins, directing their movement to a proteasome where they will be degraded/destroyed
to heal wounds or breaks
to stay small for better transport and efficiency
nucleus makes proteins at a limited rate
why do cells reproduce?
cell proliferation
the process of cells rapidly growing and dividing
growth factors
cells release proteins/hormones that bind to a cell to stimulate cell proliferation
Regulate only a small portion of the cell cycle
Cells deprived of growth factors enter G0, when growth factors are added they will return to division
cyclins
proteins that are made internally and destroyed rapidly; stimulate certain stages of the cell cycle
kinase
enzyme that transfers a phosphate group from ATP to another molecule (typically a protein), causing it to change shape and become energized
proto-oncogens
overactive form of proteins that are associated with cancer
Cancer cells don’t respond to signals that regulate growth and reproduction of cells; thus divide uncontrollably, absorb excessive nutrients, block nerve connections, prevent invaded organs from functioning normally
Growth causes change in shape (and thus function)
oncogene
a cell causing cancer; mutated
contact inhibition
when cells come into contact with other cells, they’re programmed to stop dividing and form tight gap junctions & desmosomes
receptor tyrosine kinase (RTKs)
membrane receptors that transfer phosphate groups from ATP to another protein
Can trigger multiple signal transduction pathways at once
Abnormal functioning is associated w/ cancers; mutated form can’t attach to DNA to signal a stop for cell division
Receptor mutation activates cell division pathway in the absence of an appropriate ligand
Mutation results in loss of ability to produce a tumor suppressor protein
@ anaphase checkpoint, chromatids are separated w/o all centromeres being attached to kinetochore microtubules from both poles
what can cancer be caused by?
Apoptosis
Long cell cycles
Cell arrest until DNA is repaired
Failing to proceed to different stages
Functioning tumor suppressor or proto-oncogenes
these 5 things are NOT cancer
apoptosis
cell is systemically dismantled and digested, triggered by signals that activate a cascade of suicide proteins
direct
gap junctions are what kind of contact between cells?
growth factors, neurotransmitters
ex of local regulators
hormones
ex of long distance singalong molecule
plasmodesmata
for cell-cell contact, plants use…
gap junctions
for cell-cell contact, animals use…
gap junctions and plasmodesmata
connect cytoplasm of 2 adjoined cells and pass on chemical signals quickly (including hydrophilic ones)
major histocompatibility complex
group of genes that code for proteins on the cell surface that help the immune system recognize foreign substances
paracrine signaling
form of local signaling, cells secrete short lived chemical signals to local cells to elicit a joined response
endocrine
form of distance signaling, production of hormones by glands that travel through the circulatory system to cells
reception
detection of signal molecule (ligand) from outside cell
transduction
convert signal to form that can cause cellular response
response
specific cellular response to ligand occurs in the nucleus or cytoplasm
plasma membrane receptor
water soluble, hydrophilic ligands involved in reception
intracellular receptors
inside the cytoplasm/nucleus, small or hydrophobic ligand molecules involved in reception
protein changes shape
ligand binds to receptor → _________ → initiates transduction signal
transduction
cascades of molecular interactions relay signals from receptors that move to target molecules
phosphorylation cascade
enhance and amplify signal by taking a phosphate from an ATP molecule and attaching it to an amino acid
secondary messengers
small, non protein molecules/ions that relay signals inside cells
cAMP
activities protein kinase A
ligand gated ion channel
acts as a gate when receptor changes shape, allows specific ions through
gene expression
what mainly happens during a response?
GLUT4
acts as a channel to let glucose in the cell
cells can grow more rapidly
why is asexual reproduction beneficial?
growth factors
proteins and hormones are examples of..
46
how many chromosomes are in a cell?
46
how many strands of DNA are in a cell?
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
what is the order of the phases of mitosis?
92
in anaphase and telophase, there are ___ chromosomes
endocrine
the thyroid and epinephrine are examples of what type of signaling?
synaptic signaling
uses a neuron to send a signal over a small gap to bind
kinetochore
protein that links chromatids to spindle fibers
quorum sensing
bacteria can sense the presence of other bacteria nearby using chemical signals
checkpoint
point in the cell cycle that stops to regulate the cell cycle and make sure it’s good to proceed
neurotransmitters
local regulators ex
negative
body temperature regulation is an example of what type of feedback response?
positive
birth and lactation are examples of what type of feedback loop?
protects neighboring cells from damage, used for animal development and maintenance
what is apoptosis used for?
direct
the major histocompatibility complex uses which type of signaling?
phosphorylation, secondary messengers
transduction can occur by _______ or _______
amplify
transduction can cause the signal to do what?
insulin
used when there’s high blood sugar
glucagon
used when there’s low blood sugar