Lecture 5
5.0(2)Studied by 10 people
Card Sorting
1/52
Earn XP
Last updated 5:03 PM on 2/17/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
1
New cards
\
Caries of pit fissures origin
Caries of enamel-smooth surface origin
Root-surface caries
Caries of pit fissures origin
Caries of enamel-smooth surface origin
Root-surface caries
According to their anatomical site
2
New cards
Backward Caries
Forward Caries
Forward Caries
Based on Pathway of Caries Speed
3
New cards
Backward Caries
When spread of caries along dentinoenamel junction (DEJ) exceeds the adjacent caries in enamel.
4
New cards
Forward Caries
Caries cone in enamel is larger or at least the same size as that in dentin (pit & fissure caries)
5
New cards
Primary Caries
Residual Caries
Secondary Caries
Residual Caries
Secondary Caries
According to whether it is a NEW LESION or RECURRENT CARIOUS LESION
6
New cards
Primary Caries
Lesions on unrestored surface;
Original carious lesion of the tooth
Original carious lesion of the tooth
7
New cards
Residual Caries
Caries that is not removed during restorative procedure, either by accident, neglect or intention
8
New cards
Secondary Caries (recurrent)
Occurs at the junction of a restoration and the tooth and may progress under restoration.
9
New cards
Incipient Caries
Cavitated Caries
Cavitated Caries
Extent of Caries
10
New cards
Incipient Caries
First evidence of caries activity in the enamel
Consists if demineralized enamel which has NOT extended to DEJ.
This lesion can be remineralized by proper preventive procedures.
Consists if demineralized enamel which has NOT extended to DEJ.
This lesion can be remineralized by proper preventive procedures.
11
New cards
Cavitated Caries (non-reversible)
The enamel surface is broken & usually the lesion has advanced into dentin.
12
New cards
\
Acute
Chronic
Rampant
Acute
Chronic
Rampant
Rate of Caries
13
New cards
Acute Caries
Is when the disease is rapid in damaging the tooth.
Usually in the form of many, soft, light-colored lesions in a mouth and is infectious.
Usually in the form of many, soft, light-colored lesions in a mouth and is infectious.
14
New cards
Chronic Caries (Slow/Arrested)
Slowly progressing long-standing caries.
Lesions is hard in consistency & dark-colored.
Lesions is hard in consistency & dark-colored.
15
New cards
Rampant Caries
Multiple carious lesions occurring in the same patient, frequently involving surfaces of teeth that are usually caries free
16
New cards
Early Childhood
Bottle/Nursing
Xerostomia Induced Rampant
Bottle/Nursing
Xerostomia Induced Rampant
3 types of rampant caries
17
New cards
Early Childhood Caries
Used to described dental caries present in the primary dentition of young children
18
New cards
Bottle or Nursing Caries
Used to describe a particular form of rampant caries in the primary dentition of infants and young children.
The clinical pattern is characteristics, with the four (4) maxillary deciduous incisors most severely affected.
The clinical pattern is characteristics, with the four (4) maxillary deciduous incisors most severely affected.
19
New cards
Radiation Rampant Caries
Commonly observed that after radiotherapy of malignant areas of or near the salivary glands because of radiotherapy salivary flow is very much reduced.
20
New cards
Simple Caries
Compound Caries
Complex Caries
Compound Caries
Complex Caries
Cavities according to the number of surface involved
21
New cards
Simple Caries
Caries involving only one (1) tooth surface
22
New cards
Compound Caries
Two (2) surfaces are involved
23
New cards
Complex Caries
More than two surface are involved
24
New cards
Abrasion
Erosion
Attrition
Abfraction
Erosion
Attrition
Abfraction
Non-carious tooth defects terminology
25
New cards
Abrasion
Abnormal tooth surface loss resulting from direct friction forces between the teeth and external objects or from frictional forces between contacting teeth components in the presence of abrasive medium
a. IMPROPER TOOTH BRUSHING TECHNIQUES
b. HABITS - holding pipe stem by the teeth
c. TOBACCO CHEWING
d. Use of toothpicks
a. IMPROPER TOOTH BRUSHING TECHNIQUES
b. HABITS - holding pipe stem by the teeth
c. TOBACCO CHEWING
d. Use of toothpicks
26
New cards
Toothbrush Abrasion
Sharp, V-shaped notch in the gingival portion of the facial aspect of the teeth
27
New cards
LOSS of TOOTH STRUCTURE at site of wear
POSSIBLE SENSITIVITY
POSSIBLE SENSITIVITY
Clinical Features of toothbrush abrasion
28
New cards
Repetitive mechanical habit:
Using a HARD TOOTHBRUSH
IMPROPER TOOTHBRUSHING TECHNIQUE along the gumline
GRINDING or CHEWING HARD objects or food
Using a HARD TOOTHBRUSH
IMPROPER TOOTHBRUSHING TECHNIQUE along the gumline
GRINDING or CHEWING HARD objects or food
Etiology of toothbrush abrasion
29
New cards
Prevention:
RESTORATION
FLUORIDE APPLICATIONS
TOOTH-COLORED BONDING
RESTORATION
FLUORIDE APPLICATIONS
TOOTH-COLORED BONDING
Treatment of toothbrush abrasion
30
New cards
Once the GUMS begin to recede:
ROOT SURFACES become EXPOSED
SENSITIVITY to HOT & COLD temperatures soon follow.
ROOT SURFACES become EXPOSED
SENSITIVITY to HOT & COLD temperatures soon follow.
Prognosis of toothbrush abrasion
31
New cards
Well-defined horizontal radiolucency
On a dental radiograph, toothbrush abrasion appears as ________ along the cervical region of the tooth
32
New cards
HARD, HIGHLY DEFECT
Clinically, The areas affected by abrasion appear as _________________ in dentin and should NOT be confused with root caries that appears brown and leathery.
33
New cards
Erosion
Progressively loss of dentin tissue by chemical means not involving bacterial actions;
The wear or loss of tooth surface by
chemicomechanical action.
Regurgitation of stomach acids
Habitual sucking of lemons
The wear or loss of tooth surface by
chemicomechanical action.
Regurgitation of stomach acids
Habitual sucking of lemons
34
New cards
Attrition
Mechanical wear of the incisal or occlusal surface as a result of FUNCTIONAL or PARAFUNCTIONAL MOVEMENTS of the mandible.
Affects proximal contact areas.
Affects proximal contact areas.
35
New cards
Abfraction
Microfractures occur as the cervical of the tooth flexes under loads.
36
New cards
Wedge-shaped notching at cervical areas of involved teeth.
Adults
Adults
Clinical features of abfraction
37
New cards
Biochemical forced on teeth
Etiology of Abfraction
38
New cards
Once the enamel is gone, then dentin is exposed & the teeth are more susceptible to decay, sensitivity and more wearing down
Prognosis of Abfraction
39
New cards
FALSE. It is different
TRUE OR FALSE. Is abfraction the same with toothbrush abrasion?
40
New cards
Overbrushing with a hard bristle toothbrush
Toothbrush abrasion is caused by
41
New cards
Excessive pressure applied to the teeth by severe bruxing habits.
Abfraction is caused by
42
New cards
Notch
Toothbrush abrasion tends to ________ in the tooth surface just above the gumline
43
New cards
Dished out
Abfraction tends be a ______________ defect
44
New cards
Fractures
Incomplete fracture not directly involving vital pulp → GREENSTICK FRACTURE
Complete fracture not involving the vital pulp
Fracture involving vital pulp
Complete fracture not involving the vital pulp
Fracture involving vital pulp
45
New cards
Non-hereditary enamel hypoplasia
Occurs when the ameloblasts are injured during enamel formation
Seen on anterior teeth and first molars; opaque white or light brown areas with smooth intact hard surface.
Seen on anterior teeth and first molars; opaque white or light brown areas with smooth intact hard surface.
46
New cards
Amelogenesis Imperfecta
Enamel is defective either in form or calcification as a result of heredity
47
New cards
Dentinogenesis Imperfecta
Hereditary condition in which dentin is defective.
48
New cards
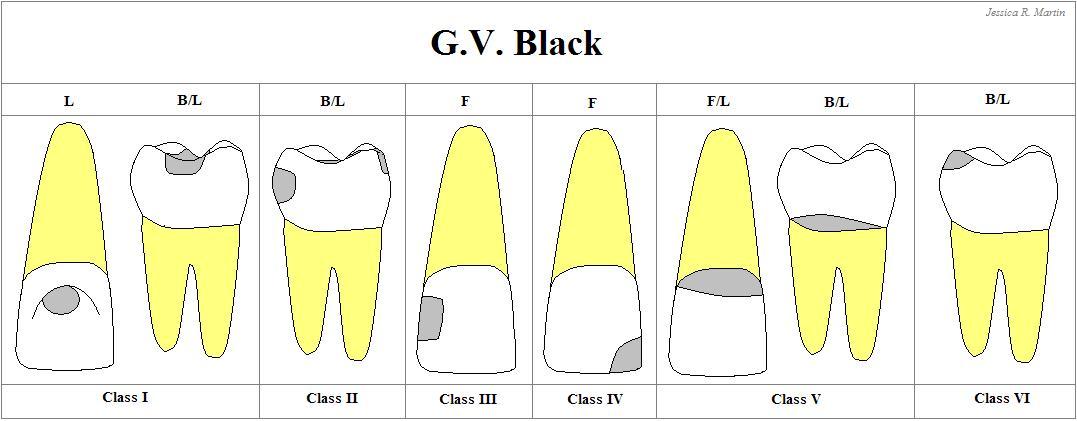
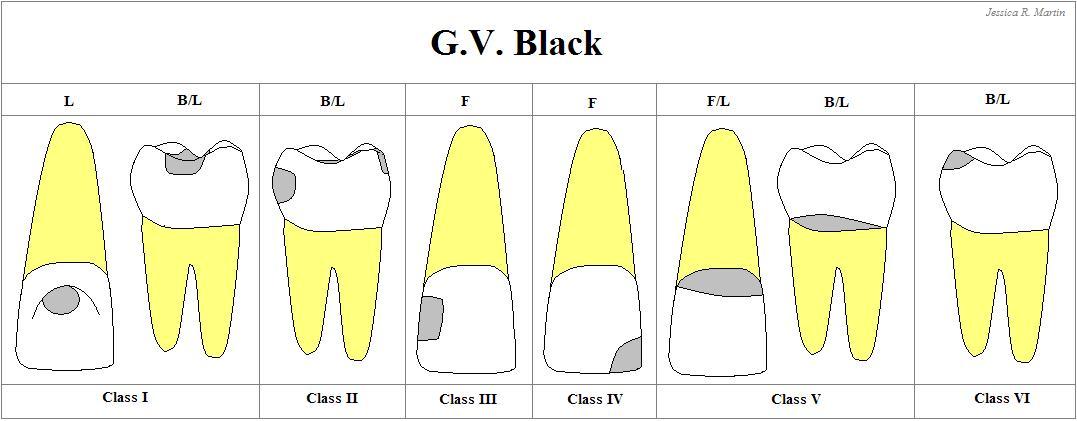
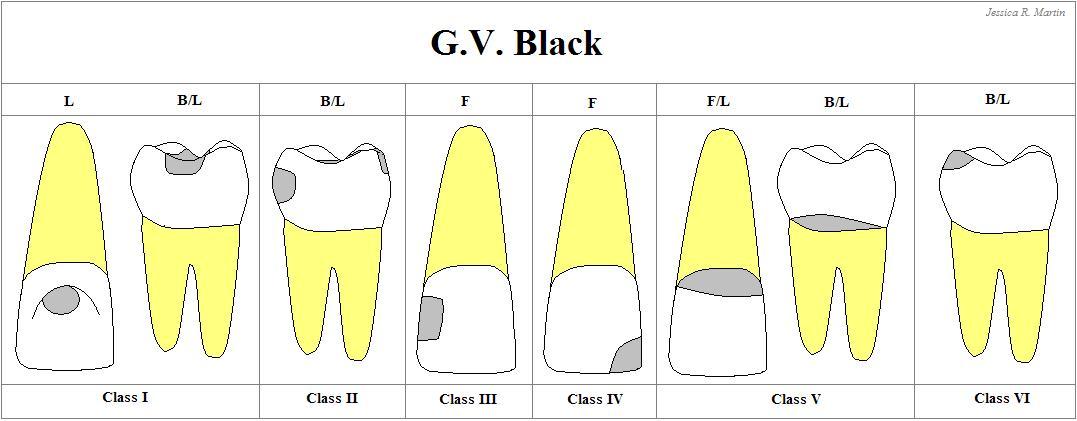
Class I
Carious lesion that are located in Pits & fissures of the occlusal surfaces of molars and premolars
Occlusal 2/3 of the buccal & lingual surfaces of molars, and + lingual surface of anterior teeth
Occlusal 2/3 of the buccal & lingual surfaces of molars, and + lingual surface of anterior teeth
49
New cards
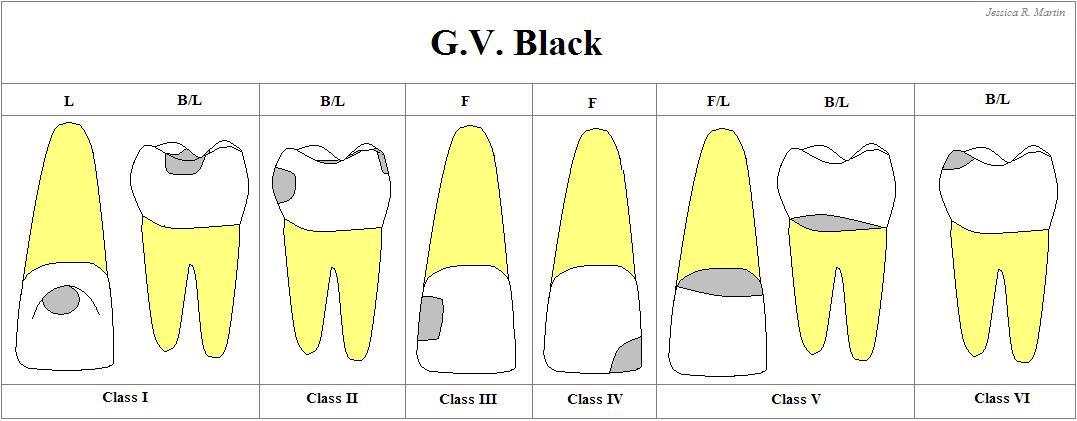
Class II
Carious lesions that are located on the PROXIMAL SURFACES of the premolars & molars
50
New cards
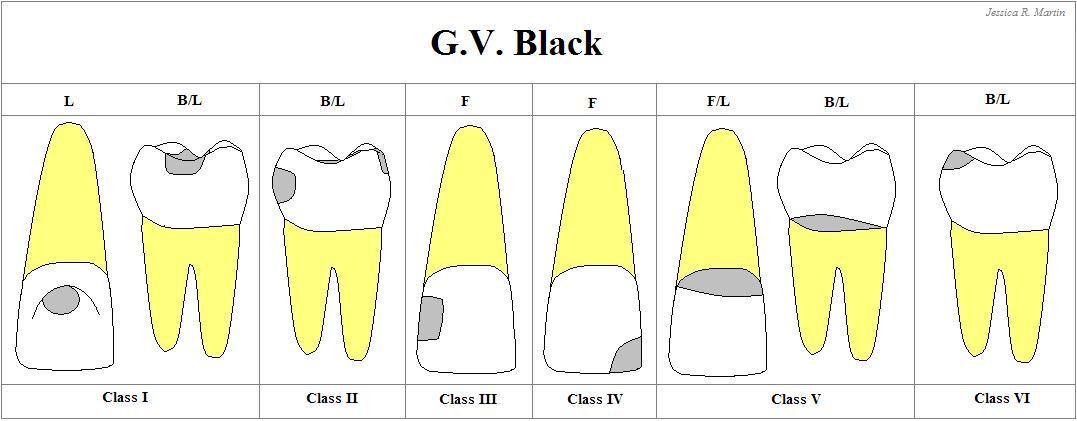
Class III
Carious lesions that are located in the PROXIMAL SURFACES of anterior teeth that do NOT involved the incisal angle
51
New cards
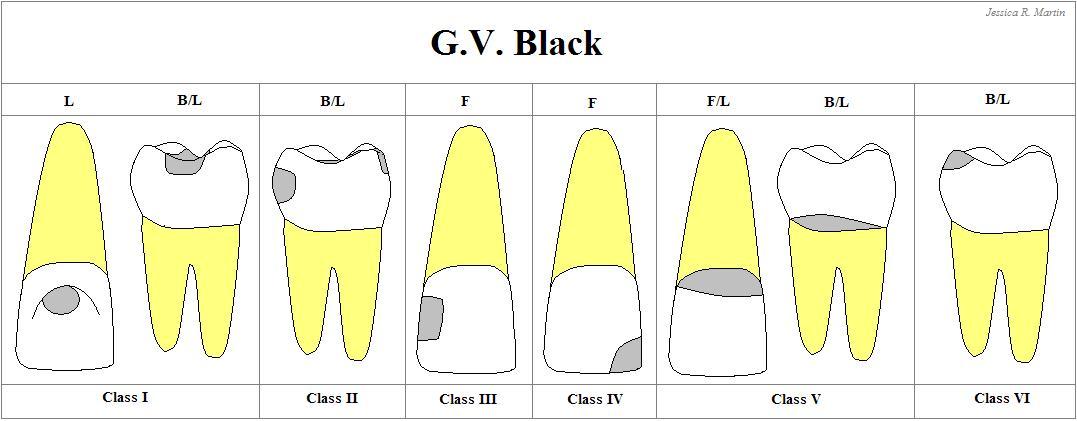
Class IV
Carious lesions that are located on the PROXIMAL SURFACES of anterior teeth that involving the incisal angle.
52
New cards
Class V
Carious lesions that are located on the GINGIVAL 1/3 of facial & lingual surface of anterior & posterior teeth.
53
New cards
Class VI
Cavities on the INCISAL EDGES and CUSPS TIPS