Unit 7 - Rotation and Torque
0.0(0)Studied by 3 people
0%Unit 7: Torque and Rotational Motion Mastery
0%Exam Mastery
Build your Mastery score
Supplemental Materials
Card Sorting
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:51 PM on 4/5/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
1
New cards
Angular position
θ
radians
radians
2
New cards
Angular displacement
\
Δθ
radians
Δθ= θf - θi
Δθ
radians
Δθ= θf - θi
3
New cards
Angular velocity
⍵
rad/sec
rad/sec
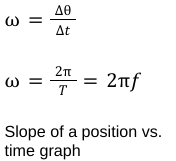
4
New cards
Angular acceleration
⍺
rad/s/s
rad/s/s
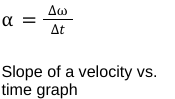
5
New cards
Counterclockwise rotation (CCW)
\+
6
New cards
Clockwise rotation (CW)
\-
7
New cards
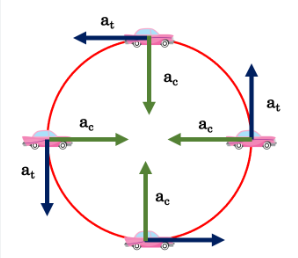
* centripetal acceleration
* tangential acceleration
* tangential acceleration
An object traveling in a circle has 2 types of acceleration
8
New cards
Centripetal acceleration
* changes object’s direction of velocity
* perpendicular to velocity
* points toward the center
* perpendicular to velocity
* points toward the center
9
New cards
Tangential acceleration
* changes magnitude of object’s velocity
* antiparallel or parallel to velocity
* tangent to the circular path
* antiparallel or parallel to velocity
* tangent to the circular path
10
New cards
Torque
* The ability of a force to cause angular acceleration
* 𝜏
* Nᐧm
* 𝜏=rFsin(θ)
* 𝜏
* Nᐧm
* 𝜏=rFsin(θ)
11
New cards
Torque due to gravity
𝜏 = r(mg)sin(θ)
12
New cards
Newton’s 1st Law for Rotation
* net torque will change its angular velocity
* net torque of 0 = no rotation or rotating at a constant angular velocity
* net torque of 0 = no rotation or rotating at a constant angular velocity
13
New cards
Static equilibrium
Fx=0
Fy=0
𝜏=0
Fy=0
𝜏=0
14
New cards
Newton’s 2nd Law for Rotation
𝜏net=I⍺
15
New cards
Rotational inertia
* property of an object
* depends on mass and how it is distributed
* I=mr^2
* The further the mass is “pushed out” from the axis, the greater the rotational inertia
* depends on mass and how it is distributed
* I=mr^2
* The further the mass is “pushed out” from the axis, the greater the rotational inertia
16
New cards
s (linear position) =
θr
17
New cards
v =
⍵r
18
New cards
a =
⍺r
\
\