Year 12 Physics - Wave Particle Duality and Quantum Theory
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
describe Young’s Double Slit Experiment
monochomatic light shone through a double slit shows diffraction
bright lines are constructive interfernce and dark lines are destructive interference
diffraction is evidence for the wave nature of photons
describe the photoelectric effect
shining light on a metal plate releases electrons
increasing light intensity will increase electrons emitted
there is a threshold frequency of the incident light below which, no electrons are emitted despite increasing intensity and time applied
the existence of a threshold frequency is evidence for the particle nature of photons
if light was a wave, how would it behave in the photoelectric effect
increasing the intensity would increase the light energy, and given time, the electrons would gain enough energy to be removed
what is the work function representative of
the amount of energy needed to only break the bonds hodling an electron so it can be removed
what is threshold frequency
the minimum frequency of the light, to remove an electron
if the photon has less energy than the work function then the electron won’t be released
when do electrons transfer energy
when transferring between energy levels
what is excitation
when an electrons gains an exact amount of energy to transition up a level
what is de-excitation
when an electron emits an exact amount of energy as a photon to transition down an energy level
what is ionisation
when an electron gains enough energy to be removed from orbit around the atom
any excess energy is kinetic
describe line spectra production
when an electron transitions down, it releases energy as a photon which corresponds to a wavelength of light which can sometimes fall in the visible spectrum
if we diffract the light emitted by an atom, we get a spectrum of bright spectral lines unique to that element
it complements an absorption spectrum
describe the stopping voltage
a positive plate attracts electrons regardless of kinetic energy, but a negative plate will repel
therefore only electrons with sufficent energy will reach a negative plate
the minimum voltage at which no electrons reach a negative plate is the stopping voltage
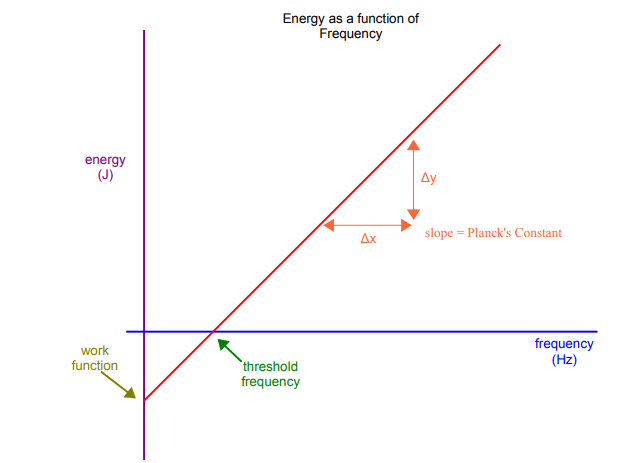
descrieb what the features on a voltage/frequency graph represent
y intercept → work function
x intercept → threshold frequency
gradient → plancks constant
what did DeBroglie suggest
that matter can have wave like properties if it has momentum
when are DeBroglie wavelengths significant
at atomic level
at a larger scale mass becomes larger and hence the wavelength becomes nearly negligible
what can absorption spectra reveal
star density → thickness of lines
motion of star → shift of lines to lower or higher frequency
what evidence is there that electrons behave like waves
electron diffraction
The double slit experiment fired electrons at two slits and a diffraction pattern was observed, which is only possible if they are waves
how can the wave nature of electrons be described using quantised energy levels
electrons act as a wave
hence orbitals are standing waves around the nucleus, based on factors of wavelengths
therefore energy levels of orbitals are quantised
why are absorption spectra formed
becuase when a continuous spectrum is shone through an atmosphere, the elements will absorb specific wavelengths to excite electrons and thus these wavelengths are removed from the spectrum
describe a blackbody
an ideal absorber which absorbs all incident radiation
it is in equilibrium with its surroundings, radiating and absorbing energy at the same rate, hence maintaining a constant temperature
how do incandescent globes produce light
a filament is heated to a very high temperature and the thermal motion of free electrons produces electromagnetic radiation
a continuous spectrum results
what does LED stand for
light emitting diode
describe an LED
a semiconductive device which uses the excitation of electrons to produce light
electrons move from the valence band to the conductive band when supplied with a voltage, across the band and move as an electric current before dropping back down and releasing photons
what does laser stand for
light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation
describe how a laser works
gas atoms need to be in an excited state, and then there must be mirrors on each side of the gas chamber
one mirror should be partially silvered to allow light to escape
some of the light emitted during de-excitation will reflect back into the gase chamber and stimulate further emission of the same wavelength. this process then repeats
all the waves are also in phase
describe a synchotron
a machine which uses electric fields and magents to accelerate charged particles
when electrons are accelerated they release electromagnetic radiation
how can you find maximum kinetic energy when given voltage
W = qV =Ek (max)
how do you find the work function
subtract maximum kinetic energy from photon energy
how do you find threshold frequency
equate the work function to the energy of the photon and solve for the frequency