JAPAN-KUN
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Who is the current prime minister
Prime Minister Shigeru Ishiba
Who is the current emperor
Emperor Naruhito
What kind of land is Japan
archipelago
How many islands and their names
four main islands
Hokkaido,
Honshu,
Shikoku,
Kyushu
Which island is the largest? (descending order)
Honshu is the largest, followed by Hokkaido, Kyushu, and Shikoku
Japanese archipelago is divided into ___ prefectures
47 prefectures:
4 categories of prefectures
Two urban prefectures (fu): Osaka and Kyoto
One metropolis prefecture (to): Tokyo
One circuit/district/regional prefecture (dō): Hokkaido
43 standard prefectures (ken)
The Japanese were gatherers, fishers and hunters. Jomon is the name of the Era’s pottery.
Jomon Period (13000 BC to 300 BC)
Era where agriculture was first introduced.
social classes started evolving into powerful land owners.
Chinese Travellers of the Han and Wei dynasties report that a queen called Himiko ruled
Japan at the time.
Yayoi Period (300 BC to 250 AD)
Central power develops in the Kinai Plains country gets
Unified as Yamato Japan by 400AD which the political center was the Province of Yamato (present day Nara prefecture).
hint: name comes from the word kofun or tomb
Kofu period / Yamato Japan(250-538AD)
Buddhism was introduced in japan.
Prince Shotoku played an essential role in promoting Chinese ideals. He wrote the
Constitution of Seventeen Articles on moral and political principles
Integrated, Confucianism and Taoism and Legalism in government.
Asuka Period (538-710)
Minamoto Yoritomo wins Genpei war after defeating Taira clan in 1185 and establishes the
Kamakura Shogunate in 1192.
Mongol Invasion attempt on Kyushu Islands in 1127
Kamakura Period (1192-1333)
Emperor Go-Daigo was able to restore imperial power to Kyoto after overthrowing the
Kamakura Shogunate.
Christianity was first introduced in this era in 1542 by Portugese traders and Jesuit
Missionaries upon arriving in Kyushu most notable is the Jesuit Sir Francis Xavier
Muromachi Period (1333-1573)
This period had civil wars and militant sects that Oda Nobunaga dealt with as he emerged as
the most power daimyo at the time and toppled the Ashikaga Shogunate
Toyotomi Hideyoshi, his successor, continued to eliminate enemies of Nobunaga during his
dominance
Azuchi-Momoya Period (1573-1603)
Marked by the transfer of the imperial capital to Heian Kyo (present day
Kyoto) and was a period of flourishing culture and the rise of court
aristocracy
“risturyō” system
Dominated by the Aristocratic Fujiwara Family,
Heian Period (794-1185)
refers to a historical legal and governmental system in
Japan which was heavily influenced by the Chinese Legal Administrative models..
“risturyō” system,
Final period of traditional Japan, where it is often remembered as a time of
internal peace, stability (political), and economic growth under the
Shogunate established by Tokugawa Ieyasu after the Battle of Sekigahara.
Iemitsu implemented the Sakoku Policy
Tokugawa or Edo Period (1603-1868)
was a series of directives that
restricted Japan and enforced self-isolation of the country. This banned Christianity
and prohibited Japanese People from traveling or returning from trips overseas. Such
directives aso Included restriction from foreign trade with various countries
Sakoku Policy
was restored after the Tokugawa shogunate fell.
Growing popular rights movements, which were encouraged by Liberal Western Ideas,
called for the creation of the constitutional government and wider participation through
deliberative assemblies. With pressure from those movements, the government stated in
1881 that it would promise a constitution by 1890.
the Country was well on its way to becoming modernized and
industrialized.
Meiji Period (1868-1912)
Japan occupied Indochina and had a joint protectorate with Vichy France on 1940. The U.S
responded with a freeze of assets and embargoing oil. This prompted Japan to bomb Pearl
Harbor after some, negotiations from the Konoe Cabinet and Washington, on December 7
1941.
World War II (1941-1947)
Japans goal of expansionism in the________ In the Philippines, Japanese troops occupied Manila in January 1942;
Singapore fell in February; so did the Dutch East Indies and Rangoon (modern Burma)
by March
Greater East Asia Co-prosperity Sphere-
Post War Reforms- After the surrender, Japan became an _____ occupied state of which was headed by _____, who was the Supreme
Commander for Allied Powers (SCAP).
Allied occupied state
headed by General Douglas MacArthur
Japan underwent d_____ and d______
democratization and demilitarization.
when was Japans constitution made
1947 Constitution
What special provision in their constitution states that they cannot initiate war—Why Japan Is Considered Pacifist?
Article 9:
Clause 1 renounces war as a sovereign right of the nation and the threat or use of force to settle international disputes.
Clause 2 states that Japan will not maintain land, sea, or air forces or other war potential. It also denies the right of belligerency of the state.
in the RUSSO-JAPANESE STRUGGLE what was it about
KURIL ISLANDS - seperares the sea of Okhotsk from the North Pacific Ocean
This treaty enabled Russian empire to gain control of the entire group of Islands
Treaty of Shimoda
in 1875 this treaty was issued to address another conflict on the island of Sakhalin (russian owndership was ceded to Japan of the entire Kuril Chian in exchange for Sakhalin)
1875 Treaty of Saint Petersburg
following Japans victory in the russo japanese war, this treaty retained the comtrol of the kuril chain to japan and re aquired control of the southern sakhalin island
Porthsmouth Peace Treaty
treaty that forced japan to give up its hold over kuril, but did not recognize soviet sovereignty
1951 San Franciso Peace Treaty
in the KOREA-JAPAN DISPUTE what was it about
DOKDO/ TAKESHIMA DISPUTE
between Japan and south korea,
Dokdo Island
Liancourt Islands(takeshma)
in the JAPAN-CHINA DISPUTE what was it about
SENKAKU/DIAOYU ISLANDS
what is Japans political system
Constitutional monarchy with a Parliamentary system
Democratic and Unitary state
what are the branches called
Cabinet[ executive branch ]
Japanese Diet [ legislative branch ]
Judiciary [judicial branch ]
what is the composition of the Cabinet[ executive branch ]
emperor( ceremonial)
prime minister (appointed by house of reps)
what is the composition of the Cabinet Japanese Diet [ legislative branch ]
popularly elected and consists of two houses (bicameral).
The House of Representatives (Shugiin), or the lower house, [4 yrs]
then the House of Councillors (Sangiin), or the Upper House. [ 6 yrs, elex every 3 yrs ]
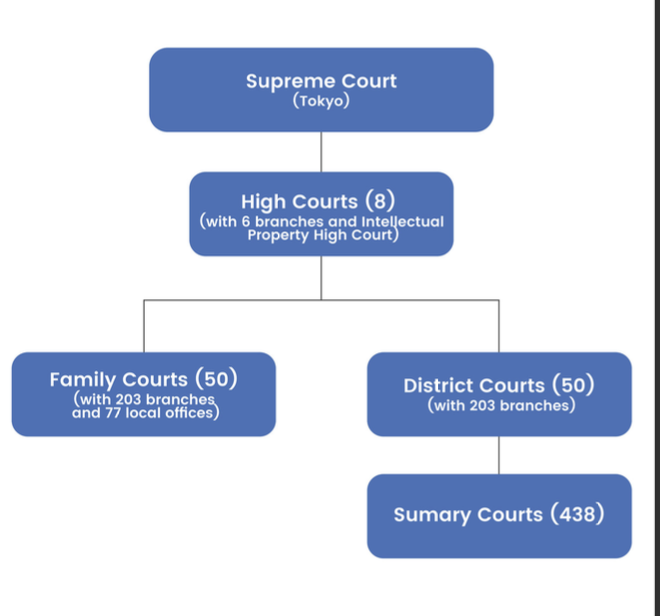
what is the composition of the Judiciary [judicial branch ]
three (3)
levels: The Supreme Court, 8 High (appellate) Courts, a
District court, and a Family Court in each prefecture
(except Hokkaido, which has four).
What voting system does japan use
upper house: A MIXED-MEMBER MAJORITARIAN REPRESENTATION (MMM) ( SINGLE-SEAT CONSTITUENCY AND PROPORTIONAL REPRESENTATION).
lower house: closed list proportional representation system
total seats in congress
465 [ lower house]
289 voting blocks
176 PROPORTIONAL REPRESENTATION
248 [ upper house]
124 elected every 3 years
74 ARE ELECTED FROM PREFECTURAL DISTRICTS (
50 ARE ELECTED THROUGH A NATIONWIDE PROPORTIONAL
REPRESENTATION LIST.
POLITICAL PARTIES
LIBERAL DEMOCRATIC PARTY (LDP)
JAPANESE COMMUNIST PARTY
CONSTITUTIONAL DEMOCRATIC PARTY (CDP)
JAPAN INNOVATION PARTY (JIP)
DEMOCRATIC PARTY FOR THE PEOPLE
(DPFP)
social movements
ANTI-NUCLEAR MOVMENT
KUTOO MOVEMENT
ANTI-SECURITY LAW PROTESTS
POLITICAL CULTURE
apolitical society.
collective mobilization are quite low
stance on ISRAEL-HAMAS conflict
supports a two-state solution where
Israel and a future Independent Palestinian state can live
side by side in peace and security above all else.
stance on RUSSIAN INVASION OF UKRAINE
Japan takes the consistent stance that
Russia’s “outrageous” act should not be tolerated and that it is
necessary to advance support for Ukraine and its neighboring
countries (Ibid)