MCAT Organic Chemistry - Alcohols
1/22
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
hydroxyl group (alcohols)
-OH
are capable of intermolecular hydrogen bonding → significantly higher melting and boiling points (additive) + solubility in water
IUPAC: root alkane - -e + -ol
common: alkyl group + alcohol
not highest priority: hydroxy-
phenols
hydroxyl groups attached to aromatic rings; particularly acidic due to resonance within the phenol ring
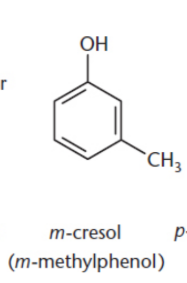
two substituents - indicate relative positions
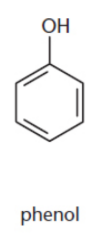
ortho–/o–
Two groups on adjacent carbons on a benzene
meta–/m–
Two groups separated by a carbon on a benzene
para–/p–
Two groups on opposite sides of the ring
hydrogen bond
the partially positive hydrogen of one molecule electrostatically attracts the partially negative oxygen of another molecule, generating a noncovalent bonding force
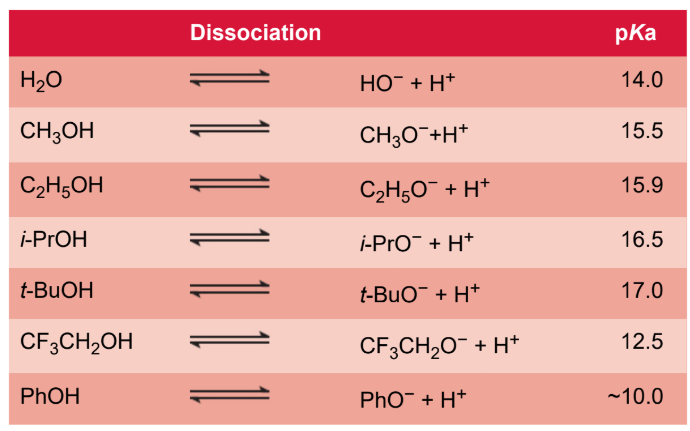
acidity of alcohols
hydroxyl hydrogen is weakly acidic; can dissociate into protons and alkoxide ions in the same way that water dissociates; electron-withdrawing substituents increase acidity, and electron-donating groups decrease acidity
pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC)
mild anhydrous oxidant
oxidises primary alcohols to aldehydes; does not continue
Secondary alcohols can be oxidized to ketones
geminal diols (1,1-diols)
other oxidizing agents (not PCC) oxidise aldehydes, which can be easily oxidized to carboxylic acids
ex. sodium and potassium dichromate salts (Na2Cr2O7 and K2Cr2O7)
Tertiary alcohols
cannot be oxidized because they are already as oxidized as they can be without breaking a carbon–carbon bond
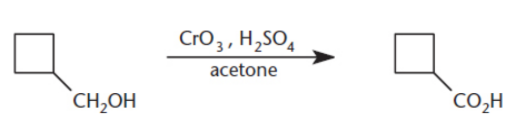
Jones oxidation
chromium trioxide, CrO3, dilute sulfuric acid, H2SO4, in acetone; oxidizes primary alcohols to carboxylic acids and secondary alcohols to ketones
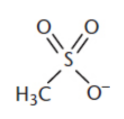
mesylate
−SO3CH3
derived from methanesulfonic acid
made from methylsulfonyl chloride and an alcohol in the presence of a base
good leaving group, good protecting group
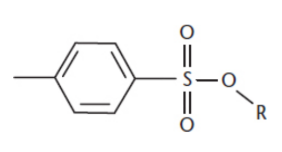
Tosylates
−SO3C6H4CH3
derived from toluenesulfonic acid
are produced by the reaction of alcohols with p-toluenesulfonyl chloride, forming esters of toluenesulfonic acid
good leaving group, good protecting group
acetals
primary carbons with two −OR groups and a hydrogen atom
ketals
secondary carbons with two −OR groups
deprotection
acetal or ketal can be reverted back to a carbonyl with aqueous acid
protection
save a ketone/aldehyde from reacting by reacting with diol then deprotecting
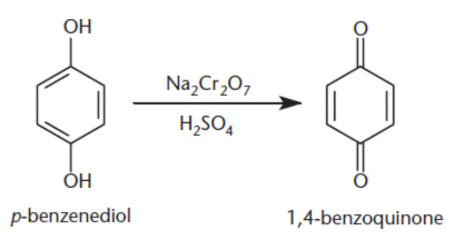
quinones (2,5-cyclohexadiene-1,4-diones)
treatment of phenols with oxidizing agents; resonance-stabilized electrophiles but not necessarily aromatic; electron acceptors biochemically
number carbonyl position + quinone
ex. vutamins K1, K2
Vitamin K1 (phylloquinone)
2-methyl-3-[(2E)-3,7,11,15-tetramethylhexadec-2-en-1-yl]naphthoquinone
important for photosynthesis and the carboxylation of some of the clotting factors in blood
fat-soluble vitamins that play a role in carboxylation of clotting factors II, VII, IX, and X, and proteins C and S in blood
Vitamin K2 (menaquinones)
protective effect on bone mineral density and reduced risk of hip, vertebral and non-vertebral fractures
fat-soluble vitamins that play a role in carboxylation of clotting factors II, VII, IX, and X, and proteins C and S in blood
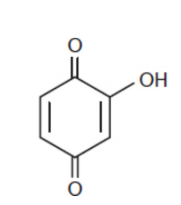
Hydroxyquinones
quinones with one or more hydroxyl groups; behave like quinones with electron-donating groups - slightly less electrophilic
ex. Tetrahydroxybenzoquinone; 5-hydroxynaphthoquinone; 1,2-dihydroxyanthraquinone.
hydroquinone
benzene ring with two hydroxyl groups
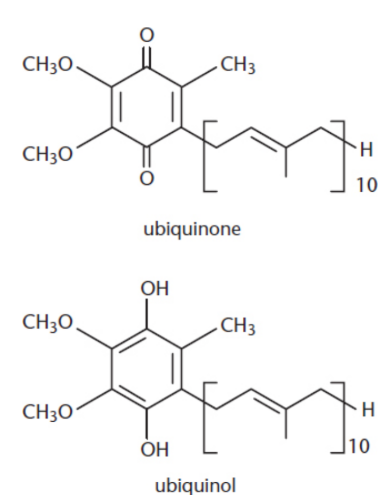
Ubiquinone/coenzyme Q
biologically active quinone; vital electron carrier associated with Complexes I, II, and III of the electron transport chain
reduced to ubiquinol upon the acceptance of electrons