3 neurology
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
know what ion blocker each drug is but nothing more for mechanism
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
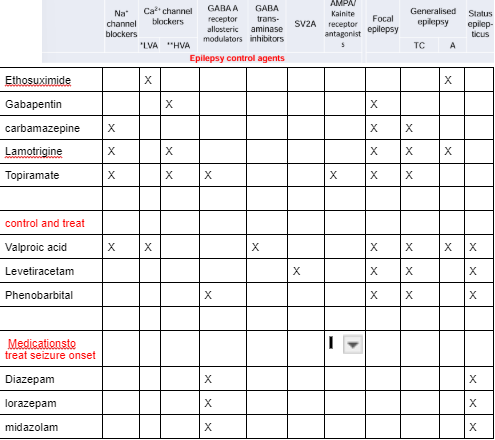
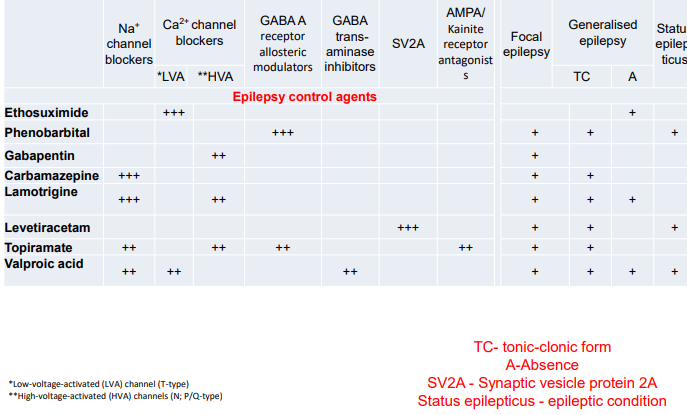
Epilepsy control agents
Carbamazepine
Lamotrigine
Topiramate
Gabapentin
Ethosuximide
Phenobarbital
Levetiracetam
Valproic acid
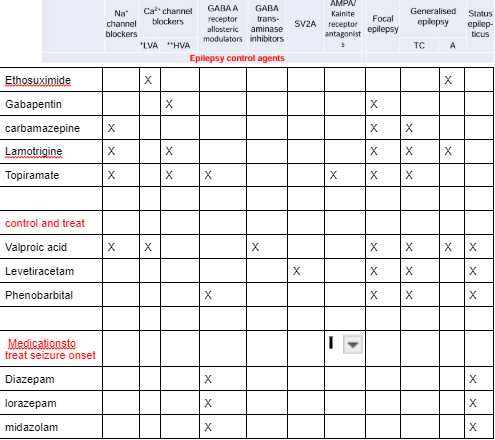
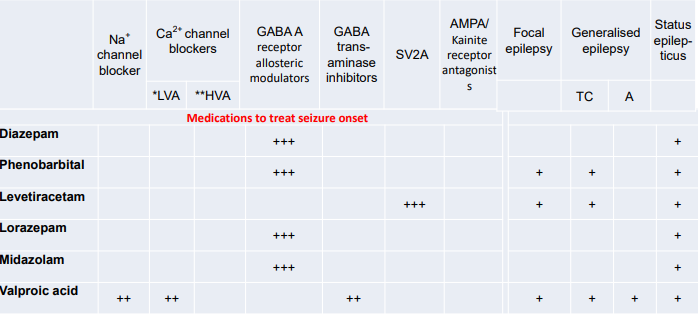
medications to treat seizure onset
Diazepam
Midazolam
Lorazepam
Phenobarbital
Valproic acid
Levetiracetam
Antiparkinsonian agents
Dopamine precursors and dopamine receptor agonists:
Levodopa / Benserazide
Carbidopa
Pramipexole
COMT inhibitors
Entacapone
Tolcapone
MAO inhibitors
Selegiline
Centrally acting cholinoblocker
Trihexifenidil
NMDA receptor antagonists
Amantadine
Parkinsons disease - A disturbed balance between dopamine inhibitory and ACh activating effects on GABA-ergic neurons. → on nigrostriatal tract → tremor, bradykinesia, rigidity and postural instability
TC, A
TC-tonic-clonicform, increased muscle tone with twiching
A-Absence (just loose contiousnes)
valproic acid
anticonculsant effect (control of epilepsy), mood stabilization
indication: generalized (TC,A) and focal epilepsy, status epilepticus, bipoar.
Side effect: teratogenic activity, (special care with women of childbearing potential)
(Blockade of voltage-dependent Na + and Ca2 + channels in neurons, inhibits GABA transaminase (prolongs GABA activity).)
Ethosuximide
anticonvulsant effect (control of epilepsy)
indication: generalized epilepsy (A)
(blockage of Ca2 channels in neurons)
Lamotrigine
anticonvulsant activity (control of epilepsy), mood stabilization
indication: generalized (TC,A) and focal epilepsy, bipolar
(Blockade of voltage-dependent Na + and Ca2 + channels in neurons,)
Carbamazepine
anticonvulsant activity (control of epilepsy), mood stabilization, co-analgic
indication: generalized (TC), focal epilepsy, bipolar, neuropathic pain
(Blockage of voltage-dependent Na + channels in neurons,)
Gabapentin
anticonvulsant effeect (control of epicleps, coanalgesic effect)
indication: focal epilepsy, neurophatic pain (diabetes neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia), chronic pain syndrome
(Structural analogue of GABA Inhibition of voltage-sensitive Ca2 + channels,)
Levetiracetam
Binds to synaptic vesicle protein 2A (SV2A) on glutamatic synapse, affects neurotransmitter exocytosis
Indication: generalized (TC) and focal epilepsy, status epileticus
Topiramate
blocks: Kainate/AMPA, Na & ca channels, GABA-A on glutamate receptor
indication: generalized (TC) and focal epilepsy
Phenobarbital
antiepileptic control and treat
anticonulsant and status epilepticus,
GABA agonist
ind: focal epilepsy TC
Carbidopa, benserazide
DCI - peripheral levodopa inhibitors of metabolism
dont cross blood brain barier
Indication: reduce dopamine-induced gastrointestinal & cardiovascular side effects. Parkinsons disease, parkinsonism
Side effect Neuroleptic malinant syndrome (if ended quickly), develop motor complications, develp ‘‘wearing off’’ (involuntery movment)& ‘‘on-off’’ (bradykinesia)
(Dopamine Prodrugs: L-DOPA + decabroxylase inhibitors (DCI)
By converting L-dopa to dopamine in the nigrostriatal tract, restores neurotransmission in Corpus striatum reduces EPS )
Pramipexole
Dopaminergic agents Non-selective agonists of striatal dopamine D2 receptors
Selegiline
➢ MAO-B inhibitors
Entacapone (does not cross BBB) Tolcapone (Crosses BBB)
COMT inhibitors
indication: parkinson, hyperprolactineamia
Trihexyphenidyl
➢ Cholinolytic agents
M1 choline blocker → blocks Ach-induced EPS
indication: parkinsonism, correction of EPT induced by antipsychotic agents
(Dopamine acts as an ACh antagonist normaly. (parkinson → low dopamin)
Amantadine
NMDA receptor antagonists
indicaion: parkinsons disease
(NMDA receptor blockade suppresses glutamatergic activity,promotes dopamine synthesis and secretion, inhibits dopamine presynaptic reuptake)
Memantine
Anti-dementia agents, NMDA receptor antagonists
indication alzheimers dementia
Donepezil
Anti-dementia agents, Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors
Rivastigmine (also inhibition of butyrylcholinesterase)
side effect: cholinergic hyperactivation
IA: : Medicines with anticholinergic properties (1st generation histamine receptor blockers, tricyclic antidepressants)
indication alzheimers, vascular dementia, parkinsons demetia