2.02 Organisational Structure
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Organizational Structure
Human resources can be organized in different ways. Most businesses needs a formal and organized structure for accountability and responsibility (in charge of what, what position)
Role and Ranking
There are many roles in a company, which can be organized in a hierarchy of importance or power.

Delegation
It is not possible for one person who handle all the work in an organization. The passing of control and authority is known as delegation. (assigning tasks and responsibilities to employees)
Effective Delegation
Effective delegation and save time and allow managers to focus on other issues. It could further motivate and develop employees.
Poor delegation
Poor delegation can lead to confusion, feelings of inadequacy, and demotivate staff.
SMARTER Delegation
Specific, Measurable, Agreed, Realistic, Time-bound, Ethical, Record.
Span of Control
Refers to the number of people who are directly accountable (under) to manager. Someone higher up in the hierarchy, will have a wider span of control. CEOs only have control over a board of director so its narrow, indirectly, its very wide.
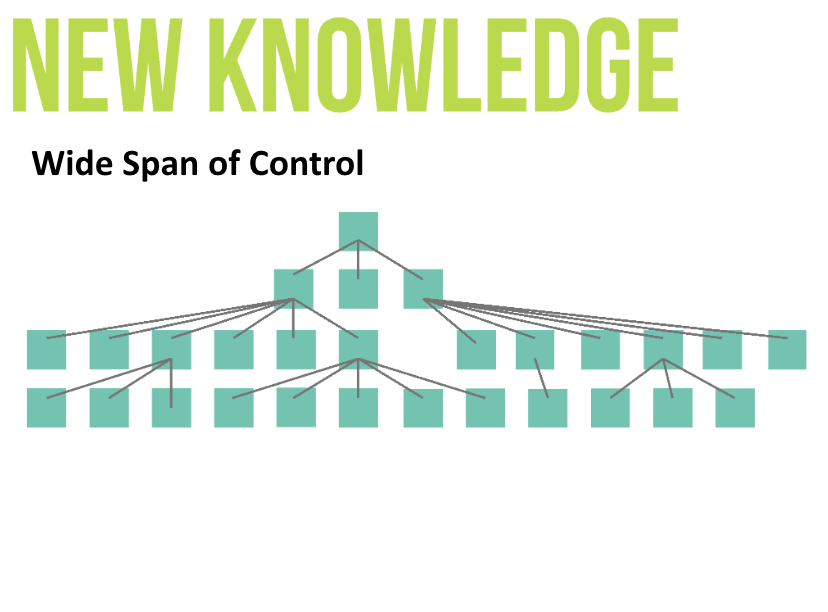
Wide Span of Control
Fewer layers in the hierarchy, less cost due to less managerial positions in the firm.
Communication would be more effective (in terms of speed and accuracy).
Narrow Span of Control
Fewer subordinate accountable to a manager. Easier to communicate and control, smaller teams can be more productive due to cohesiveness and spirit. This system can be more costly.
Manager’s Degree of Control - MOST
Manager - skills and experience
Organization structure - there might be cultures that require managers to closely monitor and control subordinates.
Subordinates - skilled staff are likely to work in smaller teams, managers having a wide span of control
Task - higher complexity task needs narrow span of control.
Levels of Hierarchy
Refers to organizational structure formed from a ranking system. At the top is CEO, chairperson, board, and at the other end is unskilled employees.
Pro/Con Hierarchal Structures
+Clear lines of communication, can improve coordination and productivity.
+Sense of belonging in different hierarchies.
- Departmentalisation, workers isolated to teams
- Inflexibility – hard to combat external changes
Chain of Command
The formal line of authority where orders are passed down. This can be seen through an organization chart. Few levels of hierarchy result in short chain of command.
Delayering
Delayering is the process of removing one or more levels in the hierarchy to flatten the organizational structure. This will widen span of control.
Pro/Con Delayering
+Reduce costs
+Improve communication speed
+ Encourages Delegation
- Create anxiety and sense of insecurity
- Overload staff
- Longer decision-making
Downsizing vs. Delayering
Downsizing involves reducing the workforce, maybe due to redundancy, while delayering means removing at least one level in the hierarccy, without anyone necessarily losing their jobs.
Bureaucracy
The execution of tasks that are governed by official administrative and formal organization rules. Bureaucratic organizations are characterized by policies, standardized procedures, formal hierarchies structures.
Excessive Administration in Bureaucracy
Frequent requirement to fill tedious paperwork
Staff working in multiple department, reporting to multiple managers.
Too many committees
Long chains of command
Managers with overlapping roles.
Bureaucratic organizations are governed by several principles:
Continuity - The establishment follows rules and regulations rather than taking high risks to maintain continuity.
Rules and regulations - Business activity is done according to official policies. There are clear lines of authority, responsibility, autonomy.
Hierarchical structures - Authority and responsibilities are part of formal hierarchies.
Accountability - Business activity is conducted with written evidence complying to the firm’s policies. Formality makes worker accountable.
Bureaucracy - Drawbacks
Most experts feel that bureaucracy hinders or prevent creativity and risk-taking, also slowing down decision-making, making organizations highly inflexible.
Centralization and decentralization
Decision-making power can be shared amongst the workforce or amongst a few people. The extent of dilution or concentration of authority depends on the skills and traits of employees in the organization. Decentralization means power is extended to a lot of people, centralization means limited amount of people.
Pro/Con Centralization
+ Rapid decision making
+ Better control
+ Efficiency
- Add pressure, stress to senior staff
- Inflexibility.
- Demotivating
- Delays in decision making
Which to choose: Centralization or Decentralization
Organization size - larger = greater need for decentralization
Scale of importance in the decision - decisions with high-cost risks will be centralized
Level of risk - high risk decisions will be centralized
Corporate culture
Matrix Structure
Task-oriented and based on teams. It tends to overcome many problems associated with traditional/hierarchical structures. It is a combination of vertical chain of command, operated through departments, and horizontal projects of product teams.
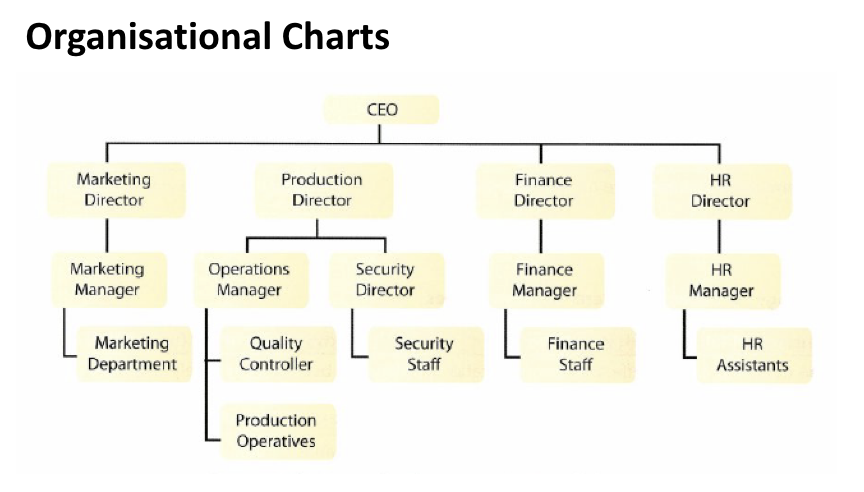
Organization Charts
An organizational chart is a diagram representation of the firm’s formal structure. It shows the functional departments, chain of command, span of control, communication channels and hierarchy levels.
Tall/Vertical Organization Structure
Multiple hierarchy levels: Narrow span of control
Centralized decision-making: Directors and seniors makes decisions.
Top-down communication: Decision flow from the top levels.
Emphasis on Hierarchy: Seniority is respected
Clear career path: Promotion for senior roles.
Slow decision-making: Hinder response to external change.
High cost: Large management structure is expensive.
Flat/Horizontal Organizational Structure
Fewer hierarchical levels: Wider span of control
Decentralized Decision-Making: More autonomy at lower levels
Increased delegation: Managers handle more employees.
Efficiency and Flexibility: Fast decision-making and adaptability.
Limited supervision: Close oversight can be difficult with many direct reports.
Organizational Structure by Functions
Department-Based: Hierarchy revolves around functions like marketing, HR, and finance.
Specialization: Experts work in their specific areas.
Coordination challenges: Difficult for departments to align.
Growth issues: Departments can compete for resources, potentially prioritizing their needs over the company’s.
Organization Structure by Region
Geographical Focus: Structure based on regions (countries/continents)
Common in Global Businesses: Used by companies operating in many countries.
Regional Autonomy: Better adaptation to local markets and needs.
E.g. Multinational companies likes HSBC bank organize by geographical areas.
Organization Structure by Product
Product-focused: Employees concentrate on the specific needs of customers for a particular product/brands.
Motivation&Loyalty: High levels of commitment to specific products or divisions.
Autonomy: Divisions may have significant control over finance and decision making.
Isolation risk: Decisions made without considering overall business objectives.
E.g. BBC organizes divisions based on services like music, news, media.
Technology Impacts on Communication
More information for decision-making via data (e.g. loyalty cards)
Shift towards decentralization: Junior employees can make data-supported decisions
Rise in flatter structures: Faster response to customer feedback (social media)
Social media management: Teams responding quickly to customer issues.
Culture Impacts on Communication
Language proficiency is a highly valued communication skill. Knowing the native language are vital in many occupations in certain parts of the world.
Accents can hinder communication
Cultural ignorance can cause offense to others.
The main solution is to recruit bilingual or multilingual employees.