vital signs
1/64
Earn XP
Description and Tags
exam 1 (5 questions)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
learning objectives
recall physical assessment techniques for bp, pulse, respiratory rate, and temperature measurement
interpret vitals signs measurements
demonstrate proper vital sign measurement (skills lab session)
why do we measure vital signs?
vital signs: objectively quantify several essential bodily functions
measure/asses is performed routinely in every healthcare setting
data to determine pt’s:
state of health
response to med treatment
psychological/physiological stressors
what is body temperature?
a measurement of balance btwn heat lost/produced by body
indicates body’s metabolic status
can be sign of infection/invasion of harmful organism
what is core temperature? how does it deviate? where do you measure?
temp of deep tissue of bod (abdominal/pelvic cavity)
rel constant
rectum, tympanic membrane (ear), pulmonary artery, oral
what is surface temperature? how deviate? where measure?
temp of skin, subcutaneous tissue, fat
rises/falls in resp to environ
skin, axilla (underam)
average of oral (core temperature)?
98.6°F / 37.0°C
average of rectal (core temperature)?
99.6°F / 37.6°C
→ rectal: most reliable measurement
average of axillary (surface temperature)?
97.6°F / 36.4°C
→ axillary (underarm): least accurate measurement
average tympanic (core temperature)?
99.6°F / 37.6°C
→ tympanic = ear
average temporal (surface temperature)?
99.2°F / 37.3°F
what is the deviation of avg normal temp?
0.5°F - 1°F / 0.3°C - 0.6°C
how do you use contact thermometers? what does it commonly use? where do you measure? pros/cons?
contact/touch body for ↑ accuracy
uses electronic heat sensors
forehead, mouth, armpit, rectum
pros: records T fast (<1 min), good all ages
cons: rectum = uncomfy, oral can be affected by food/drink
how do you use remote thermometers? what does it commonly use? where do you measure? pros/cons?
x need body contact
uses infrared radiation
forehead, ear
pros: fast mesurement/easily tolerated
cons: ↑ expensive, ↓ accurate (use tech, direct sunlight, cold temp, sweaty forehead, earwax, ear anatomy)
how to convert between fahrenheit and celcius?

what body temp is hypothermic?
<35°C / 95°F
what body temp is normal/afebrile?
36.4-37.5°C / 97.5-99.5°F
what body temp is hyperthermic (febril)? low grade fever? fever?
low grade fever: 37.6-37.9°C / 99.6-100.3°F
fever: ≥38°C / ≥100.4°F
what are the hypOthermia risk factors?
exhaustion
age (older age, v young age)
cognitive deficits (dementia)
alcohol/drug use
medical conditions (hypothyroidism, diabetes, storke, spinal cord injuries)
medications (antidepressants, antipsychotics, sedatives)
what are the hypErthermia risk factors?
medical conditions (autoimmune, cancer, hyperthyroidism)
infection
heat exhaustion
vax/immunizations
medications (atropine, recreational drugs)
what is pulse? where can pulse be found?
# times heart beats per min (bpm)
wave of blood created each time left ventricle of heart contracts
pulse can be palpated over any artery
carotid (neck) and radial (wrist)
what is the normal range for pulse in adults?
60-100 bpm
what is pulse rate? how to measure?
rate: # pulse beats per min
palpate radial artery + observe clock hand for 30 sec, multiple by 2 to get the full number of beats per min
if pulse = irreg rhythm; count to full 60 sec while palpating
what is it called when heart rate is slow? fast?
slow HR: bradycardia
fast HR: tachycardia
what is pulse rhythm? what’s normal/irregular?
pulse rhythm: regularity (equal spacing) of all beats of pulse
normal: heartbeat intervals are same duration
irregular: unequal spacing
count to full 60 seconds when palpating
what is an irregular rhythm pulse called?
dysrhythmia / arrhythmia
unequal intervals of heartbeat
what is intermittent pulse?
heart occasionally skips heat
normal
what is the strength of the pulse influenced by?
force of the heartbeat
what does the force of the heart beat reflect?
pt’s blood volume, arterial wall status, hydration levels
what is the pulse grading scale?
strong, bounding, not obliterated w P
normal, strong, easy to palpate, not easily obliterated w P
difficult to palpate, may be obliterate w P
difficult to palpate, diminished/weak, may be obliterated w P
not palpable
what are the five factors that influence pulse rate?
air temp
body position
emotions
body size
medication use
influence pulse rate: babem (body pos, air temp, body size, emotions, med use)
explain how the five factors influence pulse rate.
air temp: ↑T/humidity = heart pump ↑ blood: = ↑ pulse
body pos: sititng → standing: ↑ pulse
sign of POTS (postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome)
emotions: stress = ↑pulse
body size: very obese pts: ↑resting pulse
athletes: ↓resting pulse
medication use: epinephrine blockers ↓pulse (b-blockers) + excess thyroid med: ↑pulse
what’s the normal range for pulse?
60 - 100 bpm
bradycardia. symptoms? cuases?
bradycardia ( <60 bpm); brad is a little sLOW
symptoms
syncope/near fainting
dizziness/light
fatigue (esp w exertion)
chest pain
confusions or memory prob
causes
heart tissue dmg rel to aging/disease
medication (antiarrhythmics, anti-hypertensives)
tachycardia. symptoms? causes?
tachycardia (>100 bpm)
symptoms
shortness of breath
lightheadedness
heart palpitations
chest pain
fainting (syncope)
causes
excess caffeine/alc
fever
↑/ ↓ BP
stress
medications (stimulants)
what is respiration? what does it consist of? what is equal to one respiration? when is it taken?
act if breathing; exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide
consists of 1 expiration + 1 inspiration
exhalation: diaphragm relaxes/moves up
inhalation: diaphragm contracts/moves down
1 respiration = each rise and fall of pts chest
taken at same time as pulse/immediately after
what are the four characteristics of respiration?
rate: # respirations/min
rhythm: pattern/regularity of respirations (spacing btwn breaths) → regular/irregular
depth: amnt of air inhaled/exhaled
normal, shallow, deep
breath sounds
(respiration term) describe stridor.
high-pitched and noisy (most common in children)
(respiration term) stertorous.
noisy breathing, sounds like snorting
(respiration term) crackles/rales.
high-pitched rattling
(respiration term) rhonchi.
coarse, low-pitched breathing
(respiration term) wheezes.
high-pitched whistling
(respiration term) apnea.
temp suspension of breathing/absence of ventilation
(respiration term) eupnea.
normal rate, depth, regular rhythm
(respiration term) hyperventilation.
fast rate and increased depth
(respiration term) tachypnea.
v fast; faster rate, shallow depth, reg rhythm
(respiration term) bradypnea.
v slow; slow rate, shallow or normal depth, reg rhythm
(respiration term) orthopnea.
difficulty breathing in postures other than erect
(respiration term) dyspnea.
difficulty breathing
what are the 4 factors that alter respiration?
age (younger: ↑O₂ demands)
pain (↑HR/BP → ↑respiratory rate)
emotions (∆pattern, rate, depth breathing)
air passage resistance (↑resistance —| air enter lunch during each cycle → ↑O₂ demand)
whats the relationship bwtn oxygen demand and respiration?
↑O₂ demand: ↑respiration rate
what are the 4 steps to measuring respiration?
clinical skills pearl: measure the respiratory rate immediately following measurement of pulse
continue hold wrist + watch chest
one rise one fall = one respiration
(x see chest) hold pt’s arm across chest, feel chest move
count respirations for 15-30 sec and multiply by 4/2 to get 60 seconds
look/listen for any signs of abnormal breathing
bradypnea. symptoms? causes?
bradypnea (<12 breaths per min)
symptoms
lightheadedness/dizziness
headaches
altered mental status
causes
medical conditions (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, sleep apnea, etc.)
medication (optiods, benzodiazepines, sleep aids)
tachypnea. symptoms? causes?
tachypnea (>20 respirations per min)
symptoms
shortness of breath
chest pain
cyanosis (blueness) of lips/fingers
causes
excess caffeine/alc
exercise
fever
high/low BP
sudden stress
medications (stimulants)
whats the normal range of respiration?
12 - 20 respirations per min
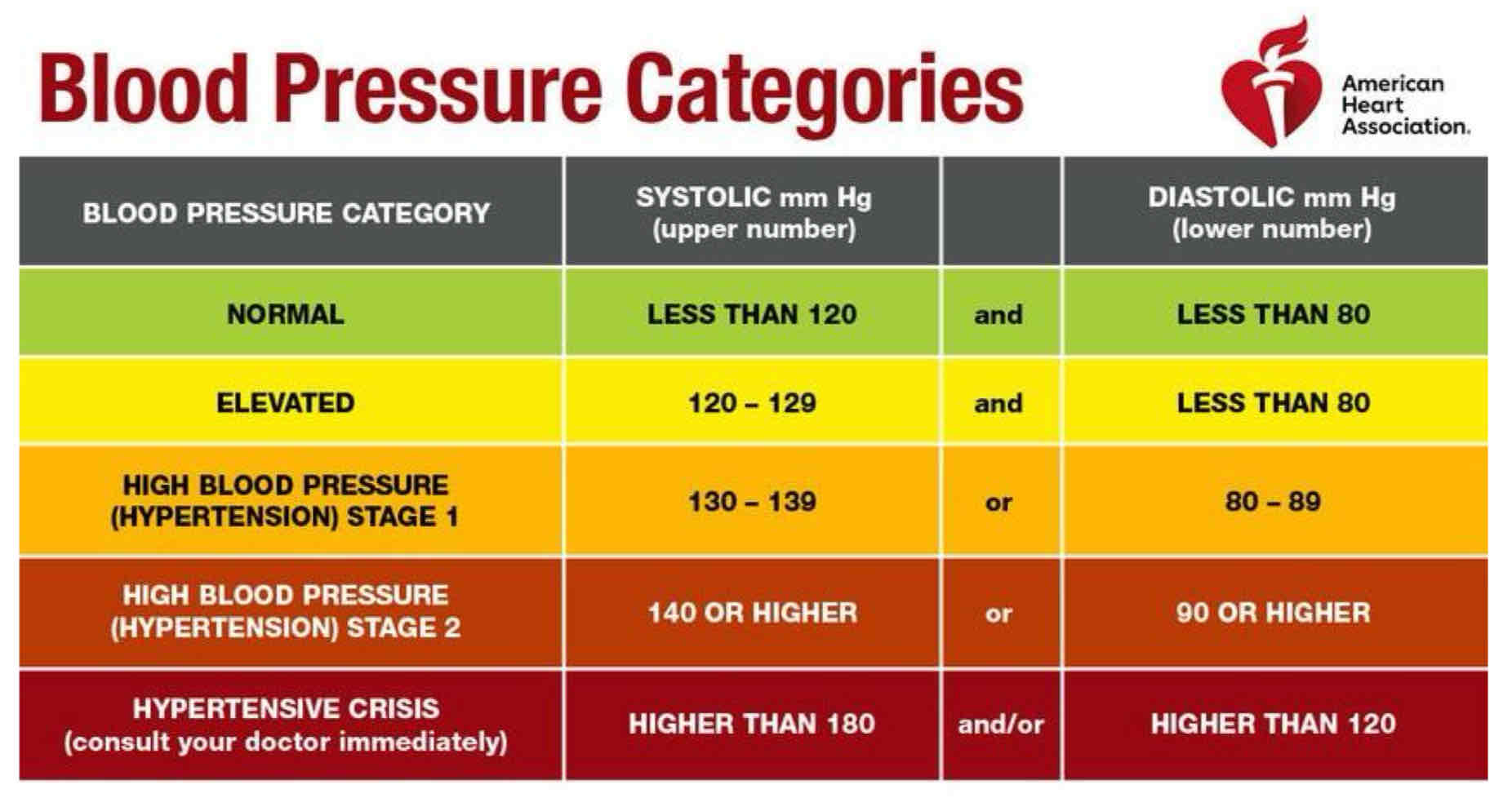
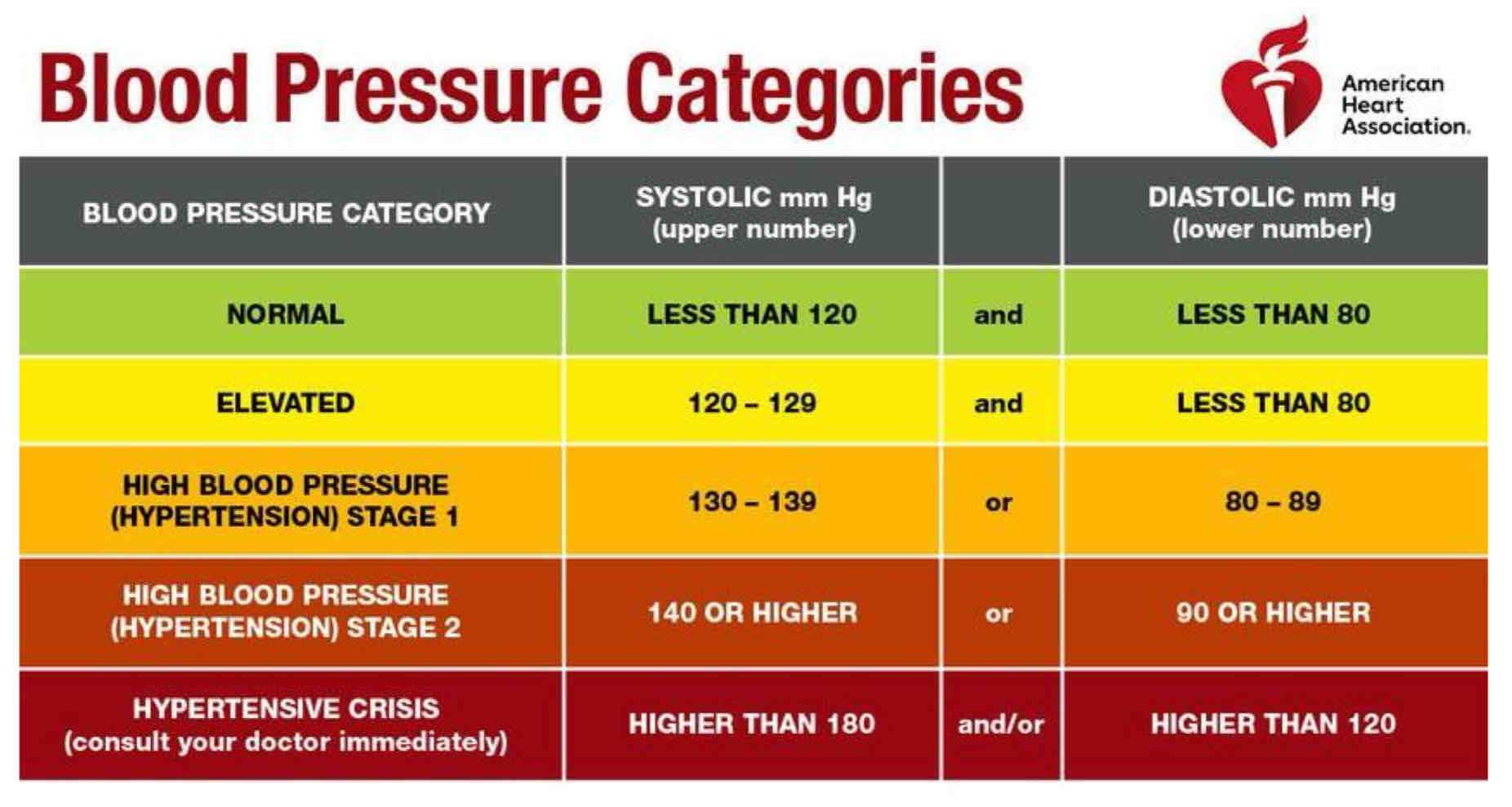
what denotes hypertension?
systolic BP ≥ 130 mmHG or
diastolic BP ≥ 80 mmHG or
taking medication for hypertension
what is hypertension? what is it broken down into? define such.
BP: force of blood pushing against walls of arteries that carry blood from heart to other parts of bod
no symptoms of hypertension
BP broken down to 2 numbers
systolic BP: artery P when heart beats
diastolic BP: artery P when heart relaxes
what 4 things should pts avoid doing 30 mins before BP measurement?
caffeine (↑BP)
smoking (↑BP)
exercise (↑BP)
eating a meal (↑BP: using O₂ in blood to digest food)
what should pts rest from for 5 mins before BP measurement? what does this help?
rest wo using phone 5 mins before
help w white coat hypertension
should pts completely empty bladder before BP measurement?
yes; full bladder ↑BP 10-15 mmHg
how does tightness/looseness of BP cuff translate to in readings? how do you select BP cuff?
tighter cuff: ↑BP
looser cuff: ↓BP
select size by finding mid-upper arm circumference and look on box for rec cuff size; test by interting 2 fingers into cuff = snug
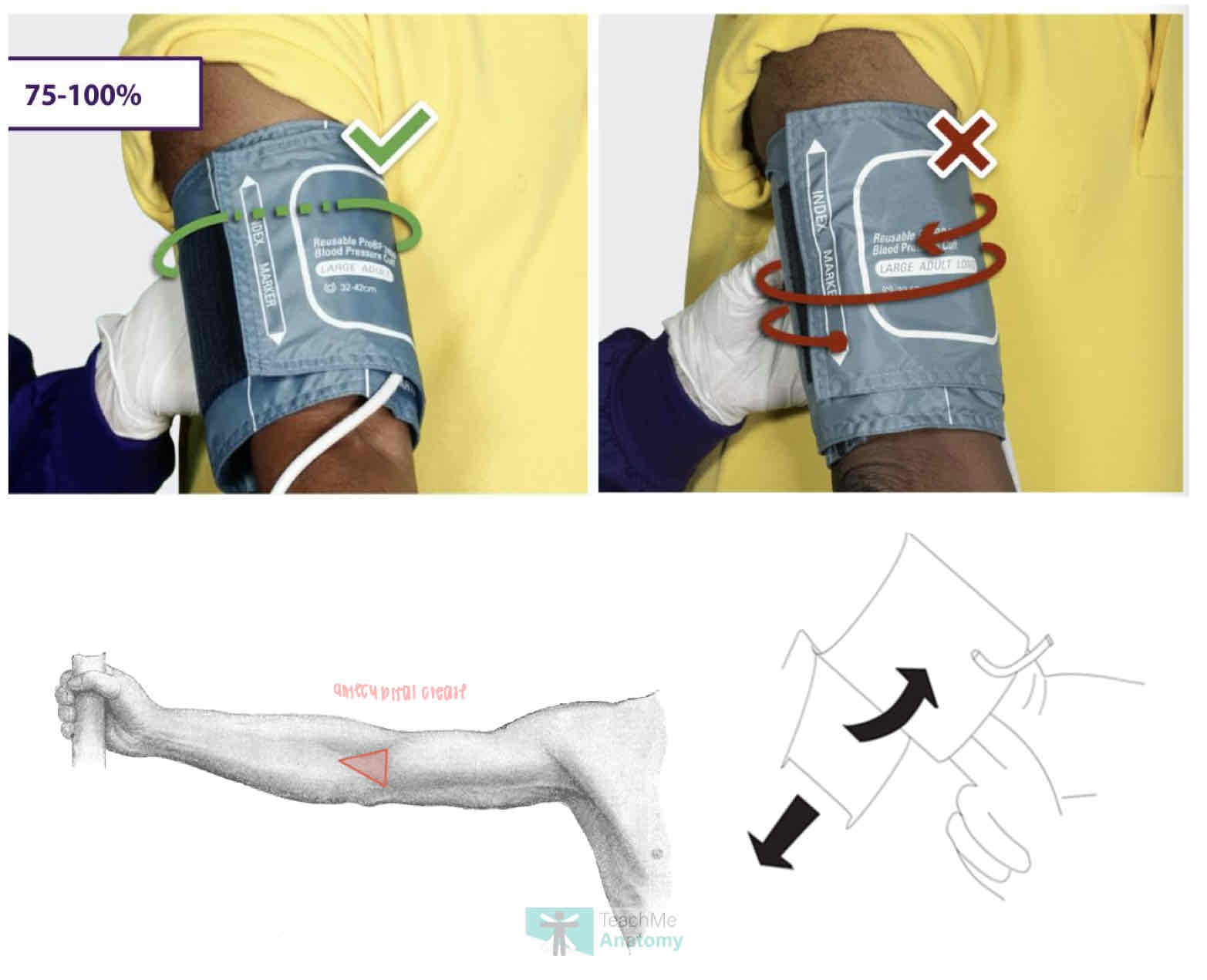
where is the BP cuff placed? how should the pt be while taking measurement?
on bare arm abt 2 fingers above antecubital crease
should be level with pts heart when arm supported
pt refrain from talking, have seated upright w back fully against chair, feet flat w legs uncrossed
what us auscultatory gap? what does it result in? how do you overcome it?
intermittent disappearance of initial korotkoff sounds after first appearance
may result in underestimation of systolic BP
overcoming auscultatory gap:
palpate radial pulse while rapidly inflating cuff to 80mmHg
slowly inflate cuff ~10 mmHg every 2-3 sec until no longer feel radial pulse = obliteration pressure
inflate bulb for an additional 20-30 mmHg after obliteration P
place stethescope directly over brachial artery
slowly deflate cuff at rate of 2 mmHg/sec and listen for korotkoff sounds
first korotkoff sounds = systolic BP
point where sound gone = diastolic BP
pick closest even number for both measurements
write down values and what arm used
how do you document BP for initial visits? follow up visits? how do you communicate readings?
inital: measure BP in both arms, document readings and which arm has highest reading
highest reading → use for future visits
follow up visits: measure 2/+ on same arm, spaced 1-2 mins apart, avg readings, document measurements/avgs
communicate readings to pt verbal/writing
how do you interpret BP readings? normal? elevated?
normal BP <120 mmHg/ <80 mmHg: within range
systolic/diastolic
≥ 120mmHg or ≥ 80mmHg: elevated/above range
what is the pharmacists role in BP screening?
counsel pts on importance of self-monitoring BP/BP screenings
normotensive pts: encourage continue healthy habits and periodic checkups
pts rsk for hypertension: encourage lifestyle modifications take active role in health
pts w hypertension: emphasize lifestyle modifications and schedule follow up appts, stress medication adherence