Research Methods Exam 1
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
empirically
conclusions based on systematic observations (scientific method)
empiricism
evidence derived from senses
producer
conduct research to answer a scientific question
produce information
consumer
reads, interprets, applies scientific findings
ex: teacher, intervention evaluator
Merton’s Scientific Norms
1) empiricism—>universalism, disinterestedness, organized skepticism
2) examines solvable problems
3) producing public knowledge
universalism
scientific claims are evaluated according to their merit
communality
scientific knowledge is created by a community and findings are for community
disinterestedness
scientists strive to discover truth; not swayed by anything
-not personally invested in income
organized skepticism
scientists question everything, including their own theories
theory data cycle
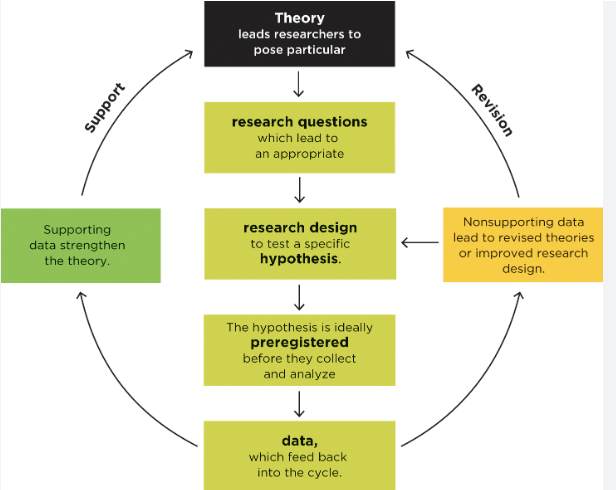
theory
set of statements that describe general principles about how variables relate to each other
hypothesis
-a falsifible prediction
-specific outcome that researchers expects to observe in a study if theory is accurate
data
set of observations
pre-registered
before collecting any data, researcher publicly states what the study outcome is expected to be
how do scientists approach work
1) single theory—>endless hypothesis
2) single study does NOT test an entire theory, only part
3) researchers test theories with senses of studies, each addressing different hypothesis
4) when data does NOT match—> theory needs to be revised, or design should be improved
good theories
supported by data
theory supported by LARGE QUANTITY and VARIETY OF EVIDENCE
are testable
have parsimony (simplest answer is the best)
Do theories prove anything?
NO, “supported” or “not supported”
What are the two types of research?
1) applied research
2) basic research
applied research
address a particular problem, applying a method and seeing how it helps
basic research
enhance the general body of knowledge, engine of evidence
translational research
bridge between basic and applied research
example: basic research on cell membrane biochemistry might be translated into a new drug for mental health issues
Intro for APA
cites past research to explain rationale for current hypothesis
Methods for APA
recipe for study
participants, design, materials, procedure
Results APA
data analyses
Discussion APA
theoretical implications, limitations, future directions
steps for the publication process
1) scientists share research by submitting a paper
2) peer review stage: send paper to ¾ experts in the field to review
3) the process is rigorous and anonymous. manuscripts are either rejected, accepted, or accepted with revisions
two important safeguards for ethics
1) ethics codes
2) institutional review boards
Belmont Principles
1) respect for persons
2) beneficience
3)justice
respect for persons
must be treated as autonomous individuals
1) informed consent
2) make research voluntary
3) use special protections for participants with limited autonomy
beneficence
maximize benefits of research while minimizing harm to participants
1) use research methods with least possible risk
2) maintain participant confidentiality
3) carefully monitor research that involves more than minimal risk
justice
procedures need to be administered fairly among participants
1) treat research participants equitably
2) do NOT exploit vulnerable populations
passive deception (deception of omission)
withholding of truth/relevant info
active deception (deception of commision)
intentionally misinforming
Institutionalized Review Boards (IRBS)
board reviews research proposals
must have at least 5 members
1 member must be outside of institution
what is a variable?
something we manipulate or measure, something that varies
“More than 2 million U.S Youths are depressed”
variable: depression
levels: depressed and not depressed
measured variable
one that is observed and recorded
some are measured using familiar tools (IQ test, ruler)
others need a measurement to be created (gender, hair color)
manipulated variables
one that researcher controls
assigning participants to the levels of that variables
random assingment
random placement of ppts into levels of manipulated variable
constant
something that has potential to vary, but does not in a given study
example: in research on fathers, sex is constant rather than a variable
conceptual definition
a researchers definition of a variable at an abstract level (the WHAT)
operational definition
the specific way in which a concept is measured or manipulated (the WHY)
what are the 3 types of claims?
1) frequency
2) association
3) casual
frequency claims
rate/degree of a particular thing or event
how frequent or common something is
usually a percentage
example: 1=never, 2=alittle and so on
association claims
displayed on scatter plots
on variable plotted on x-axis, one variable plotted on y-axis
4 types of associations:
• Positive
• As X increases, Y increases
• Negative
• As X increases, Y decreases
• Zero
• Knowing X tells us nothing about Y
• Curvilinear
• As X increases, Y changes its pattern
• E.g. Y increases, then decreases
Casual Claims
argues that one variable is responsible for changing another
changes in “x” CAUSE changes in “y”
positive, negative, curvilinear
correlation does NOT cause
CAUSATION
third variable problem
there may be an unmeasured variable that actually causes variables to covary (change together)
directionality problem
not always possible to specify the direction in which a casual arrow points
do video games and internet ruin our relationships?
What are the four types of validities?
1) construct
2) statistical
3) external
4) internal
construct validity
how well did a study measure or manipulate a variable?
ex: 39% of teens text while driving
statistical validity
researchers use statistics to analyze their data
are the results statistically accurate?
how well do the numbers support the claim?
external validity
how well do the results generalize?
can our findings apply to other populations, contexts, times or places?
internal validity
how likely is it that one of the variables cause the change in the other?
what are the 3 criteria to establish criteria claims…?
1) covariance
2) internal validity
3) temporal precedence
covariance
are the variables associated with each other?
internal
was the study an experiment?
temporal precedence
did one happen before the other?
random selection
whole population of interest has an equal chance to be in study
random assignment
participants are randomly assigned to a level
categorial measurement
levels are categories
ex: spring, summer, fall, winter
ex: junior, senior, freshmen
quantitative measurement
continuous
meaningful numbers
inherently numerical
ordinal scale (quantitative variable)
ranked scale
uneven intervals
ex: top 10 selling books
ratio scale (quantitative variables)
equal intervals
“true 0” (0 means none)
ex: number of exam questions correct
interval scale
equal intervals
no “true 0” (0 doesnt mean none)
ex: IQ test
what are the common types of measures?
1) self-report measure
questionarre/interview
2) observational measure
observable behavior or traces of observable behavior
3) physiological measure
biological data (heart rate)
test-retest validity
scores should be consistent each time they are measured
test at a specific time, then test a few years later
most relevant for stable constructs
ex: IQ test
Interrater reliability
when we have multiple observers
consistent scores despite different observers
ex: 2 raters count how often a child smiles on a playground
Internal reliability
consistent pattern of answers despite phrasing of questions
applies to measures that combine multiple items
face validity
it looks like something you want to measure
does it pass the “vibe” check
content validity
the measure contains all the parts that your theory says it should contain
criterion validity
the measure is associated with a concrete behavioral outcome it is expected to be
look at correlational evidence
known-groups paradigm
convergent validity
does the self report measure correlate with other measures of the same construct
discriminant validity
does the self report measure NOT correlate with measures of dissimilar constructs