Year 9 Science Semester 2 Exam Overview
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Independent Variable
The variable changed in an experiment.
Dependent Variable
The variable measured in an experiment.
Controlled variable
variable that stays the same in a experiment
fair test
where only one variable changes
Electrostatic charge
A buildup of charges on the surface of an object
electric charge
A positive or negative charge that can be produced by protons and electrons and results in electricity
Electric circuit
A complete, unbroken path through which electric charges can flow
Conductors
Any material that allows an electric current to pass through it easily.
Insulator
A material that does not allow electrons to move through it easily.
Parallel circuit
A closed electrical circuit in which the current is divided into two or more paths and then returns via a common path to complete the circuit.
Series circuit
A circuit in which all parts are connected end to end to provide a single path of current.
Resistance
A material's opposition to the flow of electric current.
Voltage
The difference in electrical potential energy between two places in a circuit.
Current
A flow of electric charge around a circuit
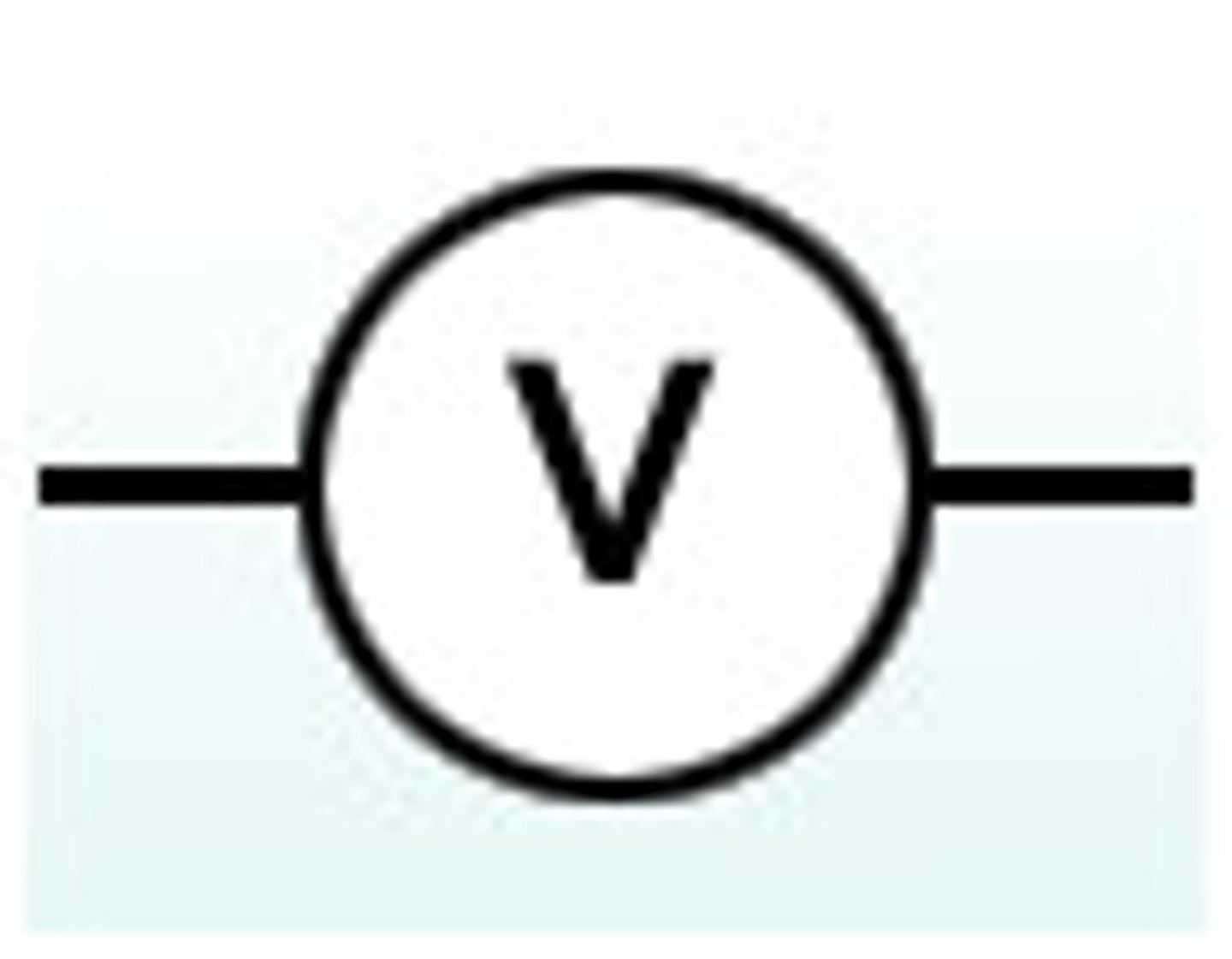
Voltmeter
A device used to measure voltage, or electrical potential energy difference across components in a circuit
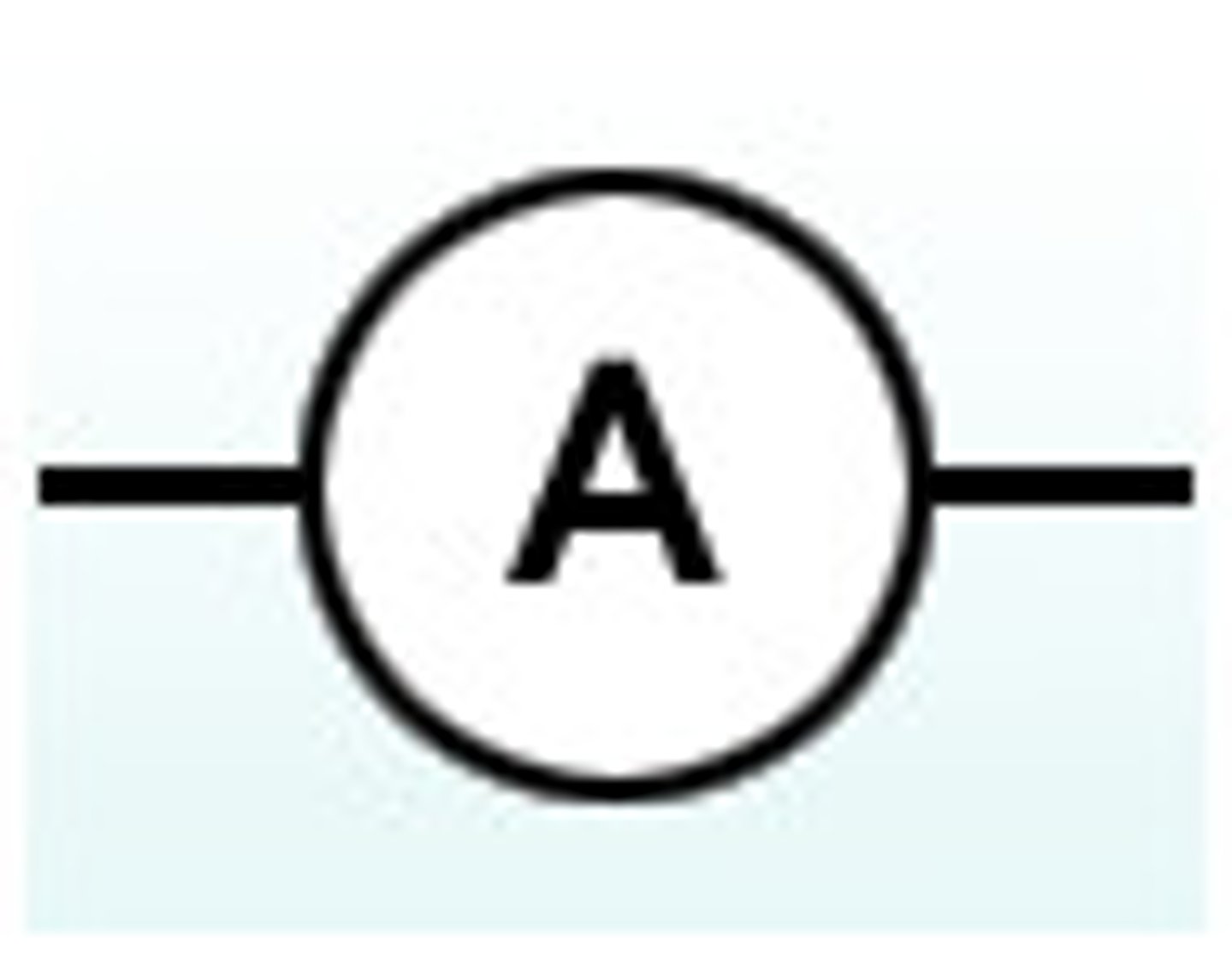
Ammeter
A device used to measure current in a circuit
Voltage in a parallel circuit
Same across each component
Voltage in a series circuit
Voltage is shared between components
Current in a series circuit
Same at all points
Current in a parallel circuit
Is shared between branches
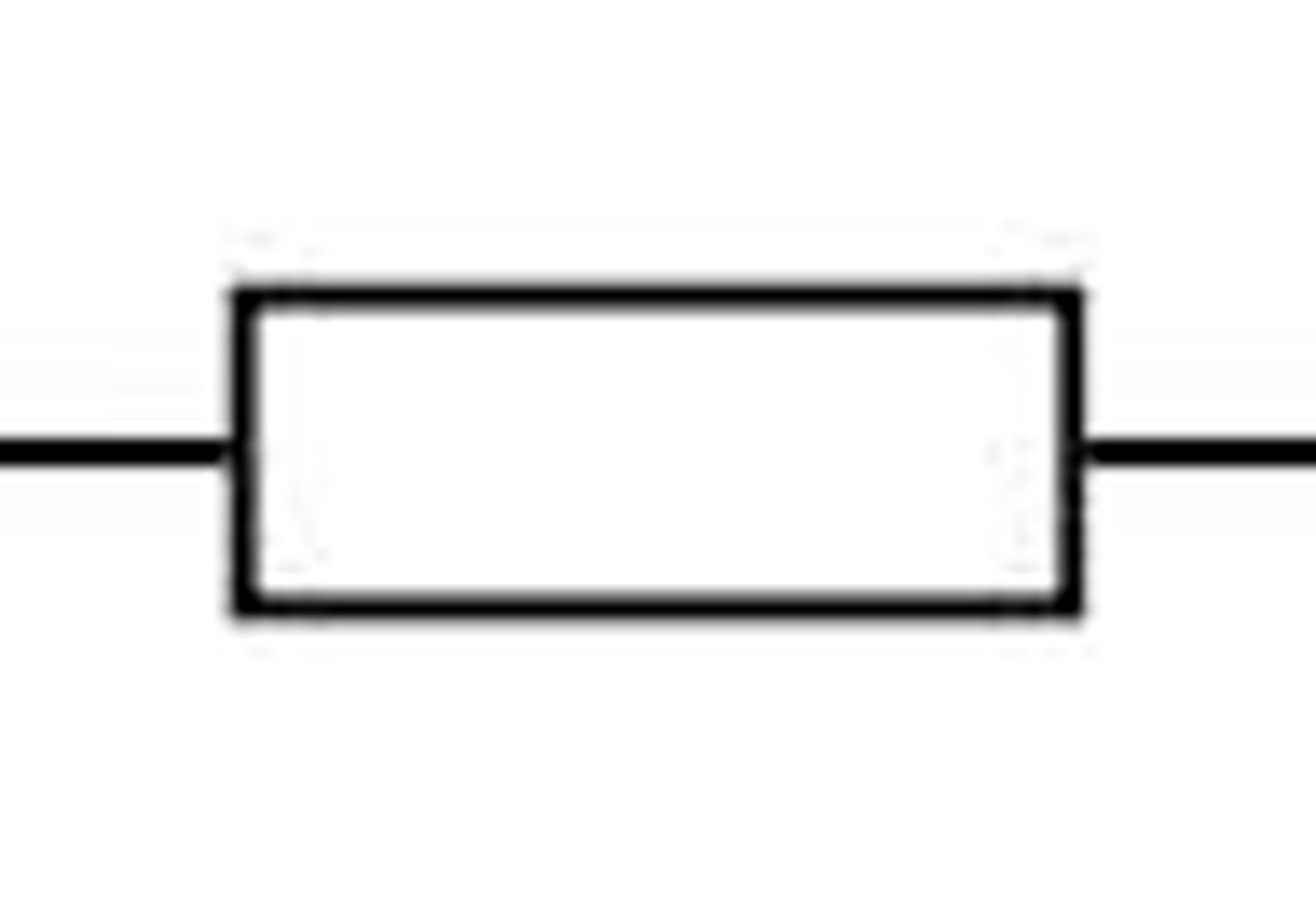
Resistor
An electrical device that resists the flow of electrical current
Ohm's Law
V=IR
I=V/R
R=V/I

Ohm
unit of resistance
what charges attract
opposite charges
what charges repel
like charges
electrical conductor examples
gold copper water
Electrical insulator examples
glass rubber wood
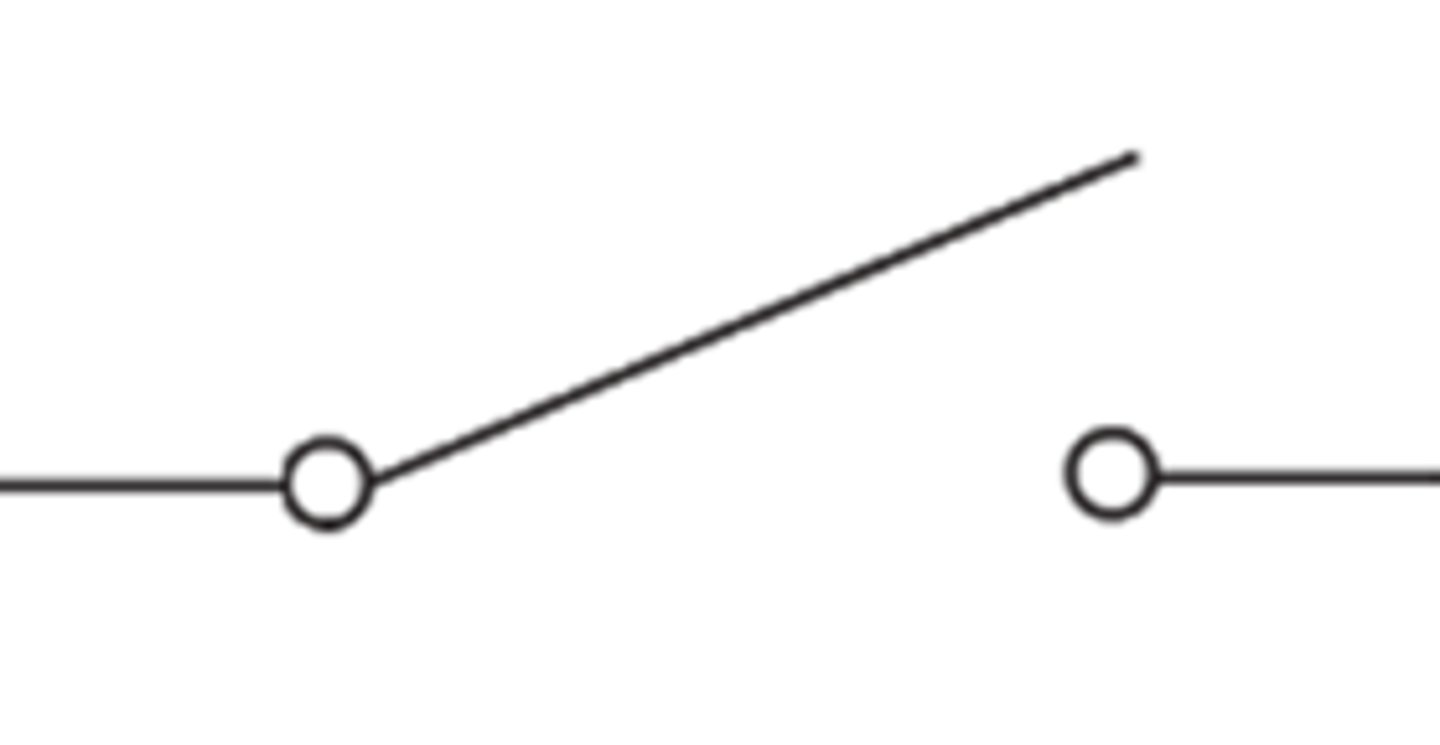
circuit switch
circuit lamp
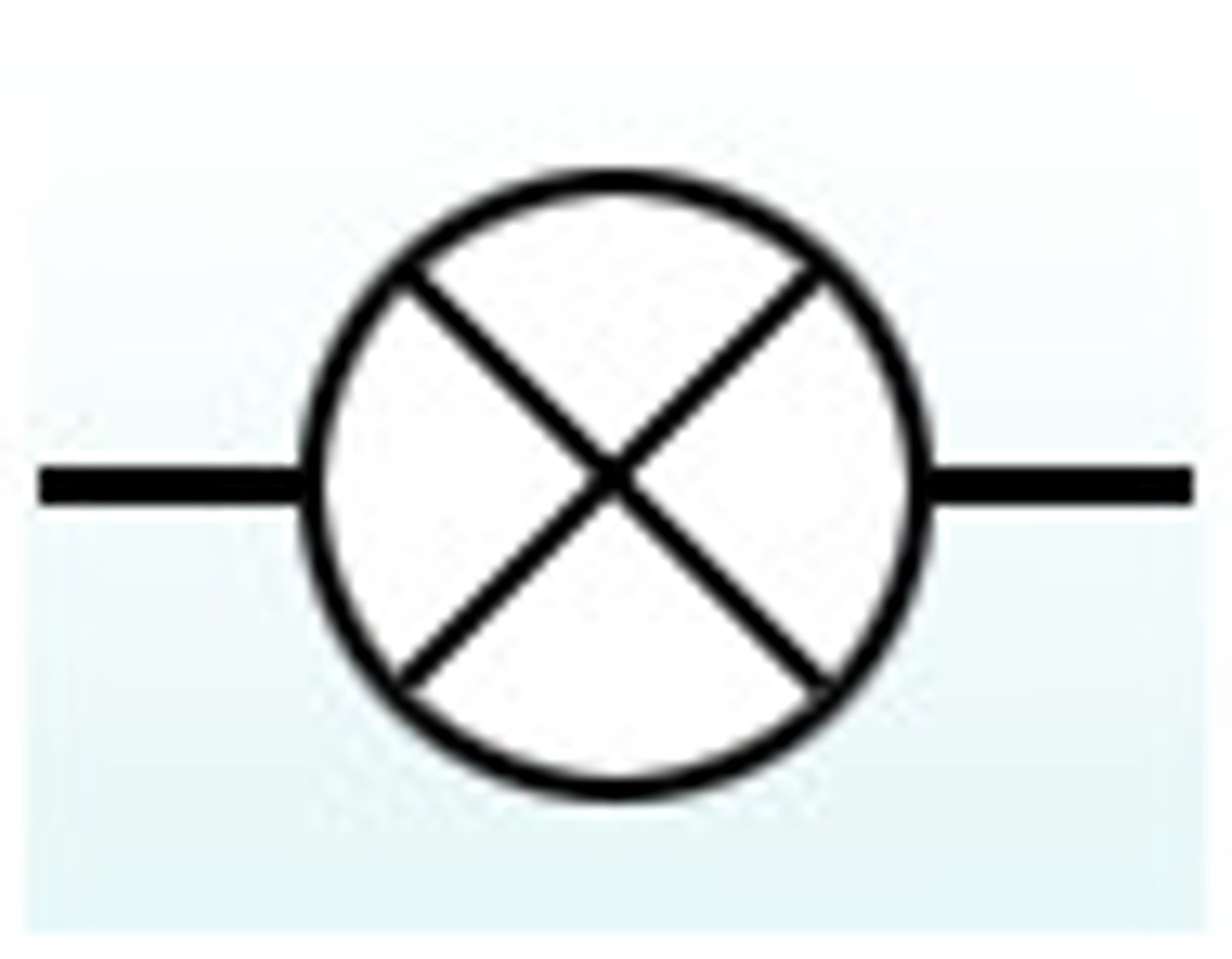
circuit voltmeter
circuit ammeter
circuit resistor
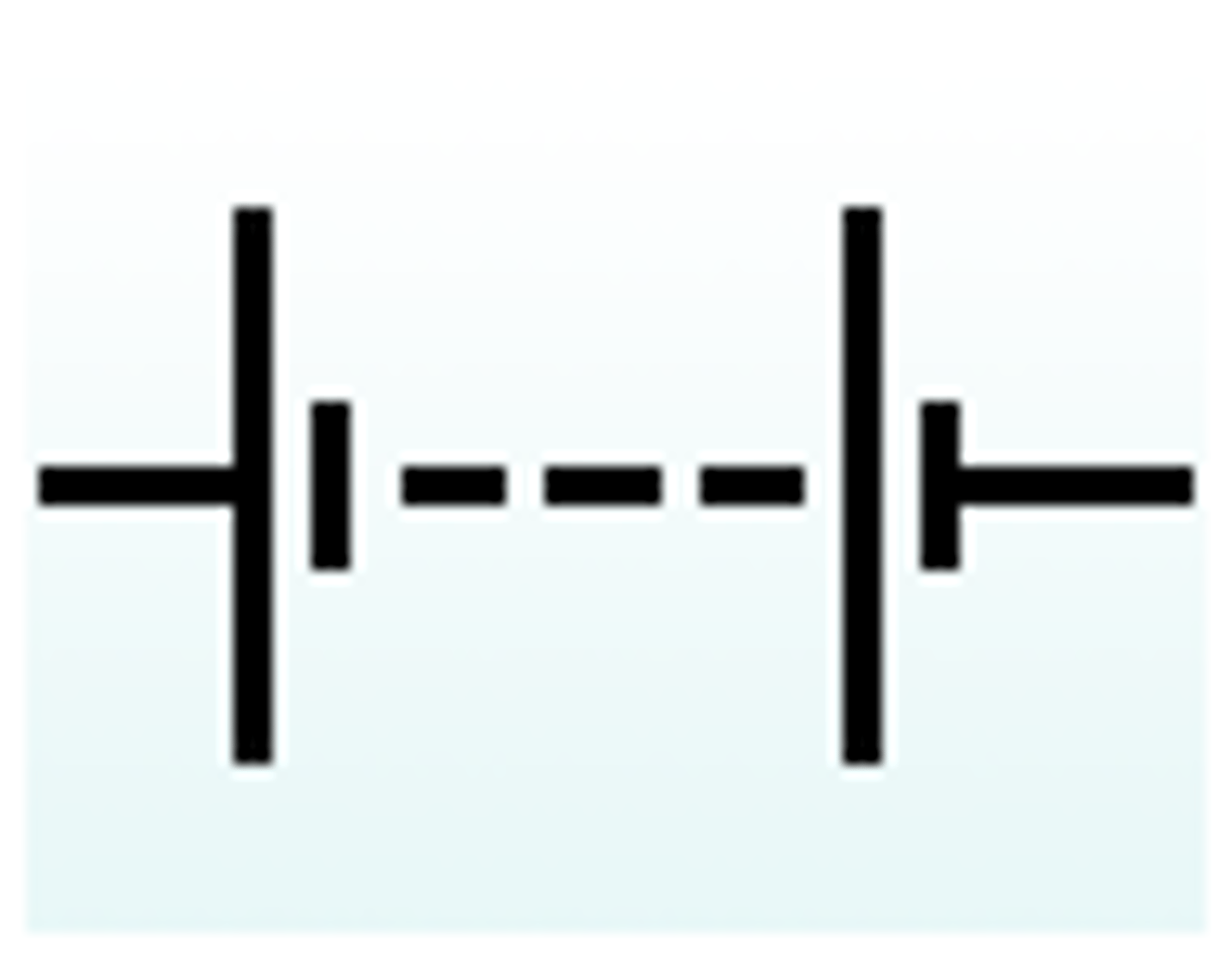
circuit battery
Biotic factors
living components of an ecosystem e.g grass log animals insects bacteria
abiotic factors
Nonliving components of an ecosystem eg water temperature light salinity soil
ecosystem
has living and non living stuff a system that uses and exchanges energy.
Food web
several interconnected food chains -show who eats who
producer
an organism that produces it's own energy
consumer
an organism that cannot produce it's own source of energy so it must eat other plants and/or animals to get energy
trophic levels
the position of an organism in a food web
characteristics of an ecosytem
biotic and abiotic factors, energy flow
names of trophic levels
producer, primary consumer, secondary consumer, tertiary consumer, quaternary consumer
How does the van der graaff generator work?
generates static electricity by rubbing two insulators together. One insulator transfers some of its electrons to the other, causing both to become electrically charged. The metal dome at the top of the generator collects these electrons. The electrons have nowhere to go on the dome, there is no path for them and that's why the Van de Graaff generates static electricity.
Why do styrofoam peanuts fly off the generator?
When the negative charges on the peanuts repel the negative charges on the generator, the peanuts push off the sphere.
What is static electricity?
Static electricity is the buildup of the electrical charge in an object when it is rubbed against another object
how is static electricity measured
The static charge is measured in terms of kV with a static meter
How are electrical charges created
An electrical charge is created when two materials come into contact or are rubbed together.
how can charge be conserved?
whenever charges are created there is a proton and electron which cancel each other out so the charge is always 0
static electricity v current electricity
Current is a continuous movement of charges (electrons) over time.
Static electricity is the transfer of static charges (electrons) from one surface to another due to an imbalance in charge between the surfaces.
hormone
chemical messenger in your body
adrenal gland
adrenaline and estrogen
Pancreas
glucagon (more blood sugar) and insulin (less blood sugar)
Helps you sleep
Melatonin (pinal gland)
What is homeostasis?
Maintaining a stable internal environment
What is the periphal nervous system?
nerves that runs throughout the body. It carries messages to and from the CNS
Why is the endocrine system slow acting?
Because the chemical messengers (hormones) act much slower but have longer lasting effects.
Why do hormones target certain cells
A target cell responds to a hormone because it bears receptors for the hormone (lock and key)
estrogen
Female sex hormone (ovaries)
testosterone
regulating sex drive, mood and bone and muscle strength. making blood cells.
link between endocrine and nervous system
hypothalamus
pituary gland
Multiple growth hormones
What is the Endocrine system?
A collection of glands that release hormones
Messengers in the NS
Pathway of transmission NS
nerve impulses
Neurons
Messengers in the ES
Pathway of transmission ES
Hormones
Bloodstream
How is temperature maintained at 37℃?
sweating-As the water in the sweat evaporates, the surface of the skin cools.
Blood vessel dialating -increases blood flow to the skin which helps the body to release heat through thermal radiation.
negative feedback loop
the effects of a reaction slow or stop that reaction. -sometimes reactions can be over the top negative feedback loop sorts that out
neuron
nerve cell
dendrites
collects the electrical messages.
sysnapse
gap between two neurons
what is stimuli
A change in the internal or external environment
What is an axon
Transmit impulses AWAY from cell body of neuron
What is the myelin sheath
A layer of tissue that covers axons.