Unit 5: Neoplasia General + Canine (Cram)
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
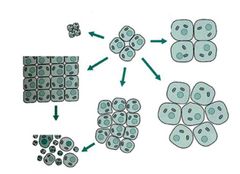
Abnormal developmet or growth of tissue, organs, or cells
Dysplasia
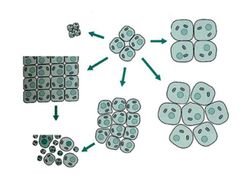
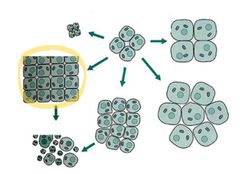
Increase in the number of cells
Hyperplasia
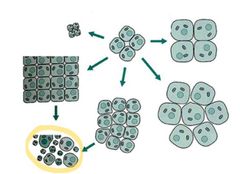
Loss of differentiation of cells, can be a feature of neoplasia
Anaplasia
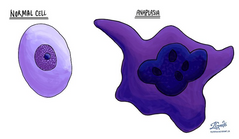
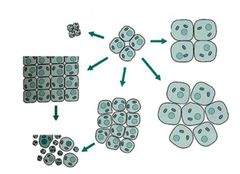
Conversion of a mature tissue type into a different type
Metaplasia
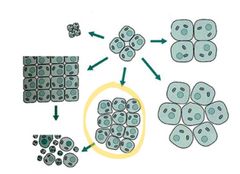
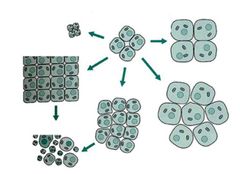
Shrinkage in the size of the cells in response to stimulus
Atrophy
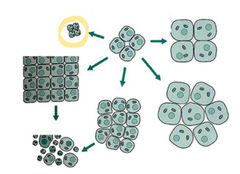
Increase in the size of cells in response to stimulus
Hypertrophy
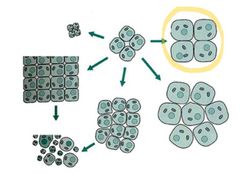
Uncontrolled proliferation of abnormal cells to form neoplasms (cancer or tumors)
Neoplasia
Group of cells that have lost normal growth control mechanisms. They can be malignant or benign
Neoplasm
Term used to mean the spread from one part of the body to another
Metastasize
Term exclusively used to refer to a malignant neoplasm
Cancer
Term that means swelling, but often misused to mean neoplasm
Tumor
The study of cancer
Oncology
Giving rise to cancer
Oncogenic
Any substance with the potential to cause neoplasia
Carcinogen
Cells of mesodermal origin that are capable of developing into connective tissues, blood, and lymphatic and blood vessels
Mesenchymal
How is the structure (resemblance to normal cells) of benign and malignant neoplasias described respectively?
Benign – Resemblance to normal cells
Malignant – Abnormal
How is the effect on the host of benign and malignant neoplasias described respectively?
Benign – Slight harm
Malignant – Significant harm
What is the prefix used to denote a tumor that originates from fibrinous tissue?
Fibro–
What is the prefix used to denote a tumor that originates from bone?
Osteo–
What is the prefix used to denote a tumor that originates from cartilage?
Chondro–
What is the prefix used to denote that a tumor has a glandular origin?
Adeno–
What is the suffix that denotes a benign tumor of any source?
–oma
What is the suffix that denotes a malignant tumor of supporting tissue origin?
–sarcoma
What is the suffix that denotes a malignant tumor of epithelial tissues?
–carcinoma
What is the suffix that denotes a tumor of embryonic origin?
–blastoma
Are blastomas usually malignant or benign?
Malignant
Can tumor be of mixed origin?
Yes
Growth pattern where benign tumors grow as well defined and discrete masses that may be freely movable and often have a capsule surrounding them
Direct expansion
Growth pattern where cells grow directly into the tissue surrounding the tumor
Invasion/ infiltration
Growth pattern where cells spread to another area not directly connected with the original site
Metastasis
What are the three steps of metastasis?
Remember: (This unit is) Really Too Long
Release from a primary site
Transport to new site
Lodging and survival at the secondary site
What is a common place for metastatic neoplasias to lodge?
Lungs
What are the three routes metastatic neoplasias can take in order to spread?
Bloodstream
Lymphatics
Transplantation (rubs off onto nearby tissue)
What are the three ways neoplasias are collected for microscopic examination?
Fine needle aspirate/punch biopsy
Exfoliate cytology
Impression smear
Tobacco smoke, papilloma virus, estrogens, testosterones and helicobacter are all examples of what?
Carcinogens
What are the two risk (predisposing) factors associated with neoplasia?
Age
Genetics
Which is the animal species most commonly affected by cancer?
Dogs
What is the most common tumor of dogs?
Canine mammory tumors
The incidence of mammary tumors is directly related to the number of _____ the bitch experiences
heat cycles
Mammary tumors may contain hormone receptors that stimulate growth in the presence of female hormones. When should you spay your dog to best avoid mammary tumors?
Before the first heat
What percent of mammary tumors are benign and malignant respectively?
Benign – 50%
Malignant – 50%
What are the three most common types of testicular cancer in dogs?
Sertoli cell tumors
Interstitial cell tumors (aka Leydig cell tumors)
Seminomas
Which condition predisposes a dog to Sertoli cell tumors?
Cryptorchidism (undescended testes)
What percent of Sertoli cell tumors will produce estrogen, resulting in feminization, hair loss, anemia, and attraction of male dogs?
30% produce estrogen
Which testicular tumor shows very few symptoms? Occassionally it is associated with increased production of androgens which can cause aggression or increased libido
Interstital cells tumor
Which testicular tumor arises from the cells of the testicle that normally produces sperm. It does not secrete hormones
Seminomas
What are the four well recognized anatomic forms of canine lymphoma?
Multicentric
Alimentary
Mediastinal
Extra nodal
What are some breeds of dogs that are commonly affected by canine lymphosarcomas?
Golden retrievers, Rottweilers, Pit Bulls, Poodles, German Shepherds, Boxers, etc.
Which canine lymphosarcoma is the most common?
Multicentric (80%)
Which canine lymphosarcoma is not common?
Alimentary (10%)
What is the canine neoplasia that is most common in Saint Bernards, Rottweilers, Great Danes, Golden Retrievers, Irish Setters, Doberman Pinschers, and Labrador Retrievers (giant and large breeds)?
Canine osteosarcoma (OSA)
What demographic and which breed is most affected by canine hemangiosarcoma (HSA)?
Older large breed dogs, German Shepherd most common
What is the most common site of canine hemangiosarcoma tumor development?
Spleen (but it can arise in any tissue with blood vessels: heart, subQ, and liver also common)