OED EXAM
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
Risk
The potential to gain or lose something of value, e.g. life, health, equipment,
Causal factor
something that causes/contributes to the risk
risk management strategy
a strategy to minimise the risk of an activity
4 risks for canoeing
Falling out of canoe
Hit by branch
Flipping the canoe
Colliding with another canoe
causal factor - people risk 1-4 canoeing & risk management
Falling out of canoe
Hit by branch
Flipping the canoe
Colliding with another canoe
Little canoe experience - having ample practice
not communicating between members in canoe - keeping communication in the canoe
little canoe experience - having ample practice
no communication between canoes - keeping communication between the canoes
causal factor - equipment risk 1-4 canoeing & risk management
Falling out of canoeHit by branch
Flipping the canoe
Colliding with another canoe
Too small of a canoe - having the correct canoe for the people
wrong size paddle - making sure they have the correct paddle for them
too heavy bags - packing bags correctly
wrong size paddle - making sure they have the correct paddle for them
causal factor - environment risk 1-4 canoeing & risk management
Falling out of canoeHit by branch
Flipping the canoe
Colliding with another canoe
Increased water level/flow - monitoring weather and making decisions
fallen trees due to storms - avoiding densely foliaged areas
increased water level/flow - monitoring weather and making decisions
increased water level/flow - monitoring weather and making decisions
What is PPE
Equipment that is used to minimise the risk in an activity
Canoeing PPE and why
PFD- keeps you afloat
Helmet-keeps head safe from knocks.
thermal/rashie - to keep warm
spray jacket- to keep wind off and dry
shoes - protects feet during launch and landing
hat - sun off face
3 phases of a canoe stroke
1.Catch- blade is first inserted into the water, power has not been applied
2.Propulsion- working part of the stroke
3.Recovery- blade exists the water and is moved to catch position of next stroke
How to hold the canoe paddle (proper terminology)
Grip: hand always over top of the ‘T’ grip
featuress of a forward stroke in each of the 3 phasses
•Paddlers paddle on opposite sides and do not change
1 •Reach forward with both arms straight
2 •Place entire paddle blade VERTICALLY in the water and pull back with straight arms, only bend the arms at end of stroke
3 •Stroke ends at paddlers hips. Return paddle to starting position, keep it close to the canoe
features of a reverse/backwards stroke in each of the 3 phases
reach back with arms straight
Place entire paddle blade VERTICALLY in the water and push forward with straight arms,
stroke ends infront of paddler, Return paddle to starting position, keep it close to the canoe
featuress of a sweep stroke in each of the 3 phasses
•Will turn the boat away from the paddle side
•This will counteract if both forward sweep, so use individually or one forward sweep whilst other reverse sweeps
•Paddle kept horizontal, using the drive side of the blade sweep the paddle around in a wide arc
•Blade kept shallow, top edge just breaks the water
How to perform an emergency stop canoeing
place paddle in water and push forward continuosly in sharp powerful movements until stopped
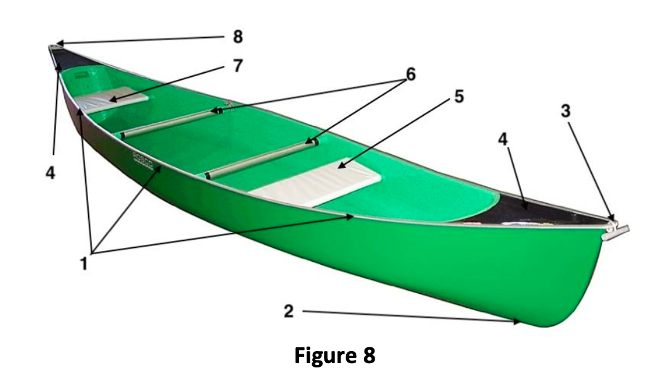
8 parts of canoe
gunwhales
keel
bow
deck
front seat
thwart
back seat
stern
1 whistle canoeing
attention
2 whistles canoeing
attention and come to me
3 whistles canoeing
emergency
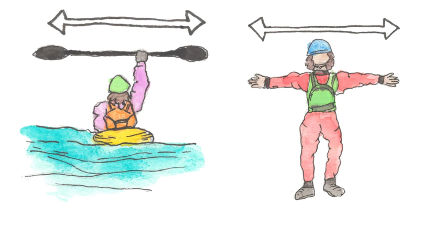
stop -danger

all clear
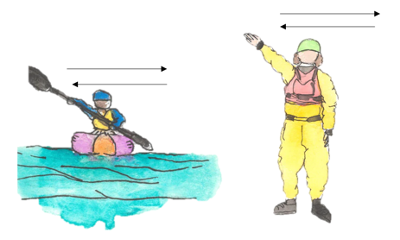
all clear in direction of pointing

okay
5 H safety check and explanation
Helmet - secure helmet properly, adjusted, hair properly secured
harness - positioned correctly, buckles secured
Hardware - rope is correctly through (smily face), karabiner is locked, rope not twisted
Hands - gloves either fitted or ready for use
Hooves- ensure suitable footwear
4 risks for abseiling
falling
hit in head by rocks
rope burn
equipment/person caught in rope
causal factor - equipment risk 1-4 abseiling & risk management
falling
hit in head by rocks
rope burn
equipment/person caught in rope
having broken equipment- making sure equipment is functioning and safe
wrong size helmet - having correct size helmet
not wearing gloves - make sure wearing glove
straps too long on harness - correct size harness or tidy
causal factor - people risk 1-4 abseiling & risk management
falling
hit in head by rocks
rope burn
equipment/person caught in rope
brake person not ready to stop fall - communicating between abseiler and braker
not adjusting hemet - making sure helmet fits and is adjusted
forgetting to put gloves on - checking eachother for gloves
not tying hair back - making sure hair is tied back
causal factor - environment risk 1-4 abseiling & risk management
falling
hit in head by rocks
rope burn
equipment/person caught in rope
Slippery surface due to rain - avoiding wet surfaces and checking weather
rainfall moving rocks - avodiing rainy days and checking weather
wet ropes causing slipping of equipment, and burning hands
wind blowing hair/tags around - securing all lose partss properly
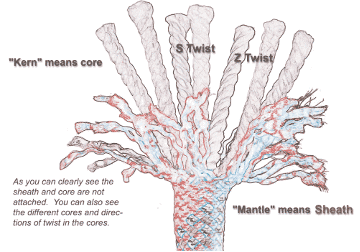
Describe the construction of an abseiling rope
The mantle is the outer braided sheath, the kern is the inner core, they are not connected
Explain what makes an abseiling rope so durable
the tight cover keeping the kern in good condition
what rope for climbing
dynamic
what rope for absiling
static
static rope characteristics
High strength
low stretch
less malleable
low shock absoprtion
dynamic rope characteristics
lower strength
higher stretch
easy to handle
high shock absorption
Your friend is abseiling for the first time. Detail how you would explain to this student the steps and good technique for safe abseiling.
perform the 5 H safety check, and once clipped onto rope, slowly wiggle feet back and lean back into the harness, with front hand through the karabiner and back hand behind you, sitting into the harness, and slowly take small steps.
1) Identify the PPE required for abseiling and explain why (list as many as you can).
Helmet- to prevent damage from falling rocks
shoes- to protect feet
gloves - to protect hands
harness - to keep on rope
1) Identify the different calls used when abseiling and explain what they mean.
rope below - a warming below to indicate a rope is being thrown over an edge
Below- indicates tha an object has been dislodged and is falling
Descending line _ - abseiler is rigged ready to abseil but before proceeding over edge
brake ready line _ - bottom brake is ready for abseiler to descend
brake off - abseiler ready to continue abseiling after slip/ fall
Describe the correct technique used when bottom breaking. Use any cue words that you have been taught.
hold rope above shoulders without gloves, watching for the abseiler to fall, if they do, then pull and hold the rope sharply down until they stop. If they say below than tuck into edge or back off the wall, when you are ready, say ready line 1, whem they want the brake off, they will say brake off, and oyu put the brake off.
5 qualitiess of a good knot
relatively easy to tie
easy to determine whether or not the knot is tied correctly
once tied, remains tied
it has minimal effect on rope strength
It is relatively easy to untie after loading
1) Identify the various ways to care and maintain rope (including storage).
Remove knots from rope
clean or wash rope if dirty
col, hand or stuff in rope bag,
store rope off ground in hook or on shelf
store in a cool dry area away from sunlight
store away from oils and chemicals

name and use
bowline - non slip loop

name and use
round turn two half hitches - fastens to bar or post

name and use
clove hitch- temporary around round knot
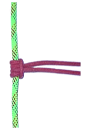
name and use
prussik knot - allow a rope to be climbed

name and use
figure 8 on the bight - creating a loop in the rope

name and use
alpine butterly - creating a loop int he middle of the rope

name and use
figure 8 follow through - a loop around an object

name and use
double fishermans - tying two ropes together
1) Describe how to flake and hank a rope.
to flake - pull the rope through your hand feeling for issues and wear, then hold in hand, grab with other hand and pull outstetched, and pass over head, then bring arms together and repeat. talke ropes off and tie wraps and finish
1) Outline the purpose of both flaking and hanking a rope.
flaking - to check for wear and issues
hanking - to have the rope in a neat, tidy way
1) Outline the features on a topographic map using the BOLTSS acronym
Border
Orientation
Legend
Titile
Scale
source
1) Outline what a contour line is and describe what it represents on a map
a contour is a line that shows the elevation, and represents increase/decreases in elevation
1) Explain how to use the two different scale systems on a map (representative and linear)
representative- expressed as a factor e.g.1:50 000
linear - a line showing the distance
Convert the scale 1:75,000 in to metres
750m
Convert the scale 1:25,000 in to metres
250m
Convert the scale 1:50,000 in to metres
500m
Outline the 6 point grid reference system used to pinpoint features on a map.
outlines the location on a map, each box is numbered.
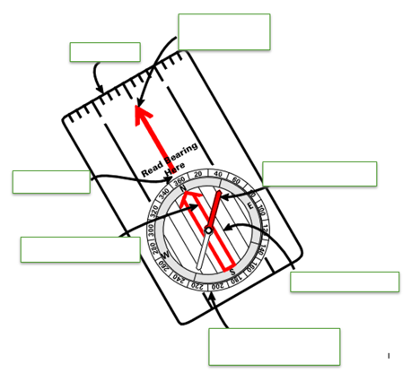
Label going clockwise
ruler
direction of travel arrow
magnetic needle
orienting lines
compass housing with degree dial
orienting arrow
index line
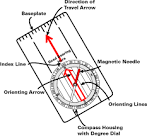
1) Outline an easy to follow, step by step guide for taking a grid bearing from a map
place the compass along the path of travel, with the direction of travel arrow pointing the way that you want to go, line the orienting lines with the grid lines on the map, and read the bearing
LNT principle 1 give a specific example for canoeing, abseiling and whilst on an expedition
Plan ahead and prepare
Canoeing: -packing bags watertight
Abseiling: - preparing equipment
Expedition food preparation and packing bags
LNT principle 2 give a specific example for canoeing, abseiling and whilst on an expedition
Travel and camp on durable services
Canoeing: not going through grasses
Abseiling: - picking solid and uninhabited surfaces to abseil
Expedition - walking separatly, pitching camp in desired area
LNT principle 3 give a specific example for canoeing, abseiling and whilst on an expedition
Dispose of waste properly
Canoeing: your rubbish you take out with you
Abseiling: rubbish and equipment is taken out
Expedition rubbissh and equipment is taken out and disposed of properly
LNT principle 4 give a specific example for canoeing, abseiling and whilst on an expedition
Leave what you find
Canoeing: not taking anything that you find with you
Abseiling: not taking anything that you find with you
Expedition not taking anything that you find with you
LNT principle 5 give a specific example for canoeing, abseiling and whilst on an expedition
minimise impact of fire
Canoeing: n/a
Abseiling: n/a
Expedition burying, making sure fire is completely out, in designated pit
LNT principle 6 give a specific example for canoeing, abseiling and whilst on an expedition
Respect wildlife
Canoeing: Staying quiet and not disturbing animals
Abseiling: minimising impact of equipment on wildlife.
Expedition being quiet and not feeding
LNT principle 7 give a specific example for canoeing, abseiling and whilst on an expedition
Be considerate of your hosts and other visitors
Canoeing: Letting other visitors go before you and staying out of their way
Abseiling: Letting them go first and do what they want,
Expedition:
Moving off the path whilst they are walking
Define
Weather
Is the day-to-day state of the atmosphere, and its short term variation in minutes to weeks
People generally think of weather as a combination of temp, humidity, precipitation, cloudiness, visibility, and wind
Weather can change within a few minutes or hours
1) Define
Climate
Is the weather of a place averaged over a period of time, often 30 years.
Climate information includes the statistical weather information that tells is about the normal weather, as well as the range of weather extremes for a location
Climate takes a very long time to change
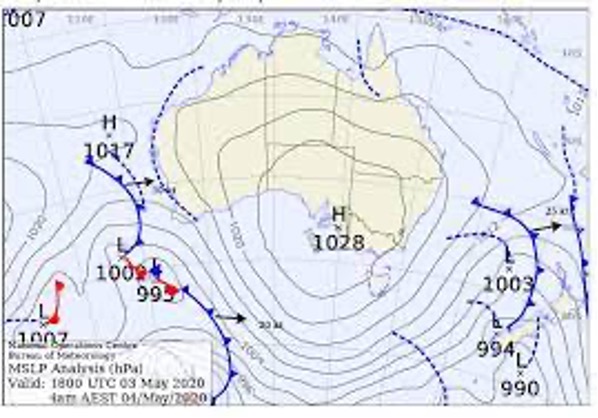
What type of map is this
synoptic chart
Define air pressure, including the unit or measurement.
It is the force exerted on a surface by the air above it as gravity pulls it to Earth. - hectopascals
1) Define isobar:
•Isobars join areas of equal pressure. Therefore, isobars can also indicate wind strength
1) Outline what isobars that are close together indicate about the wind
stronger winds
1) Outline what isobars that are further apart together indicate about the wind
lighter winds
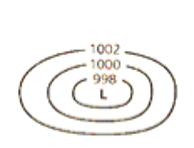
Describe the features/weather that is associated with the weather code
low pressure system
•Indicates an air mass of low pressure
•In an area of LOW air pressure the air rises and cools producing rain
•Low air pressure system = below 1013hPa (hectopascal)
•In the Southern Hemisphere winds travel in a clockwise direction and inwards

Describe the features/weather that is associated with the weather code
warm front
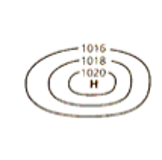
Describe the features/weather that is associated with the weather code
high pressure system
•Indicates an air mass of high pressure
•In an area of HIGH air pressure the air descends and warms up, becomes more stable and clear
•High air pressure system= above 1013hPa
Winds travel in an anticlockwise direction and outwards

Describe the features/weather that is associated with the weather code
cold front
Identify the most important person in an emergency:
yourself
2 minor canoeing injuries and treatment
pinched finger - ice
blisters on hands - apply cream if neccasary
2 major canoeing injuries and treatment
cracked head open on canoe - stop bleeding, clean area, rest, cover area , get help
unconscious in water - CPR and defib if neccesary
2 minor abseiling injuries and treatment
hair pulled out after stuck - pain relief if neccesary
rope burn - antiobiotic cream and cover
2 major abseiling injuries and treatment
rock landed to head - stop bleeding, clean area, rest , get help
broken arm - sling, ice, rest
2 minor cooking injuries and treatment
minor burn- cool water submerged
small knife cut - clean the cut, and bandaid
2 major cooking injuries and treatment
major oil burns - cool water, bandage
large knife cut - stop bleeding, clean area, apply bandage
How should the OED class be managed in an emergency
They should be kept calm, and supervised, communicating
3 types of leadership
Autocratic Democratic Laissez-faire (abdocratic)
Autocratic leadership description and example in OED context working well
Authoritarian approach, leader has complete power.
Decisions made without consultation
works well when immediate decision must be made, the quality of the decision is more important than its acceptance, an where the decision would not change with input.
e.g. kieran telling us our line when canoeing on the rapids- telling us exactly what to do without consulation
Democratic leadership description and example in OED context working well
-shared decision making with leader and members
Leadership by consultation
Leader offers help when asked, provides alternatives, allows team members to make choices
e.g. giving checkpoints by leader for the team to get to
Laissez-faire (abdocratic) leadership description and example in OED context working well
Leader in minimal role,
group makes decision
group learns from mistakes
works well without time restraints
e.g. at camp deciding what to do
what is the aim of an expedition planner
to identify the objectives - to properly prepare for what will happen and organise things
Outline the aspects of an expedition planner
Research
Expedition brief
Participant information
Goals
Schedule
Leadership
Route
Emergency considerations
LNT
Equipment
menu planning
What factors should you consider when selecting clothing for an expedition
The temperature , climate, season, weather, rainfall, wind, activities that you are doing, where you are
outline the menu planning principles
Nutrious
Lightweight
small
non-perishable
easy prepared
tasty
Outline the purpose of an expedition journal and when it should be completed by the participant.
to write anything that you need
completed during/before /after
SMART GOALS - with examples
S - Specific - What is it
M - Measurable - How do you measure it
A- Attainable - Is it attainable
R - relevant It is relevant to you
T -Time - when is it happening
e.g. I want to run a marathon (specific) (measurable), and i have already run a half marathon (attainable), and i want to improve my fitness (relevant ) by the end of the year.
purpose of a debrief
to communicate peoples thoughts and feelings towards what happened, what they learnt
a suitable time and setting for a debrief to occur
e.g. when everyone is together and not stressed to do things, such as when cooking or around fire
3 stages of a debrief
reaction/description, analysis/understanding, and application/summary,
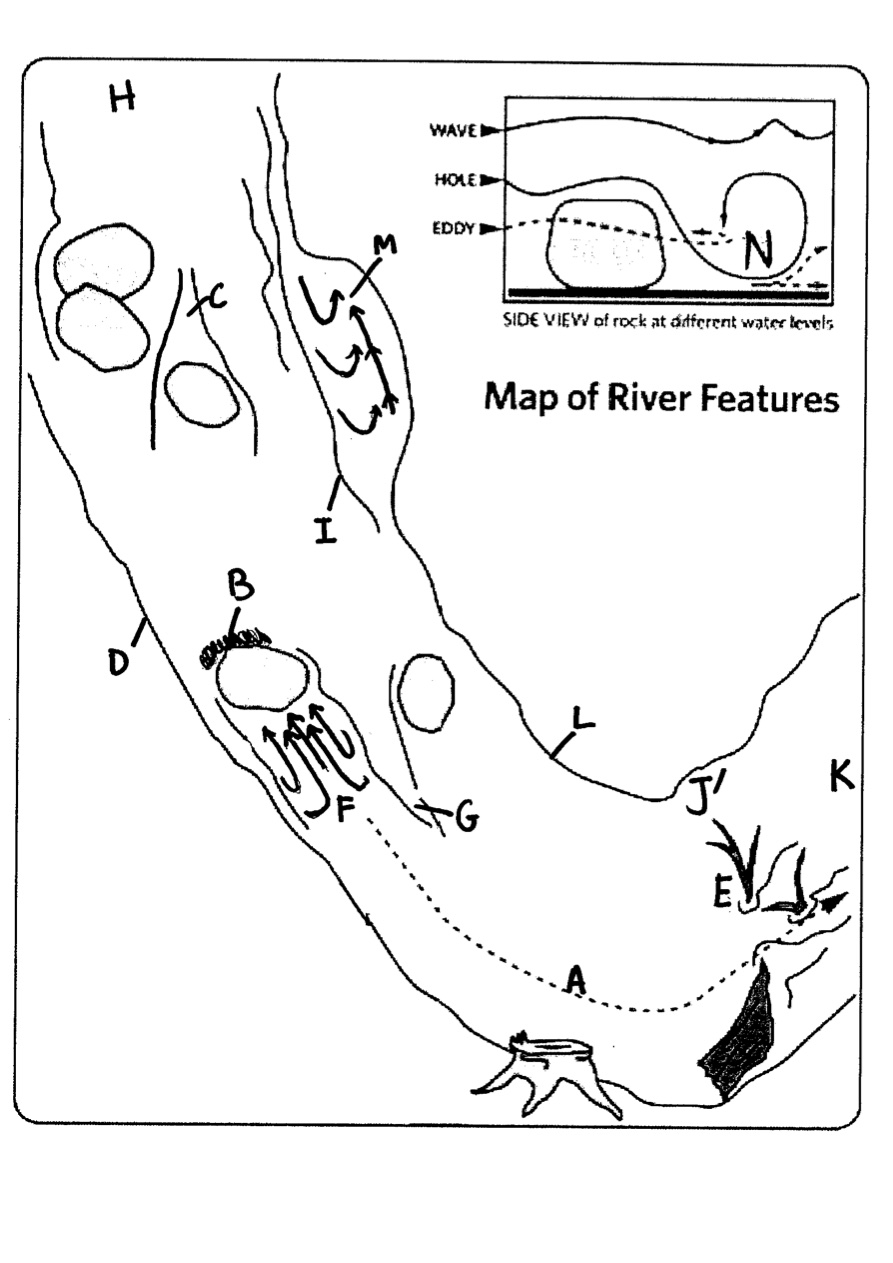
label
A | STRONGEST CURRENT |
B | PILLOW |
C | UPSTREAM V |
D | RIVER RIGHT |
E | STRAINER |
F | EDDY |
G | DOWNSTREAM V |
H | UPRIVER |
I | EDDY FENCE |
J | SHALLOW & SLOW |
K | DOWNRIVER |
L | RIVER LEFT |
M | SHORELINE EDDY |
N | HYDRAULIC |
10 steps bag packing
1. Lay out all your gear on the ground before you start.
2. Sort your gear into the four categories:
Big & Bulky, Hard & Heavy, Light & Handy, Small & Fiddly.
3. Loosen all straps and draw-cords on your pack.
4. If expecting ‘wet’ conditions, use a pack-liner like a large, heavy-duty garbage bag. Double-bag important items.
5. Put bulky gear into 2-3 smaller bags rather than one huge bag; e.g. clothes, food. It is easier to manipulate within your pack.
6. Start packing with Big & Bulky, finish with Small & Fiddly
7. Fill all air spaces with smaller squashable items, e.g. socks, sarong
8. Use your fist to jam gear in tight, don’t be scared to use some force. Be careful not to catch fingers in zips and stitching.
9. Pad or protect hard and lumpy items next to your back.
10. Try to keep all gear inside your pack. (It’s better balanced, easier to negotiate narrow paths and there is less risk of losing stuff).