Chapter 3: Motion
1/49
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Equation for speed with the units
speed (ms-1) = distance (m) / time (s)
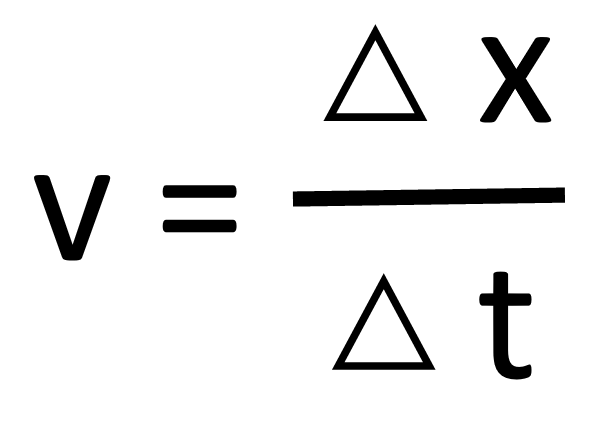
Definition of speed
Rate of change of distance
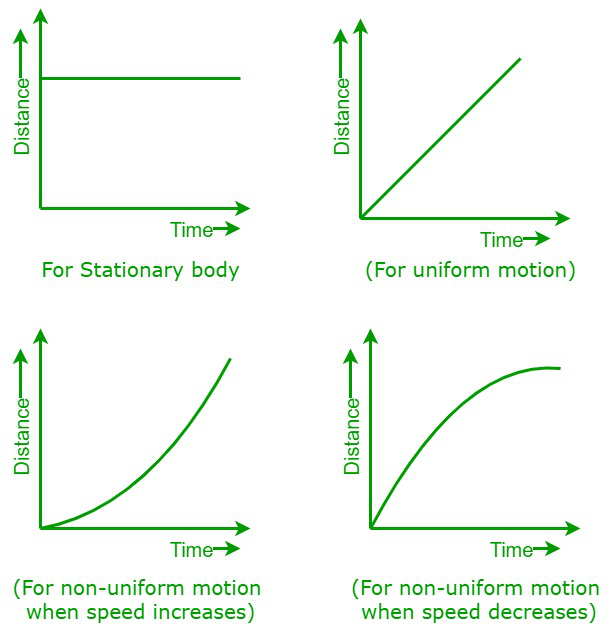
The x-axis and y-axis on a distance-time graph
x-axis: Time (s)
y-axis: Distance (m)
How are:
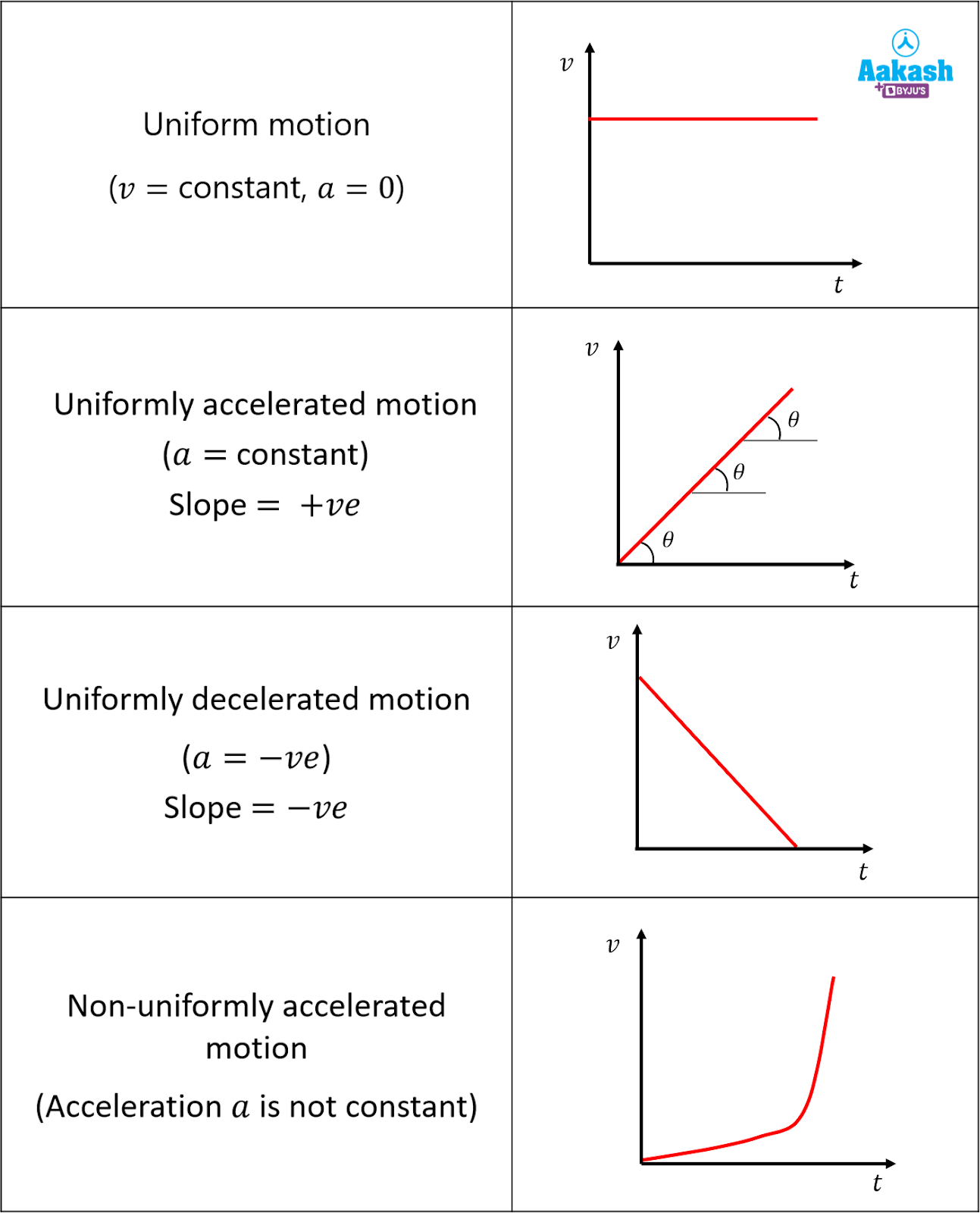
Stationary objects
Objects moving at a constant speed
Objects with varying speed
portrayed on a distance-time graph?
Stationary objects: horizontal line
Constant speed: sloping straight line
Varying speed: curved line
Instantaneous speed
The speed at any given point in time
Finding the instantaneous speed on a distance-time graph
Draw a tangent
Calculate the gradient of the tangent = speed
How is the acceleration found on a speed-time graph?
The gradient
How is the speed found on a distance-time graph?
The gradient
How is the distance found on a speed-time graph?
Area under the graph
How is the velocity found on a displacement-time graph?
The gradient
Equation for velocity with units
velocity (ms-2) = change in displacement (m) / time (s)
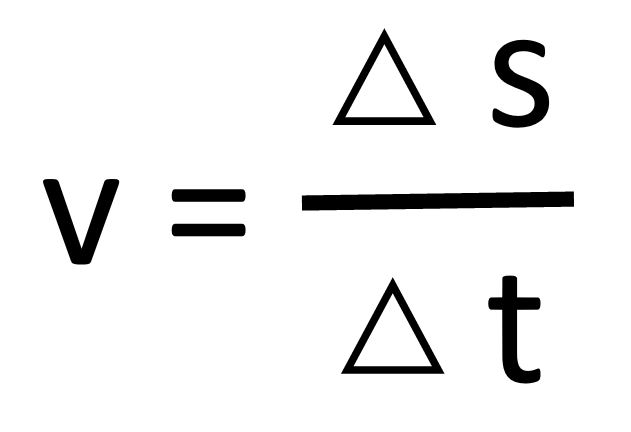
Definition of velocity
Rate of change of displacement
Equation for acceleration with units
acceleration (ms-2) = change in velocity (ms-1) / change in time (s)
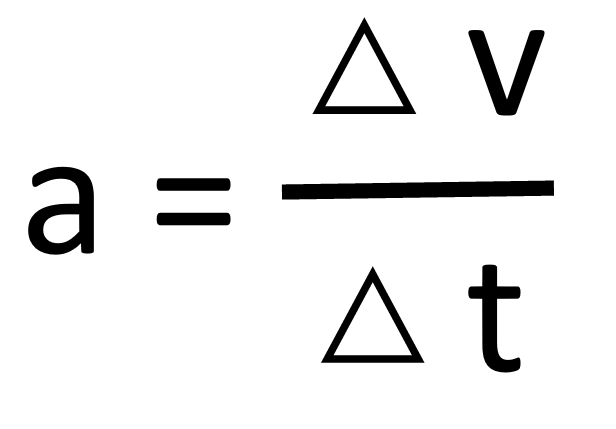
Define acceleration
Rate of change of velocity. Is a vector quantity.
How are:
Stationary objects
Objects moving at a constant velocity
Objects with varying velocity
Objects with increasing / decreasing velocity
portrayed on a velocity-time graph?
Stationary objects: horizontal line along the x-axis
Constant velocity: horizontal line not on the x-axis
Varying velocity: curved line
Increasing velocity: straight line +ve gradient
Decreasing velocity: straight line -ve gradient
What is the area under a velocity-time graph?
Distance / displacement
The distance of a non-linear velocity-time graph
Count the squares under the graph - only if the majority is under the curve
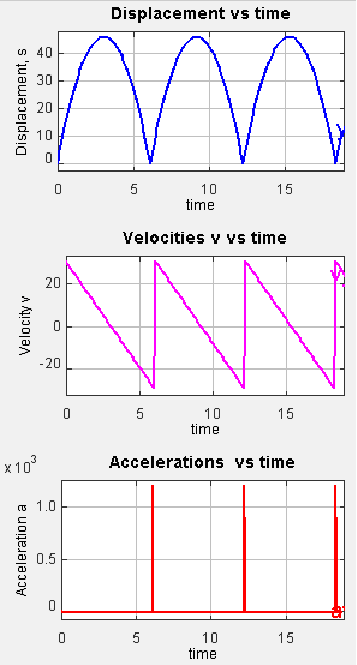
Draw a these graphs for a bouncing ball:
displacement-time graph
velocity-time graph
acceleration-time graph
What are SUVAT equations used for?
constant acceleration
What does
S U V A T
stand for?
S displacement
U initial velocity
V final velocity
A acceleration
T time taken for the change in velocity
If an object starts from rest, what is the initial velocity / time taken for the change in velocity?
u = 0
t = 0
If an object’s initial velocity isn’t mentioned, what is the initial velocity?
u = 0
What can be infered if an object is falling due to gravity in regards with SUVAT equations?
a = g = 9.81 ms-2
Components of the stopping distance
Thinking distance
Braking distance
Thinking distance
Distance travelled by the vehicle from when the driver sees a problem and applies the brake
Formula of the thinking distance
Thinking distance = initial speed x reaction time
Proportional to the initial speed (u)
Time taken for the driver to respond to the problem
Factors affecting the thinking distance
initial speed
tiredness
age
distraction
medication
eyesight
under the influence
Braking distance
The distance travelled by the vehicle after the driver has applied to the brake
Equation for braking distance
Time period when brakes are applied x average speed
Equation for work done by the brakes
Work done = braking force x braking distance x ½ mv2
Proportional to the square of the initial speed (u2)
All of the vehicles kinetic energy (½ mv2) must be dissipated by the brakes in order to stop
Factors affecting braking distance
mass of the vehicle
weather conditions
initial speed
car condition (e.g. tyres, brakes etc.)
The interaction with the thinking and braking distance and speed
Thinking distance increasing proportionally with speed:
if the speed doubles, the thinking distance doubles
the braking distance increases at an even faster rate
Acceleration due to gravity
Objects with mass (mass-energy) exerts a force upon objects that have a force, known as gravitational force. The earth is very big so it forces objects to accelerate towards the centre of the Earth.
Free-fall
When an object is falling with no other forces acting on (ONLY IT’S OWN WEIGHT)
What is free fall denoted by?
g - 9.81 ms-2
Variation in the value of g
Varies slightly around the Earth due to longitude, latitude and the local geology as it's not a perfect sphere
Projectile
An object thrown at an angle to the horizontal
Analysing projectile motion
the horizontal and vertical components of the object’s motion are analysed independantly, but the time is interchangeable
assume there is no air resistance
Time of flight of a projectile
How long the projectile is in the air
Maximum height of a projectile
The height at which the projectile is momentarily at rest
Range of a projectile
The horizontal distance travelled by the projectile
The horizontal acceleration of a projectile
Zero
The horizontal velocity of a projectile
Constant
The vertical acceleration of a projectile
9.81ms-2 downwards
When is a projectile at the maximum height?
When the vertical v = 0
When does a projectile reach the ground?
When the vertical s = 0
What is the time taken to reach the maximum height (for a projectile?)
Half the total time in the air
The components of the horizontal vector (Fx)
Fx = F (cos (θ) )
in the x direction
The components of the vertical vector (Fy)
Fy = F (sin (θ) )
in the y direction
The angle made by the vector to the horizontal
tan θ = Fy / Fx