chemistry - addition polymers
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
what is a polymer?
a substance of high relative molecular mass made by joining lots of small repeating units known as monomers
what do monomers of addition polymers contain?
carbon carbon double bonds
how does the property of monomers of addition polymers allow them to join to become polymers?
the double bonds make them unsaturated meaning they can join together to form long chains
what structure do addition polymers have?
simple molecular - so low bp
how do you name a polymer?
poly(monomer)
how do you write the molecular formula of a polymer?
(monomer)n
are there any by products of addition polymerisation?
no
what conditions are required for addition polymerisation?
high temperature and pressure
how do you draw the repeat unit of a polymer?
join carbons in a row with no double bond (exception is poly(propene) where the final CH3 is drawn below the CH2)
bracket the repeating bit with n after
draw a a bond from the end through the brackets to show continuation
which four polymers do you have to know?
poly(ethene)
poly(propene)
poly(chloroethene)
poly(tetrafluoroethene)
give the displayed formula of poly(ethene)
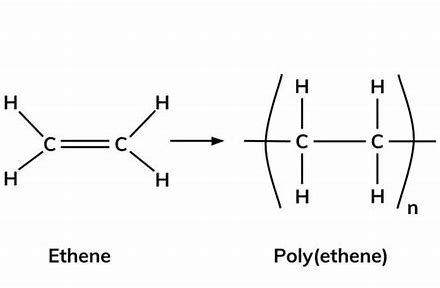
give the displayed formula of poly(propene)
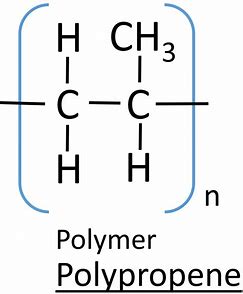
give the displayed formula of poly(chloroethene)
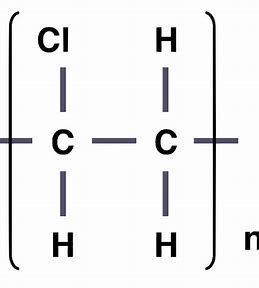
give the displayed formula of poly(tetrafluoroethene)
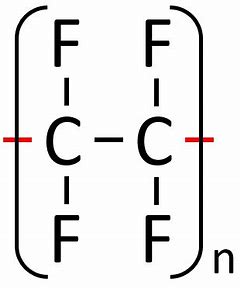
how reactive are most addition polymers?
inert/unreactive because of strong covalent bonds between atoms within the molecules which aren’t easily broken
what does biodegrade mean?
be broken down by bacteria or microorganisms
can addition polymers biodegrade?
no - take a very very long time - because they are inert
what happens if addition polymers are burnt?
toxic gases are released
what is the best way to dispose of addition polymers?
reuse and recycle