Halogenoalkanes
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
What is a primary halogenoalkane?
when a maximum of one alkyl group is bonded to carbon atom that is bonded to the halogen
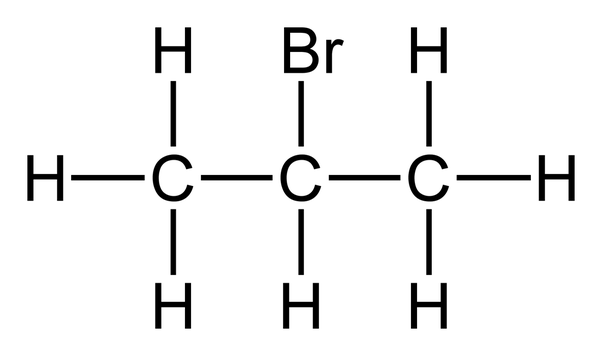
Example of primary halogenoalkanes
What is a secondary halogenoalkane?
has 2 alkyl groups bonded to carbon to carbon bonded to halogen
What is a tertiary halogenoalkane?
has a 3 alkyl groups bonded to carbon bonded to halogen
When naming complex halogenoalkanes, halogens are placed in an ____________ order
alphabetical
such as Bromo-Chloro-Iodo
Halogens are _____ electronegative than carbon
more
Halogens attract _________ electrons more than carbon causing carbon to have a partial ___________ charge (δ+). Carbon can then be attacked by _____________.
bonding
positive
nucleophiles
What are nucleophiles
species which can donate an electron pair they must have a lone pair.
What are substiution reactions?
they occur when a nucleophile replaces the halogen atom in a halogenoalkane
What is alkaline hydrolysis?
Reaction between a halogenoalkane with aqueous base such as NaOH(aq)
Many organic compounds are __________, and when heated would escape to atmosphere before reaction is complete
volatile
Volatile products would also be _____
lost.
Why is a reflux used in a nucleophilic substitution reaction?
used when heating a reaction mixture. By cooling vapours from mixture, chemicals are contained within the reaction flask as they condense and run back.

Diagram of reflux
What equation can we use to represent this reaction?
Rx + OH⁻(aq) —> ROH + X⁻(aq)
Alcohol and Halide ion is formed
How can the halide ion that was produced in the reaction be identified?
Halide ion can be identified using nitric acid and silver nitrate solution.
What equation can we use to represent the testing for Halide ion?
Ag⁺(aq) + X⁻(aq) —> AgX(s)
where X is the halogen
What colour precipitate would AgCl form?
White
What colour precipitate would AgBr form?
Cream
What colour precipitate would AgI form>
Pale Yellow
What is AgCl solubility in dilute ammonia?
Soluble
What is AgBr solubility in dilute ammonia?
Insoluble
What is AgI’s solubility in dilute ammonia?
Insoluble
What is AgCl’s solubility in concentrated ammonia
Soluble
What is AgBr’s solubility in concentrated ammonia
Soluble
What is AgI’s solubility in concentrated ammonia
Insoluble
The ____ pair of electrons on nucleophile attacks the ______ positive charge (∆+) on the carbon. A bond forms between the oxygen and carbon and the carbon halogen bond.
lone
partial
The relative ease of _________ of the halogenoalkanes can be explained by the_____ _______ of the carbon–halogen bond.
hydrolysis
bond strength
What is the rate of hydrolysis?
Iodoalkanes > Bromoalkanes > Chloroalkanes
The ____ bond is the least polar therefore the __________ bond and most easily broken and Iodoalkanes are most reactive
C-I
weakest
What are elimination reactions?
When a halogenoalkane is mixed with hydroxide ions such as Ethanolic NaOH and heated to high temperature under alcoholic conditions.