The Cardiovascular System
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
97 Terms
Varicose veins
superficial veins
distended
damaged valves can’t maintain normal venous pressure
can progress to chronic venous insufficiency where there’s insufficient venous return to tissue
Thrombus
blood clot attached to vessel wall
Thromboembolus
blood clot which becomes detached
DVT
clot which has formed in large veins
Why won’t DVT cause stroke?
clot goes into right side of heart first
this then goes to lungs
3 causes of DVT
venous stasis
venous endothelial change
hypercoagulable states
Venous stasis
pooling or stagnation of blood in veins
due to problems with venous circulation and valve function
Venous endothelial damage
impaired function of endothelium
leads to reduced vasodilation and increased vasoconstriction
Hypercoagulable states
blood has increased tendency to form clots
Signs and symptoms of DVT
pain in leg
hot
red
swollen
breathlessness = PE
Primary hypertension
mix of environmental and genetic factors
no underlying cause
Secondary hypertension
associated with primary underlying disease
kidney disease
endocrine disorders
acute stress
drugs
pregnancy
Risk factors for hypertension
age
family history
ethnicity
unhealthy lifestyle choices (diet, inactivity, smoking, excessive alcohol)
medical conditions (kidney disease, diabetes, thyroid problems)
Cardiac output
vol. of blood pumped around heart
End diastolic vol. (EDV)
vol. of blood in ventricles before heart contracts
End systolic vol. (ESV)
vol. of blood remaining in ventricle at end of systole
Stroke vol. definition
vol. of blood pumped around heart
Stroke vol. equation
SV = EDV - ESV
What is stroke vol. affected by?
venous return (vol. of blood going in)
filling time
autonomic innervation (nervous system’s part of cardiac cycle)
hormones
vasodilation or vasoconstriction
Ejection fraction
% of blood pumped out of heart (as there’s blood left in heart)
Frank-Starling mechanism
(chronologically)
more blood in heart
more increase in tension
stretches heart
higher the force of pumping blood out
vol. of blood ejected by ventricle depends on vol. of blood present in ventricles
Aneurysm
localised dilation or outpouching of vessel
most commonly occurs in thoracic or abdo aorta
5 types of aneurysm
fusiform
pseudoaneurysm
saccular
dissecting
ruptured
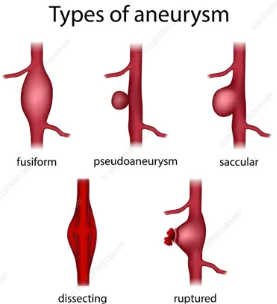
Rupture (in relation to aneurysm)
when it bursts
Dissection (in relation to aneurysm)
fast or slow
when weakened wall of aorta tears
causes blood to leak between layers that make up walls of arteries
Ischaemia
reduced amount of blood flow to part of body
dislodging creates a thromboembolus
Embolism
bolus of matter circulating in bloodstream
5 types of embolism
thromboembolism
air embolism
amniotic fluid embolism
bacterial embolism
fat embolism
Thromboembolism
vascular obstruction from a dislodged thrombus
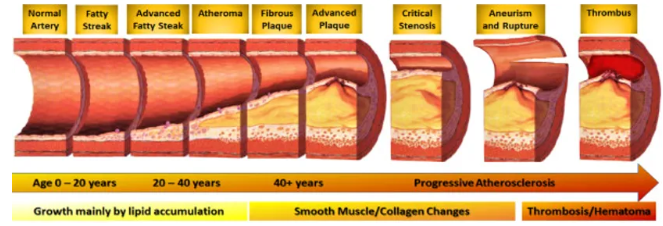
Atherosclerosis
thickening and hardening of vessel caused by accumulation of lipid laden microphages within arterial wall
forms lesion called plaque
results in ischaemic syndromes
causes inadequate tissue perfusion
How thrombus forms due to atherosclerosis
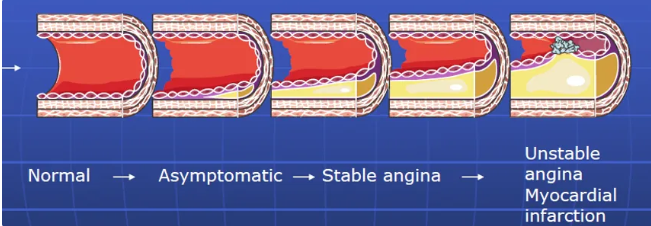
Coronary artery disease (CAD)
when coronary arteries blocked, often due to atherosclerosis
CAD, myocardial ischaemia, ACS and MI are all continuum of same disease
Risk factors for CAD
age
sex
family history
htn
diabetes
obesity
smoking
preeclampsia
menopause
Myocardial ischaemia
when supply of blood from coronary arteries cannot meet demand of myocardium for oxygen and nutrients
Angina pectoris
chest pain caused by myocardial ischaemia
Stable angina
episodes of chest pains in response to predictable stressors
eased by rest and nitrate
blood vessels have become hardened and narrowed and can’t adequately respond to increased demand
Unstable angina
random episodes of chest pain
fissuring of erosion of plaque leads to transient episodes of occlusion and vasoconstriction
reperfusion occurs before significant myocardial necrosis occurs
not full blockage
resolves itself
reversible myocardial ischaemia
Acute coronary syndrome (ACS)
sudden coronary obstruction caused by rupture of plaque
Decision tree on chest pain at rest
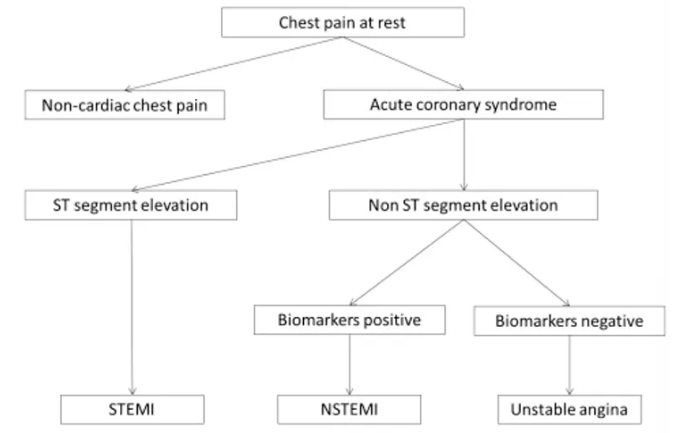
ECG changes in unstable angina
ST depression
t wave inversion
Myocardial infarction (MI)
when coronary blood flow interrupted for an extended period
causes myocyte death
mostly caused by atherosclerotic CAD
Pericarditis
fluid can collect in space between pericardial sac and heart
causes tamponade
causes ECG changes - ST elevation
Cardiomyopathy
disorders of heart muscle
can be acquired or genetic or idiopathic (disease of unknown cause)
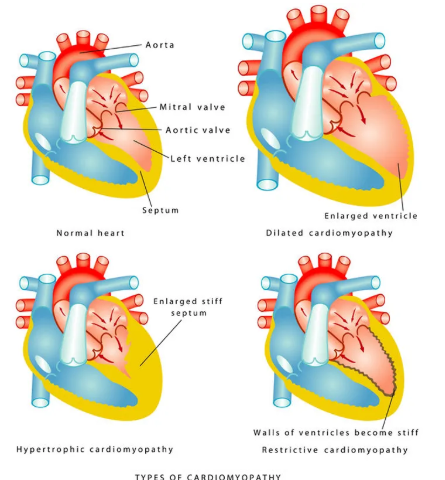
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
muscle wall of heart becomes thickened
Symptoms of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
sob
chest pain
palpitations
light-headedness
fainting
arrhythmias
heart block
endocarditis
sudden cardiac death
Dilated cardiomyopathy
muscle becomes stretched and thin
Causes of dilated cardiomyopathy
mutation of one or more genes - 50% chance of inheriting
viral infections
uncontrolled bp
problems with heart valves
Symptoms of dilated cardiomyopathy
sob
swelling of ankles or abdo
excessive tiredness
palpitations
arrhythmias
blood clots
chest pain
Endocarditis
inflammation of endocardium
Causes of endocarditis
bacteria in bloodstream
thrombi
Valvular disorders
heart valves made of endothelial tissue
causes stenosis or regurgitation or both
valves of left side of heart more commonly affected
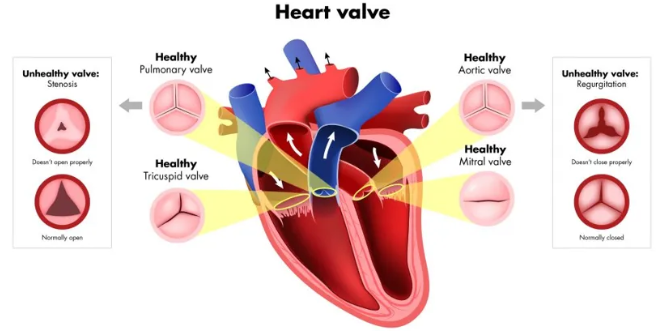
Stenosis
valve orifice is narrow or constricted
impedes forward blood flow
increases ventricular workload
Regurgitation
valve cusps do not shut completely
prevents forward flow stopping
causes backflow of blood
Heart failure
heart unable to generate adequate cardiac output in order to meet metabolic needs of body
functional or structural impairment causing inadequate ventricular filling or ejection of blood
cardiac reserve lost and minimal activity can use up all cardiac reserves
Cardiac reserve
capacity of heart to increase output during periods of increased activity
Causes of heart failure
CAD
htn
idiopathic cardiomyopathy
valvular heart disease
arrhythmia
Vol. overload or heart failure decompensation
anaemia
af or other arrhythmias
fluid overload
fluid retention
pulmonary causes
Patho of heart failure
increased preload (vol. overload)
increased sv per min
aortic valve incompetence
mitral valve incompetence
increased afterload (pressure overload)
outflow resistance increased
aortic stenosis
systemic htn
myocardial dysfunction
failure of contractile tissue
following MI
cardiomyopathy
Systolic dysfunction in heart failure
impaired contractility
thin/weak heart muscle
low ejection fraction
causes:
ischaemic heart disease
chronic htn
dilated cardiomyopathy
myocarditis
Diastolic dysfunction
impaired filling/relaxation
stiff/thick heart muscle
normal ejection fraction
causes:
htn with lv hypertrophy
restrictive and hypertrophic cardiomyopathies
fibrosis
constrictive pericarditis
valvular disease
Causes of left sided heart failure
CAD
valvular disease
htn
Causes of right sided heart failure
lung disease
pulmonary hypertension
MI
How does right sided heart failure affect digestive system
venous congestion
reduced blood flow
GI tract and liver congestion
causes anorexia, weight loss, impaired function
How does left sided heart failure affect respiratory system?
decreased cardiac output
decreased tissue perfusion
pulmonary congestion
impaired gas exchange
leads to cyanosis and hypoxia
pulmonary oedema
cough with frothy sputum
orthopnea
paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea
Compensatory mechanisms of heart failure
baroreceptor response
RAAS activation, decreased GFR
increased ventricular wall tension
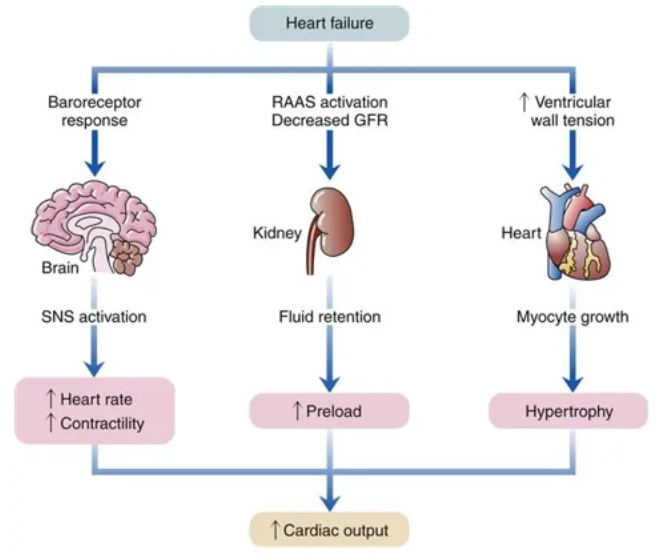
Sympathetic nervous system as compensatory mechanism of heart failure
baroreceptor response
stimulation of SNS leads to increased sympathetic tone
increase in adrenaline and noradrenaline levels
increased hr and contractility
increased cardiac outpu
Renin-aldosterone-angiotensin as compensatory mechanism of heart failure
RAAS stimulated to increase water and sodium retention via aldosterone release in response to low GFR and renal blood flow
fluid retention
increased preload
increased cardiac output
Increased ventricular tension as compensatory mechanism of heart failure
increased preload
increased stretching of myocardial fibres
increase in contractility
frank-starling mechanism
RAAS system
Manifestations of heart failure
fluid retention and oedema
resp problems
fatigue
cognitive impairment
cachexia/malnutrition
cyanosis
arrhythmias
Acute pulmonary oedema
fluid moves in alveoli
increased ventricular filling pressure
hence pulmonary venous pressure increased
fluid accumulation within legs
work of breathing increased by
reduced lung compliance and vital capacity
bronchoconstriction secondary to PO
increased pulmonary venous htn
alveolar membrane thickened/oedematous
gas exchanged impaired - arterial hypoxaemia
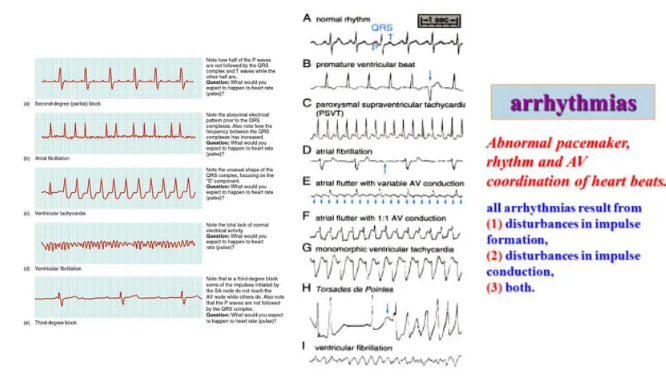
Arrhythmias
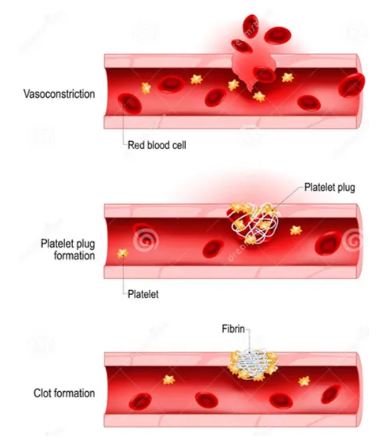
Haemostasis
process of stopping bleeding from blood vessel via clot
3 stages of haemostasis
vascular constriction
formation of platelet plug
blood coagulation
Clotting cascade
convert prothrombin to thrombin
thrombin converts fibrinogen to fibrin
Fibrin
insoluble substance that meshes together to form platelets and other blood components to form blood clot
Shock
acute failure of circulatory system leading to inadequate blood supply to major organs and peripheral tissues resulting in cellular hypoxia
Shock patho
hypoperfusion of organs
lack of oxygen leads to anaerobic metabolism pathway being utilised
leads to build up of lactic acid in cells
disruption of ATP pump leads to sodium ion build up of inside cells and potassium ion build up outside of cells
sodium in cell leads to cellular oedema and increased membrane permeability
lack of oxygen/nutrients and build up of waste products in cells causes cellular injury
causes inflammatory mediators to be released
cause structural changes in microvascular circulation which further compromises perfusion
vicious cycle where further compromise causes further cellular injury and can end in irreversible organ damage
Compensatory mechanisms for shock
sympathetic NS
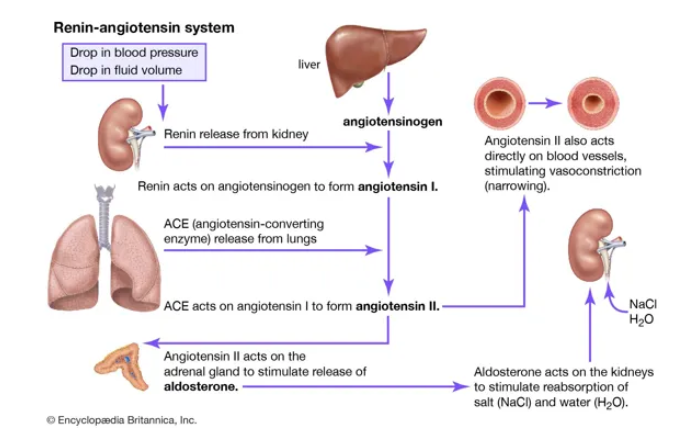
RAAS system activated
angiotensin
Sympathetic NS compensatory mechanism for shock
activation of alpha and beta receptors by adrenaline and noradrenaline leads to vasoconstriction, increase in hr in myocardial contractility, relaxation of bronchioles
RAAS system as a compensatory mechanism for shock
leads to increase in vasoconstriction
increase in sodium and water retention so increase in blood vol.
Angiotensin
hormone that regulates blood pressure and fluid balance by constricting blood vessels and stimulating sodium and water retention
4 types of shock
distributive/neurogenic
hypovolaemic
cardiogenic
obstructive
Hypovolaemic shock
due to large loss of fluid
Compensatory mechanisms of hypovolaemic shock
absorption of fluid from interstitial spaces in vascular compartment
sympathetic NS
activation of alpha and beta receptors with adrenaline and noradrenaline
stimulates increase in hr and vasoconstriction
blood transferred from liver to main circulation
RAAS system activates to increase Na reabsorption, increase thirst and water retention via ADH
Signs and symptoms of hypovolaemic shock
slight dip in bp which will fix itself quickly
increased rr
increased
hr
decreased bp
hypothermia
clammy
everything gets worse
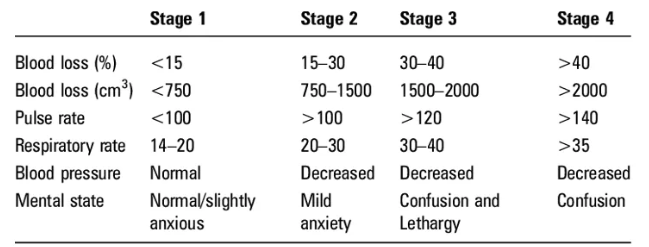
Cardiogenic shock
failure of heart to pump adequately
decrease in SV leads to decrease in CO
decreased CO, hypoperfusion, tissue hypoxia
adequate IV vol.
decreased myocardial contractility, increased afterload and high preload
Signs and symptoms of cardiogenic shock
hx of cardiac issue
heart failure
tamponade
cyanosis
altered mental state
low bp
narrow pulse pressure
decreased urine output
pulmonary oedema
ECG abnormality
abnormal heart sounds - 3rd heart sound
Neurogenic/distributive shock
vasodilation (problem with brain) but same vol. of blood
caused by decreased sympathetic control of blood vessels
due to damage to vasomotor centre in brain stem or sympathetic outflow to vessels
usually involves spinal injury
Signs and symptoms of neurogenic/distributive shock
usually involves spinal injury
bradycardia
skin warm and dry below injury
cold and clammy above injury
Obstructive shock
caused by a thrombus
Signs and symptoms of obstructive shock
cold and clammy above occlusion
warm and dry below occlusion
Complications of shock
acute respiratory distress syndrome
lethal pulmonary injury
rapid onset of dyspnoea, hypoxaemia which cannot be corrected - changes to permeability of alveolar membrane/capillaries
acute kidney injury
low blood vol. causes impaired renal perfusion
GI complications
GI tract vulnerable due to changes in blood flow to mucosa
disseminated IV coagulation (DIC)
widespread coagulation with clots in small and medium vessels
multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS)
affects multiple organ systems
life threatening
Stages of the cardiac cycle
ventricular and atrial diastole: filling
atrial systole: ventricular filling
ventricular systole: ventricular emptying
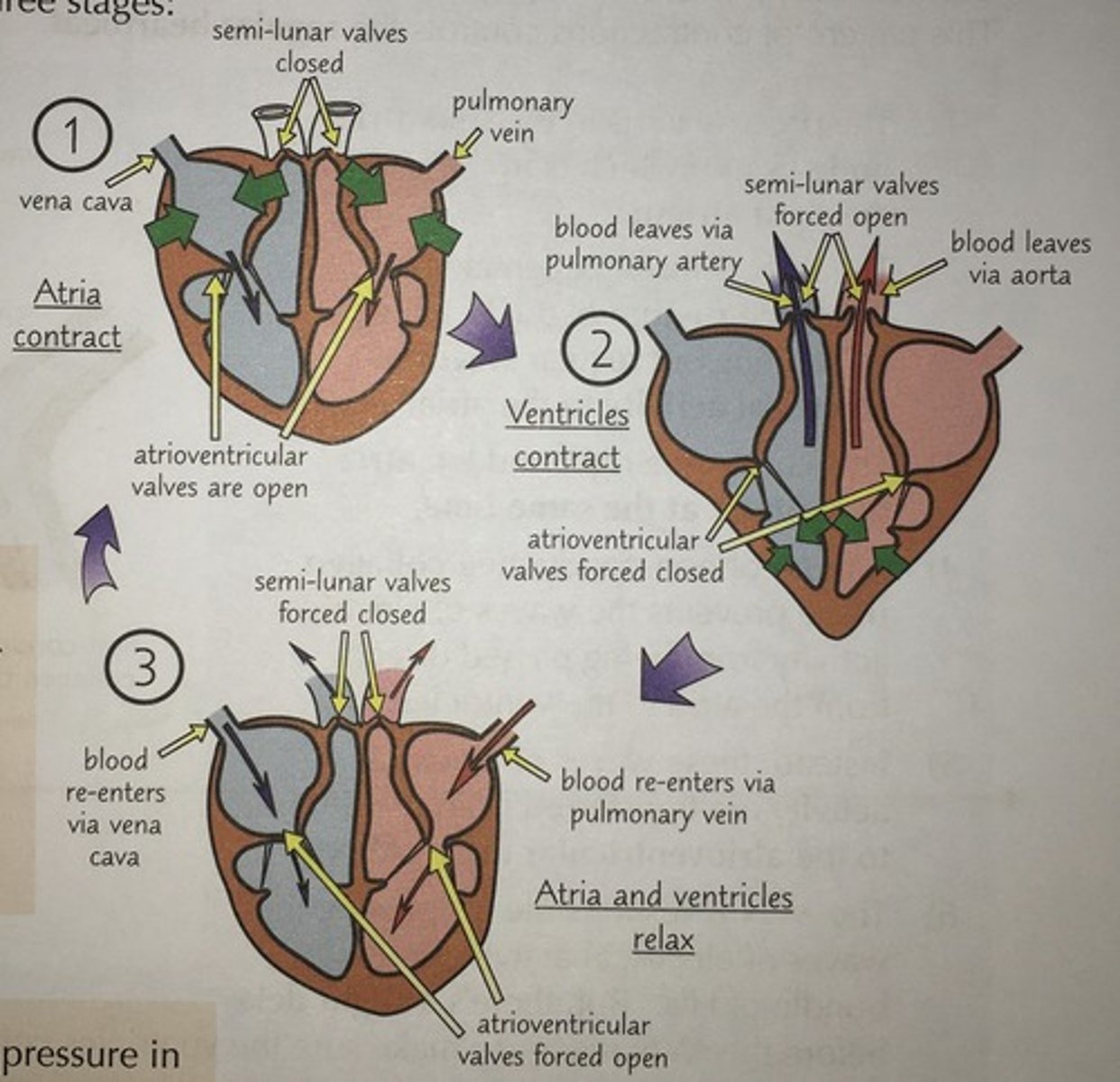
Diastole
chambers relax
both atria and ventricles fill with blood
Atrial systole
atria contract
remaining blood pushed into ventricles
ventricles larger so need longer to fill
Ventricular systole
ventricles contract
blood pushed out through aorta and pulmonary artery