Parts of the brain
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
(Mid Brain) Tectum
Roof of the midbrain.
(Mid Brain) Superior colliculus and inferior colliculus
Processes sensory information.
(Mid Brain) Tegmentum
Contains nuclei for cranial nerves and part of the reticular formation.
(Mid Brain) Substantia nigra
Gives rise to the dopamine-containing pathway facilitating readiness for movement.
What is the brain stem made up of?
Hindbrain, midbrain, and other central brain structures make up the brain stem.
(Hind Brain) Medulla oblongata
Influences the brain centers that regulate sleep and waking and also helps control respiration and circulation.
(Hind Brain) Pons
Directs communication between the cerebellum and the forebrain and helps control circulation and breathing.
(Hind Brain) Cerebellum
Integrates what we see, hear, and feel; it coordinates movement and balance.
laminae
Layers of cell bodies that are parallel to the surface of the cerebral cortex and separated from each other by layers of fibers.
Frontal lobe
Abstract reasoning, decision making, executive function, motor movement (precentral gyrus).
Parietal lobe
Spatial and numerical information, actions, sensory info (postcentral gyrus).
Occipital lobe
Vision perception.
Temporal lobe
Auditory information, memory and learning, language.
Cerebral cortex
Outside of the brain made up of neurons and glia (Gray Matter).
Cortical Homunculus
How our bodies are represented in the brain (Wilder Penfield weird looking model).
Limbic System
Complex set of structures located deep within the brain, primarily involved in emotion, memory, and behavior regulation.
(Limbic System) Cingulate gyrus
Cortex on lateral walls of groove separating hemispheres (above corpus callosum). Receives and relays information across the brain also involved in emotion regulation, pain perception, and decision-making.
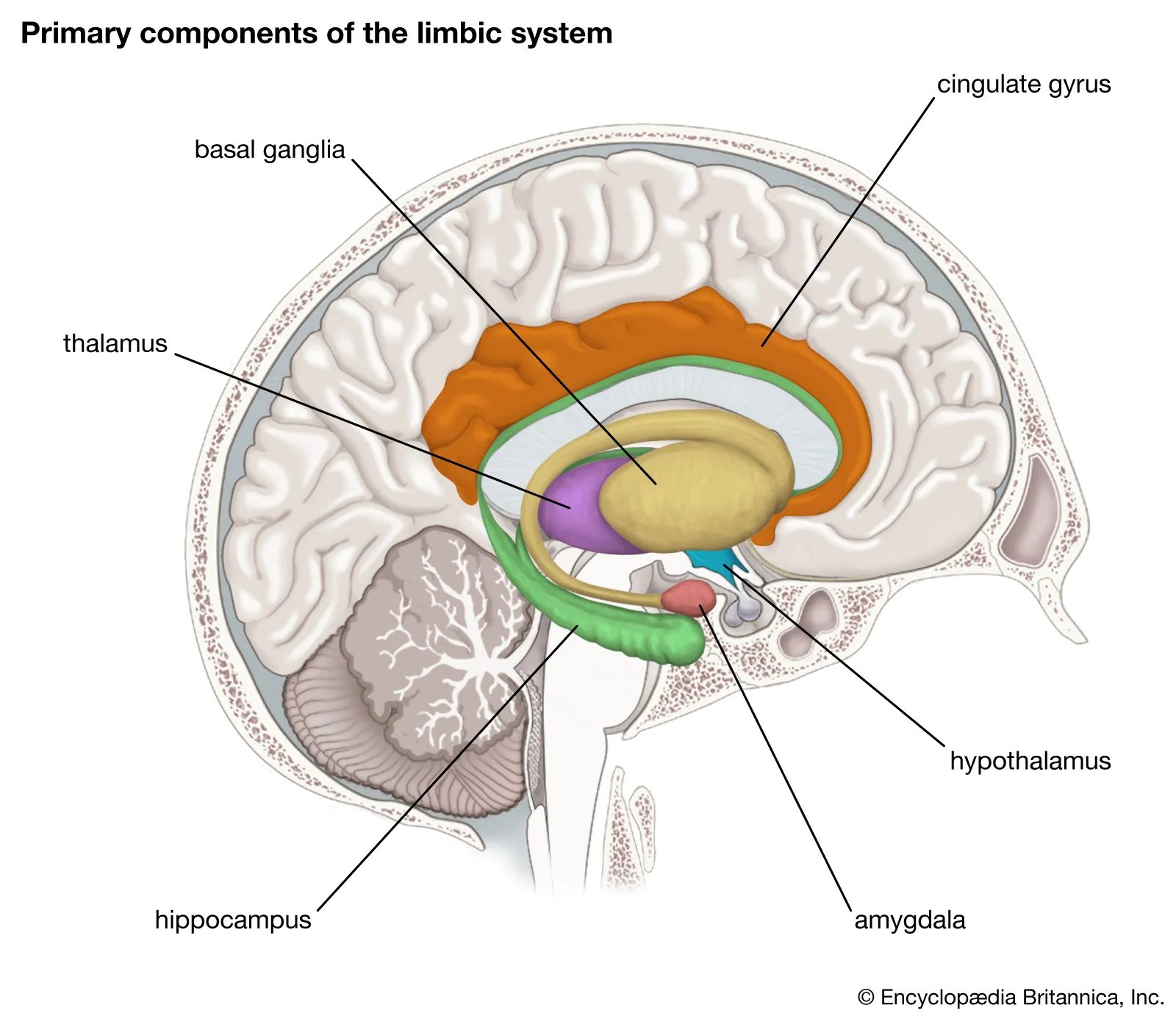
(Limbic System) Hippocampus
Forebrain structure in temporal lobe. Formation of new memories and spatial navigation and consolidation information from short-term to long-term memory.
(Limbic System) Amygdala
Structure in interior temporal lobe. Processing emotions, particularly fear and aggression, and emotional memory.
(Limbic System) Thalamus
Projection fibers connect to the cortical surface to relay sensation, spatial and motor signal information. Gateway to higher cortical function. Regulates consciousness, sleep, alertness.
(Limbic System) Hypothalamus
Controls the autonomic nervous system and endocrine system. Influences stress responses and emotional reactions. Regulates autonomic functions (e.g., hunger, thirst, temperature control).
(Limbic system) Mammillary bodies
A protrusion of the bottom of the brain at the posterior end of the hypothalamus. Contains some hypothalamic nuclei. Serves as relay stations in reflexes related to the sense of smell.
(Limbic System) Olfactory Bulb
A pair of nerve cell clusters in the brain that process information about smells.
What does the limbic system include?
Structures that form the epicenter of emotion and behavioral expression (Responsible for things like emotions, PTSD, depression, anxiety, etc.).
Anterior Pituitary (Master Gland)
Releases tropic hormones that control secretion/production of hormones in other glands of the endocrine system.
nucleus basalis
A forebrain structure that lies on the ventral surface; receives input from the hypothalamus and basal ganglia; sends axons to areas in the cerebral cortex.
Basal Ganglia
Subcortical nuclei involved in coordinating voluntary movements, motor learning, and reward processing (Crucial for building new habits and skills).
Basal Ganglia is comprised of
The caudate nucleus, putamen, and globus pallidus.