Biology Quiz Organelles+Cells
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
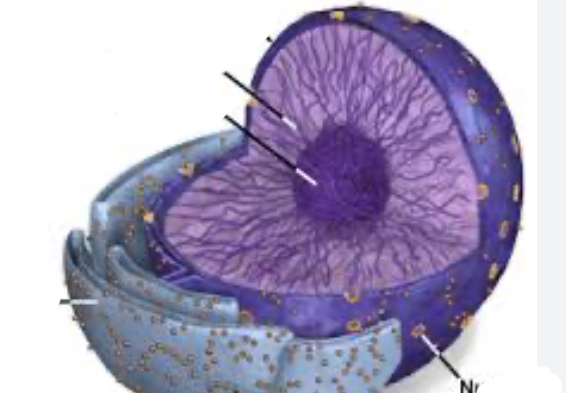
Nucleus, contains and protects genetic material
Found inside the nucleus or just floating
DNA/chromosomes, information for making proteins
Ribosomes, make proteins using messenger RNA, which is crucial to structure, function, and regulation
Found in: cytoplasm and rough ER, EU and PRO
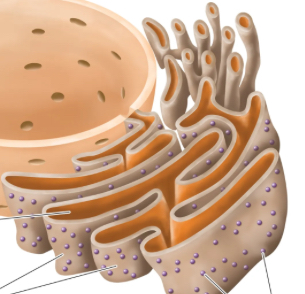
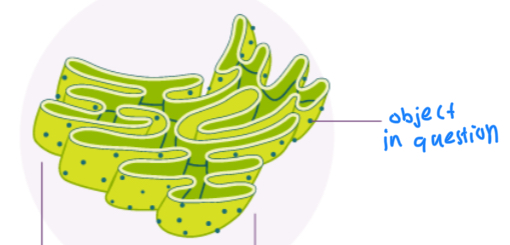
Endoplasmic Reticulum, transports and finishes proteins and other biological molecules
2 types: rough ER, studded ribosomes, synthesis and modification of proteins
Smooth ER: hydrolysis, carbohydrate metabolism, detoxification, no ribosomes on it, lipid manufacturing
Found in: EU
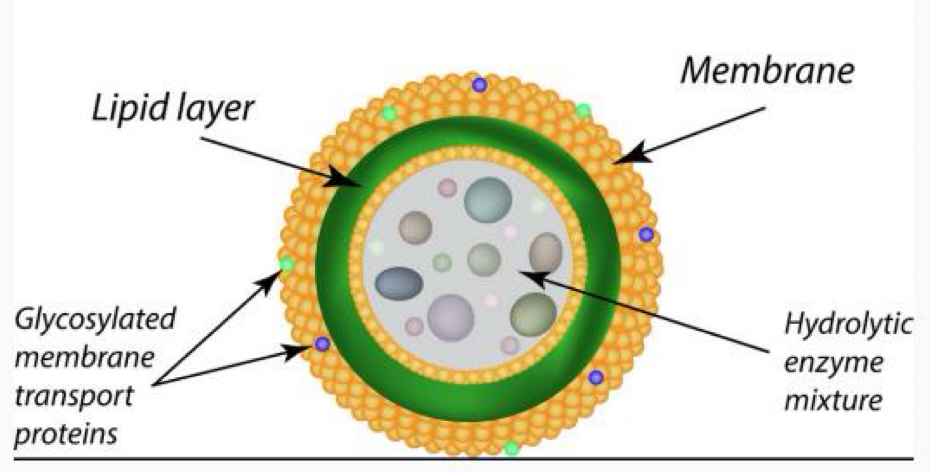
Lysosomes, help clean up the cell using enzymes (break lipids, carbs, and proteins)
Mitochondria, create ATP energy, contain own genetic info, from mother
Found in: EU, animal + plant
Golgi apparatus, sending things where they need to go in or out of cell
-membrane bound vesicles take packages to the plasma membrane
-composed of cisternae
Found in: EU, plant +animal
Cytoplasm- cytosol
-space for work to be done
-gel-like matrix
-intercellular space
-plays crucial role in biochemical reactions, energy production, substance transport
Storage unit near the ER
Vesicles, cellular package containing products such as protein
Found in: EU, maybe PRO**
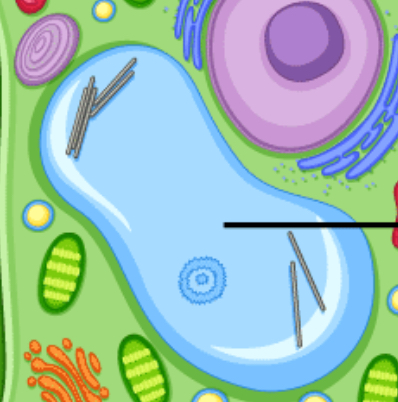
Vacuole, storage, sometimes defense and digestion
-central vacuole for plants
Found in: plant cells, animal cells, EU and PRO
Part of cell membrane
Pores/gated channels, points of entry and exit for materials
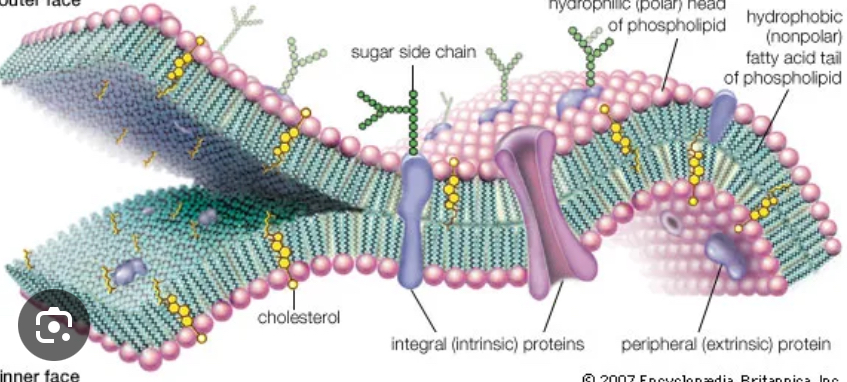
Cell membrane, controls what goes in and out of the cells
Compound Light Microscope
-typical
-uses two lenses to pass light through a specimen and magnify it
-objective+ ocular lens
-1 millionth of a meter
-light limits magnification
-stains are needed
Electron microscopes
-view smaller structures than compound light
-focused electron beam created by the magnetic field in a vacuum
-1 billionth of a meter
-high resolution
-nothin living
-scanning and transmission microscope
Transmission microscopes
-cell structures/large protein molecules viewed
-thin slices for the electrons
-2d images
Scanning microscopes
-electron beam scans specimen
-3D images
Anton van Leeuwenhoek
First to observe living microorganisms after first microscope, pond water
Robert Hooke
Inspected cork and discovered chambers he called cells
Cell
Smallest functioning unit of all living things, produced by division of other cells, all living things are made of cells, smallest unit of life
Mathias Schleiden and Theodore Schwann
Mathias proposed that plants are made of cells, later Theodor added animals
Living Organisms:
-have DNA
-change overtime
-use materials and energy
-grow and develop
-respond to environment
-reproduce
-maintain homeostasis
Prokaryotic
-simple
-genetic material in cytoplasm
-lack defined nucleus
-bacteria cells
Eukaryotic
-have defined nucleus
-plant
-animal
-protist
-fungal
-larger
-complex (organelles and internal membranes)
Protist
-some have cell wall
-no differentiated tissues
Fungal
-chitin cell wall
Space outside the cell
Extra cellular space
Nucleus parts
Nuclear pores- allow materials to move in and out of the nucleus
Nucleolus- involved in making ribosomes, attract messenger RNA
Chromatin
Chromatin=
chromosomes but extra proteins
Protein Synthesis
Proteins are assembled on ribosomes
Targeted for export to cell membrane/specialized locations within the cell, complete assembly on ribosomes bound to the rough ER
Newly assembled proteins are carried from the rough ER to Golgi apparatus in vesicles
Golgi further modifies before sorting and packaging them in membrane bound vesicles
Vesicles are shipped to final destination in or out of cell
Cytoskeleton- cell shape and involved in movement
Composed of: microtubules, microfilaments, intermediate filaments
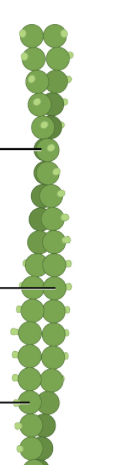
Microfilaments
-thin, thread like
-made of ACTIN
-supports cell, aids movement
Microtubules
Hollow structure
made of protein Tubulin
Maintain cell shape
-needed for cell division
-cilia and flagella
Flagella and cilia
Structures for movement, flagella for elongated and enable movement in liquid environments, cilia for shorter and create coordinated flow on cell surface
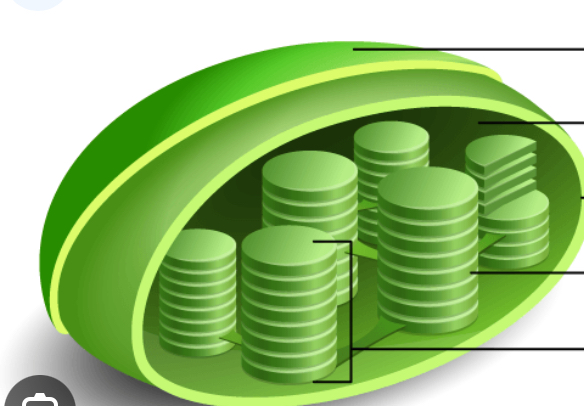
Chloroplasts- solar to chemical energy
-synthesize glucose
Cell walls- can be porous to let in substances
Found in: PRO, EU, plant, fungi
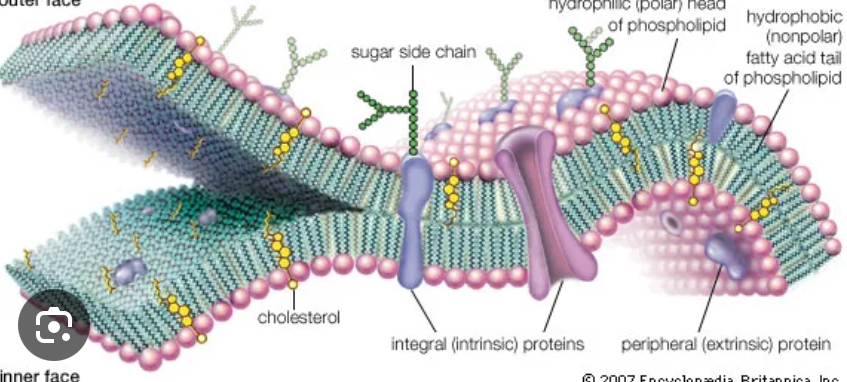
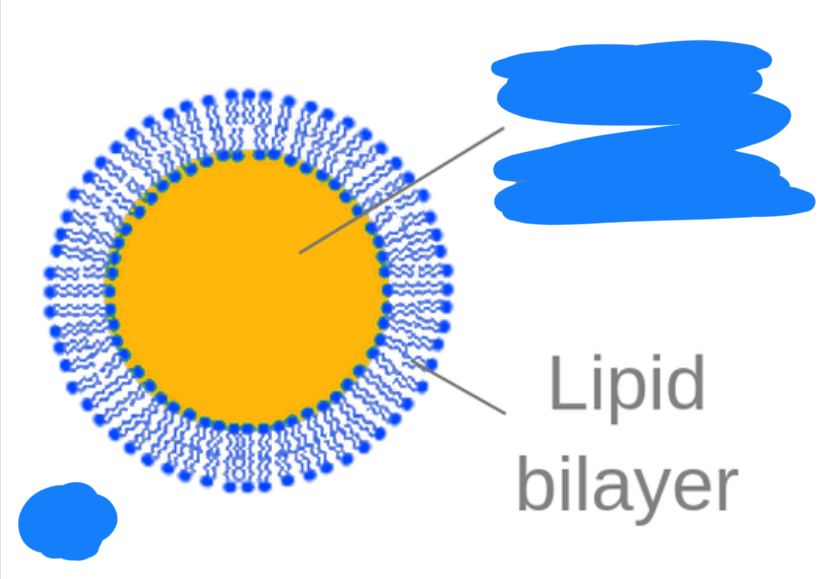
Cell membranes- double lipid bilayer (phospholipid)
-regulates entry and exit
-supports protects cell
Found in: all cells
Animal cell parts
-cell membrane
-nucleus (DNA)
-RER
-ribosomes
-SER
-Cytoskeleton*
-Centrioles*
-lysosome*
-Mitochondrion
-vacuole
-Golgi apparatus
-vesicle
Plant cell parts
Cell membrane
Cell wall
Vacuole
Golgi apparatus
Vesicle
Nucleus
RER
Ribosomes
SER
Central vacuole
Cytoskeleton
Chloroplast
Mitochondrion
Prokaryotic Cell parts
DNA
Ribosomes
Cell membrane
Cell wall
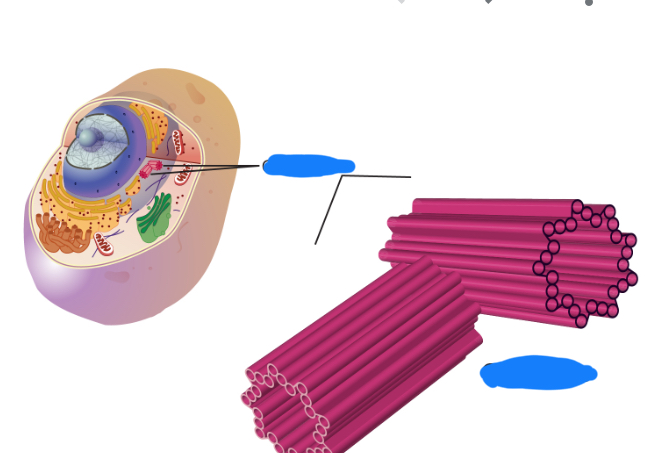
Centrioles- barrel shaped organelles, organize microtubules, organizing division of cells
Identify
Spirilum, coccus, bacillus