AP Art History Unit 3 Vocab
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
113 Terms
aisle
The portion of a basilica flanking the nave and separated from it by a row of columns or piers.
ambulatory
A covered walkway, outdoors (as in a church cloister) or indoors; especially the passageway around the apse and the choir of a church.
anamorphic image
A distorted image that must be viewed by some special means (such as a mirror) to be recognized.
apostle
Greek, "messenger." One of the 12 disciples of Jesus.
apse
A recess, usually semicircular, in the wall of a building, commonly found at the east end of a church.
arcade
A series of arches supported by piers or columns.
Arcadian (adj.)
In Renaissance and later art, depictions of an idyllic place of rural peace and simplicity. Derived from Arcadia, an ancient district of the central Peloponnesus in southern Greece.
archivolt
The continuous molding framing an arch. In Romanesque or Gothic architecture, one of the series of concentric bands framing the tympanum.
atrium
the open, colonnaded court in front of and attached to a Christian basilica.
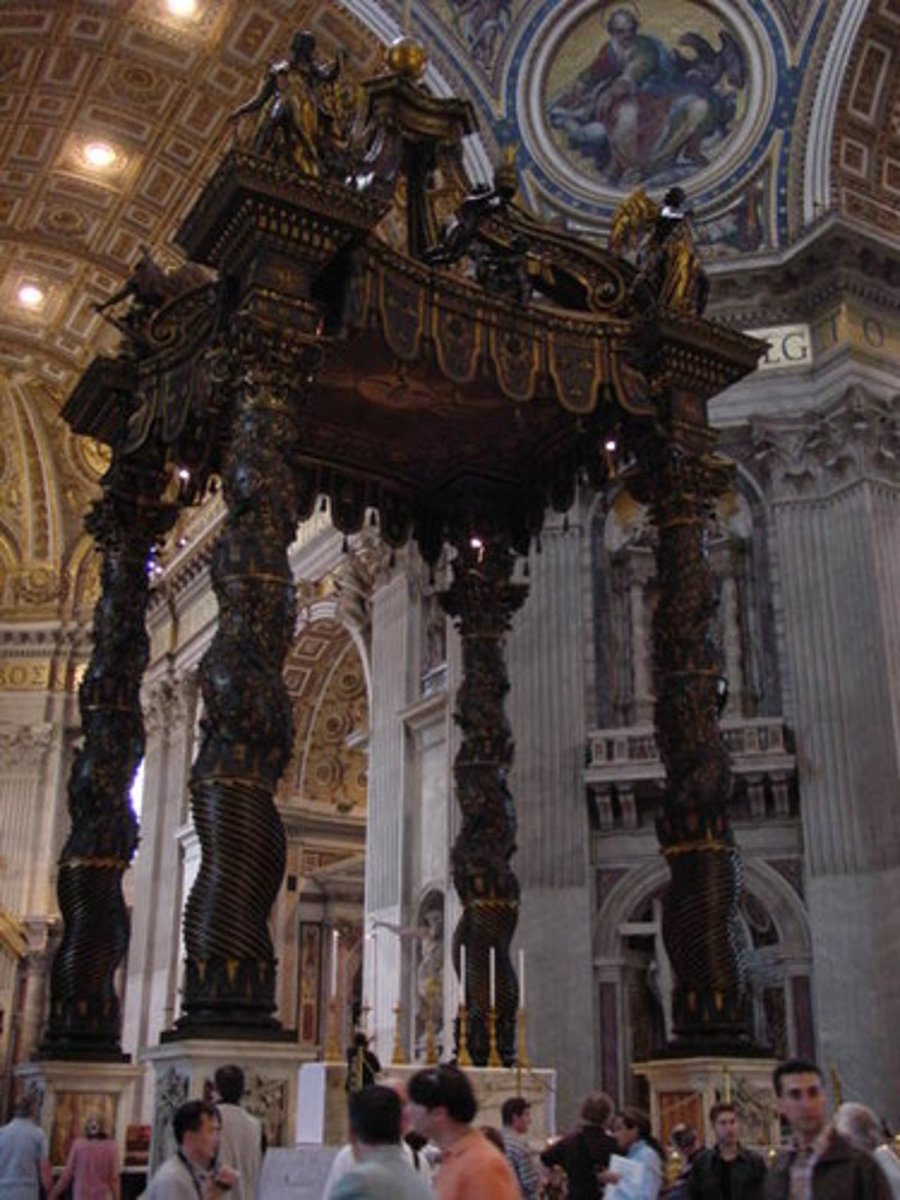
baldacchino
A canopy on columns, frequently built over an altar. See also ciborium.

baldric
A sashlike belt worn over one shoulder and across the chest to support a sword.
baptistery
In Christian architecture, the building used for baptism, usually situated next to a church.
Baroque
The traditional blanket designation for European art from 1600 to 1750. The stylistic term Baroque, which describes art that features dramatic theatricality and elaborate ornamentation in contrast to the simplicity and orderly rationality of Renaissance art, is
most appropriately applied to Italian art of this period. The term derives from barroco, Portuguese for "irregularly shaped pearl."
campanile
A bell tower of a church, usually, but not always, freestanding.
cassone (pl. cassoni)
A carved chest, often painted or gilded, popular in Renaissance Italy for the storing of household clothing.
cathedral
A bishop's church. The word derives from cathedra, referring to the bishop's seat.
Caroline minuscule
The alphabet that Carolingian scribes perfected, from which our modern alphabet was developed
Carolingian (adj.)
Pertaining to the empire of Charlemagne (Latin, Carolus Magnus) and his successors.
carpet page
In early medieval manuscripts, a decorative page resembling a textile.
catacombs
Subterranean networks of rock-cut galleries and chambers designed as cemeteries for the burial of the dead.
choir
The space reserved for the clergy and singers in the church, usually east of the transept but, in some instances, extending into the nave.
central plan
The horizontal arrangement of the parts of a building or of the buildings and streets of a city or town, or a drawing or diagram showing such an arrangement. In an axial plan, the parts of a building are organized longitudinally, or along a given axis; in a central plan, the parts of the structure are of equal or almost equal dimensions around the center.
chancel arch
The arch separating the chancel (the apse or choir) or the transept from the nave of a church.

chasing
The engraving or embossing of metal.
Chi-Ro
Christian symbol for Christ (a Christogram): the first two letters of Christ in Greek [Kristos]. Often shown with the Greek letters Alpha (A) and Omega (lower case ώ or upper case Ω), the first and last letters of the Greek alphabet
![<p>Christian symbol for Christ (a Christogram): the first two letters of Christ in Greek [Kristos]. Often shown with the Greek letters Alpha (A) and Omega (lower case ώ or upper case Ω), the first and last letters of the Greek alphabet</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/85415a41-17da-4455-aac6-c174c4943605.jpg)
chiaroscuro
An Italian word literally meaning "light-dark." Used to describe the skillful management of value to create the illusion of three-dimensional forms in a drawing or painting.
chiaroscuro woodcut
A woodcut technique using two blocks of wood instead of one. The printmaker carves and inks one block in the usual way in order to produce a traditional black and white print. Then the artist cuts a second block consisting of broad highlights that can be inked in gray or color and printed over the first block's impression.
cloison
French, "partition." A cell made of metal wire or a narrow metal strip soldered edgeup to a metal base to hold enamel, semiprecious stones, pieces of colored glass, or glass paste fired to resemble sparkling jewels.
cloisonné
A decorative metalwork technique employing cloisons; also, decorative brickwork in later Byzantine architecture.
cloister
A monastery courtyard, usually with covered walks or ambulatories along its sides.
compound pier
A pier with a group, or cluster, of attached shafts, or responds, especially characteristic of Gothic architecture.
codex (pl. codices)
Separate pages of vellum or parchment bound together at one side; the predecessor of the modern book. The codex superseded the rotulus. In Mesoamerica, a painted and inscribed book on long sheets of bark paper or deerskin coated with fine white plaster and folded into accordion like pleats.
colorito
Italian, "colored" or "painted." A term used to describe the application of paint. Characteristic of the work of 16thcentury Venetian artists who emphasized the application of paint as an important element of the creative process. Central Italian artists, in contrast, largely emphasized disegno, the careful design preparation based on preliminary drawing.
cuerda seca
A type of polychrome tilework used in decorating Islamic buildings.
crossing
The space in a cruciform church formed by the intersection of the nave and the transept.
crossing square
The area in church formed by the intersection of the nave and the transept of equal width, often found in Ottonian Churches
Crusades
In medieval Europe, armed pilgrimages aimed at recapturing the Holy Land from the Muslims.
cruciform
Cross shaped.
crypt
A vaulted space under part of a building, wholly or partly underground; in churches, normally the portion under an apse or a chevet.
cubiculum (pl. cubicula).
A chamber in an Early Christian catacomb that served as a mortuary chapel.
diaphragm arch
A transverse, wall-bearing arch that divides a vault or a ceiling into compartments, providing a kind of firebreak.

diptych
A two-paneled painting or altarpiece; also, an ancient Roman, Early Christian, or Byzantine hinged writing tablet, often of ivory and carved on the external sides.
disegno
Italian, "drawing" and "design." Renaissance artists considered drawing to be the external physical manifestation (disegno esterno) of an internal intellectual idea of design (disegno interno).
enamel
A decorative coating, usually colored, fused onto the surface of metal, glass, or ceramics.
escutcheon
An emblem bearing a coat of arms.
Eucharist
In Christianity, the partaking of the bread and wine, which believers hold to be either Christ himself or symbolic of him.
fibula (pl. fibulae)
A decorative pin, usually used to fasten garments.
folio
A page of a manuscript or book.
feudalism
The medieval political, social, and economic system held together by the relationship between landholding liege lords and the vassals who were granted tenure of a portion of their land and in turn swore allegiance to the liege lord.
grisaille
A monochrome painting done mainly in neutral grays to simulate sculpture.
Greek cross
A cross with four arms of equal length.
historiated
Ornamented with representations, such as plants, animals, or human figures, that have a narrative as distinct from a purely decorative function.
icon
A portrait or image; especially in Byzantine churches, a panel with a painting of sacred personages that are objects of veneration. In the visual arts, a painting, a piece of sculpture, or even a building regarded as an object of veneration.
iconoclasm
The destruction of images. In Byzantium, the period from 726 to 843 when there was an imperial ban on images. The destroyers of images were known as iconoclasts. Those who opposed such a ban were known as iconophiles.
iconoclast
In Byzantium, the period from 726 to 843 when there was an imperial ban on images. The destroyers of images were known as iconoclasts. Those who opposed such a ban were known as iconophiles.
iconostasis
In Byzantine churches, a screen or a partition, with doors and many tiers of icons, separating the sanctuary from the main body of the church.
illuminated manuscript
A luxurious handmade book with painted illustrations and decorations.
illumination
Decoration (usually in gold, silver, and bright colors), especially of medieval manuscript pages.
Landschaft
German, "landscape."
liturgy (adj., liturgical)
The official ritual of public worship.
loculi
Openings in the walls of catacombs to receive the dead.
loggia
A gallery with an open arcade or a colonnade on one or both sides.

lostwax (cire perdue) process
A bronzecasting method in which a figure is modeled in wax and covered with clay; the whole is fired, melting away the wax (French, cire perdue) and hardening the clay, which then becomes a mold for molten metal.
lunette
A semicircular area (with the flat side down) in a wall over a door, niche, or window; also, a painting or relief with a semicircular frame.
mandorla
An almond-shaped nimbus surrounding the figure of Christ or other sacred figure.
maniera
Italian, "style" or "manner." See Mannerism.
Mannerism
A style of later Renaissance art that emphasized "artifice," often involving contrived imagery not derived directly from nature. Such artworks showed a selfconscious stylization involving complexity, caprice, fantasy, and polish. Mannerist architecture
tended to flout the classical rules of order, stability, and symmetry, sometimes to the point of parody.
Mass
The Catholic and Orthodox ritual in which believers understand that Christ's redeeming sacrifice on the cross is repeated when the priest consecrates the bread and wine in the Eucharist.
Messiah
The savior of the Jews prophesized in the Old Testament. Christians believe that Jesus of Nazareth was the Messiah.
modeling
In painting, drawing, or mosaic, the technique of creating the illusion of three- dimensionality by the use of gradations of value.
monastery
A group of buildings in which monks live together, set apart from the secular community of a town.
monastic
Relating to life in a monastery.
mosaic
Patterns or pictures made by embedding small pieces (tesserae) of stone or glass in cement on surfaces such as walls and floors; also, the technique of making such works.
mosaic tilework
An Islamic decorative technique in which large ceramic panels are fired, cut into smaller pieces, and set in plaster
muqarnas
Stucco decorations of Islamic buildings in which stalactitelike forms break a structure's solidity.
narthex
A porch or vestibule of a church, generally colonnaded or arcaded and preceding the nave.
nimbus
A halo or aureole appearing around the head of a holy figure to signify divinity.
orant
In Early Christian art, a figure with both arms raised in the ancient gesture of prayer.
Ottonian (adj.)
Pertaining to the empire of Otto I and his successors.
Pantokrator
Greek, "ruler of all." Jesus as ruler and judge. Byzantine iconography
parchment
Lambskin prepared as a surface for painting or writing.
paten
A large shallow bowl or plate for the bread used in the Eucharist.
pebble mosaic
A mosaic made of irregularly shaped stones of various colors.
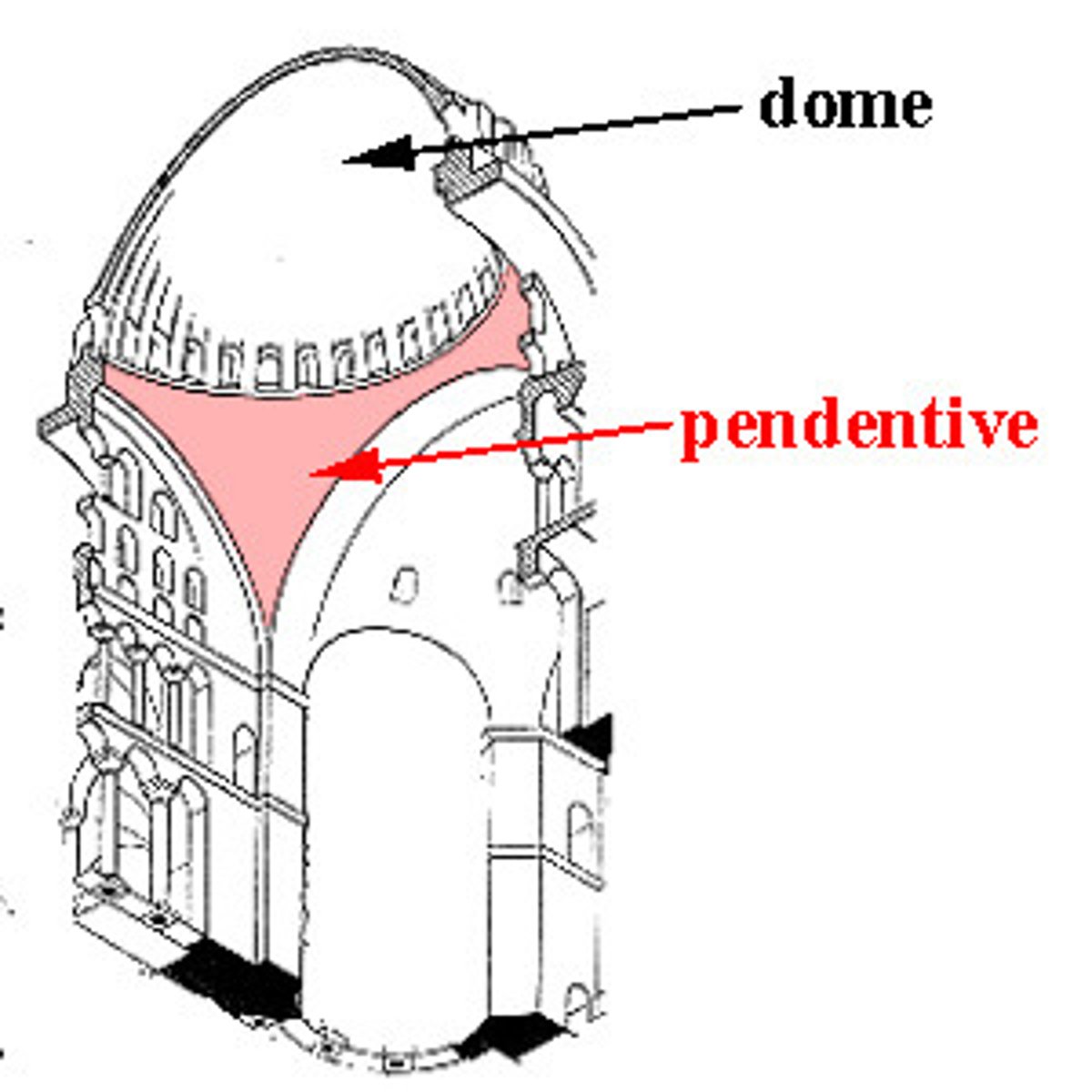
pendentive
A concave, triangular section of a hemisphere, four of which provide the transition from a square area to the circular base of a covering dome. Although pendentives appear to be hanging (pendant) from the dome, they in fact support it.
Pentateuch
The first five books of the Hebrew Scriptures.
piazza
Italian, "plaza."
Pietà
A painted or sculpted representation of the Virgin Mary mourning over the body of the dead Christ.
platero
A style of Spanish architecture characterized by elaborate decoration based on Gothic, Italian Renaissance, and Islamic sources; derived from the Spanish word platero, meaning "silversmith."
poesia
A term describing "poetic" art, notably Venetian Renaissance paintings, which emphasizes the lyrical and sensual.
pointed arch
A narrow arch of pointed profile, in contrast to a semicircular arch.
prefiguration
In Early Christian art, the depiction of Old Testament persons and events as prophetic forerunners of Christ and New Testament events.
psalter
A book containing the Psalms.
quoins
The large, sometimes rusticated, usually slightly projecting stones that often form the corners of the exterior walls of masonry buildings.
radiating chapels
In medieval churches, chapels for the display of relics that opened directly onto the ambulatory and the transept.
relics
The body parts, clothing, or objects associated with a holy figure, such as the Buddha or Christ or a Christian saint.
reliquary
A container for keeping relics.
rib
A relatively slender, molded masonry arch that projects from a surface. In Gothic architecture, the ribs form the framework of the vaulting. A diagonal rib is one of the ribs that form the X of a groin vault. A transverse rib crosses the nave or aisle at a 90 degree angle.
Romanesque
Romanlike. A term used to describe the history, culture, and art of medieval western Europe from ca. 1050 to ca. 1200.
sacra conversazione
Italian, "holy conversation"; a style of altarpiece painting popular after the middle of the 15th century, in which saints from different epochs are joined in a unified space and seem to be conversing either with each other or with the audience.
sedes sapientiae
Latin, "throne of wisdom." A Romanesque sculptural type depicting the Virgin Mary with the Christ Child in her lap