Reproduction , fertility and contraception
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
What does reproduction involve?
The joining of two gametes, the sperm and the ovum (the egg)
What are the components of the male reproductive system?
Bladder, urethra, penis, scrotum, testis, sperm tube, prostate gland
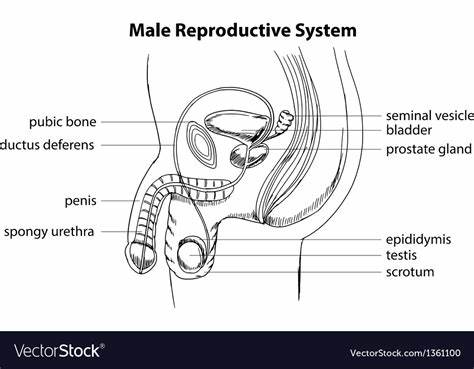
What is the bladder?
Muscular bag to store urine
What is the urethra?
Tube through the penis which carries sperm out of the penis
What is the penis?
Organ that releases sperm into the vagina
What is the scrotum?
Sac that holds testes at slightly lower than body temperature.
What are the testes?
Produce sperm
What is the sperm tube?
Tube which carries sperm from testes to urethra
What is the prostate gland?
Adds fluid to nourish sperm (semen)
How are sperm adapted?
They have a flagellum to help them swim
Mitochondria for energy production
Haploid nucleus
What are the components to the female reproductive system?
The oviduct, ovary, uterus wall, uterus, cervix, vagina
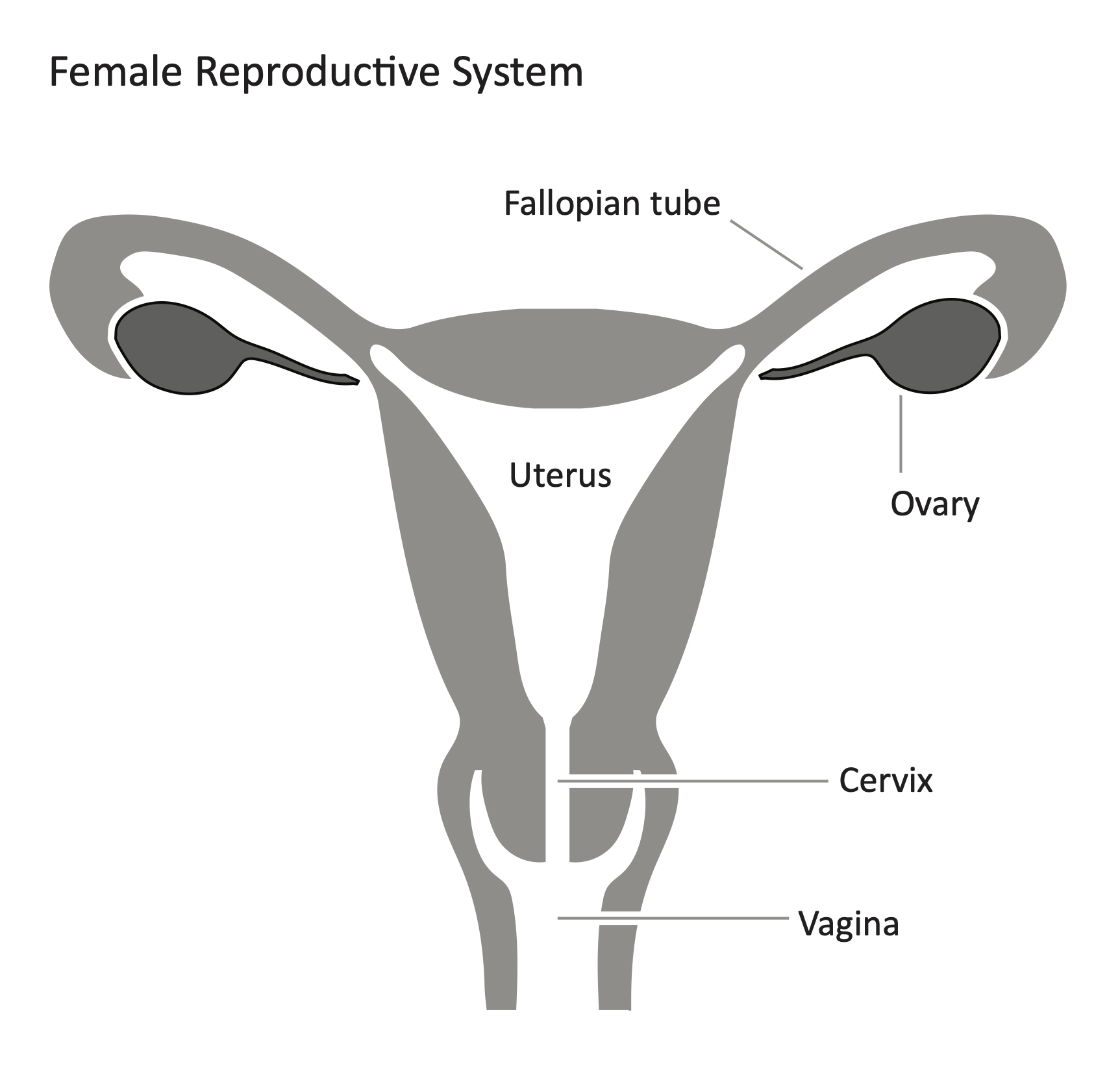
What is the oviduct?
Carries ova to the uterus
What is the ovary?
Where the ova are produced
What is the uterus wall?
Where the placenta forms after fertilisation
What is the uterus?
Where the foetus develops and is nourished
What is the cervix?
The opening of the uterus- it widens during birth
What is the vagina?
Where the penis is placed during intercourse
What is the male sex hormone?
Testosterone and it is produced in the testes
What is the female sex hormone?
Oestrogen and it is produced in the ovaries
What happens during fertilisation?
The fusion of an ovum and a sperm in the oviduct
What are the steps of fertilisation?
Haploid nuclei of ovum and sperm fuse and form a diploid
fertilised egg is now a zygote
Zygote divides by mitosis, form an embryo as it travels down oviduct to the uterus
What are the adaptations of the placenta?
There is a rich network of blood vessels to increase blood flow
There is a large number of villi to increase surface area
Large SA needed for exchanging dissolved nutrients
What is the umbilical cord?
Contains the umbilical artery and vein to allow for exchange of gases, nutrients, waste products between the mother and foetus
What is the amnion?
The membrane containing the amniotic fluid protecting the embryo
What is the amniotic fluid?
Cushions the developing embryo
What is the menstrual cycle?
The renewal of the blood rich lining of the uterus- this is to provide a suitable environment for a developing embryo
How long does the menstrual cycle last?
Approximately 28 days
What are the stages of the menstrual cycle?
Menstruation (1-5), following menstruation (6-13), ovulation (13-15)
What is menstruation?
The breakdown and removal of the uterus lining at the end of each cycle. Lasts from puberty to 44-55 years
What happens in the days after menstruation?
The rebuilding of the uterus lining to prep for fertilisation
What is ovulation?
The release of an ovum from the ovary
What does oestrogen do in the menstrual cycle?
Causes the repair and build up of uterus lining and stimulates ovulation
What does progesterone do in the menstrual cycle?
Maintains the build up of uterus lining and prepares uterus for pregnancy
What time is fertilisation most likely to occur during?
Days 13-15
What do fertility drugs do?
Increase egg production and release
What are the steps of in vitro fertilisation?
Stimulation, egg retrieval, insemination, pregnancy
What are sperm cells?
specialised cells formed by meiosis
Where does fertilisation take place?
oviducts when the haploid sperm and egg nuclei fuse to give a diploid zygote
What are some causes of infertility?
Blocked Oviducts
Eggs are not released
Low Sperm Count
Impedience
What do male condoms do?
Barrier to prevent sperm entrance
What are the pros and cons of male condom?
Easily obtained
Protects against STIs
Unreliable if not used properly
What do female condoms do?
Barrier for sperm passing
What are the pros and cons of female condoms?
Easily obtained
Protects against STIs
Unreliable if not used properly
What do contraceptive pills do?
prevents releasing eggs and changing hormone levels
What are the pros and cons of contraceptive pills?
Very reliable
Weight gain
Risk of blood clots
Need to remember to take pills
What do implants do?
Small 4cm tubes inserted under the arm and releases hormones over longtime period to prevent the development and release of eggs
What are the pros and cons of implants?
Very reliable
Can work up to 30 years
Prevents menstruation
What do vasectomies do?
Cutting off sperm tubes and prevents it from entering the penis
What are the pros and cons of vasectomies and female sterilisation?
100% reliable
Impossible to reverse
What does female sterilisation do?
Cutting off oviducts prevents fetilisation