Physics final
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
• What object is used to detect a gravitational field?
Any mass - when released it falls in the direction of the field
What object was used to detect an electric field?
A positively charged test particle - when released it moves in the direction of the field
What object would be used to detect a magnetic field?
A compass - the north pole points in the direction of the magnetic field
Specific heat capacity formula and heat formula
C=Q/m🔺t..... Q=mc🔺
Magnetic field lines point from....
• Magnetic Field lines point from the north pole to the south pole of the magnet
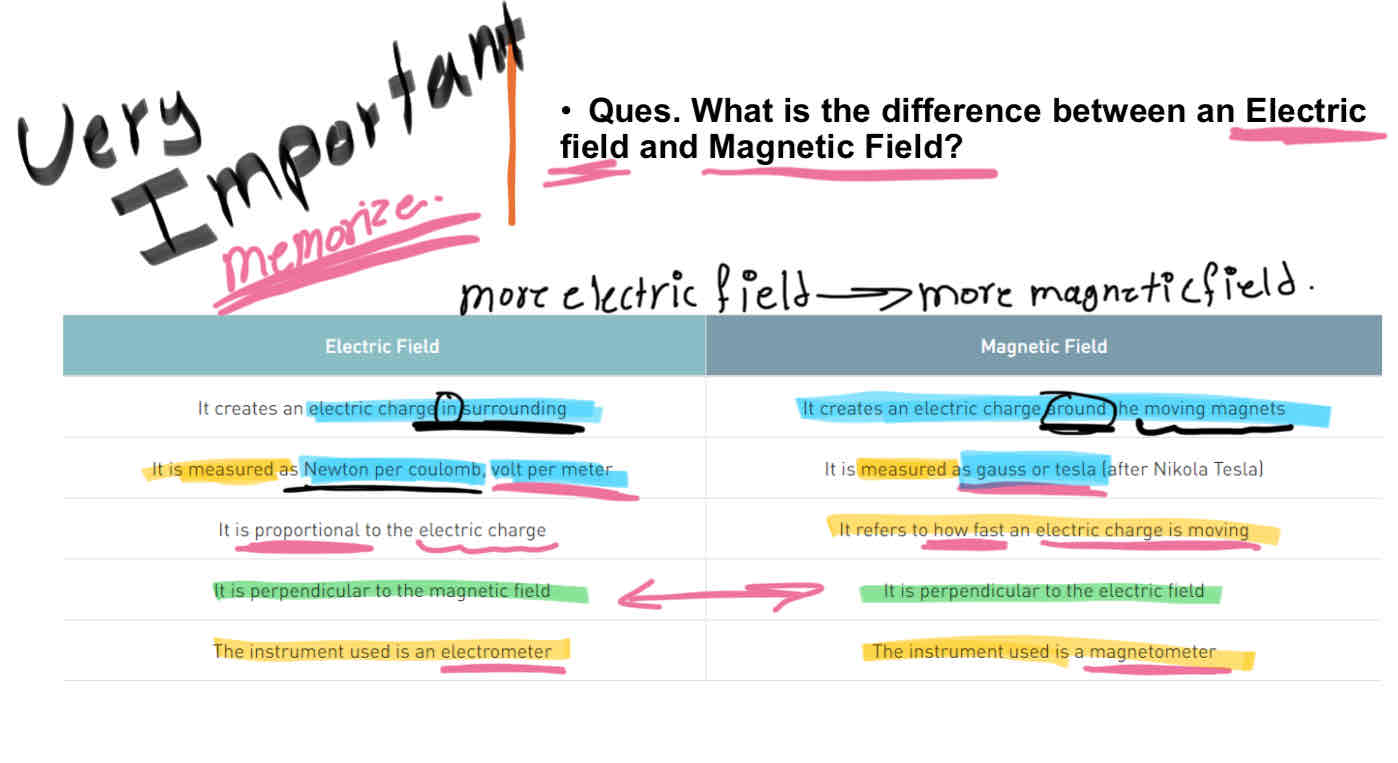
Ques. What is the difference between an Electric field and Magnetic Field? Check photos
Magnetic poles always occur in
Pairs
If you break a magnet what happens
Each piece will have a north and a South Pole.
What is a wave?
• A wave is a disturbance that carries energy through matter or space.
What is a periodic wave?
If the disturbances continue at a constant rate, a periodic wave is generated.
Transverse wave is one that vibrates perpendicular to the direction of the wave's motion. For example: Light waves or a swinging rope wave.
longitudinal wave is one that vibrates parallel to the direction of the wave's travel. Fore example: Sound waves or a spring compression wave.
Surface waves has characteristics of both transverse and longitudinal waves.
Mechanical Waves
• It is a type of wave in which it require a medium to travel through.
Mechanical waves can be either transverse or longitudinal.
A wave pulse
is a single bump or disturbance that travels through a medium.
Electromagnetic waves
A wave that Does not require a medium to travel through.
What type of waves are electromagnetic waves
transverse waves.
Any wave has some constant properties that doesn't change over time like
wavelength, periodic time, frequency and amplitude.
Amplitude is
the maximum extent of the wave vibration.
Crest
• The positive amplitude is called Crest and it is the farthest point the wave can reach in the positive direction
Trough .
• The negative amplitude is called Trough and it is the farthest point the wave can reach in the negative direction
Wavelength
it is the amount of distance by the wave after completing one complete oscillation.
Wavelength is represented by
the letter Lambda 𝜆
Frequency :
it is the amount of completing oscillations that happen in one second.
• Frequency is represented by the letter 𝜇 and is measured in 𝑠−1 or Hertz (Hz). Just a note
Periodic time
it is the amount of time required for one complete oscillation.
Periodic time and Frequency are the multiplicative inverse of each other. Note 𝑃𝑒𝑟𝑖𝑜𝑑𝑖𝑐 𝑇𝑖𝑚𝑒 = 1 𝐹𝑟𝑒𝑞𝑢𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑦
The product of the wavelength and frequency of a wave gives us the speed of the wave. 𝜆 × 𝜇 = V
Speed of light number
c = 3.00×10^8 m/s
Spectrum of electromagnetic waves
Radio microwave infrared visible light ultraviolet x ray gamma rays
What is a diode?
A diode is an electrical device that enables the current to flow only in one direction.
What is P-N Junction?
A P-N junction is an interface or a boundary between two semiconductor material types, namely the p-type and the n-type, inside a semiconductor.
Biasing
The process of applying the external voltage to a p-n junction semiconductor diode
Forward biasing
Anode (+) positive terminal p type—> cathode (-) negative terminal n type current flows
Reverse biased
Negative connected to p side(anode terminal) positive terminal connected to the n side ( cathode terminal) and the diode acts as an insulator(object that inhibits electricity )and no current flows and the depletion layer width start increasing
Logic gates are
digital circuits which either allow a signal to pass through it or to stop it.Logic gates are the basic building blocks of any digital circuit.Made using digital circuits and components like transistors resistors and diodes.
Truth tables
A table showing all possible input value and the associated output values
AND GATE
accepts two input signals If both are 1, the output is 1 otherwise, the output is 0
NOT GATE
accepts one input signal (0 or 1) and returns the opposite signal as output
OR GATE
accepts two input signals If both are 0, the output is 0 other wise, the output is 1
NAND GATE
accepts two input signals If both are 1, the output is 0 otherwise 1
NOR GATE
accepts two input signals If both are 0, the output is 1 otherwise, the output is 0 or answer opposite of or
What are Logic Gates Used For?
Digital Computers Control Systems Communication Systems
3 ways heat can transfer
Conduction convection and radiation
Which heat transfer methods travels through particles and which don't?
Conduction and convection and the no particles radiation
Conduction
When you heat a metal strip at one end, the heat travels to the other end./ direct contact
Convection
The particles spread out and become less dense. Fluid movement ex liquid to gas
Thermal equilibrium
is the state in which two bodies in physical contact with each other have identical temperatures.The temperature of any two objects in thermal equilibrium always lies between their initial temperatures.
Thermal contact
Two objects are in thermal contact with each other if energy can be exchanged between them.
Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics
If objects A and B are separately in thermal equilibrium with a third object C, then A and B are in thermal equilibrium with each other. C is the thermometer Since they are in thermal equilibrium with each other, there is no energy exchanged among them.
The Specific Heat Capacity is
the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of a unit mass through one degree.
Specific heat capacity formula
c = q/mΔT and Q=mc🔺t
Note more difference in temperature the higher rate for heat loss to occur
Note mass has to be in kg if in g divide by 1000
Q unit joules kilojoules and calories c is j/kgxk or j/kgxc m is kg t is k f c