Ecology and Evolution - FINAL - Unit 1
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Hypothesis
Testable explanation for a phenomenon
Scientific theory
Explanation of a phenomenon (has underlying mechanisms)
Scientific law
Description of a phenomenon under certain conditions
inductive VS deductive reasoning
Inductive: Specific → General
Deductive: General → Specific
Explain the relationship between hypotheses and the two forms of reasoning
Inductive reasoning → creates hypotheses
Deductive reasoning → Tests hypotheses
Distinguish between 'absolute truth' and 'degrees of confidence’
Absolute Truth: 100% certain, unchanging fact. Science cannot claim this because new evidence or observations may always challenge ideas.
Degrees of Confidence: How sure scientists are in a conclusion based on evidence. Confidence grows with repeated testing and consistent results.
Why can science pursue absolute truth or degrees of confidence but not the other
Science pursues increasing confidence, not absolute truth, because all knowledge is provisional and open to revision.
Describe the major factors that affect global climate patterns
Seasonal variation
Sunlight intensity
Air circulation/precipitation patterns
Position of land masses
Mountains
potential vs. actual range
Potential: Where organisms COULD live
Actual: Where organisms DO live
Define population
Group of individuals of a same species in a same area
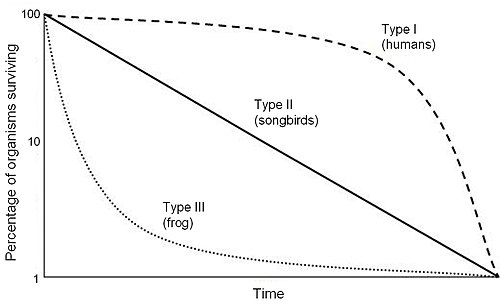
Distinguish between the three types of survivorship curves
exponential vs logistic population growth
Exponential: Growth increases over time
Logistic: Growth slows over time
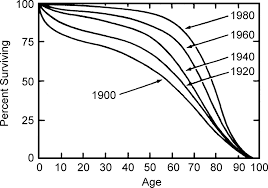
Demographic transition
Transition from a type 3 to type 1 on a survivorship curve
Explain why humans are different than other organisms in terms of b and m
Humans can control birth rates and reduce mortality