Saltatory conduction and synapses
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
What is Myelin sheath?
Myelin sheath made of Schwann cells.
Sections covered by myelin sheath depolarization
cannot occur as it prevents the movement of sodium
and potassium ions
What are nodes of ranvier?
small sections which are not insulated
These are sections of membrane with cluster s of ion pumps and channels.
These pumps and channels allow action potentials to occur
Action potential jumps from one node to the next
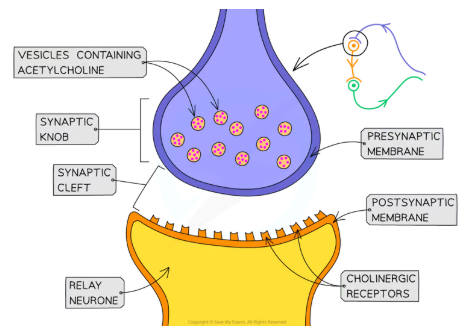
structure of synapse
A gap between the neurones known as the synaptic cleft
The neurone before the synapse is known as the presynaptic neurone and has a rounded end known as the synaptic knob
The neurone after the synapse is known as the postsynaptic neurone
Nerve impulses are passed across the synaptic cleft by the diffusion of chemicals known as neurotransmitters e.g. acetylcholine
Neurotransmitters are contained within vesicles in the synaptic knob
Roles of synapses?
unidirectionality of impulse transmission
Divergence of nerve impulse
Amplification of nerve signals by summation
Role of synapses - uni directionality of transmission
synapses enable uni-directionality of impulse transmission
Ensure one -way transmission of impulses
Impulses can only pass in one direction at synapses because neurotransmitter is released on one side and its receptors are on the other, chemical transmission cannot occur in the opposite direction
divergence of nerve impulse at synapse
divergence of nerve impulses
One neurons can connect to several other neurons at a synapse, allowing nerve signals to be sent in several directions from a single presynaptic neurone
How synapses cause amplification of nerve signals by summation
Impulse arrives at a synapse it does not always cause an impulse to be generated in the next neurone; a single impulse that arrives at a synaptic knob may be insufficient to generate an action potential in the post-synaptic neurone
• Only a small amount of acetylcholine may release into the synaptic
cleft
• A small number of sodium ion channels are opened in the
postsynaptic axon membrane
• An insufficient number of sodium ions pass through the membrane
• The threshold potential is not reached
multiple impulses added together to over come this-known as summation
How can summation be achieved
• Several presynaptic neurones converging to meet a
single postsynaptic neurone
• This is known as synaptic convergence
• Many action potentials arriving at a postsynaptic
knob in quick successio
synaptic transmission-diffusion to presynaptic neurone
Electrical impulses cannot ‘jump’ across the synaptic cleft
When an action potential arrives at the end of the axon of the presynaptic neurone the membrane becomes depolarised, causing voltage gated calcium ion channels to open
Calcium ions diffuse into the synaptic knob via calcium ion channels in the membrane
The calcium ions cause vesicles in the synaptic knob to move towards the presynaptic membrane where they fuse with it and release chemical messengers called neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft by exocytosis
A common neurotransmitter is acetylcholine, or ACh
excitatory post synaptic potential
Neurotransmitter diffuses across cleft
Attached to specific receptor site on the sodium channel
If binding results in opening of sodium ion channels sodium enters causing depolarization.
This is known as an excitatory post synaptic potential.
A number of EPSPs may be needed for the membrane to reach threshold potential.
If enough neurotransmitter molecules bind with receptors on the postsynaptic membrane, then an action potential is generated, which then travels down the axon of the postsynaptic neurone
how likelyhood of action potential being generated is increased
depends on the number of action potentials arriving at the presynaptic knob
Many action potentials will cause more neurotransmitter to be released by exocytosis
A large amount of neurotransmitter will cause many sodium ion channels to open
Many sodium ion channels opening will allow a large influx of sodium ions, increasing the likelihood of threshold being reached
what is inhibitory post synaptic potential
Neurotransmitters can also have opposite effect.
They can bind to different ion channels and cause the opening of ion channels which allow influx of negative ions.
In this case the membrane becomes hyperpolarized and this makes an action potential less likely to occur.
what are cholinergic nerves?
Actelycholine is a common neurotransmitter and it is found at the majority of synapses.
It is made in the synaptic knob (inside presynaptic neurone)
Many mitochondria present as it requires ATP to make it.
Nerves that use acetylcholine as a neurotransmitter are known as cholinergic nerves.
Break down of acetylcholine by acetylcholinesterase, hydrolysis reaction.
how acetycholinesterase hydrolysis reaction
Breakdown of acetylcholine ensures that no longer affects the
postsynaptic membrane.
Acetate and choline can then move by diffusion back to presynaptic knob to be reabsorbed into the neurone.
Resynthesizes acetyl choline.
Acetylcholine is the neurotransmitter for all nerves of the parasympathetic nervous system and all motor neurons.
what nerves use noradrenaline
Some nerves use noradrenaline in as their neurotransmitter. These are known as adrenergic nerves.
how noradrenalin works
Noradrenaline will only bind to receptors on the postsynaptic
neurone when its in high concentration.
Once the presynaptic knob stops releasing noradrenaline the levels will fall and then as the concetration has decreased it is released from the receptors.
It is then reabsorbed by the presynaptic knob and repackaged into vesicles.