calc bc
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Vertical asymptote
The line that a function can’t cross
Horizontal asymptote
The end behavior of a function
Linearization
Replace h with dx and remove the limit
f(x+dx)≈f(x)+f’(x)
L’Hospital’s Rule
If a limit gives 0/0 or inf/inf then we can take derivative of numerator and dominator and try again
Intervals of increase and decrease
Take the first derivative of the function and set it equal to zero
Function concavity
If the second derivative of a function is greater than 0, then the function is concave up, meaning that it’s increasing it decreasing by an increasing rate. And if a second derivative of a function is less than 0, function is concave down.
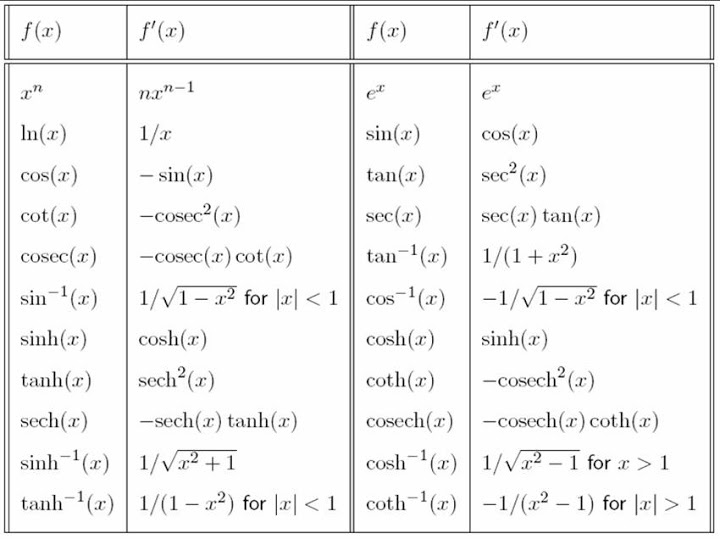
Riemann left sum
Change in top row multiplied by the bottom number excluding the last one on the right

Riemann right sum
Change in top row multiplied by the bottom number excluding the last one on the left
Trapezoidal sum
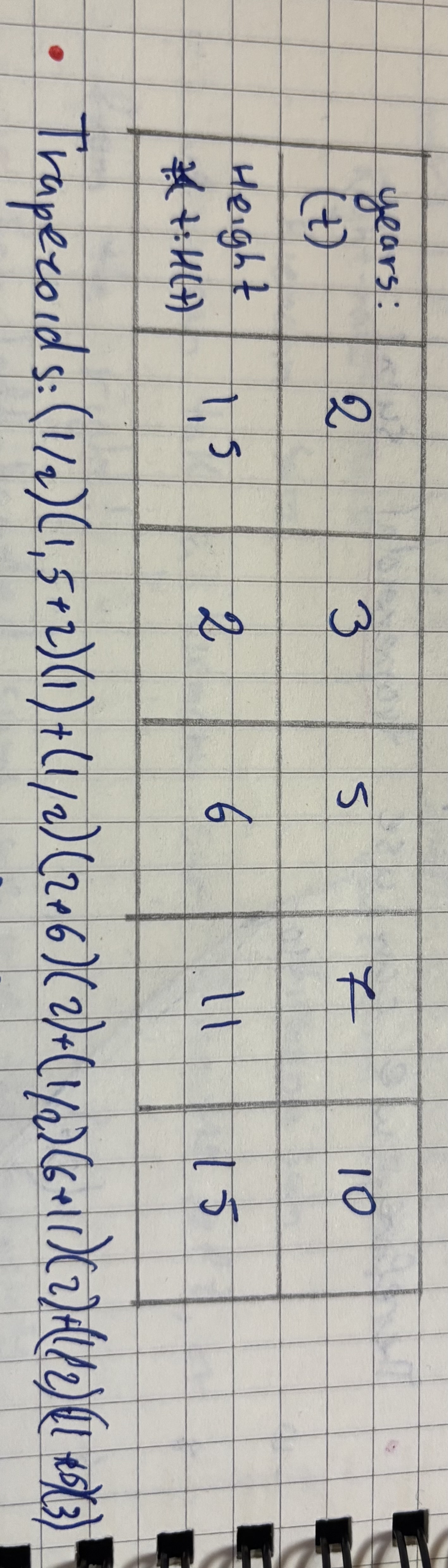
Slope fields
???
Differential equations(SIPPY)
•S: separate dx and dy on other sides
•I: integrate
•P: plus C
•P: plug in your initial condition
•Y: solve to find y
Average value of a function with integral

Area between two curves
Find the integrals and subtract the bottom function

Memory integrals

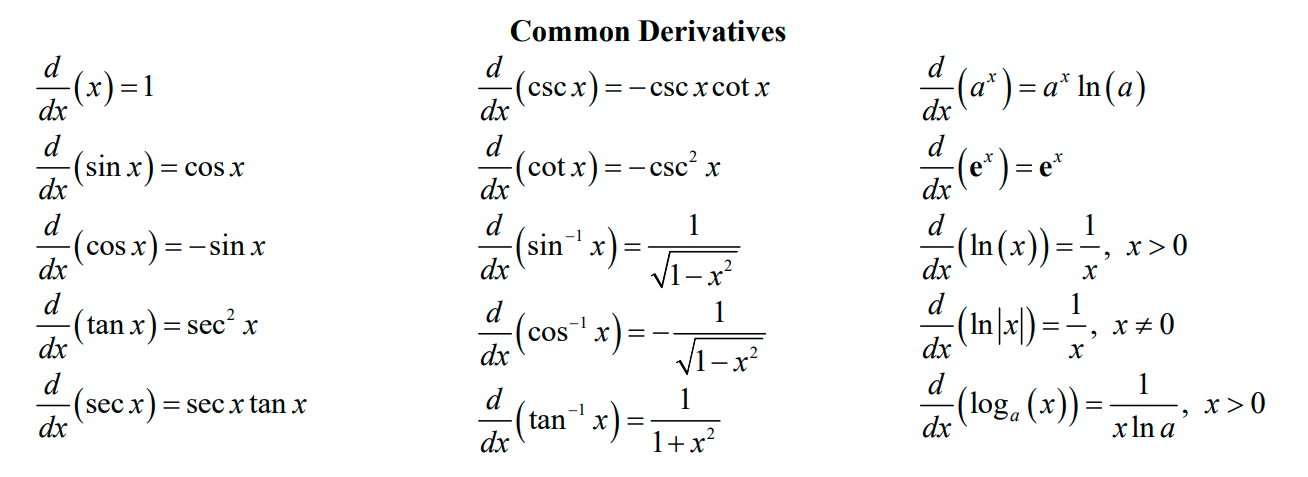
Memory derivatives