Pathology of the Kidneys and UUT Part 2 Flashcards
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC)
The most common of all renal neoplasms, accounting for 85-95% of cases.
Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC) Incidence
Twice as common in men >40 years, typically developing in the sixth or seventh decade of life.
Where are renal cell carcinomas found and where do they usually metastasize too?
Renal parenchyma; direct contact with the renal blood supply they metastasize via the renal veins (IVC→Heart→ body) and through direct invasion into adjacent structures
Why is it important to know the origin of a renal cell carcinoma?
If it started at the level of the renal veins and went superiorly then you know it’s from an RCC
Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC) Clinical Presentation
Often non-specific, but can include haematuria, flank pain, and a palpable mass.
Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC) US Presentation
Most RCCs are isoechoic, however can be hyperechoic.
Transitional Cell Carcinoma (TCC)
A rare type of kidney cancer, more common in the bladder and lower urinary tract but can also form in renal pelvis or calyces
Where do transitional cell carcinomas metastasize to?
Up or down the ureters not IVC - always extend the scan to the ureters and bladder
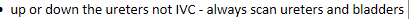
Transitional Cell Carcinoma (TCC) Clinical Presentation
Pain in the back, haematuria, and frequent urination.
Transitional Cell Carcinoma (TCC) US Presentation
Solid hypoechoic lesion/s originating within the renal pelvis or calyx.
Lymphoma
Renal lymphoma is usually seen as a part of spectrum of multi-systemic lymphoma; rarely may be seen as a primary disease
Lymphoma US Presentation
Solid hypoechoic lesion/s.
Wilm’s Tumour
Also known as nephroblastoma, most common cancer in children. It often affects children 3-4 years of age and is less common after 5 years of age.
Wilm’s Tumour Clinical Presentation
Constipation, abdominal pain, swelling or discomfort, nausea and vomiting, fever, and loss of appetite.
Wilm’s Tumour US Presentation
Large solitary, predominantly solid and echogenic mass that may contain cystic areas forming a multi-loculated mass, and can be present in utero.
Renal Metastases
The most common renal metastases arise from carcinomas (lung, colorectal, ENT, breast, soft tissue, and thyroid).
Renal Metastases Clinical Presentation
Flank pain, haematuria, weight loss.
Renal Metastases US Presentation
Variable depending on primary source of metastases