Pathology of the Kidneys and UUT Part 2 Flashcards
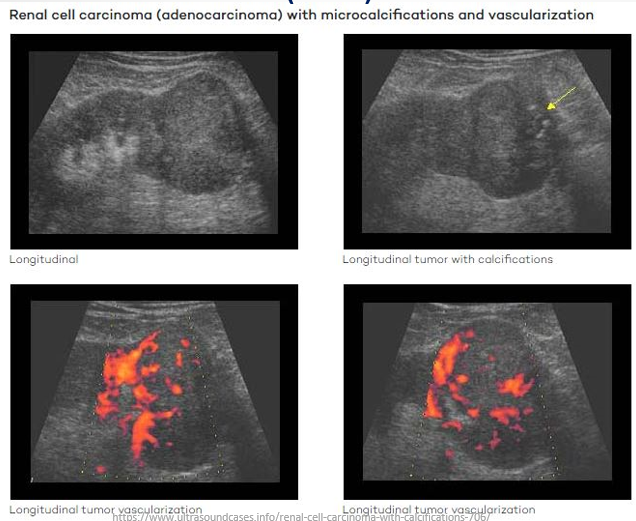
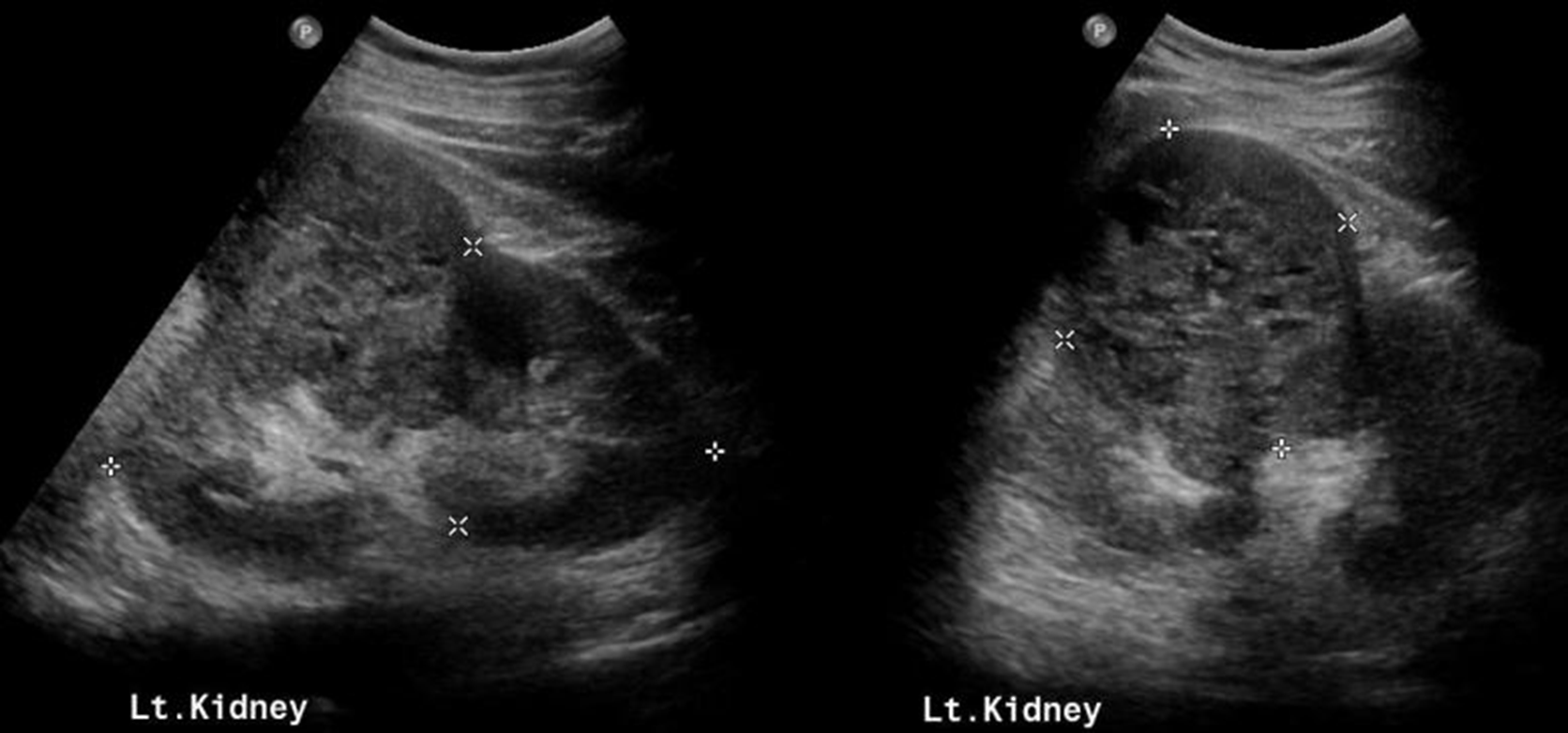
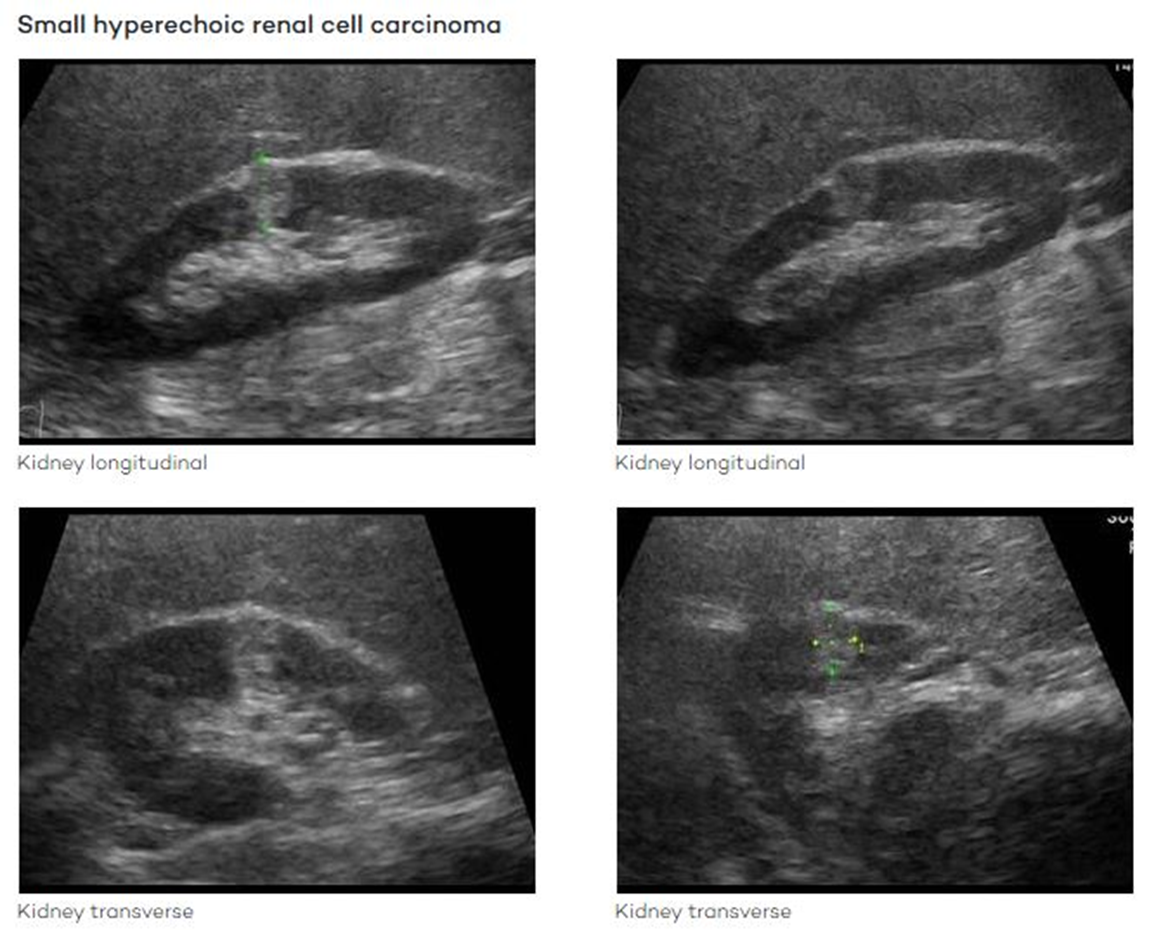
Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC)
Definition: Most common of all renal neoplasms (85-95%)
Demographics: More frequent in men, age >40 years, often develops in the sixth or seventh decade of life.
Because they are in the renal parenchyma; direct contact with the renal blood supply they metastasize via the renal veins (IVC→Heart→ body) and through direct invasion into adjacent structures
Important to know origin - if it started at the level of the renal veins and went superioly then you know it’s from an RCC
Clinical Presentation:
Often non-specific symptoms
Haematuria (blood in urine)
Flank pain and palpable mass
Ultrasound Presentation:
Most RCCs appear isoechoic but can also be hyperechoic.
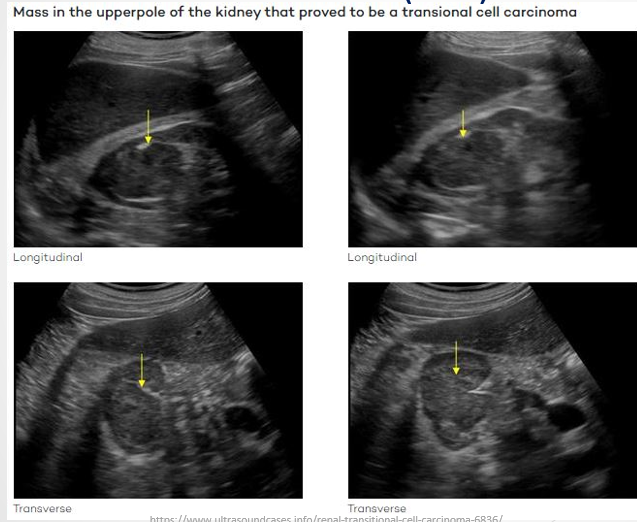
Transitional Cell Carcinoma (TCC)
Definition: Rare type of kidney cancer; more common in the bladder and lower urinary tract but can also form in renal pelvis or calyces
Metastasize up or down the ureters not IVC - always scan ureters and bladders - EXTEND THE EXAM
Clinical Presentation:
Pain in the back
Haematuria
Frequent urination
Ultrasound Presentation:
Solid hypoechoic lesions originating from the renal pelvis or calyces
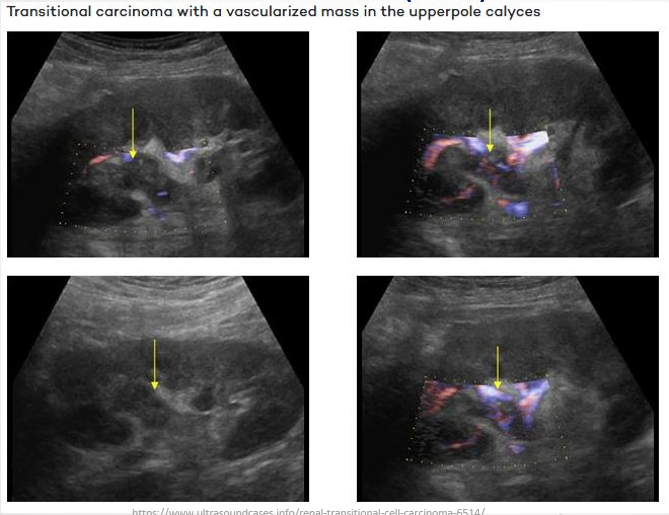
-
-
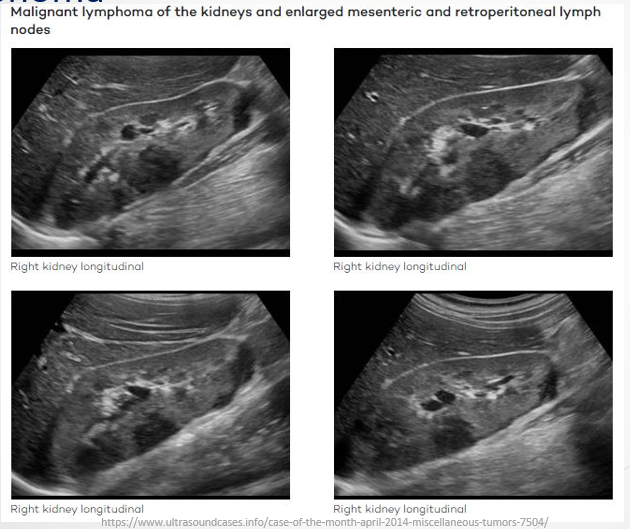
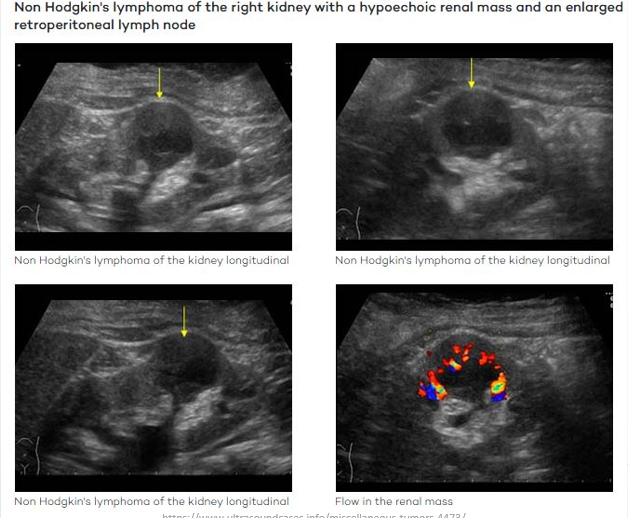
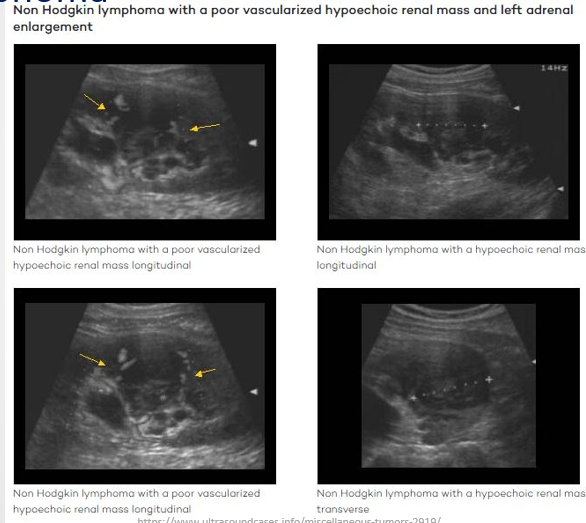
Lymphoma
Definition: Renal lymphoma typically occurs within a broader spectrum of systemic lymphoma; sometimes presents as a primary disease.
Ultrasound Presentation:
Appears as solid hypoechoic lesions.
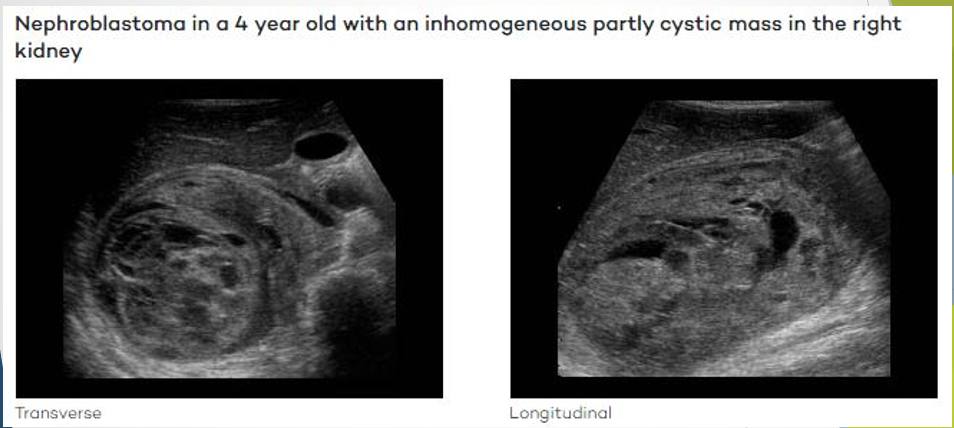
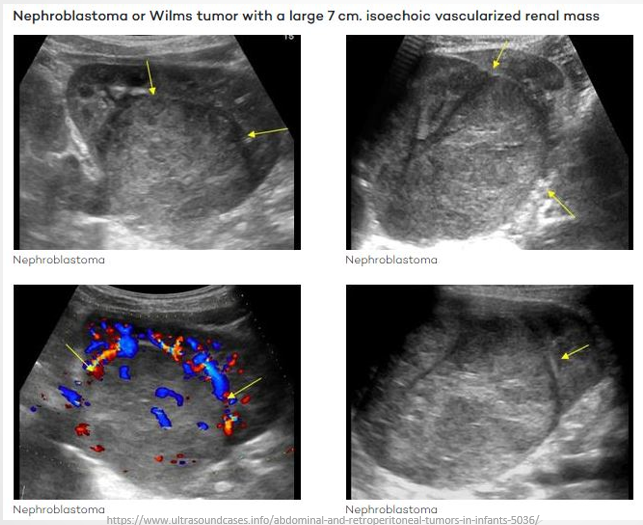
Wilm's Tumour
Also Known As: Nephroblastoma.
Demographics: Most common cancer in children, typically affects those aged 3-4 years; less common after age 5.
Clinical Presentation:
Symptoms include constipation, abdominal pain, swelling, nausea, vomiting, fever, and loss of appetite.
Ultrasound Presentation:
Large solitary, predominantly solid and echogenic mass.
May contain cystic areas, forming a multi-loculated mass.
Can be detected in utero.
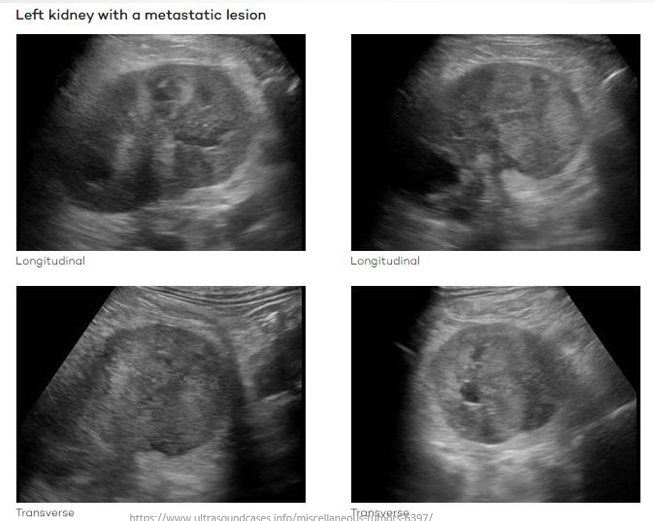
Renal Metastases
Definition: Most common renal metastases arise from carcinomas originating from various sites including lung, colorectal, ENT, breast, soft tissue, and thyroid cancers.
Clinical Presentation:
Flank pain
Haematuria
Weight loss
Ultrasound Presentation:
Variable imaging characteristics depending on primary source of metastases.
Review Questions
Describe using sonographic terminology pathologies mentioned in this lecture as well as differential diagnoses.
Given a solid hypoechoic lesion within the left kidney with internal vascular flow on color Doppler, what are the differential diagnoses?
Given a solid lesion within the calyx with internal colour Doppler flow, what would be the provisional diagnosis?