Lecture 6
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/62
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
1
New cards
Operative Instruments
Wide variety of dental instruments are used in dental procedures.
2
New cards
CARBON STEEL
STAINLESS STEEL
CARBIDE STEEL
STAINLESS STEEL
CARBIDE STEEL
Types of steel used to manufacture hand instruments
3
New cards
Carbon Steel
Hardness and sharpness
Susceptibility to corrosion and fracture
Susceptibility to corrosion and fracture
4
New cards
Stainless steel (Material of choice)
Bright in appearance
Does not corrode
Tends to lose their sharpness with repeated use
Can be sterilized by steam or dry heat
Does not corrode
Tends to lose their sharpness with repeated use
Can be sterilized by steam or dry heat
5
New cards
Carbide Steel
Hard and wear resistant
Brittle
Brittle
6
New cards
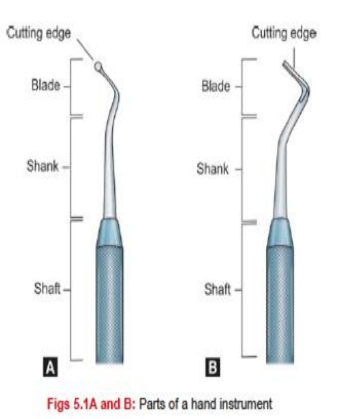
Handle/Shaft
Shank
Blade/NIB
Shank
Blade/NIB
Parts of Hand Instruments

7
New cards
Handle or Shaft
Where the instrument is held by the operator
Available in various sizes and shapes (Small,,medium or large, smooth or serrated)
Available in various sizes and shapes (Small,,medium or large, smooth or serrated)
8
New cards
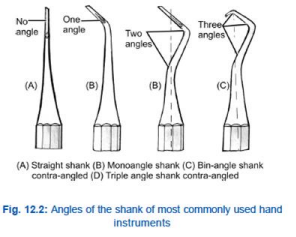
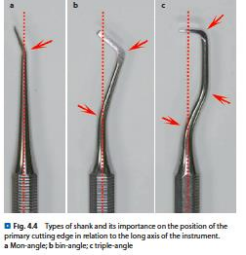
Shank
Part of the instrument that connects the blade to the handle; may be STRAIGHT or ANGLED
Black classified instruments on the basis of the number of shank angle as:
STRAIGHT → Having no angle
MON - ANGLE → One angle
BIN - ANGLE → two angles
TRIPLE - ANGLE → Three angles
Black classified instruments on the basis of the number of shank angle as:
STRAIGHT → Having no angle
MON - ANGLE → One angle
BIN - ANGLE → two angles
TRIPLE - ANGLE → Three angles
9
New cards
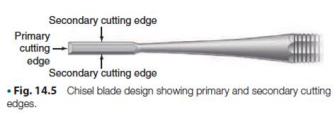
Blade or NIB
Working end of instrument
Connected to the handle by the shank;
Designed for a specific function
Connected to the handle by the shank;
Designed for a specific function
10
New cards
NIB
Part corresponding to the blade in a non-cutting instrument
11
New cards
Tip of the blade
Primary cutting edge (known as working end)
12
New cards
Side of the blade
Secondary cutting edges; cut tooth structures; bevels
13
New cards
Face
End of the nib or working surface
14
New cards
Cutting instruments
Non-cutting instruments
Non-cutting instruments
Categories of Hand Instruments
\
\
15
New cards
Cutting Instruments
Used to ASSIST IN THE DESIGN of the cavity preparation
REFINE AND DEFINE the cavity walls and margins
REFINE AND DEFINE the cavity walls and margins
16
New cards
Non-cutting instruments
Include basic examination instruments used to insert and finish amalgam and composite restorative materials.
17
New cards
Cutting Instruments (CHISEL family)
CHAD
Chisel, Hoes, Angle formers, Discoid and Cleoid
Chisel, Hoes, Angle formers, Discoid and Cleoid
18
New cards
Cutting Instruments (HATCHET family)
HEG
Hatchet, Excavators, Gingival trimmer
Hatchet, Excavators, Gingival trimmer
19
New cards

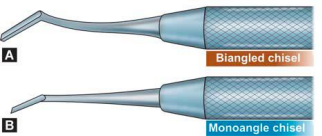
Chisel
Used to SHAPE AND PLANE (make surface flat or level) enamel and dentin walls of the cavity preparation
COMMON TYPES:
STRAIGHT CHISELS
BIN-ANGLE CHISEL
WEDELSTAEDT CHISELS
ANGLE-FORMED CHISELS
COMMON TYPES:
STRAIGHT CHISELS
BIN-ANGLE CHISEL
WEDELSTAEDT CHISELS
ANGLE-FORMED CHISELS
20
New cards
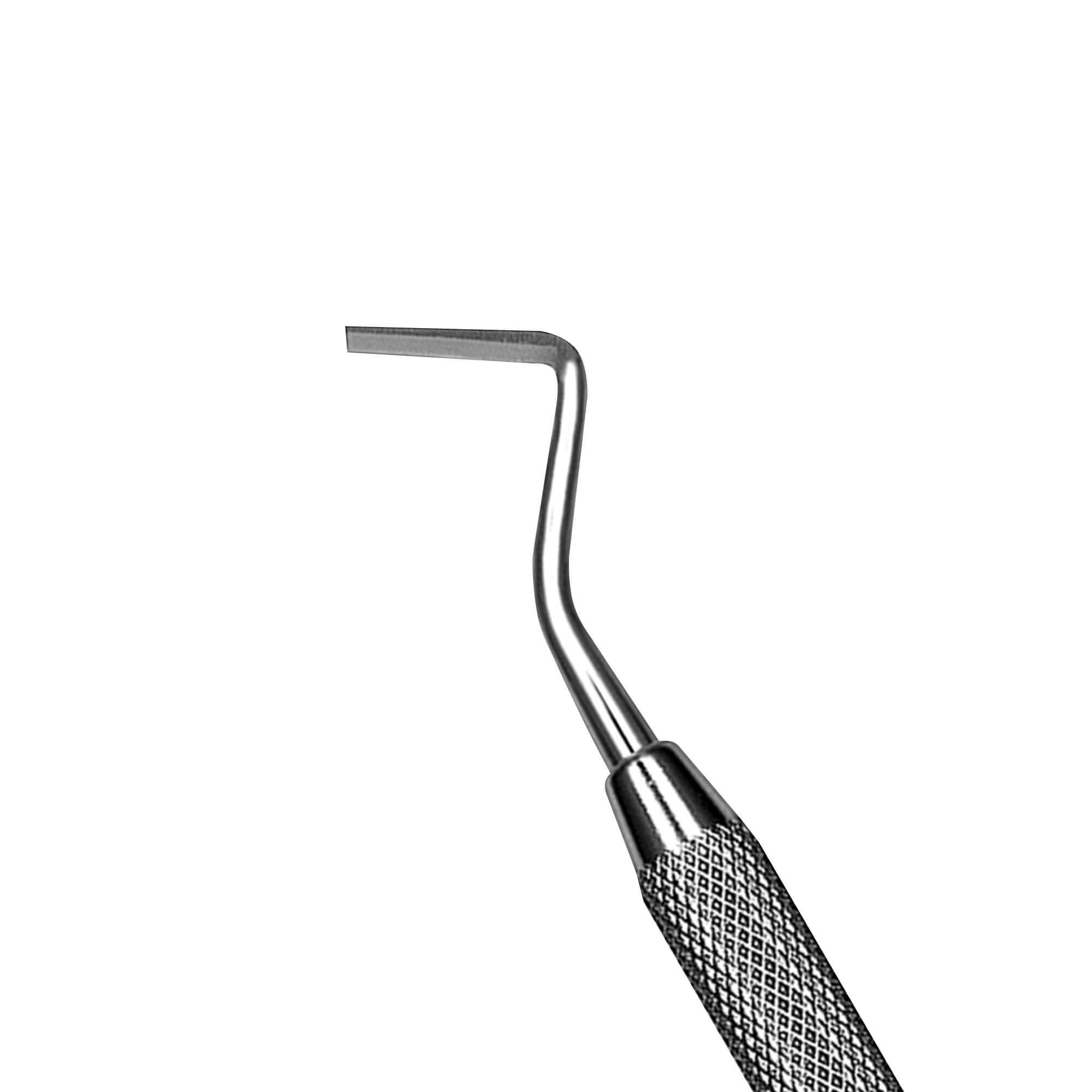
Hatchet
Sometimes called enamel hatchet
To cut, clean and smooth walls in cavity preparation
To REMOVE ENAMEL NOT SUPPORTED BY DENTIN
To cut, clean and smooth walls in cavity preparation
To REMOVE ENAMEL NOT SUPPORTED BY DENTIN
21
New cards

Hoes
To clean and smooth floor and walls in cavity preparation with a push-pull action.
22
New cards
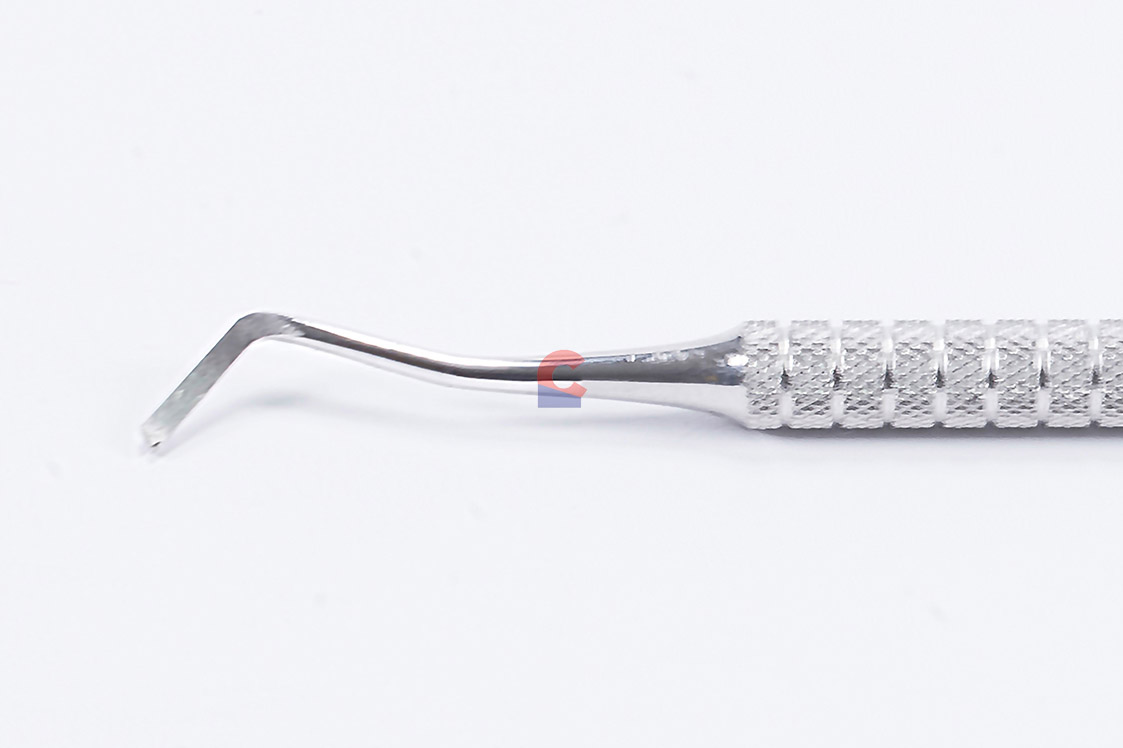
Gingival Margin Trimmers
To ELIMINATE UNSUPPORTED ENAMEL on gingival walls of proximal preparations; bevel the margin wall of the cavity preparation
SIMILAR IN DESIGN TO THE ENAMEL HATCHET except the blade is curved and the primary cutting edge is at an angle to the axis of the blade
DOUBLE-ENDED AND PAIRED INSTRUMENT; one end curves toward the left and the other end curves toward the right
SIMILAR IN DESIGN TO THE ENAMEL HATCHET except the blade is curved and the primary cutting edge is at an angle to the axis of the blade
DOUBLE-ENDED AND PAIRED INSTRUMENT; one end curves toward the left and the other end curves toward the right
23
New cards
Angle Formers
Used in a DOWNWARD PUSHING MOTION to form and define point angles and to sharpen line angles
SIMILAR TO THE HOE except the cutting edge is angled liked the gingival margin trimmer
SIMILAR TO THE HOE except the cutting edge is angled liked the gingival margin trimmer
24
New cards
Excavators
Also known as SPOON EXCAVATOR
Used to REMOVE CARIOUS MATERIAL AND DEBRIS from the teeth
Working end that is CIRCULAR OR ELONGATED
Used to REMOVE CARIOUS MATERIAL AND DEBRIS from the teeth
Working end that is CIRCULAR OR ELONGATED
25
New cards
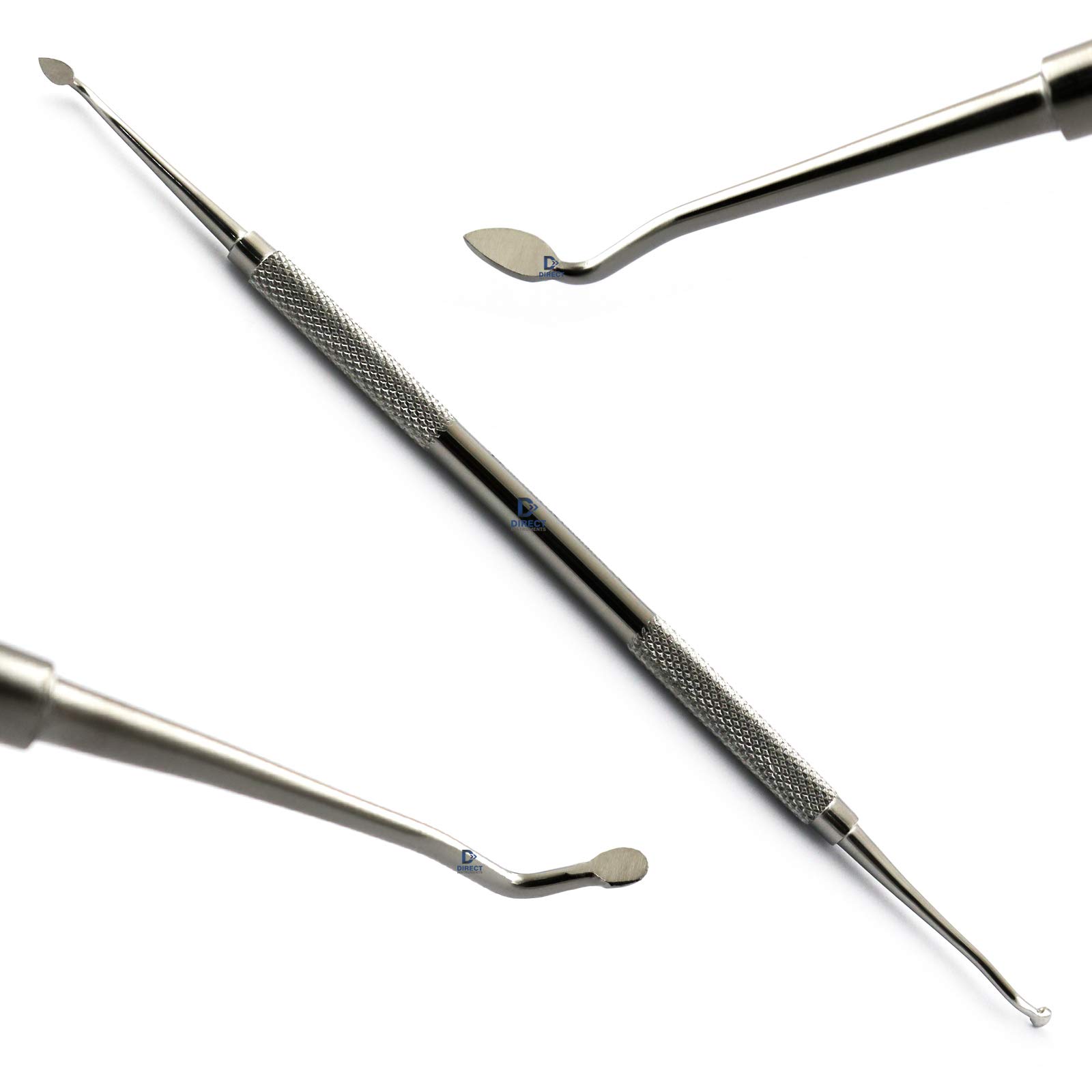

Cleoid - Discoid
It is MODIFIED CHISEL with different shape of cutting edges
In cleoid, it is CLAW-LIKE in discoid it is DISK-LIKE and the edge is rounded
Used for REMOVING CARIES and CARVING AMALGAM OR WAX PATTERN
In cleoid, it is CLAW-LIKE in discoid it is DISK-LIKE and the edge is rounded
Used for REMOVING CARIES and CARVING AMALGAM OR WAX PATTERN
26
New cards
What are non-cutting instruments?
Basic Instruments: Mouth Mirror, Explorer, Cotton
Burnishers
Carriers
Carvers
Composite Instrument
Condensers
Files
Finishing knives
Plastic filling Instruments
Burnishers
Carriers
Carvers
Composite Instrument
Condensers
Files
Finishing knives
Plastic filling Instruments
27
New cards
Non-cutting instruments
AMALGAM CONDENSER
MIRRORS
EXPLORERS
PROBES
MIRRORS
EXPLORERS
PROBES
28
New cards
Other cutting instruments
KNOVES
FILES
SCALERS
CARVERS
FILES
SCALERS
CARVERS
29
New cards
Rotary instruments
Operated in hand-piece
30
New cards
Nomenclature for the instruments
ORDER
SUBORDER
CLASS
SUBCLASS
SUBORDER
CLASS
SUBCLASS
31
New cards
Order
FUNCTION OR PURPOSE of the instrument
example:
EXCAVATOR
CONDENSER
example:
EXCAVATOR
CONDENSER
32
New cards
Suborder
POSITION, mode or manner of use
example:
PUSH
PULL
example:
PUSH
PULL
33
New cards
Class
Design or form of the working end
example:
HATCHET
SPOON EXCAVATOR
example:
HATCHET
SPOON EXCAVATOR
34
New cards
Subclass
Shape of the shank
example:
BINDANGLE
CONTRA – ANGLE
example:
BINDANGLE
CONTRA – ANGLE
35
New cards
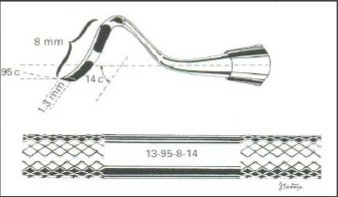
Instrument Formula #3 FORMULA
Used instruments in which cutting edge is at right angle to the long axis of the blade.
1st # Width of the blade or primary cutting edge in mm
2nd # Length of the blade in mm
3rd # Angle of the blade against long axis of handle
1st # Width of the blade or primary cutting edge in mm
2nd # Length of the blade in mm
3rd # Angle of the blade against long axis of handle
36
New cards
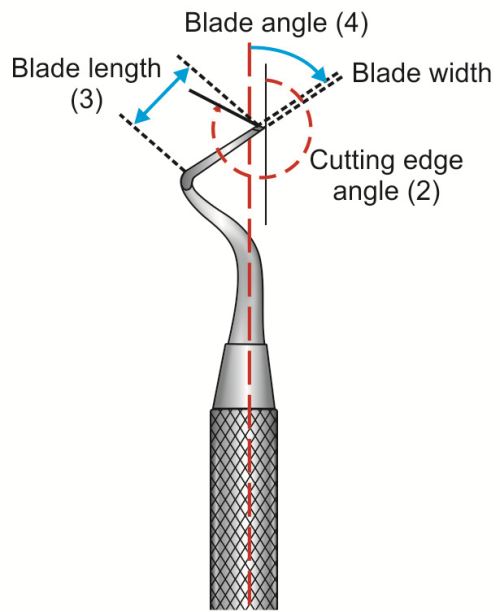
Instrument Formula #4 FORMULA
Used for the instruments in which primary cutting edge is not at right angle to the long axis of the blade.
1st # Width of the in tenths of mm
2nd # Cutting edge angle
3rd # Length of the blade in mm
4th # Angle of the blade against long axis of the handle
1st # Width of the in tenths of mm
2nd # Cutting edge angle
3rd # Length of the blade in mm
4th # Angle of the blade against long axis of the handle
37
New cards
\
EXAMINATION
HAND CUTTING (manual)
RESTORATIVE
ACCESSORY
EXAMINATION
HAND CUTTING (manual)
RESTORATIVE
ACCESSORY
Classification of General Dental Instruments
38
New cards
Examination Instruments
Allow the operator to thoroughly examine the health status of the oral cavity
39
New cards
Hand (Manual) Cutting Instruments
Allow the operator to remove decay manually and to smooth, finish, and prepare the tooth structure for its final restoration
40
New cards
Restorative Instruments
Allow the operator to “RESTORE” a tooth by placing, condensing, and carving a dental material to the original anatomy of the tooth structure.
41
New cards
Accessory Instruments
Are miscellaneous instruments and items that are used to compete a procedure.
42
New cards
\
Used for examining the teeth but are also common to all tray set-ups.
Mouth Mirror
Explorer
Cotton Pliers
Periodontal Probe - optional
Used for examining the teeth but are also common to all tray set-ups.
Mouth Mirror
Explorer
Cotton Pliers
Periodontal Probe - optional
Basic Examination Instruments
43
New cards
\
INDIRECT VISION
LIGHT REFLECTION
RETRACTION
TISSUE PROTECTION
INDIRECT VISION
LIGHT REFLECTION
RETRACTION
TISSUE PROTECTION
Use for the mouth mirror
\
\
44
New cards
Restorative Instruments
Used to place, condense, and carve the restorative dental materials back to normal anatomy of the tooth.
AMALGAM CARRIER
CONDENSER
BURNISHER
CARVERS
AMALGAM KNIFE
COMPOSITE-PLACEMENT INSTRUMENTS
AMALGAM CARRIER
CONDENSER
BURNISHER
CARVERS
AMALGAM KNIFE
COMPOSITE-PLACEMENT INSTRUMENTS
45
New cards

Amalgam Carrier
To carry & dispense amalgam into the cavity preparation
46
New cards
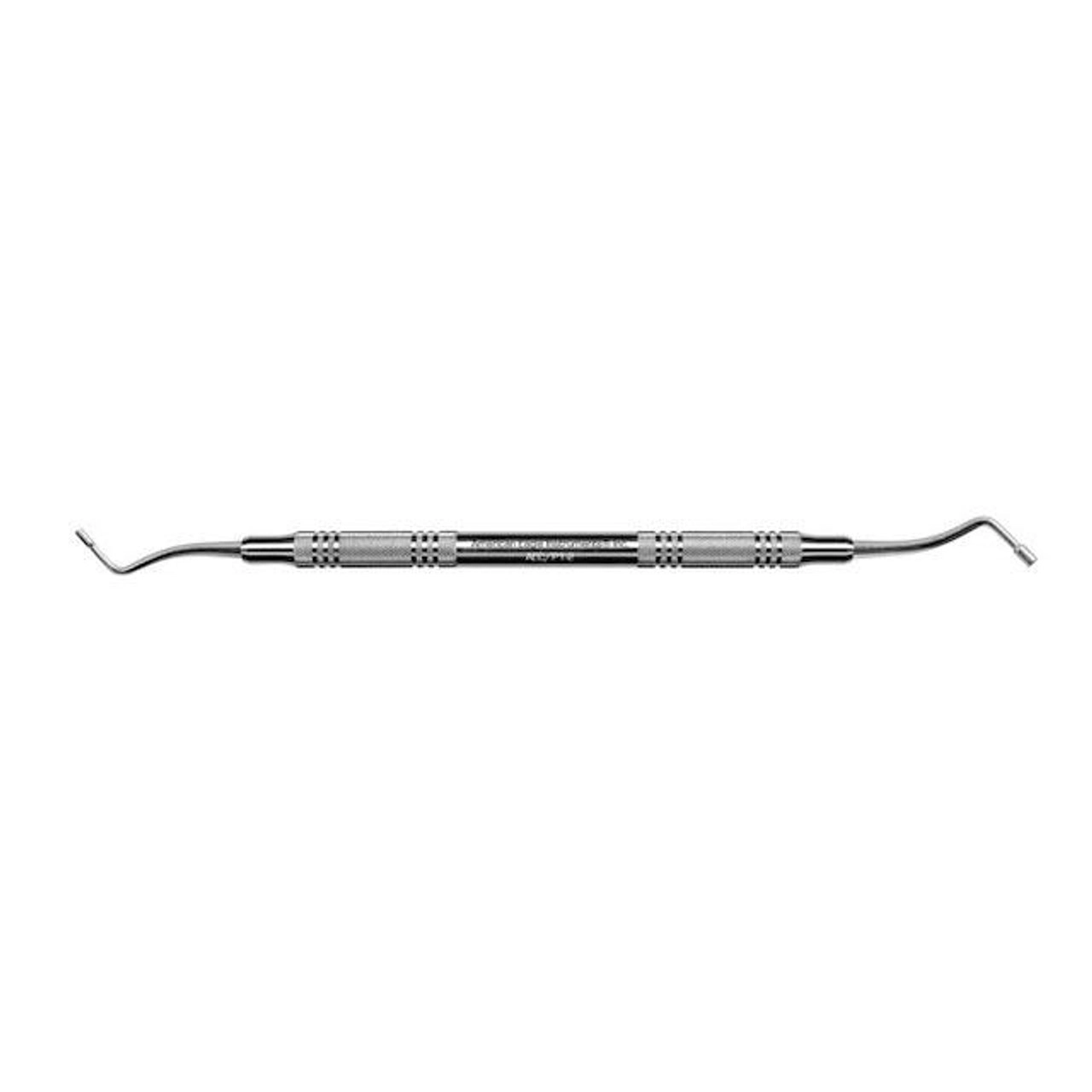

Condenser
Also known as PLUGGER
Used to condense (pack down) freshly placed amalgam into the preparation
Used to condense (pack down) freshly placed amalgam into the preparation
47
New cards
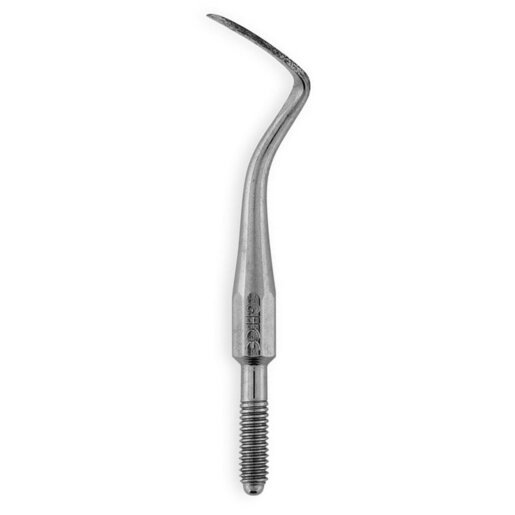
Burnisher
Used to smooth rough margins of the restoration and to shape metal matrix bands
48
New cards
Carvers
Used to remove access restorative material and to carve tooth anatomy in the restoration before the material hardens.
49
New cards
Amalgam Knife
For the removal of excess restorative material along the margin where the material and the tooth structure meet
50
New cards
Composite Placement Instruments
For the placement of composite restorative materials
Made from anodized aluminum or Teflon.
These materials prevent the composite material from being scratched
Made from anodized aluminum or Teflon.
These materials prevent the composite material from being scratched
51
New cards
\
CEMENT SPATULA
SCISSORS
AMALGAM WELL
HOE PLIERS
ARTICULATING PAPER HOLDER
CEMENT SPATULA
SCISSORS
AMALGAM WELL
HOE PLIERS
ARTICULATING PAPER HOLDER
Accessory Instruments
52
New cards
\
AMALGAM CARRIER
CONDENSER
BURNISHERS
AMALGAM CARVERS
˃ HOLLENBACK (Contour carver)
˃ DISCOID – CLEOID
˃ INTERPROXIMAL (Class II preparations)
AMALGAM CARRIER
CONDENSER
BURNISHERS
AMALGAM CARVERS
˃ HOLLENBACK (Contour carver)
˃ DISCOID – CLEOID
˃ INTERPROXIMAL (Class II preparations)
Hand Instruments for Amalgam Restorations
53
New cards
Amalgam Carriers
Transfers amalgam to cavity preparation.
Aids in dispensing and placement of amalgam into cavity preparation.
Can be used to begin condensation of amalgam
Aids in dispensing and placement of amalgam into cavity preparation.
Can be used to begin condensation of amalgam
54
New cards
Amalgam Condensers
Used to condense amalgam into all areas of preparation
Types:
ROUND
ELLIPTICAL
Types:
ROUND
ELLIPTICAL
55
New cards
Burnishers
Conforms amalgam to margins
Aids initial shaping of restorations
Types:
ACORN
ROUND
FOOTBAL
Aids initial shaping of restorations
Types:
ACORN
ROUND
FOOTBAL
56
New cards
Carvers
Used to place distinguished grooves and fossae into amalgam restoration types:
DISCOID – CLEOID
HOLLENBACK (contour carvers)
INTERPROXIMAL (for Class II preparations)
DISCOID – CLEOID
HOLLENBACK (contour carvers)
INTERPROXIMAL (for Class II preparations)
57
New cards
\
MODIFIED PEN Grasps
INVERTED PEN Grasps
PALM and THUMB Grasps
MODIFIED PALM and THUMB Grasps
MODIFIED PEN Grasps
INVERTED PEN Grasps
PALM and THUMB Grasps
MODIFIED PALM and THUMB Grasps
Instrument Grasps
58
New cards
Modified Pen Grasps
Provides four (4) points of support
Allows considerable force to be applied to instrument
Provides more control of measurement
Allows considerable force to be applied to instrument
Provides more control of measurement
59
New cards
Invented Pen Grasps
This grasps is used mostly for tooth preparations utilizing the lingual approach on anterior teeth.
60
New cards
Palm and Thumb Grasps
This grasps has limited use, such as preparing incisal retention in a class III preparation on a maxillary incisor.
61
New cards
\
CONVENTIONAL PEN GRASPS
MODIFIED PEN GRASPS
CONVENTIONAL PEN GRASPS
MODIFIED PEN GRASPS
Grasping Instruments
62
New cards
Conventional Pen Grasps
Used for writing
63
New cards
Modified Pen Grasps
Used in dentistry