IB HL BIO YR 1 UNIT THREE
1/117
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
118 Terms
carbon compounds
building blocks of life
four covalent bonds
can form chains and rings
variety: length, arrangement (linear, branching patterns, rings), number and locations of double and triple bonds
macromolecules
large molecules made up of monomers
crucial role in structure/function of living organisms
formed by condensation reaction
broken down into monomers through hydrolysis
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
monomers
individual subunits that can be linked together to form polymers
condensation reaction
polymerisation reaction in which two molecules join together
one loses hydroxyl group (-OH)
one loses hydrogen atom (-H)
forms water molecule
polysaccharide
more than two glucose molecules join together
long chains of monosaccharides connected with glycosidic linkages
energy storage (starch & glycogen)
structural material (cellulose & chitin)
complex carbohydrates
hydrolysis
reverse reaction for condensation
water molecules used to break covalent bonds between monomers
carbohydrates
macromolecules essential to life
organic molecules with carbons, hydrogens, & oxygens
C×n H×2n O×n
monosaccharide
fundamental biological molecules
serve as a source of energy for cells
involved in various cellular processes
single sugar unit that can't be broken down by hydrolysis
classified by number of carbon atoms and locations of the carbonyl group
triose (3 carbons), pentose (5 carbons), hexose (6 carbons)
can be linear or ring structure
glucose
hexose, C6 H12 O6
most common monosaccharide found in nature
two isomers which vary in the orientation of the hydroxyl group on the first carbon atom (alpha-glucose and beta-glucose)
soluble molecule because of polarity (like dissolves like, polar dissolves polar), makes it easily transported in blood plasma
can be oxidized to create ATP energy for cell during cellular respiration
stable, great material to build polysaccharides (starch, glycogen, cellulose)
alpha glucose
hydroxyl group on the first carbon atom oriented downwards
beta glucose
hydroxyl group on the first carbon atom oriented upwards
starch
serves as primary storage of glucose/energy in plants
two types (amylose and amylopectin)
compact structure allows for efficient storage
relatively insoluble
polymer of alpha-glucose
amylose
linear polysaccharide
made of alpha-glucose monomers
coiled structure
amylopectin
highly branched polysaccharide
alpha-glucose
complex 3d structure allows for more efficient glucose storage
major component of starch
glycogen
serves as primary glucose/energy storage in animals
branched polymer of alpha-glucose molecules
stored mainly in liver and muscle cells
mostly insoluble
cellulose
complex polysaccharide
polymer of beta-glucose, glycosidic linkages are different (humans are unable to break them down)
structural polysaccharide found in plant cell wall
straight long unbranched chains
glycoproteins
proteins that have one or more carbohydrates attached to them
sugar-protein molecule
cell signaling and communication (cell-cell recognition, receptors, logands, structural support)
receptors for chemical signals/chemical signals for other cells
provide structural support
lipids
class of macromolecule that are united because of their hydrophobic properties
non-polar
not polymers, not made of monomers
low solubility in water (hydrophobic, can’t form hydrogen bonds with water)
dissolve in non-polar solvents
very low proportion of oxygen to carbon
triglycerides
type of lipid
consumed in food (butter, lard, ghee)
synthesized by liver
formed by condensation of one glycerol molecule and three fatty acid molecules (ester bond)
effective thermal insulators in many organisms (help regulate body temperature)
wax
class of diverse lipids
generally long hydrocarbon chains
completely water insoluble
low melting point
solid at room temperature
ex: bee honeycombs, plants/animals use waxes to waterproof
steriods
type of lipid
four carbon rings fused together (three hexose rings and one pentose ring)
naturally occurring hormone
regulate physiological functions
non-polar
can pass through cell membrane
functional groups added to framework to give different properties
phospholipids
type of lipid
forms by condensation
one glycerol molecule modified with a phosphate group and two fatty acids (ester bond, formed during condensation reactions)
negatively charged phosphate interacting with water molecules
head = hydrophilic, tail = hydrophobic, amphipathic
major component of cell membranes in the form of a phospholipid bilayer
saturated fatty acids
straight linear shape
all single bonds
packed tightly together
solid at room temperature
typically from mammals
high melting point
aka “fats”
unsaturated fatty acids
single and double bonds
bends and kinks in chain which prevent packing closely together
liquid at room temperature
less viscous
lower melting points (more double bonds = lower melting point)
can be monounsaturated or polyunsaturated
monounsaturated fats
unsaturated fatty acid with one double bond
polyunsaturated fats
unsaturated fatty acid with more than one double bonds
endotherms
organisms that regulate body temperature
rely on metabolic reactions to generate heat and maintain constant internal temperature
require constant supply of energy (food)
phospholipid bilayer
major structural component of cell membrane
made of double layer of phospholipids
hydrophilic heads on either side of membrane
hydrophobic tails in the middle
covalent bond
electron pairs are shared between 2 atoms
hydrogen bond
interaction between slightly positing hydrogen and slightly negative other atom
ionic bond
electrons are completely transferred from one atom to another
organic chemistry
study of compounds that contain carbon
carbon
forms covalent bonds
has tetravalence
tetravalence
ability to form total of 4 covalent bonds
valence electrons
electrons in outermost shell
valence
number of covalent bonds an atom can form
carbon skeleton
provides framework for other atoms/functional groups to attach to
hydrocarbons
molecules that only contain carbon and hydrogen
functional groups
add different chemical properties to the molecule
metabolism
all chemical reactions in a cell
anabolic/catabolic pathways
anabolic pathways
synthesize (build up) large molecules from smaller ones
many monomers → polymer (forms bonds between monomers)
condensation reactions (dehydration synthesis)
endergonic (stores/requires energy)
catabolic pathways
break down complex molecules into simpler ones
polymer → many monomers (breaks bonds between monomers)
hydrolysis reactions
exergonic (releases energy)
monomers
small building block molecules
make up polymers
nucleic acid → nucleotide
carbohydrate → monosaccharide
protein → amino acid
polymers
large molecules consisting of the same/similar building blocks (monomers)
nucleic acid → polynucleotide
carbohydrate → polysaccharide
protein → polypeptide
simple sugars
monosaccharides and disaccharides
polusaccharides
energy storage
structural building material
electronegativity
“c
non-polar covalent bond
almost same electronegativity
electrons are evenly shared
C-H bond
polar covalent bond
different electronegativity
electrons shared unequally
higher electronegativity side is slightly negative
lower electronegativity side is slightly positive
basis of ability to form hydrogen bonds, O-H & N-H
hexose
6 carbons in ring
glucose, galactose (dairy), fructose (fruit)
pentose
5 carbons in ring
ribose
deoxyribose
disaccharide
2 monosaccharides (can be same or different) join during condensation reaction
connected by glycosidic linkages
simple sugar
sucrose
disaccharide
table sugar
glucose + fructose
lactose
disaccharide
sugar in milk
glucose + galactose
maltose
disaccharide
sugar in malt
glucose + glucose
chitin
structural polysaccharide
found in cell walls of fungi & exoskeletons of arthropods
polymer of modified glucose
ABO blood typing
determined by specific glycoproteins on surface
hydrophobic
does not interact with water
cant form hydrogen bonds with water
hydrophillic
interacts with water
can form hydrogen bonds with water
amphipathic
having both hydrophilic and hydrophobic parts
proteins
complex macromolecules
composed of 1+ chains of amino acids
made of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen (CHON)
do just about everything in terms of function
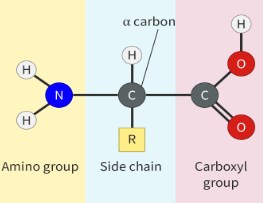
amino acids
monomers that are used to make proteins
20 unique ones
central carbon (alpha carbon) is covalently bonded to carboxyl group (-COOH) amino group (-NH2) hydrogen atom (-H) and a side chain (-R)
join together through a condensation reaction (when two join, one water molecule is released)
essential amino acids
amino acids that your body can't produce and you must obtain from food
necessary for proper growth, maintenance, and repair
animal proteins are best source, most easily absorbed
non-essential amino acids
can be produced by body from other amino acids or by breaking down proteins
have important functions
codons
groups of three nucleotides that specify the type of amino acid/stop signal required
makes up genetic code
64 different total codons, only 20 amino acids, causes silent mutations
silent mutations
a change in the DNA sequence that does not result in a change in the amino acid sequence
polypeptide
chain of 3+ amino acids
linked together by peptide bonds
makes up proteins
amino end = N-terminus
carboxyl end = C-terminus
ex: lysozyme, glucagon, myoglobin, alpha-neurotoxins
lysozyme
enzyme
129 amino acids
present in tears and saliva
antimicrobial
alpha-neurotoxins
group of polypeptides
60-75 amino acids
snake venom
target-disrupt nervous system
glucagon
hormone
29 amino acid residues
regulates blood sugar levels
myoglobin
type of protein
153 amino acid residues
oxygen-binding
stores/releases oxygen to muscle fibers
denaturation
process in which structure of a protein is altered, causing it to lose function
caused by change in pH or temperature
if temperature gets too high or pH gets too low (acidic) or too high (basic), the structure will unravel and change, which changes function
primary structure of proteins
specific sequence of amino acids joined together to form polypeptide chain
position of each amino acid determines 3D structure
secondary structure of proteins
refers to local folding patterns within polypeptide chain
alpha helices and beta-pleated sheets
hydrogen bonding between backbone (not side chains) causes coils and pleats
alpha helix
secondary structure of proteins
forms coils
hydrogen bond forms between amine hydrogen of one amino acid and carboxyl oxygen of another amino acid that is four residues away
beta-pleated sheets
secondary structure of proteins
pleated sheet-like structure
sections of polypeptide chain are parallel
hydrogen bonds form between adjacent strands
tertiary structure of proteins
further folding of the polypeptide
dependent on interaction between R-groups
includes hydrogen, ionic, and disulfide covalent bonds and hydrophobic interactions
stabilize structure
hydrogen bonds (tertiary structure of proteins)
holds distant regions of polypeptide chain together
stabilizes
ionic bonds (tertiary structure of proteins)
forms between oppositely charged ions
can undergo binding (positive charge) or dissociation (negative charge) of hydrogen ions
stabilize overall protein
disulfide covalent bonds (tertiary structure of proteins)
forms between pairs of cysteine amino acid residues
forms covalent bonds that maintain overall 3D shape
hydrophobic interactions (tertiary structure of proteins)
occur between non-polar amino acids
stabilize tertiary/quaternary structures
quaternary structure
arrangement and interaction of 2+ polypeptide chains
forms functional protein
non-covalent bonds and interactions
ex: hemoglobin and rubisco
hemoglobin
conjugated protein
transports oxygen and binds oxygen to lungs
has a quaternary structure (two alpha chains and two beta chains)
non-conjugated proteins
consist of only polypeptide subunits
conjugated proteins
have non-protein components (metal ions or carbs) in addition to polypeptide subunits
globular proteins
complex prooteins
usually spherical in shape with irregular folds
held together by hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic interactions and disulfide bonds
soluble in water
insulin
hormone
regulates amount of glucose in blood
produced by pancreas
hydrophilic exterior and hydrophobic interior
globular shape
fibrous proteins
simpler than globular proteins
long narrow shape
repeating structures designed for strength/stability
insoluble in water
collagen
main component of connective tissue in animals (skin, cartilage, bones)
3 polypeptide chains
triple helix structure
contain proline/hydroxyproline residues
strong and flexible
cis-unsaturated fatty acids
type of fatty acid
hydrogens attached to double-bonded carbon are on the same side
created bend
harder to pack
liquid at room temperature
typically from fish and plants
low melting point
aka “oils”
trans-unsaturated fatty acids
type of fatty acid
hydrogens attached to double-bonded carbon are on opposite sides
no bend
easier to pack
solid at room temp
produced during industrial process (hydrogenation)
functions of fats/oils
long term energy storage, energy released slowly
insulation, reduce heat loss
protection/cushioning/support of internal organs
adipose tissue
fat storage in mammals
can be broken down to provide cell with ATP energy
fats/oils in plants
used for long term energy storage
high levels in seeds to provide seeding with energy until photosynthesis
cholesterol
steroid
found in animal cell membranes
reduces permeability of cell membrane by reducing fluidity at high temps
increases permeability of cell membrane by increasing fluidity at lower temps
modified into other steriods
steroid hormones
class of hydrophobic hormone molecules that control wide range of physiological functions
hydrophobic so can easily pass through cell membrane to give instructions
ex: estrogen and testosterone
catalyst
substance that increases rate of (speeds up) chemical reactions
is not changed or used up in the reaction
enzymes
biological catalysts
speed up metabolic reactions in all living organisms
different enzymes required by different organisms
complex globular proteins
catalyze metabolic reactions by binding to a substrate(s)
lower activation energy, allows reaction to happen faster
most reactions in living organisms would not occur without enzymes
active site
where catabolic reactions occur
where the substrate minds
order of amino acids in polypeptide chain determines 3D structure
protein folding ensures overall 3D structure is correct
side chain
aka r-group
20 different side chains
gives amino acid properties
hydrophobic