business law cases
1/102
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
103 Terms
what brought about the case law that items displayed on shelves of shops with a price tag are invitations to treat not offers
Pharmaceutical Society of Great Britain v Boots Cash Chemists (1953

carlill v carbolic smoke ball co (1893)
The carbolic smoke ball was a product released and was advertised that anyone who used the ball three times daily for 2 weeks period and contracted influenza the would be rewarded 100 pound carlill did this and still contracted influenza and they refused to pay
Carlill v carbolic smoke ball outcome
Court of appeal said it was valid contract as 1000 being placed in bank demonstrated company sincerity in paying 100 and carlill acceptance was evident from purchasing and using so it is possible to make offer to the entire world and anyone can accept it
What case further supported the law of items displayed are invitation to treat
Fisher v bell case (1961)where a shopkeeper mr bell displayed a flick knife with a price tag and police officer fisher prosecuted bell under the restriction of the offensive weapons act 1959 it was an offence to offer for sale a flick knife

Leftkowitz v great Minneapolis surplus stores (1957)
Company placed advertisement for 2 mink scarves and stole sold for 1 dollar at Saturday 9am leftkowitz came and they refused to sell as it was only available to women
What case law did the leftkowitz v great Minneapolis surplus store (1957) bring
An advertisement in newspaper or shop window can be a offer instead of invitat To treat if it the offer is clear definite and explicit and leaves nothing open for negotiation

What case law did the partridge v Britten 1968 bring about
An advertisement in a newspaper, magazine, a billboard, on television etc is considered a invitation to treat
Payne v cave (1789)
Me cave made highest bid for good at Payne auction however before fall of the auctioneer hammer(before accepted bid) cave withdrew the bid he made
What case law did paybe v cave (1789) bring about
That the auctioneer request for bids is a invitation to treat therefore a bid at an auction is an offer which can be withdrawn by bidder at any time before acceptance

Harris v Nickerson (1872-73)
Nickerson was a auctioneer who advertised auction to include office furniture me Harris travelled for this auction but the furniture was not auctioned and he took Nickerson to court to recover losses of time and travel expenses
What case law did the Harris v Nickerson (1872-73) bring about
Auctions are invitation to treat and advertising products to be auctioned does not create obligation that items will be there or offers would be accepted
What’s a sealed bid auction
Each bidder submits bid secretly in writing and no one knows the other bids until auction closes
Harvela investment ltd v royal trust co of Canada ltd (1986)
Shares in royal trust sold through sealed competitive tender harvela offered 2175000 dollars where as second tender offered 2100000 dollars or 101000 above any other offer
What case law did harvela investments ltd v royal trust co of Canada Ltd (1986)
In a sales bid auction where the highest bid is accepted only fixed bids are valid( can’t say I’ll pay x amount more then the highest bidder)

Blackpool and Clyde Aerol ltd v Blackpool bc (1990)
Blackpool borough council invited bidders to bid for license to operate pleasure flights. Blackpool and Clyde made a bid but due to a mistake from the council it was treated as late so was not considered
What case law did Blackpool and flyde aero Ltd v Blackpool bc (1990) bring about
That even thought there was no obligation to accept a specific tender (bid) a call for tender can establish a collateral(seperate contract) for a bid to be considered (in this case it was all bids submitted on time would be considered)

Harvey v Facey (1893)
Me facey and wife owned property called bumper they got telegram from Harvey asking to sell it to them they replied lowest price is 900 and Harvey agreed to buy for 900 but they didn’t reply and did not sell to him
What case law did the Harvey v facet (1893) bring about
The offeror must show a clear intention to be legally bound by the terms as soon as they are accepted
Gibson v Manchester cc (1979)
Robert Gibson was a tenant of a council house under Manchester City control and 1970 wrote to Gibson informing him they prepared to sell house for 2725 less 20 percent on 18 march 1971 he replied requesting to purchase house but political control of council changed and they didn’t want to sell
What case law did Gibson v Manchester(1979) bring about
A request for information is not an offer capable of acceptance
Storer v Manchester cc (1974)
Council sent claimant information regarding the possibility of tenants purchasing council owned property storer completed application form and sent they then sent him agreement to sign which he did and the council would return the agreement but council didn’t and council changed political parties
What case law did storer v Manchester cc (1974)
Court of appeal held that contract was formed as letter from the council was a firm intention to proceed with the sale when storer returned the application form

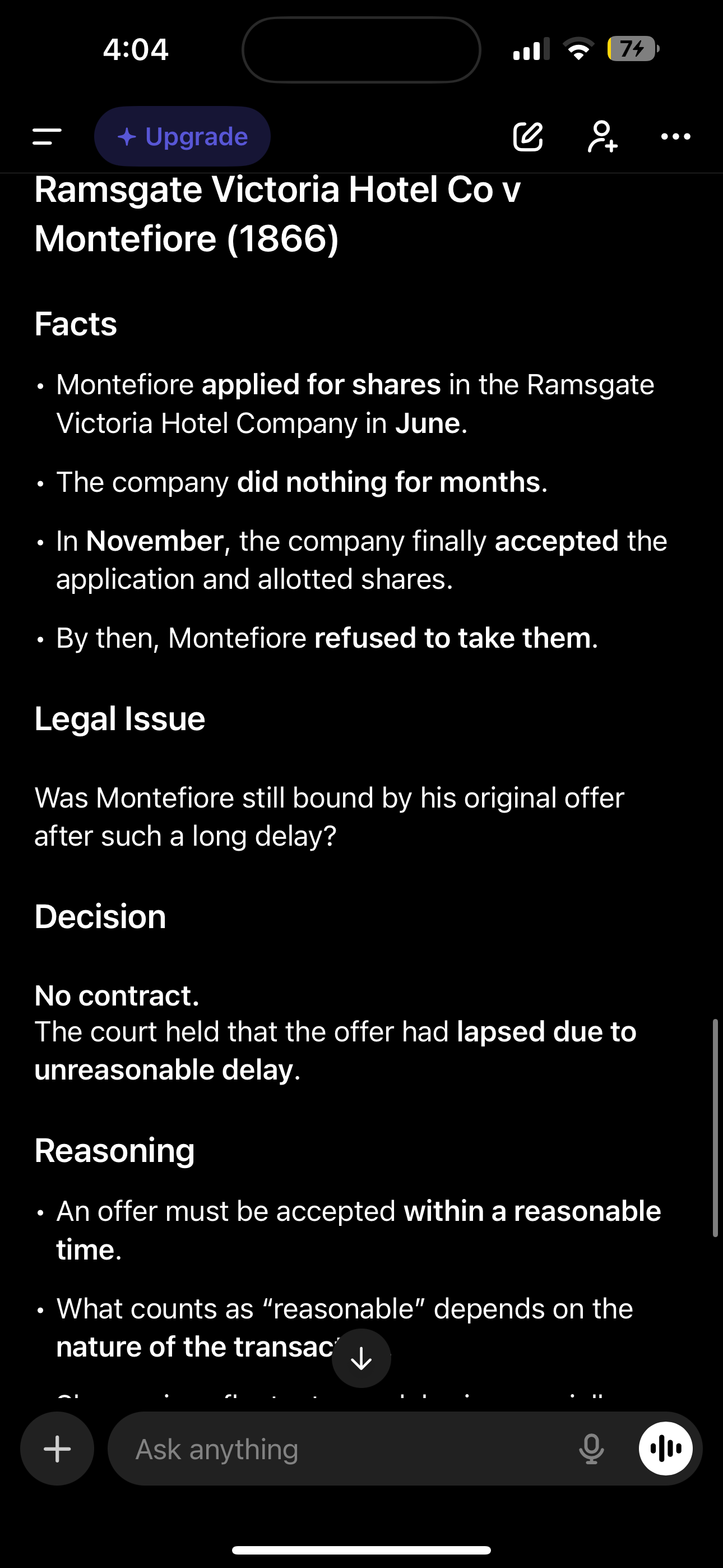
Ramsgate Victoria hotel v montefiore (1865-66)
Montefiore applied to purchase shares in hotel in June but shares not issued until November due to time delay he refused to accept shares
Ramsgate Victoria hotel v montefiore (1865-66) what case law did this bring
If there isn’t any specific time that the offer will expire the court will choose one that is reasonable in the circumstances
Hyde v wrench (1840)
6 June wrench offered to sell land to Hyde for 1000 on 8 June Hyde replied saying he will accept at 950 which was declined by wrench and then Hyde said he will buy at 1000
Hyde v wrench 1840 what case law did this bring
A counter offer terminates the original offer

Bryne & co v Leon van tienhoven & co (1879-80)
Van sent offer to claimant on 1 October and then sent revocation on 8th October however byrne received the offer on 11 October and confirmed acceptance on telegram and further sent letter of acceptance letter n 25 October on 20 October he received the revocation letter
Bryne & co v Leon van turnover and co (1879-80) what case law did this bring
The postal rules differs for revocation it’s not enough to post the revocation letter for it to be accepted it must be communicated(latter reached offeree before accepted)

When is revocation of an offer also effective
When communicated to the offeree by a reliable third party instead of the offeror
Dickinson v Dodds 1875-1876
Dodds offered to sell property for 800 and offer opened till Friday 9am on Thursday afternoon Dickinson learned from reliable third party that it was sold to someone else but Dickinson still tried to accept on Friday morning
What case law did the Dickinson v Dodds bring
Revocation of an offer can be effective through verbal communication even if done by third party and also some act inconsistent with the continuance of the offer (such as selling to someone else but the offeree has to know about it before it’s revoked
Errington v Errington and wood (1952)
Mr Errington bought house by paying a sum and the rest as mortgage balance to be paid weekly by son and daughter in law and promised he will transfer ownership to them when payments completed he died before fully repaid and the widow took son and daughter in law to court but since acceptance had already started revocation was not possible
What case law did Arrington v Errington and woods bring
Once acceptance has begun it cannot be subsequently revoked
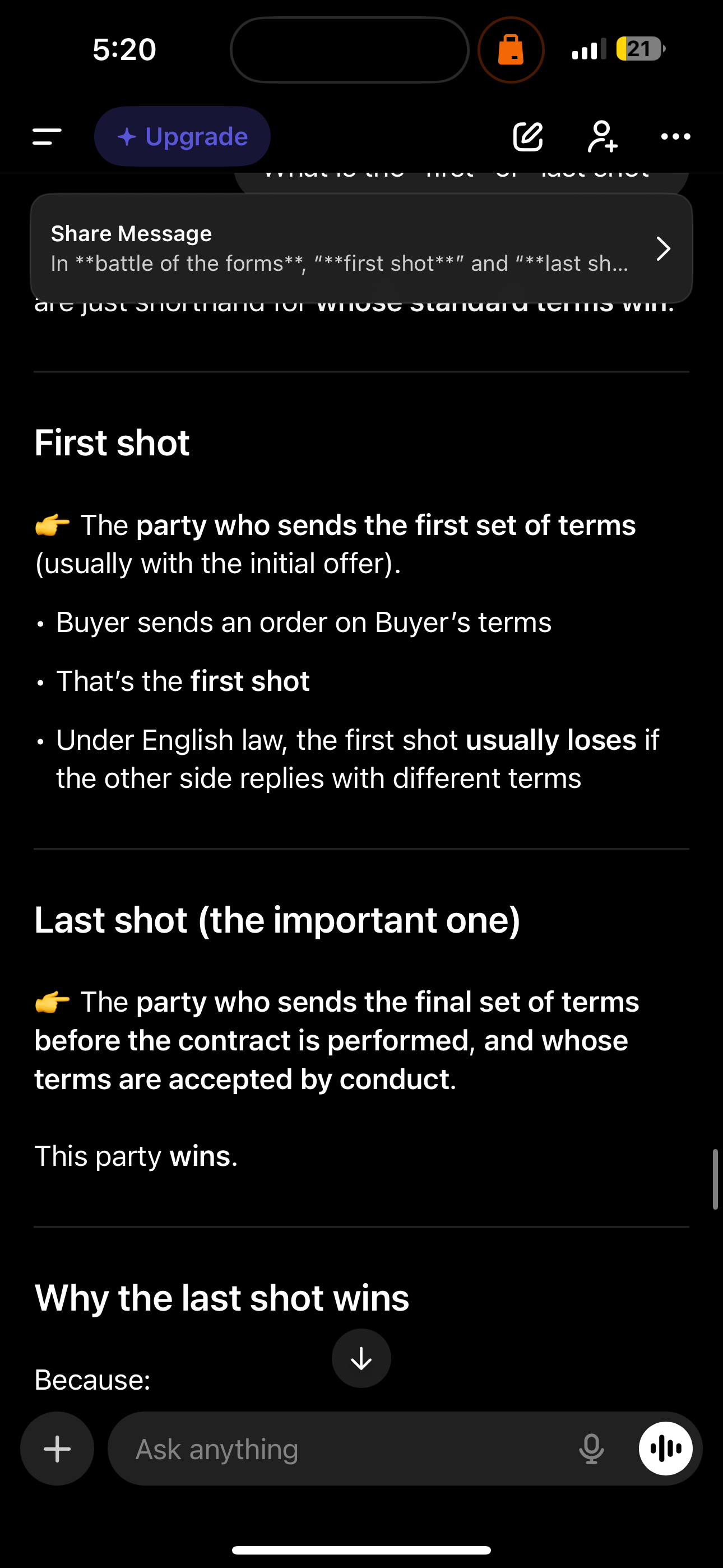
What is battle of the forms
When 2 businesses are trading and they have different terms but deal continues and there ends up being disputes the contract usually used is the one with the last shot so in this case it will be the seller as the buyer didn’t argue back

British road services v Arthur crutches ltd 1968
BRS delivered goods to ACL. BRS delivery note said received under BRS conditions the warehouse clerk stamped the note received under ACL conditions the goods was damaged after delivery and both parties went to court and it was decided on ACL terms as the stamping of the note was a counter offer and BRS accepted it by leaving goods with them
What case law did the British road services v Arthur crutchley ltd 1968 bring
The court held that by stamping the delivery note this created a counter offer that was implied to be accepted by the driver delivering the goods
Butler machine tool co ltd v ex cell o corporation England ltd (1979)
Butler offered to sell machine for 75535 delivery made in 10 monthswith a price variation clause (allows seller to increase price if raw material exchange rate labour price etc rise) then ex cell o replied with there own terms on slip which excluded price variation and butler signed it and later butler wanted to charge extra but was denied as ex cell o got the last shot
What case law did the butler fool co case bring
In agreements between businesses using standard form contracts the “first” or “last” shot approach may be adopted when identifying the operative contract
Yates building co ltd v r J pulley and sons ltd 1975
Pulleyn offered to sell land to yates under a contract and the contract required acceptance to be sent by recorded or registered post but yates sent by ordinary post so pulleyn refused to go through with the real
Case law brought by yates building case
There was no enforceable contract as there was clear terms which the acceptance was to be made
Alexander brogden v metropolitan railway co (1877)
MRC bought coal from AB. AB sent draft contract to MRC and MRC amended some terms and returned to without formally signing. Both parties started performing contract anyway until 1873 when brogden declined to continue supply of coal this lead to breach of contract
What case law did the Alexander brogden case bring
Long term relationship between parties could amount to an agreement even if not formal written acceptance of contact the parties conduct was evidence of acceptance of contractual terms
Dunlop v Higgins (1848)
The offer of sale of pig iron was accepted through posting letter however bad weather delayed the delivery of the letter and led seller to reject acceptance as being out of time and breach of contract was made
What case law did the Dunlop case create
The court stated that the acceptance has been established on the posting of the letter even if acceptance doesn’t reach destination due to outside factors
Novus aviation limited v Alubaf at Arab international bank bsc (2016)
Alubaf would provide funding to novus to purchase an aircraft to lease. Commitment letter and management agreement was signed by alubaf but not novus but the parties continued to act on contract by new companies, opening new bank accounts etc alubaf then wanted to withdraw but novus argued a contract was binding
Novus aviation limited case outcome
The court said Novus was to be awarded with damages as there was acceptance of the contract through conduct and there was nothing that explicitly said the signature slip had to be signed so the conduct was sufficient evidence o FCC acceptance
Felthouse v bindley 1968
Felthouse nephew had horses for sale at an auction before the auction his uncle wrote to him to buy the horses and if the nephew didn’t reply he would take the horses at a specific price. The nephew intended to sell to uncle so told the auctioneer to not put the horses but he mistakenly sold the horses and Felthouse couldn’t sue as he didn’t own the horses as silence is not considered acceptance
What case law did Felthouse v bindley bring
Silence is not an effective acceptance of an offer
Adams v lindsell (1818)
Lindsell offered to sell wool to Adam and asked Adam to send acceptances post which he did on same day but it was misdirected so arrived to lindsell late by then he already sold to someone else and argued the contract was not valid as received acceptance late
What was the outcome Adam v lindsell 1818
Where the post is a valid mean of acceptance(offer made through post or offeror ask acceptance to be sent by post) then acceptance is binding upon postage as long as correct adress and postage was used
Re London and northern bank ex parte jones 1900 outcome
Acceptance of an offer is effective on posting does not apply when letter has been posted incorrectly for example not posting it in postbox instead given to post office, safely sealed, correctly addressed etc
The household fire and carriage accident insurance company v grant (1878-79)
Mr grant applied to purchase shares in the insurance company his application was accepted and the company sent acceptances post which but it was lost in post grant didnt pay for shares but received dividends when the company went bust they asked grant to pay for shares but he argued no contract was formed as he didn’t receive acceptance
The household fire and carriage accident insurance company v grant Outcome
despite the letter of acceptance not reaching grant the contract was effective on posting.
Holwell securities v hughes (1974)
Hughes granted Holwell a six month option to purchase property with notice to be provided in writing (have to receive written letter) five days before the end of sixth month Holwell sent letter through post to accept but it was lost and not received Holwell argued contract was valid due to postal rule
Holwell securities v hughes 1974 outcome
Since the party required notice in writing this overrides the postal rule
Entores Ltd v Miles Far East Corporation [1955]
Entores in London made offer to buy goods from miles in Amsterdam the offer and acceptance was communicated by telex(early electronic messaging) a dispute rose when goods not delivered properly and this depended on where contract was formed
Entores Ltd v Miles Far East Corporation [1955] Outcome
Due to the instantaneous communication acceptance was established when the acceptance was recieved which was in London
White v Bluett (1853)
A son complained to his father about not having as much money as his sibling his father promised son he will lend money if he would stop complaining when father died estate attempted to recover debt from son
White v Bluey (1853) outcome
Court said there must be valid consideration to establish a binding contract
Thomas v Thomas (1842)
Thomas expressed wish for wife to stay in is house forever executors agreed as long as she paid £1 per years and kept in good repair she could stay but later executor try to evict her
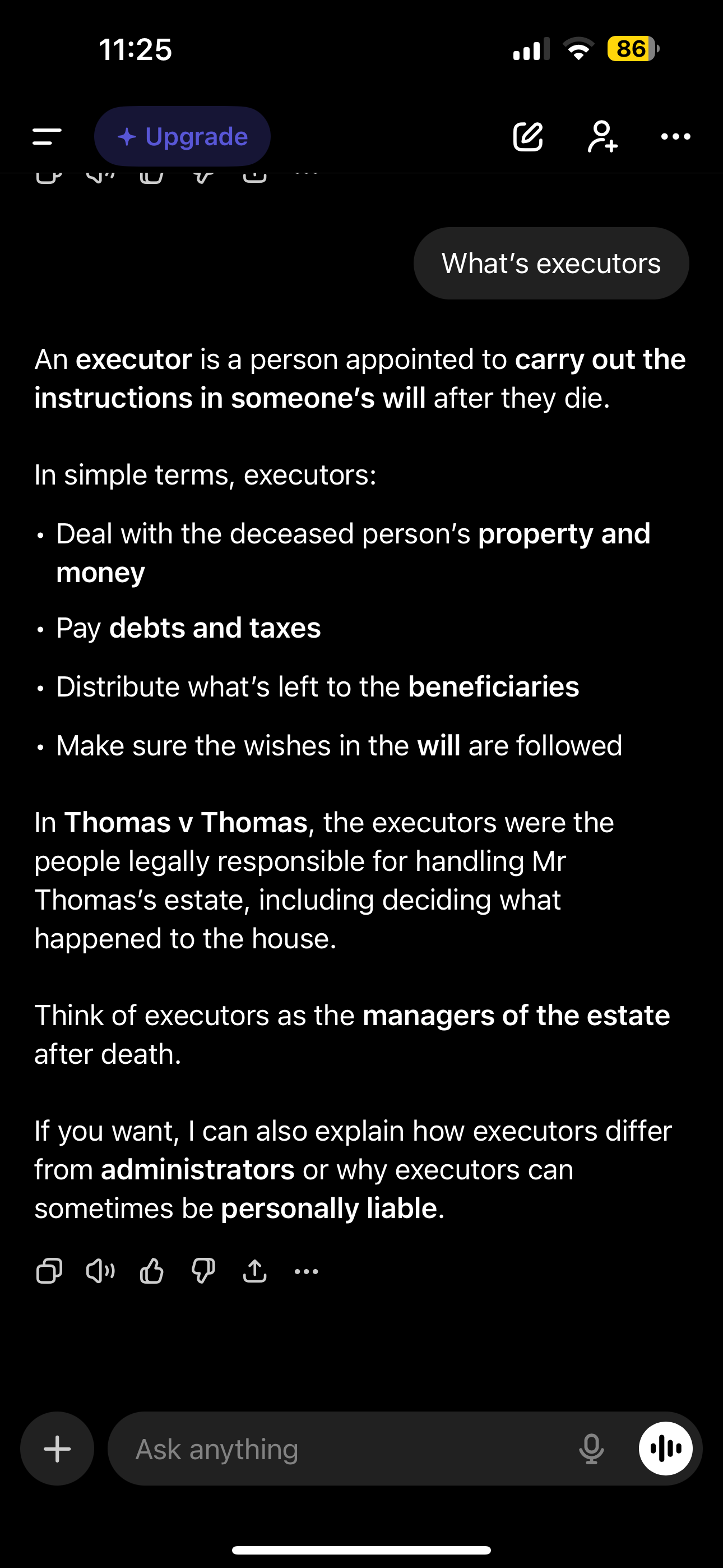
Thomas v Thomas outcome
Court decided that even though the consideration was not adequate it was sufficient as the 1 pound payment was a bargain which created binding contract which was enforceable
Chappel and co ltd v nestle co ltd (1959)
Nestle made milk chocolate products and wanted to go into contract with Chappel to sell copies of Chappel song and Chappel was to be paid a percentage of what they sold. Nestle charged (1s6d) for the cds and also 3 chocolate wrappers and argued whether the 3 chocolate wrappers counted towards the percentage they had to pay Chappel
Chappel and co ltd v nestle co ltd (1959) outcome
The outcome of this was that consideration must be sufficient not adequate so even thought the chocolate wrappers had no value they provided a benefit to nestle( as for the customer to get 3 of the wrappers to exchange they had to have bought 3 of there chocolates)
Mr McArdle Decdc(1951)
Mr McArdle died he had four children and a wife and left the property to the wife. Montague one of the kids and his wife lived in the property and his wife payed 488 to improve and repair the house and montague sent document which the brothers and sisters signed and agreed to pay and was taken to court arguing if this was enforceable
Re McArdle Decd (1951) outcome
Past consideration is not good consideration
Lampleigh v Brathwait (1615)
Brathwaith killed a man and asked lampleigh to seek pardon from king which involved lampleigh following king for many days and when completed Brathwaith promised to pay 100 for the service but he didn’t
Lampleigh v Brathwaith outcome
When there is past consideration for an enforceable contract to exit there must be the act that was done was requested by the prmisor, there must be contemplation( both parties expect) of payment being made, and all other elements of a valid contract must have existed
What would happen if no price had been established for the service
Court would look at s.51 if consumer rights act 2015 and determine reasonable price
What is a patent
A legal right granted by a government that gives the investor exclusive control over an invention for a certain period of time (so for example for a set number of years only I can use it, sell it or give permission to others to do so
Re Stewart v casey(casey patents) (1892)
Mr Casey employed Stewart to promote there patents and after he done service casey agreed to pay him 1/3 of the profits but then later tried to remove his name from patents( so meaning he wouldn’t get the share)
Re Stewart v casey (Casey’s patents) (1892)
It was not considered past consideration as the parties went into the agreement on the understanding that remuneration would be provided
Stilk v myrick (1809)
The captain of a vessel travelling from London to Baltic promised existing crew equal share of wages of the 2 sailors who left but he didn’t pay them
Stilk v myrick (1809) outcome
The court said there was no consideration as the seamen was already under an existing duty to “exert themselves to the utmost to bring the ship in safely to destined port”
When can consideration be established when it’s a existing duty
When you exceed the existing duty
Hartley v ponsonby (1857)
During a voyage (Travel)half the ships crew deserted and the remaining sailors promised additional money if they competed their voyage but then captain refused to pay
Hartley v ponsonby outcome
The court held the sailors enticed to the extra pay as they exceeded existing duties due to significant risk of continuing voyage with insufficient crew (different to previous sailor one as that one only 2 left but this 19/36 left)
Harris v Sheffield united football club ltd (1987)
Football club didn’t think had to pay police for policing football natches held at there stadium as police had duty to protect public
Harris v Sheffield outcome
Court of appeal held that supervision of football natches went beyond protecting public and maintaining law and order and counted as special police service(as may have required extra police staff etc)
what is contractor and subcontractor
A contractor is hired by the client to do the job. A subcontractor is hired by the contractor
Williams v Roffey Bros & Nicholls (contractors) ltd (1991)
Roffey Bros was main contractor for refurbishing block of flats. They subcontracted Williams but William ran into financial difficulty and couldn’t finish it by due date so roffey offered to pay William’s extra 10,300 above the 20000 if completed on agreed date as roffey would have faced late charges. He then refused to pay
Williams v Roffey Bros & Nicholls (contractors) ltd (1991) Outcome
When the promised has conferred(granted) a benefit on the promising or helped them avoid a detriment then existing duty may count as good consideration if no unfair pressure or duress was applied
Re selectmove (1995)
Selectmove owed a lot in tax and national insurance to the inland revenue. The managing director proposed to the tax inspector and asked to pay 1000 per month the inspector said he would talk to superiors if they didn’t hear from inland revenue again then it’s been accepted. Later the ir petition for company to be wound up
Re selectmove 1995outcomme
The tax inspector didn’t have authority to bind the ir and part payment of a debt is not good consideration and promises was promising a existing duty so not enforceable
What did selective argue
Providing payments was a benefit to the ir as if the company got wound up(close company) they would not receive anything but. Court argued and distinguished it from William v roffey as there case was performing act this was part payment of debt
Pinnels case (1602)
He owed (£8 10s) but ended up paying (5 2s) as agreed by both parties to count as full settlement later the claimant wanted the rest of the amount from defendant
Pinells case (1602) outcome
The court held that there is no consideration in part payment as doesn’t provide other part with benefit so full amount can be recovered except if the part payment was made early of part payment included non monetary chattel(something other then money such as an item) as this can provide benefit
Foakes v beer (1881-85)
John foakes owed £2090 19s to Julia Beer he entered an agreement where he would pay a initial sum of 500 then 150 every sixth months until full amount recovered and she agreed not to claim any interest however she later did sue foakes for interest
Foakes v beer (1881-85
House of Lords held that beer was entitled to interest on payment even thought she altered not to claim as the promise by foakes to pay money wasn’t sufficient consideration as he was only doing what he was obliged to do so no benefit to beer for the agreement
D & c builders ltd v Rees (1966)
D & c builders was in financial difficulties and Rees who owed them 482 pound offered them a 300 cheque to fully settle debt or they won’t get anything at all they accepted because desperation then brought action again Rees later for the rest
D&C builders Ltd v Rees outcome
The court of appeal held that d and c entitled to claim rest as there was no consideration due to it being part payment of debt and also financial pressure applied for acceptance means no agreement was established
Combe v Combe (1951)
A husband promised to make maintenance payments to his wife following separation he never made the payments and wife took to court arguing promissary estoppel
Combe v Combe outcome
The wife’s claim failed as promissory estoppel can only be used as a shield not a sword) so can only be used as defence
Tool metal manufacturing co v tungsten ltd (1955)
Tool metal granted tungsten a patent licence in exchange for 10% royalty and 30% compensation if sales exceeded 50kg. During the war tungsten had financial difficulties making payments so tool metal agreeed to remove it then reinstated it after war ended and wanted to recover the payments that was removed during the war
Took metal vs tungsten outcome
Tool metal couldn’t claim 30 percent payments that they voided during war due to promissory estoppel but was allowed to reinstate the payments after as promissory estoppel suspends legal rights but doesn’t extinguish them
Central London property trust v high trees house ltd (1956)
Central London property trust(landlord) leased a block of flats to high street house(tenant) for 2500 during war they struggled to pay rent so CLP reduced it by half and for the 5 years they paid the reduced rent later CLP wanted to claim full rent from those 5 years
Central London property trust g high trees house ltd
Denning a statement: when the promise makes a promise that is relied on by the promisee they will be unable to renege on it due to doctrine of promissory estoppel even if no consideration in agreement
Dunlop Tyre co v selfridge (1915)
Dunlop (tyre manafacturer) sold tyres to a wholesaler (Dew and co)and in the contract agreed that it will make sure retailers that the wholesalers sell to don’t sell below certain price chosen by Dunlop Dew and co sold to selfridge which sold below the price and Dunlop wanted to take. Action against them
Dunlop tyre v selfridge outcome
Common law established that only parties to a contract had obligation and rights to it