geometry regents
4.5(2)
4.5(2)
Card Sorting
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
1
New cards
sum of interior angles
180(number of triangles-2)
2
New cards
each interior angle of a regular polygon
180(number of triangles-2)/number of triangles
3
New cards
sum of exterior angles
360
4
New cards
each exterior angle
360/number of triangles
5
New cards
scalene triangle
no congruent sides
6
New cards
equilateral triangle
all sides are congruent
7
New cards
isosceles traingle
2 congruent sides
8
New cards
equiangular
3 congruent angles
9
New cards
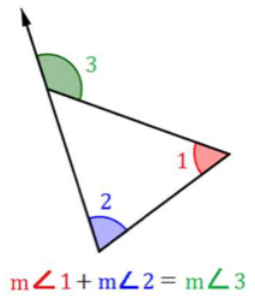
exterior angle theorem
The exterior angle is equal to the sum of the two non-adjacent interior angles
10
New cards
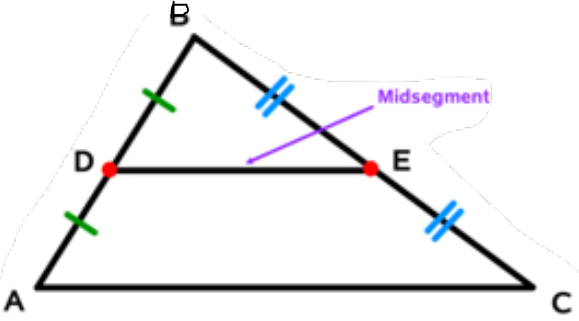
midsegment
a segment that joins two midpoints
* always parallel to the third side
* 1/2 the length of the 3rd side
* splits the triangle into 2 similar triangles
* always parallel to the third side
* 1/2 the length of the 3rd side
* splits the triangle into 2 similar triangles
11
New cards
slope intercept form of a line
y = mx + b, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept.
12
New cards
point slope form of a line
**y-y1=m(x-x1).** where m is the slope and x1 and y1 are the values of a given point on the line
13
New cards
slope formula
(y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1), where (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) are two points on a line. rise/run
14
New cards
parallel lines
have the same slope
15
New cards
perpendicular lines
have neg reciprocal slopes (flip the fraction and change the sign into its opposite)
16
New cards
collinear points
are points that lie of the same line
17
New cards
mid point formula
It involves averaging the x and y coordinates of the endpoints.
Formula: M =(x₁+x₂)/2, (y₁+y₂)/2.
Formula: M =(x₁+x₂)/2, (y₁+y₂)/2.
18
New cards
distance formula
**d = √((x2 - x1)^2 + (y2 - y1)^2)**, where (x1, y1) and (x2, y2) are the coordinates of the two points and d is the distance between them.
19
New cards
segment ratios
the ratio of the lengths of two segments that share an endpoint.

20
New cards
triangle theorems
* the sum of 2 sides must be greater than the 2 sides
* the difference of 2 sides must be less than the 3rd side
* the longest side of the triangle is opposite the largest angle
* the shortest side of the triangle is opposite the smallest angle
* the difference of 2 sides must be less than the 3rd side
* the longest side of the triangle is opposite the largest angle
* the shortest side of the triangle is opposite the smallest angle
21
New cards
isosceles triangle properties
* 2 congruent sides and 2 congruent base angles
* the altitude drawn from the vertex is also the median and angle bisector
* if two sides of a triangle are congruent, then the angles opposite those congruent angles congruent
* the altitude drawn from the vertex is also the median and angle bisector
* if two sides of a triangle are congruent, then the angles opposite those congruent angles congruent
22
New cards
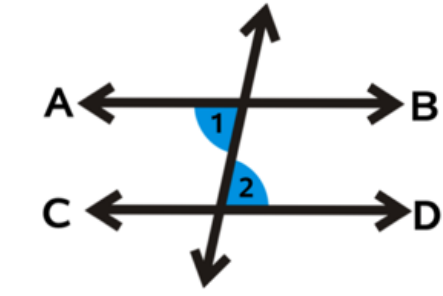
alternate interior amgles
are congruent
23
New cards
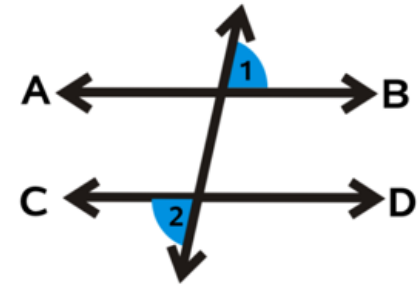
alternate exterior angles
24
New cards
corresponding angles
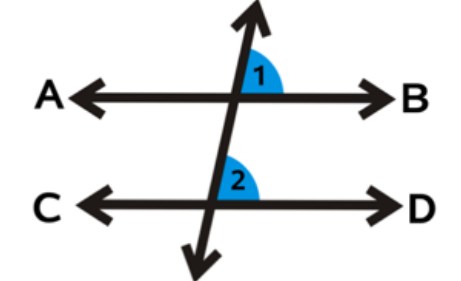
25
New cards
same side interior angles
supplemantary
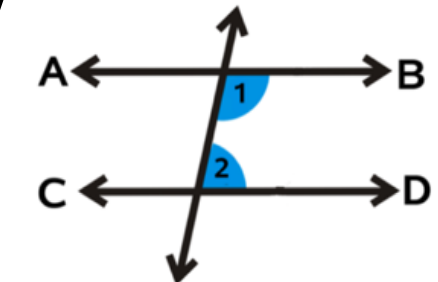
26
New cards
side splitter theorem
if a line is parallel to one side of a triangle and intersects the other two sides, it divides those sides proportionally.
27
New cards
triangle congruency theorems
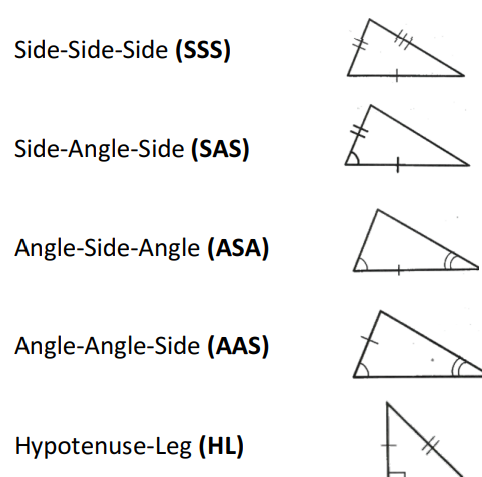
28
New cards
CPCTC
If two triangles are congruent, then their corresponding parts are congruent.
29
New cards
similar triangle theorems
* Similar figures have congruent angles and proportional sides
* CSSTP-Corresponding Sides of Similar Triangles are in Proportion
* In a proportion, the product of the means equals the product of the extremes
* CSSTP-Corresponding Sides of Similar Triangles are in Proportion
* In a proportion, the product of the means equals the product of the extremes
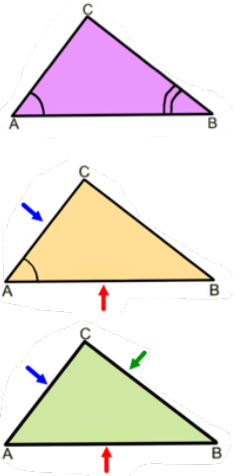
30
New cards
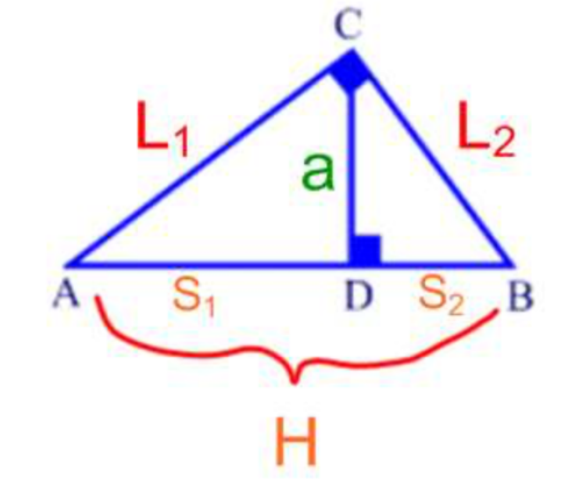
altitude theorem SAAS
The altitude is the geometric mean between the 2 segments of the hypotenuse
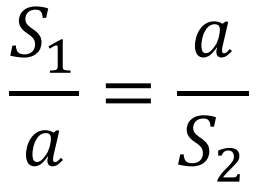
31
New cards
leg theorem
The leg is the geometric mean between the segment it touches and the whole hypotenuse.

32
New cards
confunctions
sine and cosine are confunctions which are complemntary (add up to 90)
**Ex: sin60=cos(90-60) and vice versa**
if angle a and angle b r the acute angles of a right trinaglke, then sin a = cos b
**Ex: sin60=cos(90-60) and vice versa**
if angle a and angle b r the acute angles of a right trinaglke, then sin a = cos b
33
New cards
rigid motion
A transformation that preserves distance and angle measures between objects. Examples include translations, rotations, and reflections.
34
New cards
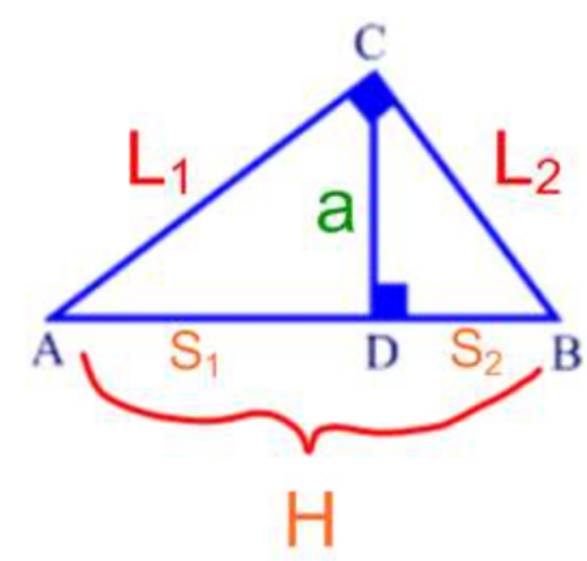
rotations
\
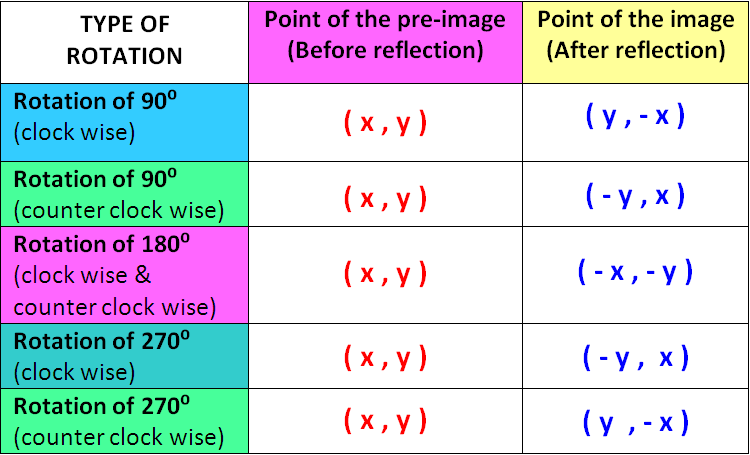
35
New cards
dilation enlargement/reduction
* create similar figures where the corresponding sides are in proportion and the corresponding angles are congruent
* do not preserve distance or congruency
multiply the x and y values by the number
ex: (2,4) reduced by a half = (2,4)x1/2=(1,2)
* do not preserve distance or congruency
multiply the x and y values by the number
ex: (2,4) reduced by a half = (2,4)x1/2=(1,2)
36
New cards
composition of transformations
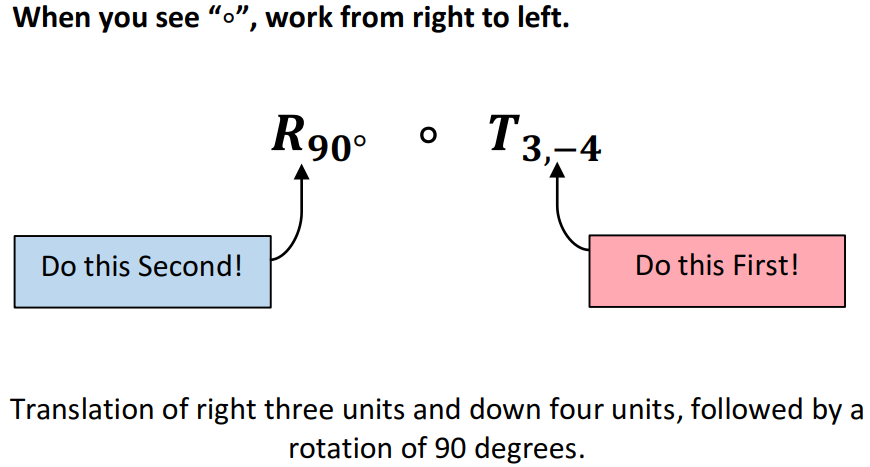
37
New cards
types of compisition trnadsfomagition
A composition of 2 reflections over 2 intersecting lines is equivalent to a ROTATION.
A composition of 2 reflections over 2 parallel lines is equivalent to a TRANSLATION.
A composition of 2 reflections over 2 parallel lines is equivalent to a TRANSLATION.
38
New cards
rotational symmetry theorem
a regular polygon with 3 or more sides always has rotational symmetry , with rotations in increments. commonly referred as “mapping the figure onto itself”.
**360/n n=3 of sides**
**360/n n=3 of sides**
39
New cards
circle equations
standard equation of a circle: where C,D and E are constants
center-radius equation of a circle: where (h, k) is the center and r is the radius
center-radius equation of a circle: where (h, k) is the center and r is the radius
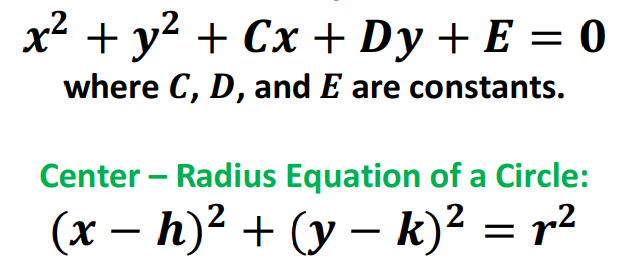
40
New cards
Chord
A line segment connecting two points on a curve or circle.
41
New cards
Secant
A line that intersects the circle in two or more points. This is a different secant than the secant in trigonometry.
42
New cards
Tangent
A line from outside a circle that intersects the border of a circle at one point but does not pass through the border to the circle’s interior. This is a different tangent than the tangent in trigonometry.
43
New cards
Central Angle
An angle whose vertex is at the center of a circle and whose legs are radii of the circle.
44
New cards
Inscribed Angle
An angle created when two chords of a circle share a point on that circle.
45
New cards
Circumscribed Angle
An angle created when two tangent lines to a circle intersect outside of that circle.