Physics - The Particulate Nature of Matter
1/81
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
Density formula
ρ=m/V
What does the kelvin scale measure and what is the equation relating it to that?
Kelvin temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of particles as given by Ek = 3kBT/2 where;
kB= Boltzmann constant
T = temperature in kelvin
What is the internal energy of a system?
The total intermolecular potential energy arising from the forces between the molecules plus the total random kinetic energy of the molecules arising from their random motion.
What does temperature difference determine?
A transfer of energy between bodies from a hotter region to a cooler region.
What does a phase change represent?
A phase change represents a change in particle behavior due to a change in energy at constant temperature.
Write the formula for thermal energy transfer using specific heat capacity (c) and define it
Q = mcΔT
The amount of energy required to change the temperature of 1 kg of a substance by 1 K (or 1°C)
Write the formula for latent heat of fusion and vaporization and define it.
The amount of energy required to change the state of 1 kg of a substance without changing its temperature
Q=mL
Describe Conduction and why some materials are bettwer conductors than others.
Two solids of different temperatures come in contact with one another, thermal energy is transferred from the hotter object to the cooler object. Conduction occurs due to the difference in kinetic energy of particles and so materials such as metals have delocalised electrons that collide - aside from atom vibrations that happen in all materials - and therefore have more K.E.
Temperature gradient formula for calculating rate of transfer of heat energy.

What is convection and radiation?
Convection - A fluid is heated causing the movement of groups of atoms or molecules due to variations in density (hotter particles expand, have lower density, then rise and vice versa)
Radiation- Heat transfer by means of electromagnetic radiation normally in the infrared region - the only way heat travels through a vacuum - doesnt need medium to propagate.
What is a black body and black body radiation?
Black body radiation - thermal radiation emitted by all bodies (can be in the form of any wavelength on the EM spectrum)
Black body - An object that absorbs all of the radiation incident on it and does not reflect or transmit any. Since a good absorber is also a good emitter, a perfect black body would be the best possible emitter too
Write the stefan boltzmann law for Luminosity or power
Sphere S.A = 4πr²

Apparent Brightness definition
The intensity of radiation received on Earth from a star (W/m²)
Define luminosity and its equation linking apparent brightness(b) and any assumptions made
The total power output of radiation emitted by a star (W)
where; d - the distance between the star and the surface of the earth
Assumptions:
Power radiated is uniform
No other absorption has occurred before reaching earth.
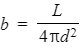
What is Wien’s displacement law?
The black body radiation curve for different temperatures peaks at a wavelength that is inversely proportional to the temperature
λmax T = 2.9 × 10^-3mK
What is a black body radiation curve and what does it tell us?
Black-body radiation curve - intensity against wavelength
As the temperature increases, the peak of the curve moves
This moves to a lower wavelength (waves with a smaller wavelength have more energy) and a higher intensity
How can the luminosity of a star be expressed?
The luminosity of a star can be expressed in watts or in terms of the luminosity of the Sun L⊙
Definition of Emissivity
The power radiated by a surface divided by the power radiated from a black body of the same surface area and temperature
Formula for Emissivity of non-black bodies
Emissivity=Power radiated per unit area/σT^4
where 𝜎σ is the Stefan-Boltzmann constant and 𝑇T is the temperature in Kelvin.
What is the emmissivity of a perfect black body?
1
Definition of Albedo
Albedo is a measure of the average energy reflected off a macroscopic system.
Formula for Albedo
albedo = total scattered power/total incident power
What is albedo dependent upon?
Cloud formations and season – the thicker the cloud cover, the higher the degree of reflection
Latitude
Terrain – different materials reflect light to different degrees
What is the solar constant?
The amount of solar radiation across all wavelengths that is incident in one second on one square metre at the mean distance of the Earth from the Sun
When calculating the solar constant, remember the conservation of energy as it travels through space.
= E/t/area or P/4πr²
Explain how to calculate incoming radiative power.
The surface area of a planet with radius r = 4πr²
The sun’s radiation covers an area of πr²
So the mean value of radiative power/intensity is
S (πr²/4πr²) = S/4
List the major greenhouse gases and their natural and human sources
Water vapour (H2O) - evaporation from the oceans / seas and plants / irrigation and industrial processes such as combustion.
Carbon dioxide (CO2) - volcanic eruptions, wildfires / burning of fossil fuels / respiration
Methane (CH4) - emission from oceans and soils as part of decomposition, termites also emit methane / landfills and agricultural (rice and livestock)
Nitrous oxide (N2O) - soils and oceans / synthetic fertilizers and fossil fuels
Explain the greenhouse effect / resonance model
Incoming UV radiation is absorbed by ozone
Re-emitted infrared radiation is absorbed by greenhouse gases and some re-emit it towards the Earth's surface and some of it into space.
This emitted radiation contributes to the greenhouse effect by trapping heat in the Earth's atmosphere, thereby warming the surface, and increased average temperatures, known as the greenhouse effect.
Explain the molecular energy model of the greenhouse effect
High-frequency UV light is energetic and able to break bonds within molecules (short wave)
Infrared light, on the other hand, causes atoms to vibrate (long wave)
The greenhouse gases have a natural frequency that falls in the infrared region
This means when they absorb infrared light, they begin to resonate, causing the molecules to heat up
They absorb the infrared radiation and subsequently emit it back towards the Earth’s surface. (long wave radiation)
What is the enhanced greenhouse effect?
The enhanced greenhouse effect refers to the intensification of the natural greenhouse effect due to human activities, particularly the increased emission of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide.
Pressure formula
P=F/A where; F is the perpendicular force
Define the number of moles (n) in terms of Avogadros constant (NA) and the relevant formula
1 mol has 6.02 × 1023 molecules (avogadro’s constant)
n = N / NA where N is the number of molecules.
How to find the mass of an element using the number of mols
1 mol of any element is equal to the relative atomic mass (mass number) grams in mass.
What is the formula for molar mass
Mr = m/n where;
m is the mass
n is the number of moles
Kinetic theory of gases
Used to model the behaviour of real gases but they are:
Point particles (negligible volume)
Internal energy is in the form of kinetic energy as intermolecular forces are not considered.
All collisions are elastic collisions
Obey Newton’s laws of motion
Random motion at high speeds
What is boyle’s law?
P1V1 = P2V2
What is charles’s law?
V1/T1=V2/T2
What is gay lussac’s law?
P1/T1=P2/T2
Ideal gas equation (2)
PV = nRT where;
n - number of moles and R = ideal gas constant
or
PV = NkBT where;
kB= Boltzmann constant
N = number of molecules
When is an ideal gas a good approximation of a real gas?
The gas pressure and density is low.
Temperature is higher than the boiling point of the substance.
What is the kinetic theory of gases equation
P = pv²/3 where;
P = Pressure of gas
p = density
v = average speed
Internal energy of an ideal monoatomic gas
Same as kinetic energy of the gas or:
U = 3NkBT/2 or U = 3RnT/2
where; N = number of molecules
n = number of moles
Work done by a closed system in terms of pressure and volume.
W = PΔV
Where;
P = pressure of the surroundings
First law of thermodynamics
Q = ΔU + W
What does change in internal energy of a monoatomic gas depend on?
Its directly proportional to temperature
What are the sign conventions for work done on/by the system?
Work done;
on system : -W
by system: +W
In a pressure volume graph what does the area under the graph represent?
Work done
What is entropy (S) ?
A thermodynamic quantity that relates to the degree of disorder of the particles in a system
e.g. gas is more disordered than solids therefore it will have more entropy
What is the difference between a reversible and irreversible process in terms of entropy?
Reversible - A process where there is no overall change in entropy as the system and its surroundings are returned to their original states
Irrreversible - A process which results in an increase in entropy as the system and its surroundings cannot return to their original states
How to calculate change in entropy
ΔS = ΔQ/T
How can entropy on a microscopic level be calculated?
S = kB ln Ω
Where; Ω is the number of possible microstates of the system
Second law of thermodynamics
In every process, the total entropy of an isolated system always increases.
Describe the entropy of a real isolated system
Processes in real isolated systems are almost always irreversible and consequently the entropy of a real isolated system always increases.
Describe the entropy of a non-isolated system
The entropy of a non-isolated system can decrease locally, but this is compensated by an equal or greater increase of the entropy of the surroundings.
Name all the 4 main thermodynamic processes and what is 0 in each one.
Isothermal = ΔU =0
Isovolumetric/choric = W =0
Isobaric = ΔP=0
Adiabatic = ΔQ = 0
What formula can be used to model the adiabatic process?
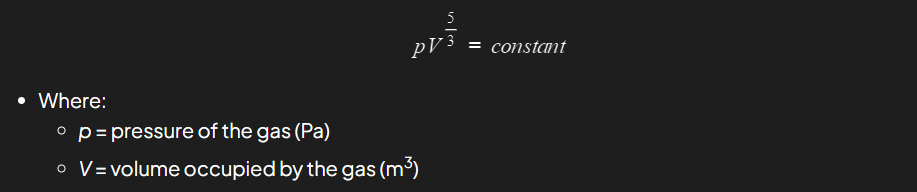
What is a heat engine?
A heat engine is a device that converts thermal energy into mechanical work
Heat engines operate through a series of thermodynamic processes which form a closed cycle
A closed cycle is one in which the system returns to its initial state
A simple heat engine consists of a gas in a cylinder with a piston
Net Work Formula of a heat engine
Wout=QH−QC, where;
Wout is the useful work output (J)
QH is the heat transferred from the hot reservoir to the engine (J),
QC is the heat transferred from the engine to the cold reservoir (J).
Formula for efficiency of heat engines according to limits set by the Carnot cycle.
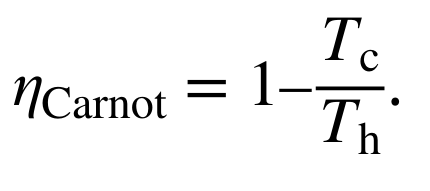
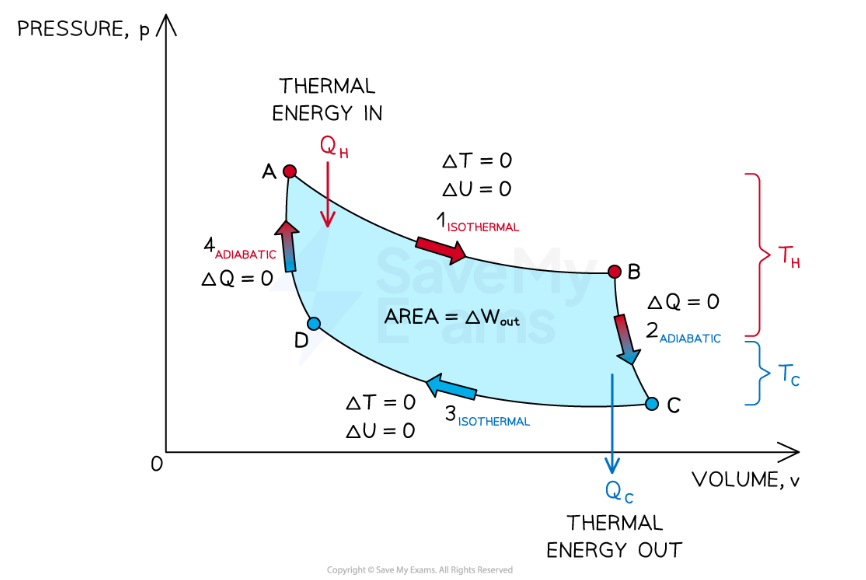
What are the 4 stages of the Carnot cycle?
Isothermal expansion
Adiabatic expansion
Isothermal compression
Adiabatic compression
Function of:
potentiometer
LDR
Thermistor
A resistor with a sliding contact to form an adjustable voltage divider.
As light intensity increases, the resistance of an LDR decreases and vice versa
As temperature increases, the resistance of a thermistor decreases and vice versa
Which way does current and electons flow?
Current - +ve to -ve
Electrons - -ve to +ve
What is e.m.f?
The potential difference across the cell when no current is flowing.
What are the two types of cells that can serve as energy sources in circuits?
Chemical cells and solar cells.
How is direct current (dc) defined in terms of charge carriers and its formula.
Direct current (dc) is defined as a flow of charge carriers, given by 𝐼=Δ𝑞/Δt
What is the electric potential difference 𝑉?
The electric potential difference 𝑉 is the work done per unit charge on moving a positive charge between two points along the path of the current, given by 𝑉=E/𝑞
What makes a material a conductor?
Conductors are made up of positively charged metal ions within a sea of delocalised electrons. An insulator has no free charges like the same.
What is electric resistance and its origin?
Resistance is the opposition to the flow of charge. Free electrons collide with metal ions which resist their flow. This transfer of energy results in an increase in the kinetic energy of the atoms in the lattice. This raises the overall internal energy of the metal
How is electrical resistance 𝑅 calculated?
V = IR
What is the formula for resistivity?
ρ = RA /L where;
R - Resistance
A - cross-sectional area
L - Length of conductor
What is the resistance of ideal voltmeter and ammeters?
An ideal voltmeter has infinite resistance
An ideal ammeter has zero resistance
Differentiate between ohmic and non-ohmic resistors
Ohmic - inversely proportional (straight line) - conatnt temperature
Non-ohmic - negative correlation (curved line) - heating effect of resistors
How is electrical power 𝑃 dissipated by a resistor calculated - 4 formulae
P = IV = I²R = V²/ R = e/t
How should you connect voltmeters and ammeters?
Ammeters - series
Voltmeters - Paralell
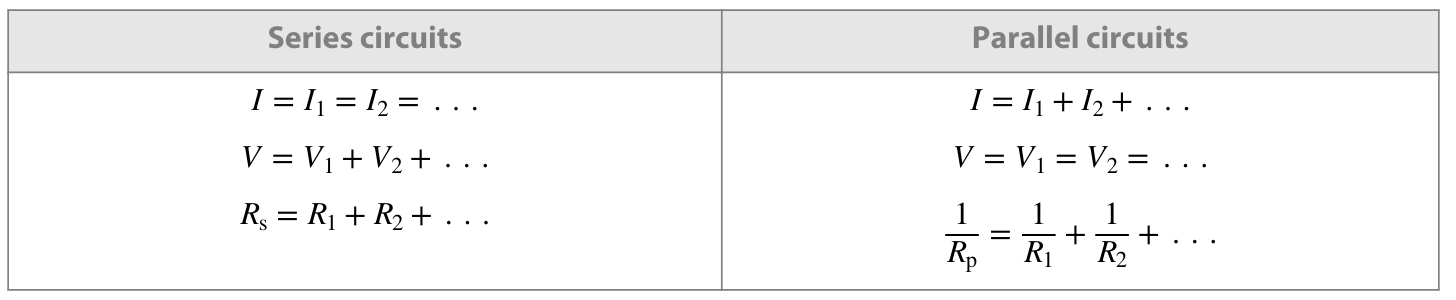
How should you calculate the total current, voltage and resistance in series and paralell?
Hwo to calculate resistance using a graph?
V/I - resistance = gradient
I/V - resistance = 1/gradient
Give examples of non-ohmic devices
Lamps
LEDs
Thermistors
Advantages of Solar Cells
Renewable
Environmentally Friendly
Low Operating Costs
Off-Grid Capability
Disadvantages of Solar Cells
High Initial Cost
Space Requirements
Energy Storage Challenges - technical
Advantages of Chemical Cells (Batteries)
Portable
Instantaneous Power
Energy Density
Diverse Applications
Disadvantages of Chemical Cells (Batteries)
Limited Lifespan
Environmental Impact
Longer Charge Time and Capacity Degradation
How to calculate e.m.f.

Why do phase changes occur at the same temperature?
Even though energy is transferred, the intermolecular P.E. changes (depending on if heat is remvoed or added) but the kinetic energy remains constant and temperature is directly proportional to K.E.