4. white lesions
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
objectives of white lesion diagnosis (DDD)
describe clinical features
develop D/D
differentiate btwn likely benign and potentially malignant
all white lesions are leukoplakias
false
flat, solid, raised area of the skin or mucosa >1cm in diameter
plaque
solid mass of tissue >1cm in diameter
tumor
rewatch: reactive, traumatic, and frictional lesions are
sharply demarcated or diffuse
four things that make oral mucosa look white (think layers)
thick keratin - protective, calluses
alteration to keratinocytes - pre-cancer, candida changes
acanthosis - response to trauma, infection, pre-cancer
fibrosis - scarring
acronym for white lesion categories
HIDEMAN
Hereditary, infectious, developmental, enviro/reactive, metabolic/med-induced, autoimmune/immune-mediated, neoplastic
white sponge nevus
(BLANK) benign intraepithelial dyskeratosis
darier disease/warty dyskeratosis
dyskeratosis congenita
hereditary
oral candidiasis and oral hairy leukoplakia
infectious
leukoedema
contact desquamation
hairy tongue
frictional keratosis
benign alveolar ridge keratosis
nicotine stomatitis
smokeless tobacco keratosis
environmental/reactive
oral lichen planus
lupus erythematosus
oral graft vs host disease
autoimmune/immune mediated
oral leukoplakia
oral submucous fibrosis
oral squamous cell carcinoma
neoplastic
most often seen
environmental/reactive
least often seen
autoimmune and hereditary
which hereditary lesion:
Rare autosomal dominant genodermatosis
Mutation in keratin 4 and keratin 13
Defective keratinization of oral mucosa
white sponge nevus
which hereditary lesion clinical features:
Appears at birth or early childhood
Asymptomatic, bilateral and symmetrical, thickened, white, corrugated or velvety, diffuse plaques of the buccal mucosa
Other oral mucosal sites
Extra oral mucosal sites less common
No treatment required
white sponge nevus
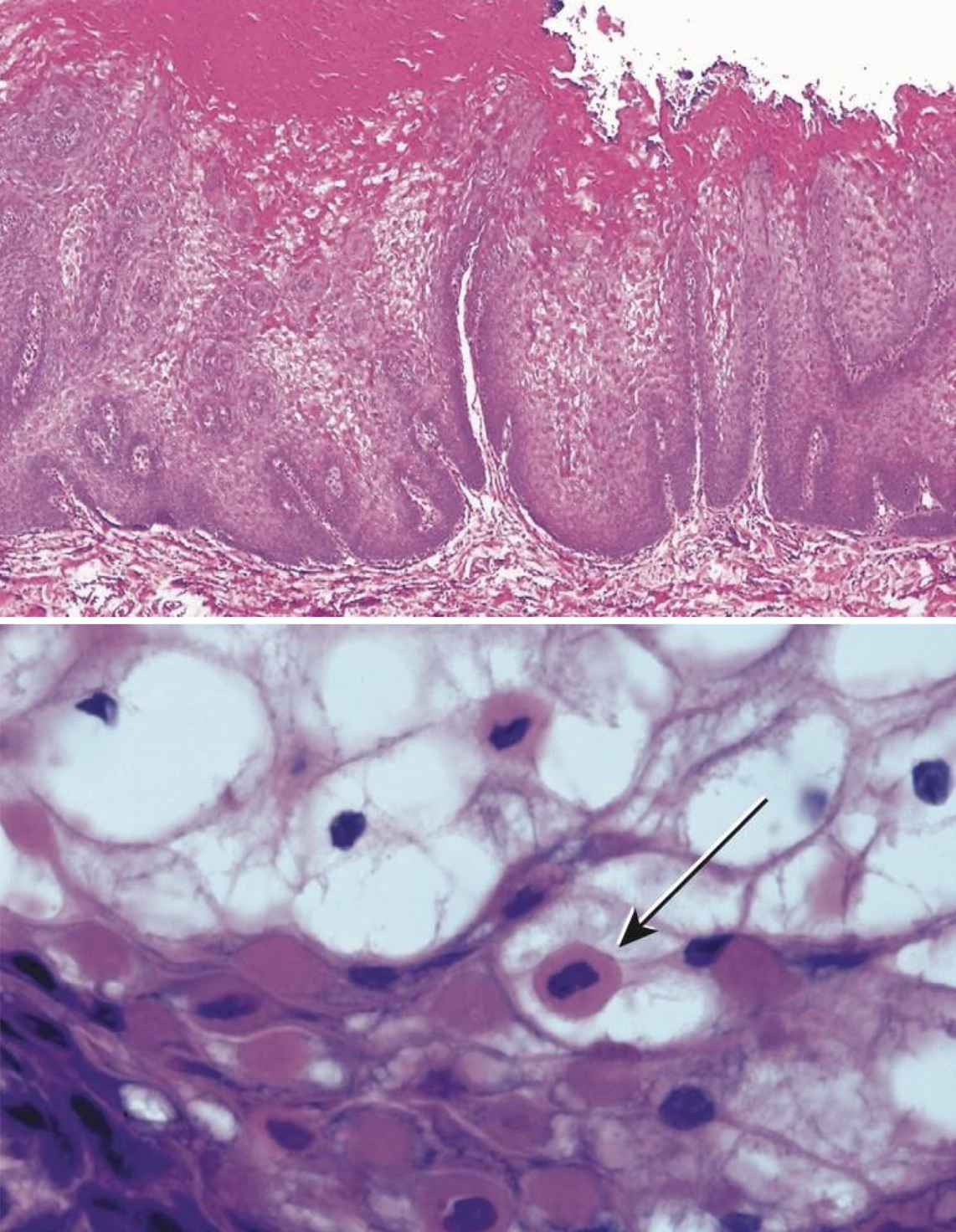
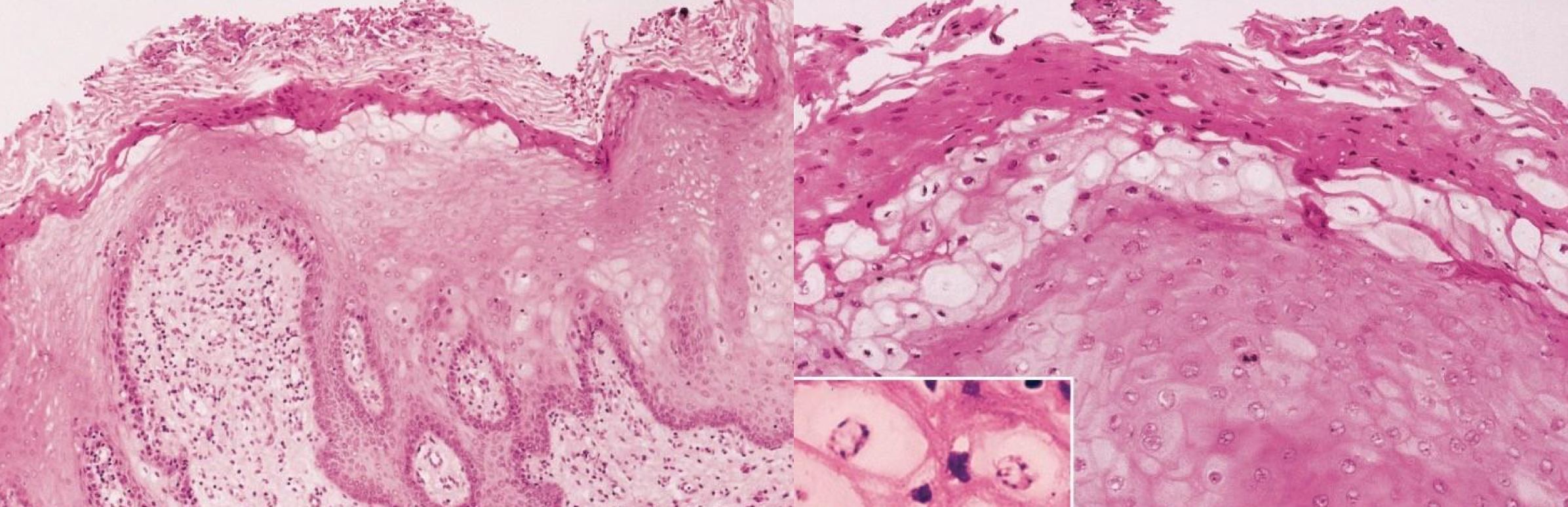
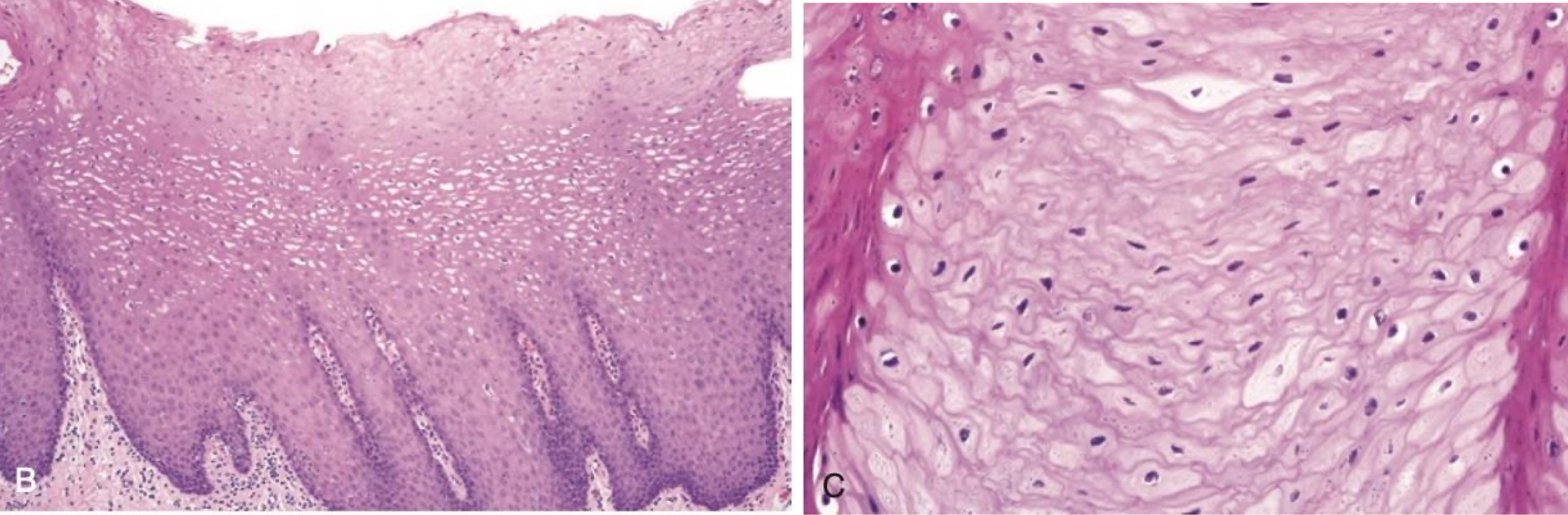
which hereditary lesion histopathological features:
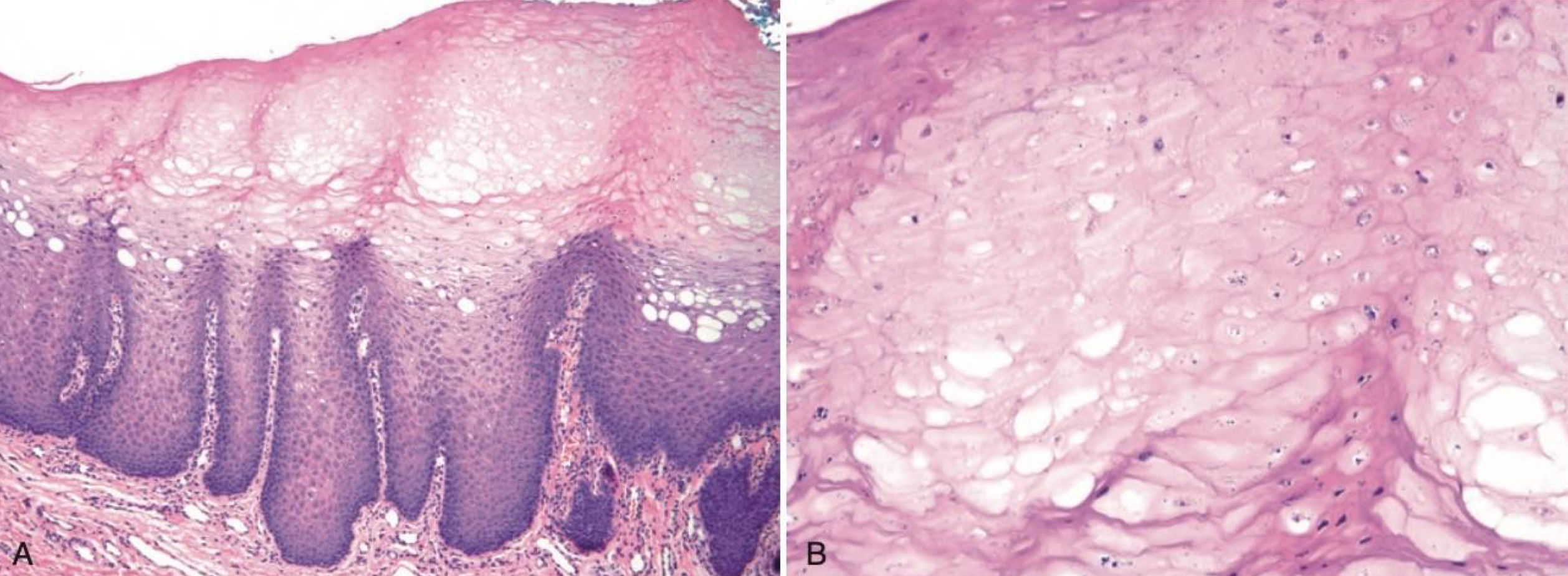
Prominent hyperparakeratosis and marked acanthosis with clearing of the cytoplasm of the cells in the spinous layer
Perinuclear condensation of keratin tonofilaments (K4 and K13 mutation → clumping and spongy)
white sponge nevus
waxy fissured thick white plaques often bilateral hereditary
white sponge nevus
which hereditary lesion:
Rare autosomal dominant genodermatosis
Descendants of Native Americans who originally lived in North Carolina
Duplication of chromosome 4q35
hereditary benign intraepithelial dyskeratosis
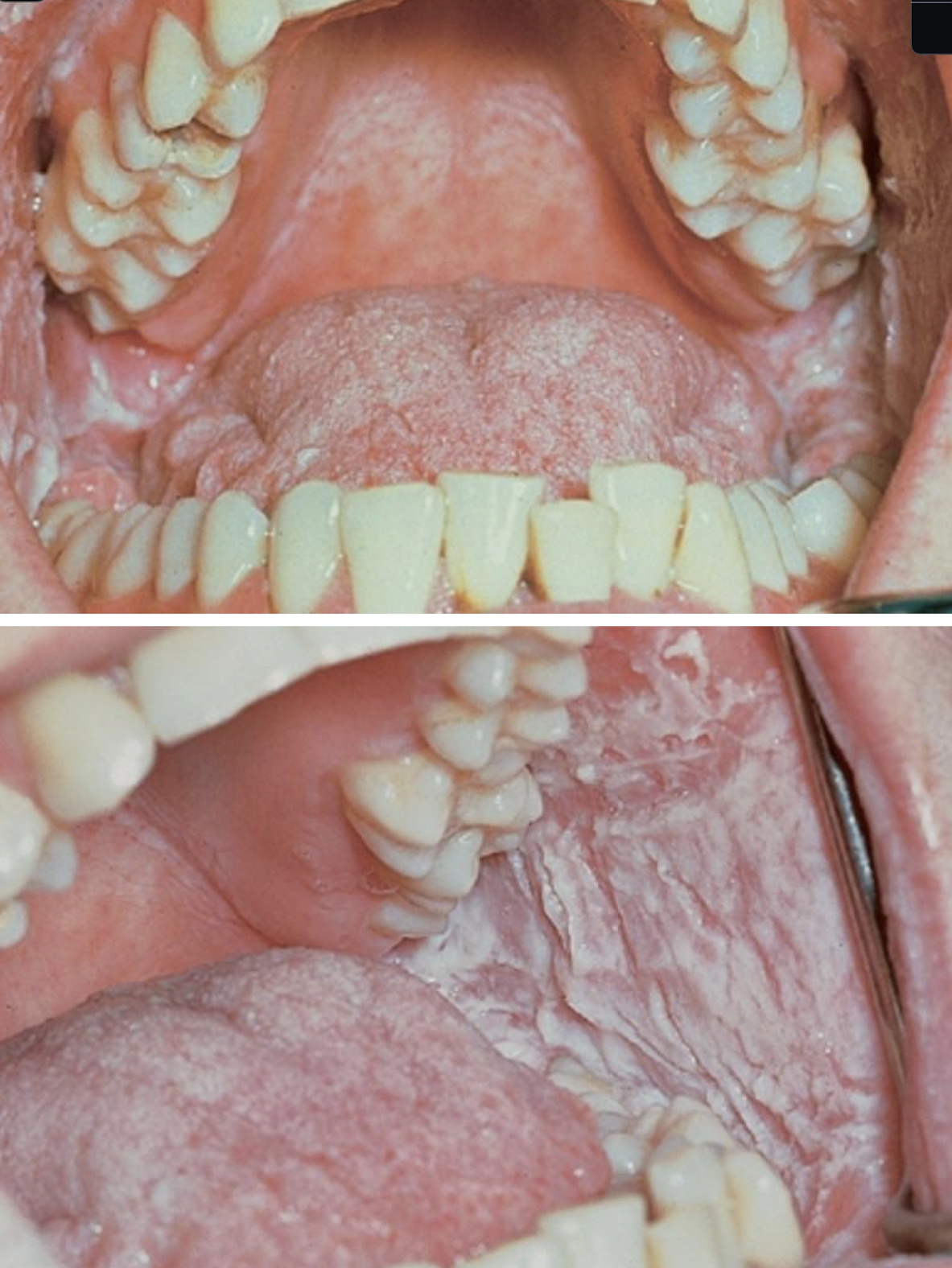
which hereditary lesion clinical features:
Develops during childhood
Thick, corrugated white plaques, buccal and labial mucosa
Other oral mucosal sites
Ocular involvement:
Thick, opaque, gelatinous plaques affecting the bulbar conjunctiva adjacent to the cornea
No treatment required
hereditary benign intraepithelial dyskeratosis
hereditary
hereditary benign intraepithelial dyskeratosis
cell w/in cell appearance hereditary
hereditary benign intraepithelial dyskeratosis
Darier disease/warty dyskeratoma aka
keratosis follicularis
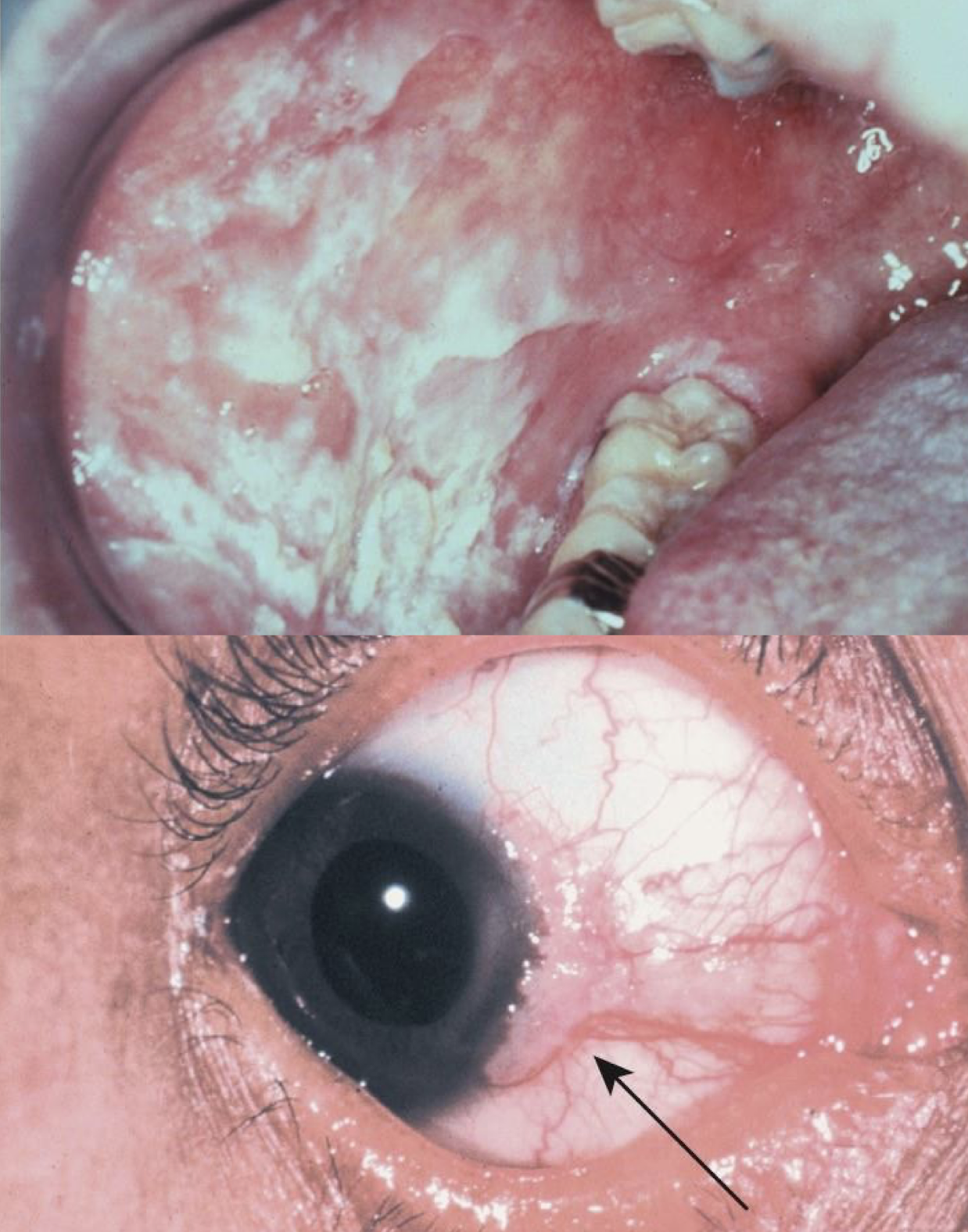
which hereditary lesion:
Autosomal dominant disorder
Mutation in ATP2A2 gene - calcium channels
Alters normal function of
White, painless, keratotic papules desmosomes (glue) and keratin or plaques, and cobblestoning of the oral mucosa
1/3 parotid or submandibular swelling
Erythematous, papules on the skin of the trunk and the scalp
Treated with topical steroids
Darier disease/warty dyskeratoma
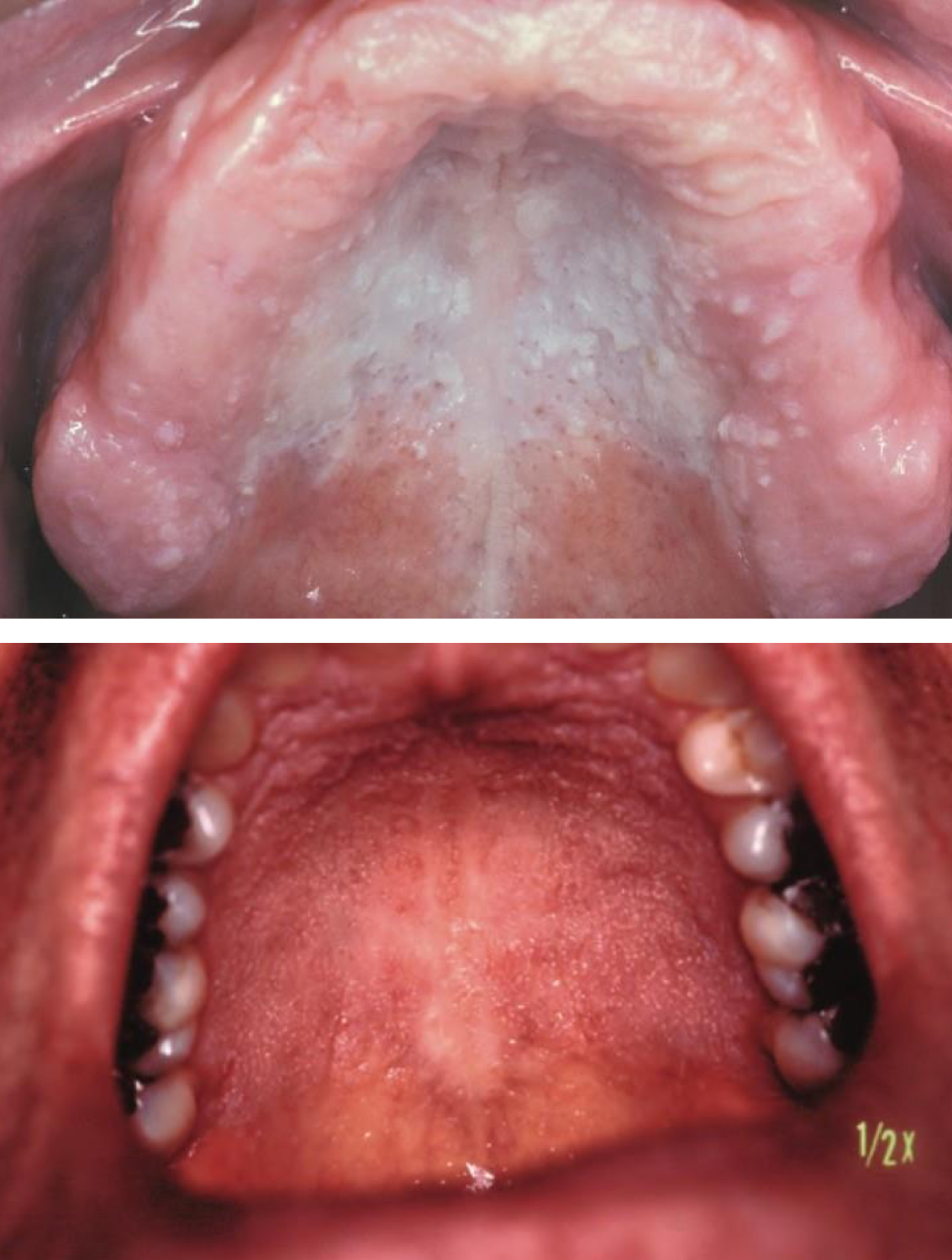
which hereditary lesion:
Darier disease/warty dyskeratoma
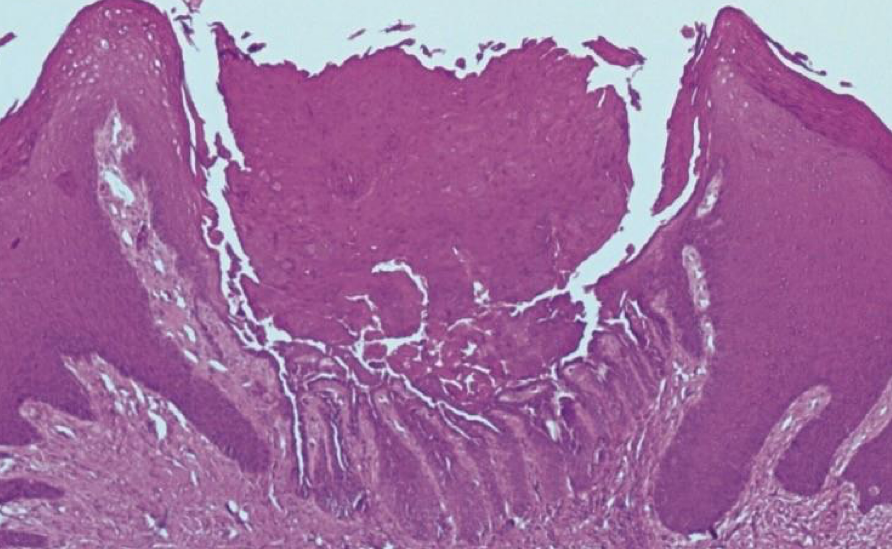
hereditary
Darier disease/warty dyskeratoma
which hereditary lesion:
Rare X-linked recessive genodermatosis (think young and severe)
Mutations in the DKC1 gene
Other mutations have been identified
Disrupt the normal maintenance of telomerase
Risk of oral cancer and aplastic anemia
dyskeratosis congenita (DKC)
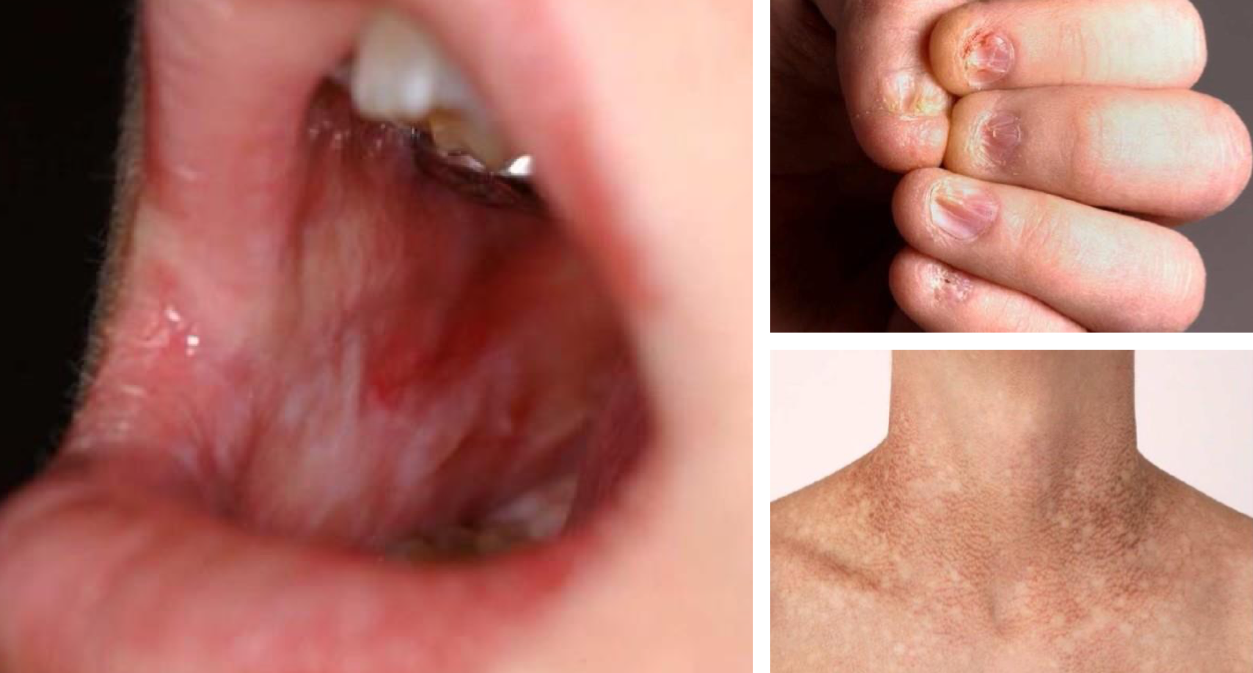
which hereditary lesion clinical features:
Apparent during first decade
Nail dystrophy
Oral leukoplakia
Abnormal skin pigmentation
dyskeratosis congenita (DKC)
which infectious lesion:
Opportunistic fungal infection
Antibiotics, inhaled/topical steroids, immunosuppression, dry mouth, denture
Clinical features:
Pseudomembranous
Erythematous
Hyperplastic
Antifungals
Nystatin suspension
Clotrimazole troches
Fluconazole
oral candidiasis
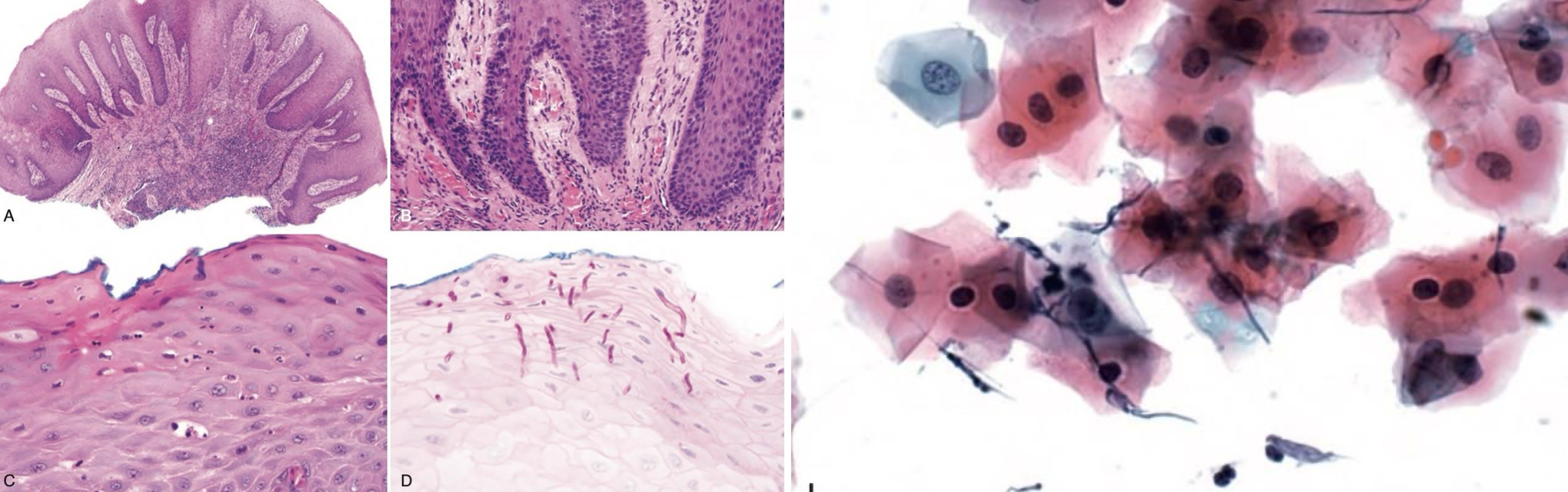
infectious lesion: hyphae w/in keratinocytes, biomorphic forms and cytology of epithelial cells
oral candidiasis
which infectious lesion:
Caused by Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)
Not a premalignant lesion
HIV/AIDS with low CD4 counts, immunocompromised, topical steroids, healthy individuals - 10%
Clinical features: White, vertical, linear lesion or plaque, lateral border of tongue
Adjustment of HIV medications and systemic immunosuppressants
May be treated with topical antivirals
oral hairy leukoplakia
infectious virally modified ballooned cells
oral hairy leukoplakia
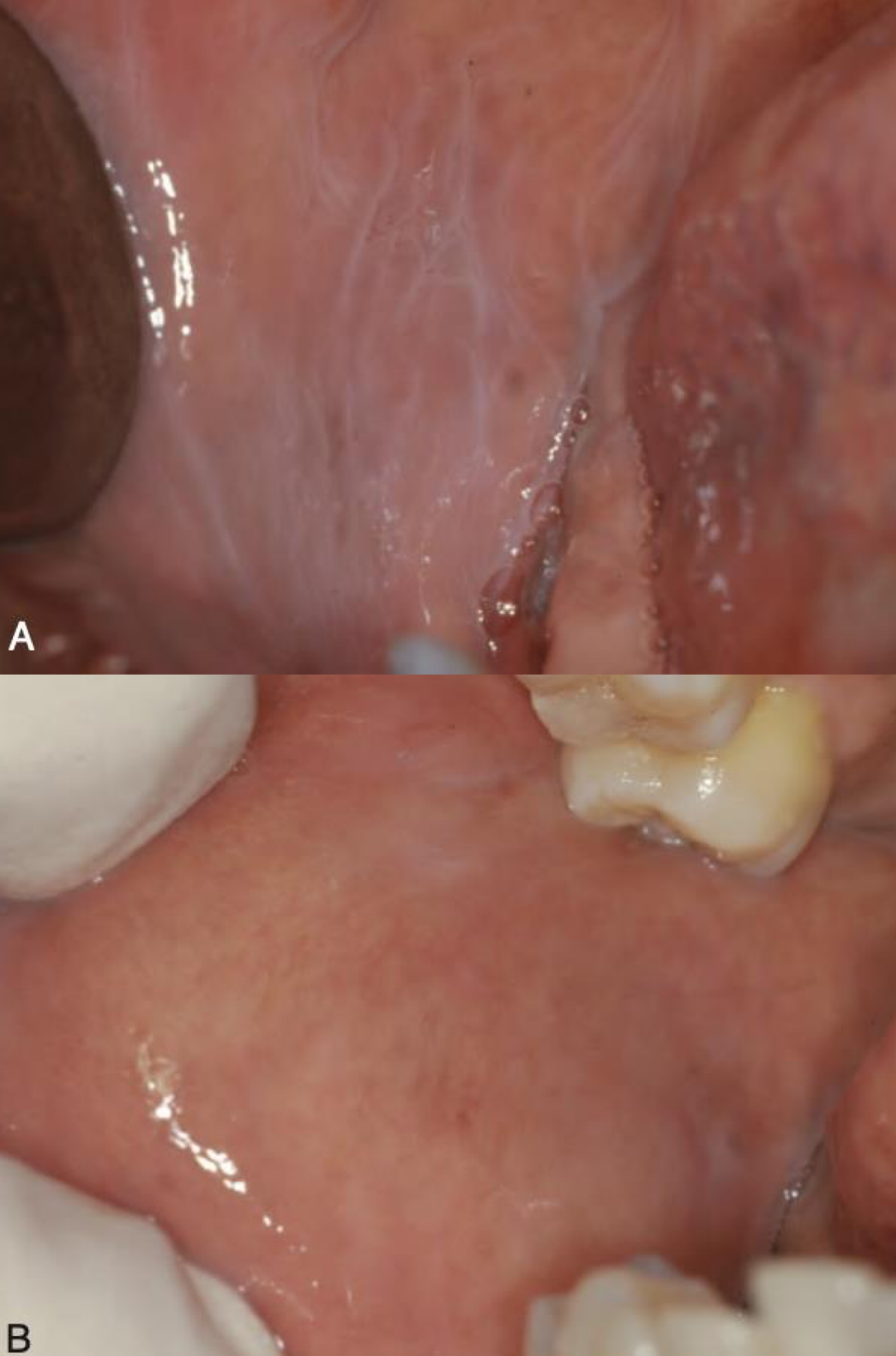
which environmental/reactive lesion:
Delicate lacy, gray-white lines on the buccal mucosa or ventral tongue
Disappears on stretching the mucosa
Very common
Mildly irritating substances
Smoke from tobacco products or marijuana
caustic oral rinses, or toothpaste
Traumatic, parafunctional habit such as mucosal sucking
No treatment required
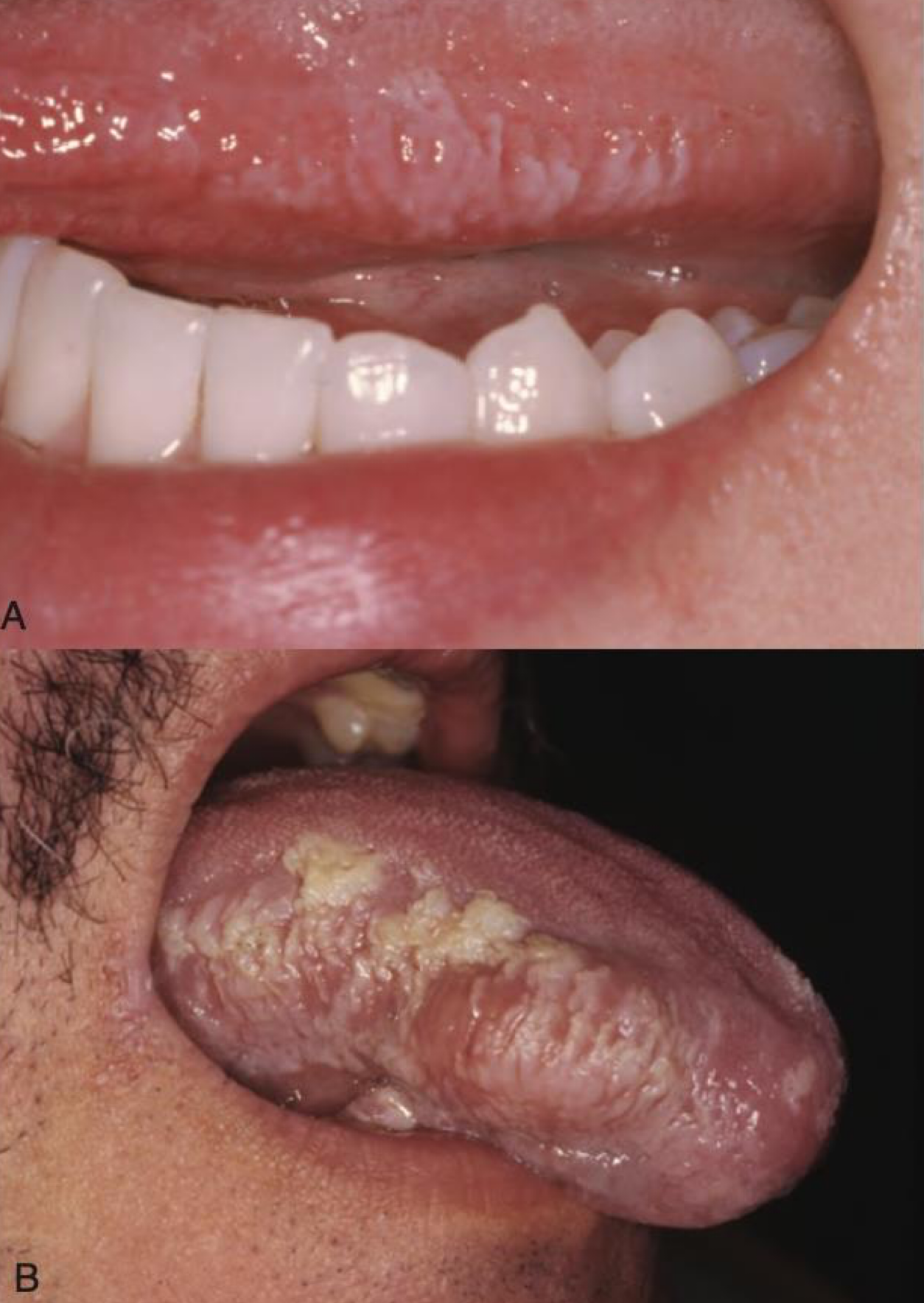
leukoedema
which environmental/reactive lesion: acanthotic edematous change
leukoedema
which environmental/reactive lesion:
Painless, thready white tissue on the mucosa, peels off leaving normal mucosa
Caustic mouth washes high in alcohol content
Strong toothpastes (whitening)
Other contactants that are irritants the mucosa
Discontinuation of offending agent
contact desquamation
which environmental/reactive lesion:
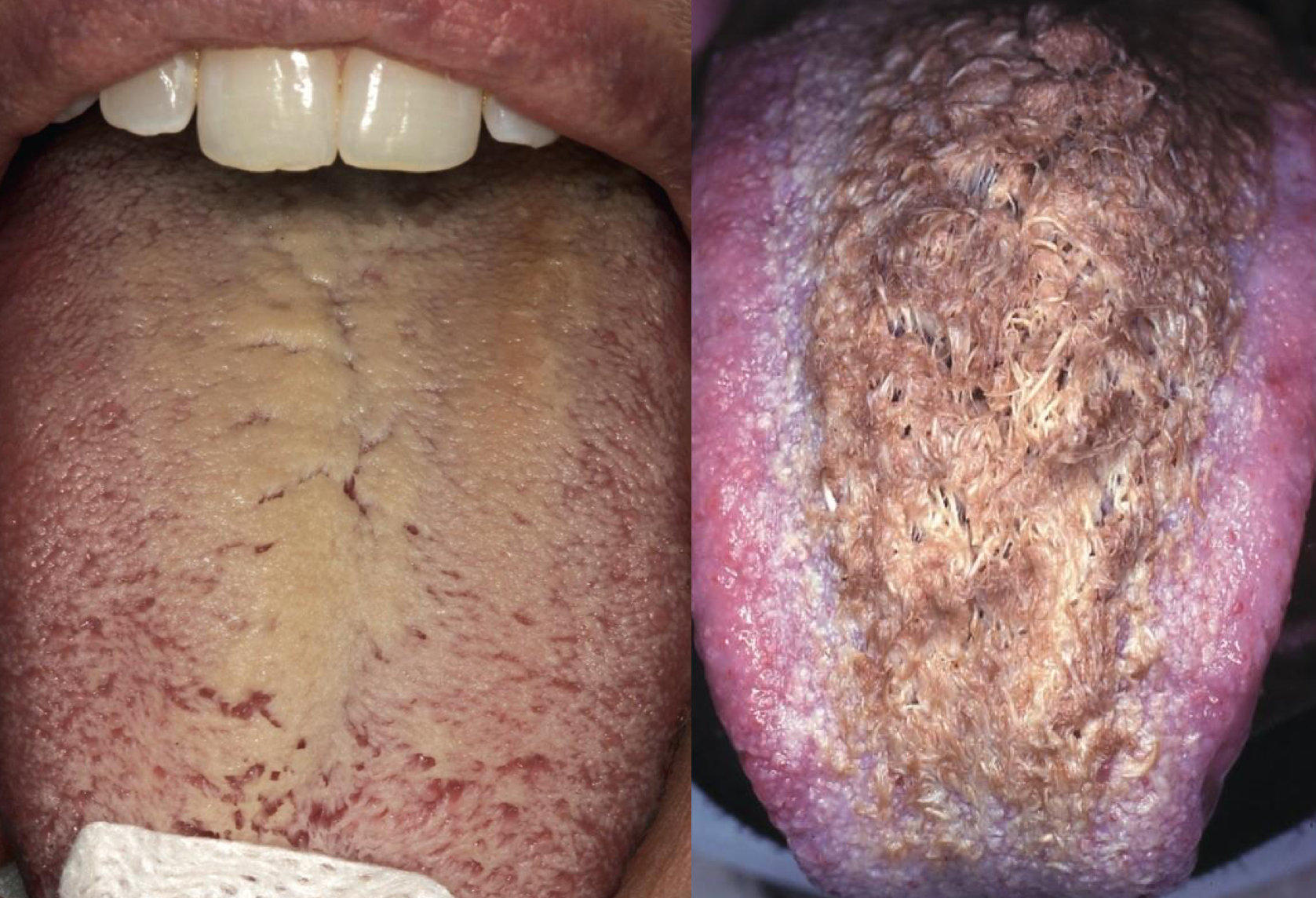
“Hairy tongue”
Elongated filiform papillae on the dorsal surface of the tongue
Yellowish white, can be discolored
Heavy smokers, poor PO intake, dehydration, poor oral hygiene
Benign, esthetic concerns
coated/hairy tongue
which environmental/reactive lesion:
hairy tongue
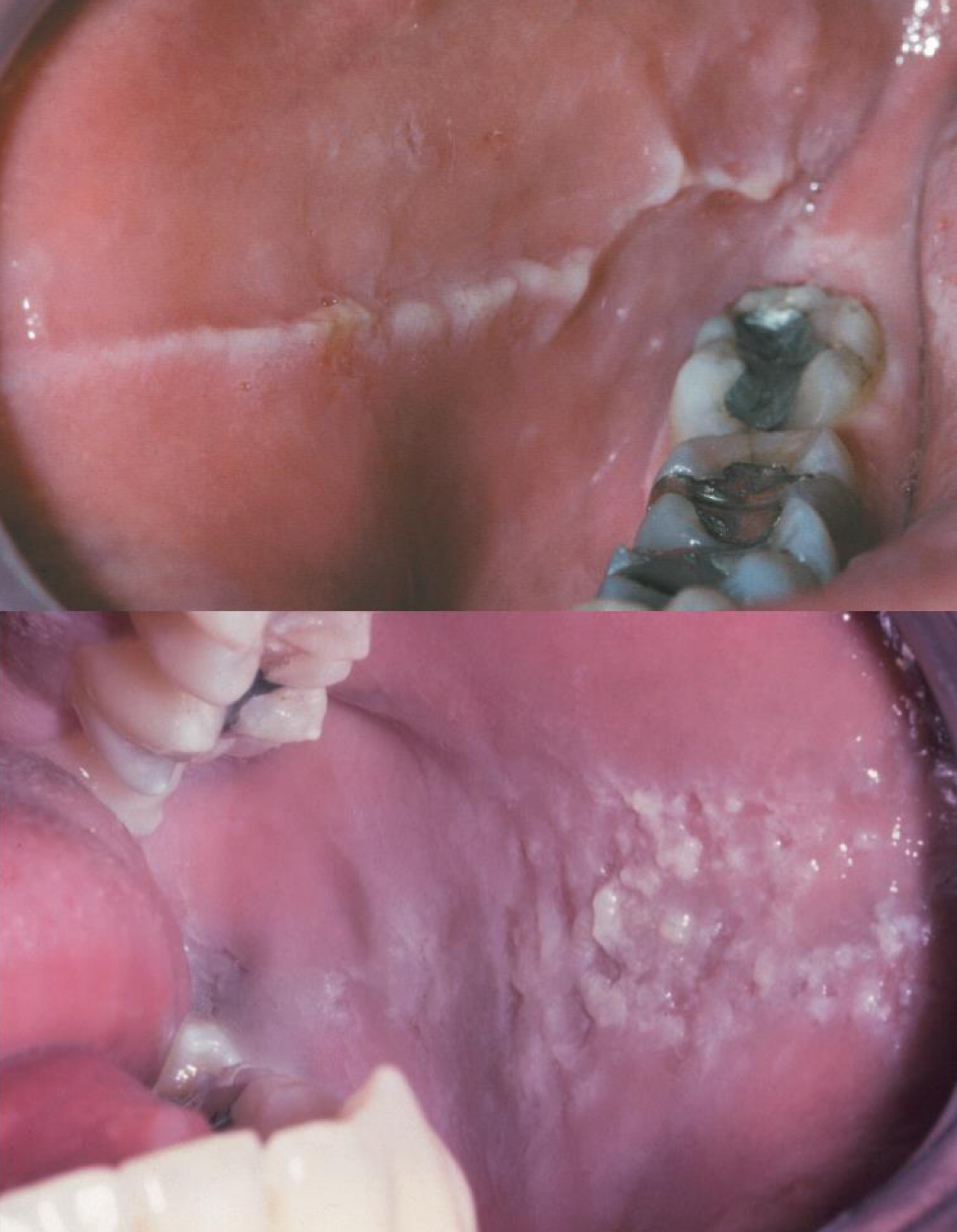
which environmental/reactive lesion:
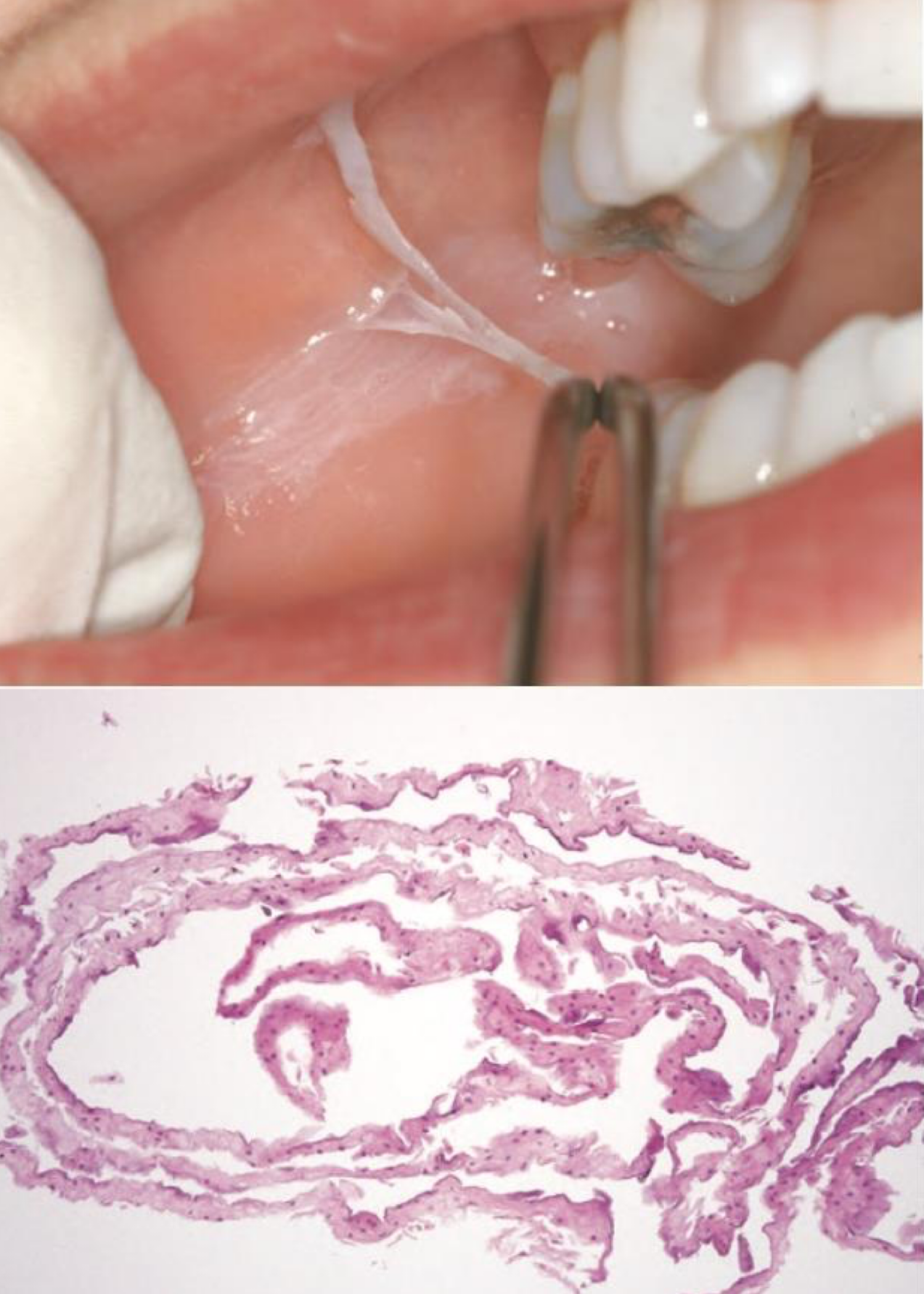
Linea alba- buccal mucosa
Morsicatio mucosae oris- chronic chewing of the oral mucosa
Biopsy is rarely indicated
No treatment required
frictional keratosis
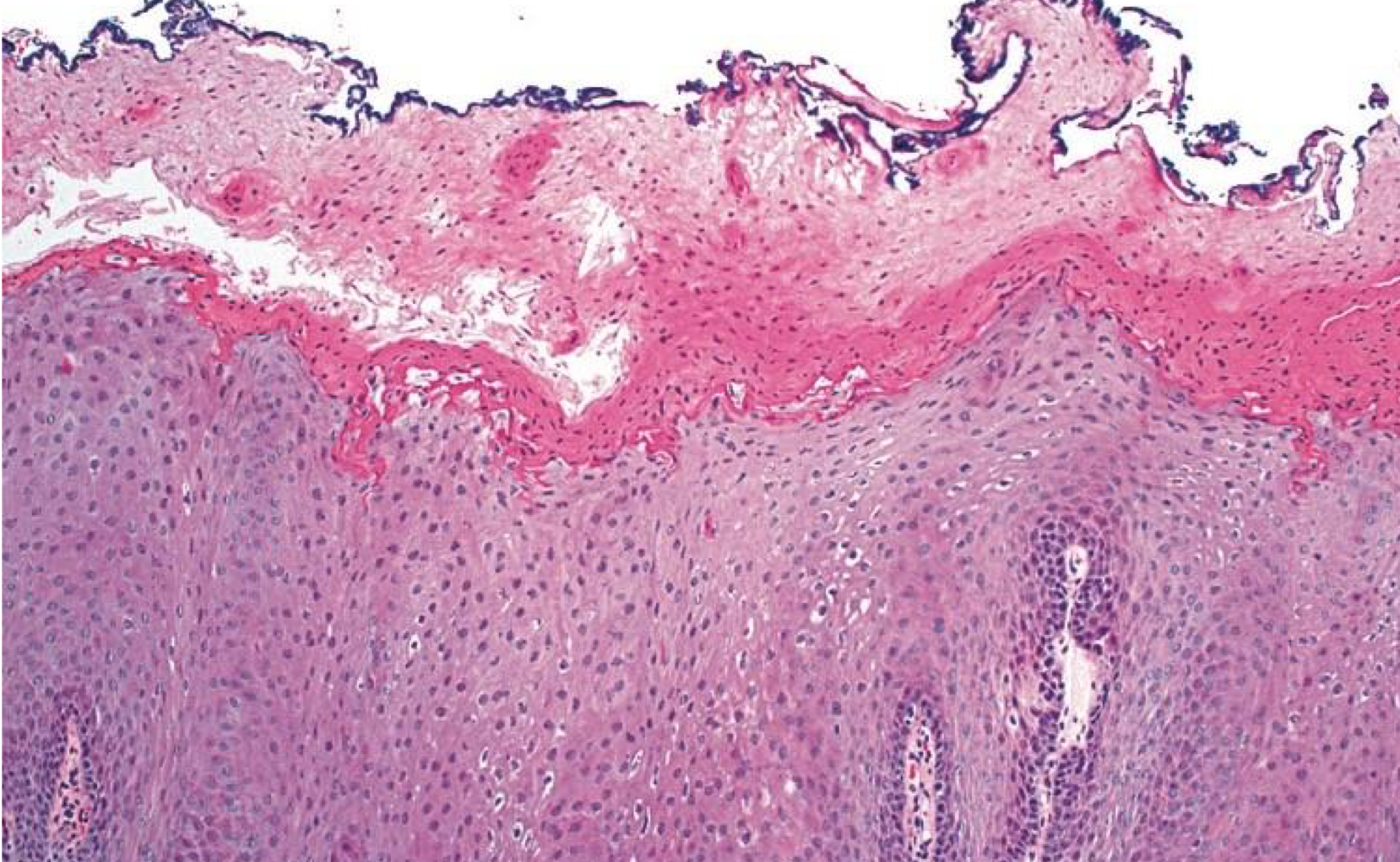
which environmental/reactive lesion: morsicatio buccarum
increased parakeratin → protective and acantosis make lesion white
frictional keratosis
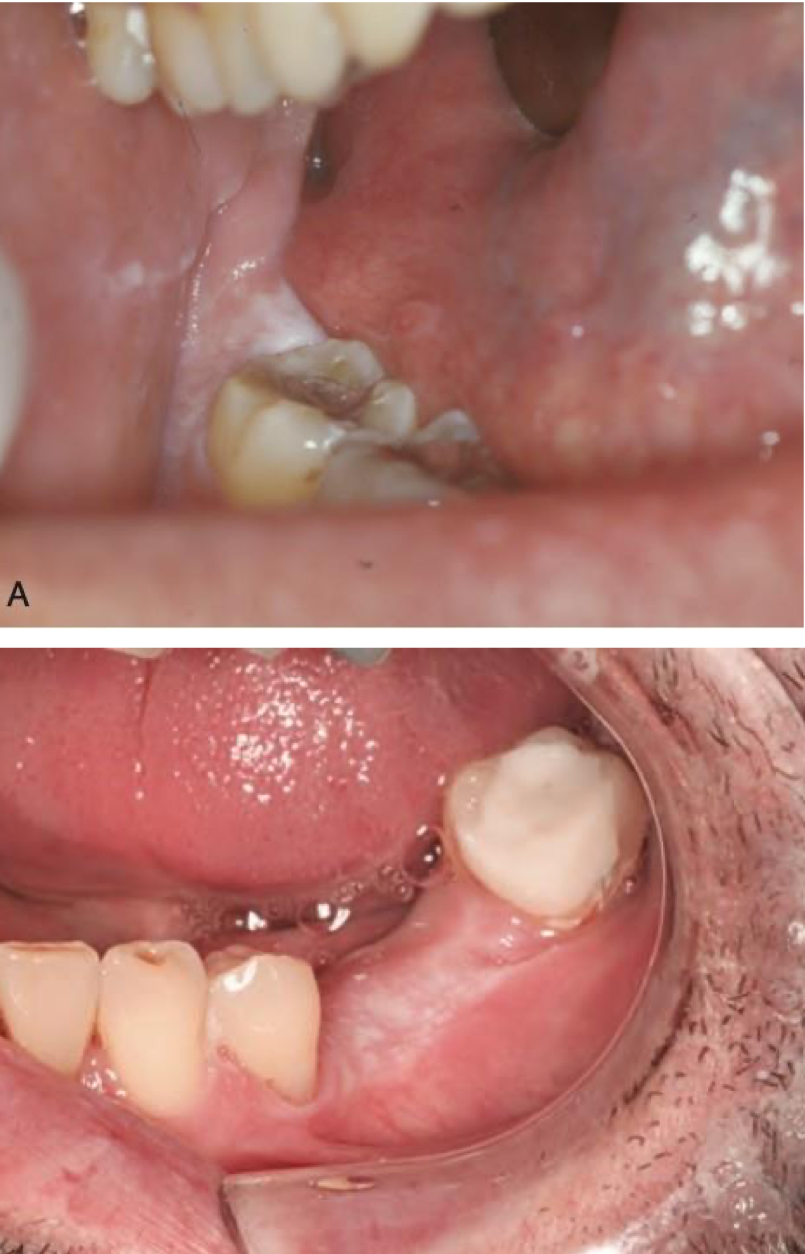
which environmental/reactive lesion:
Poorly demarcated, rough white plaque of the keratinized mucosa
Friction with food
Often confused with leukoplakia
No treatment required
benign alveolar ridge keratosis
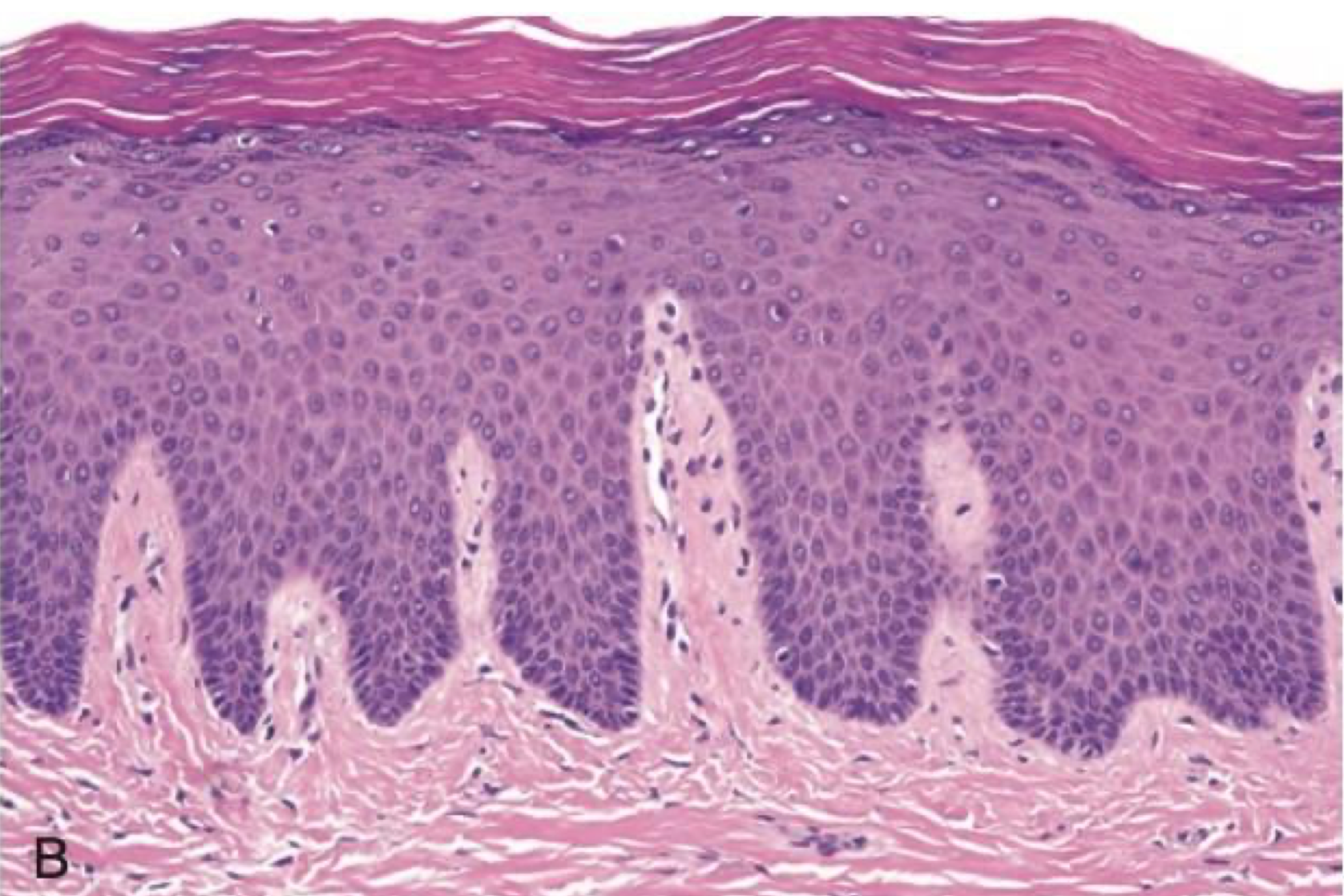
which environmental/reactive lesion:
benign alveolar ridge keratosis
which environmental/reactive lesion:
Leathery, white change of the hard palatal mucosa in long term smokers
Mucosal response to heat
No treatment required
Reversible after smoking cessation
nicotine stomatitis
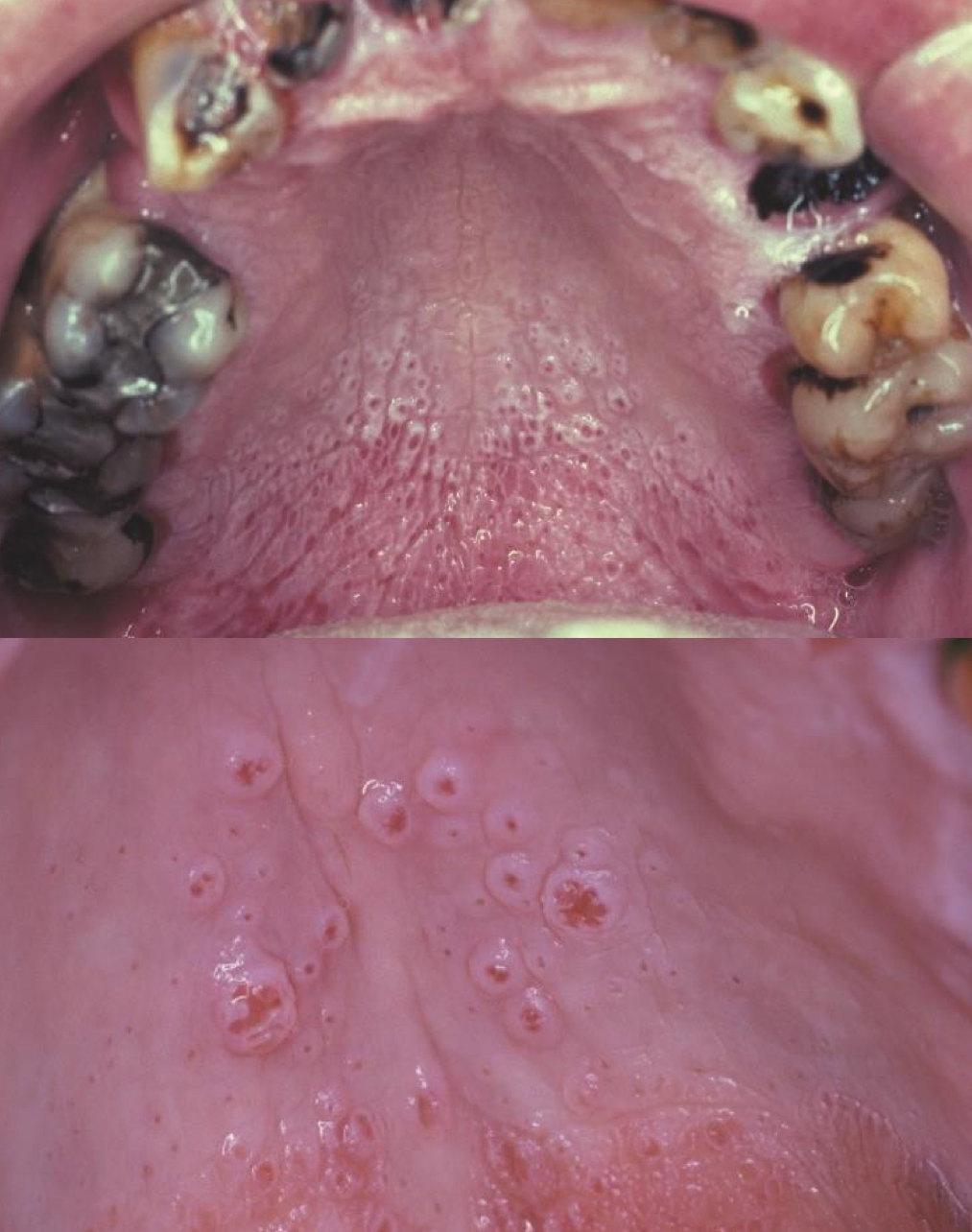
which environmental/reactive lesion: prominent salivary ducts from heat
nicotine stomatitis
which environmental/reactive lesion:
Contact with caustic agents within the tobacco
Early: grayish-white wrinkles and parallel ridges and fissures in the area where the tobacco is placed - Reversible
Advanced: well-demarcated, keratotic plaques
Must be biopsied for evaluation of dysplasia
Regular follow up
smokeless tobacco keratosis
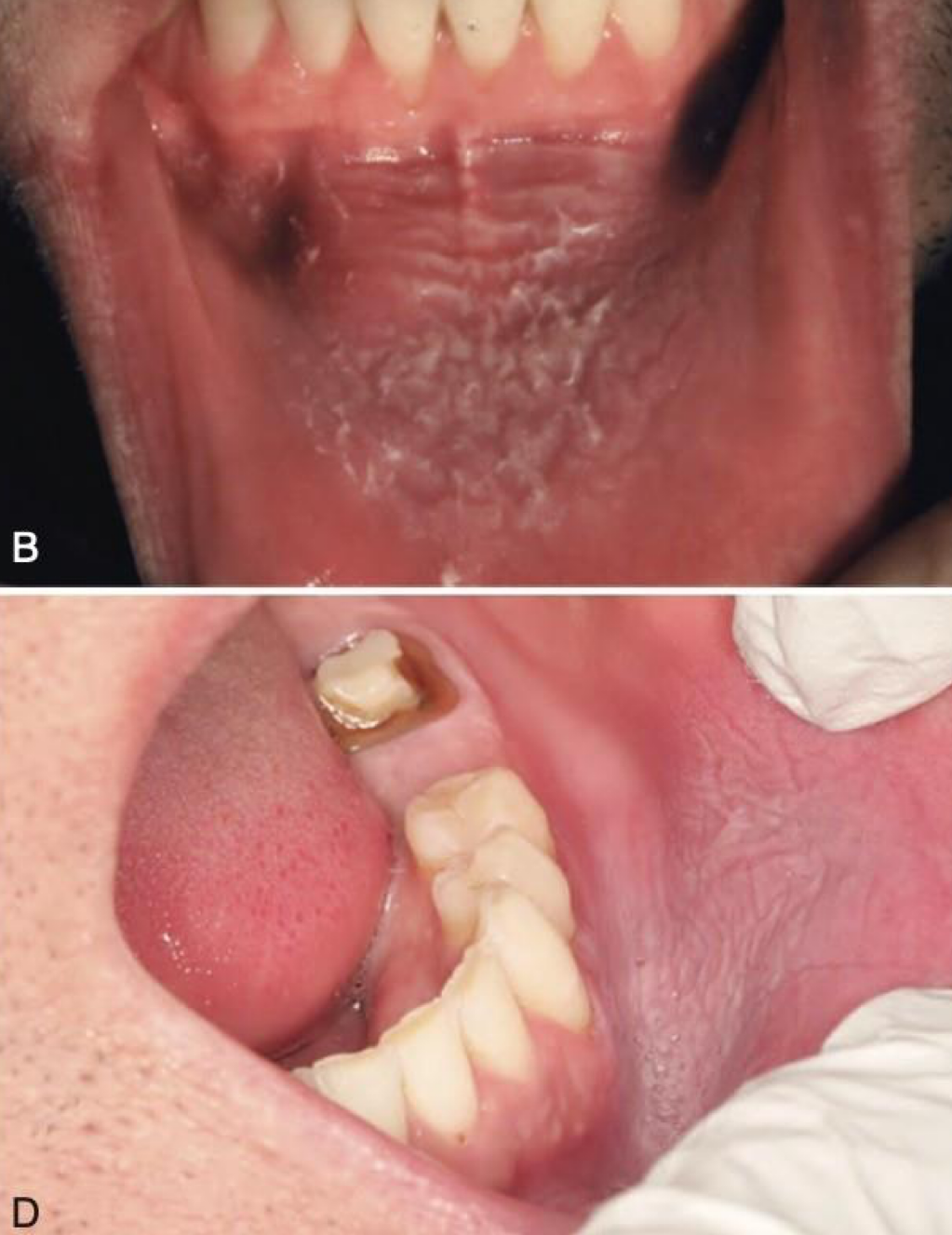
which environmental/reactive lesion:
smokeless tobacco keratosis
which environmental/reactive lesion: pale almost necrotic and edematous
smokeless tobacco keratosis
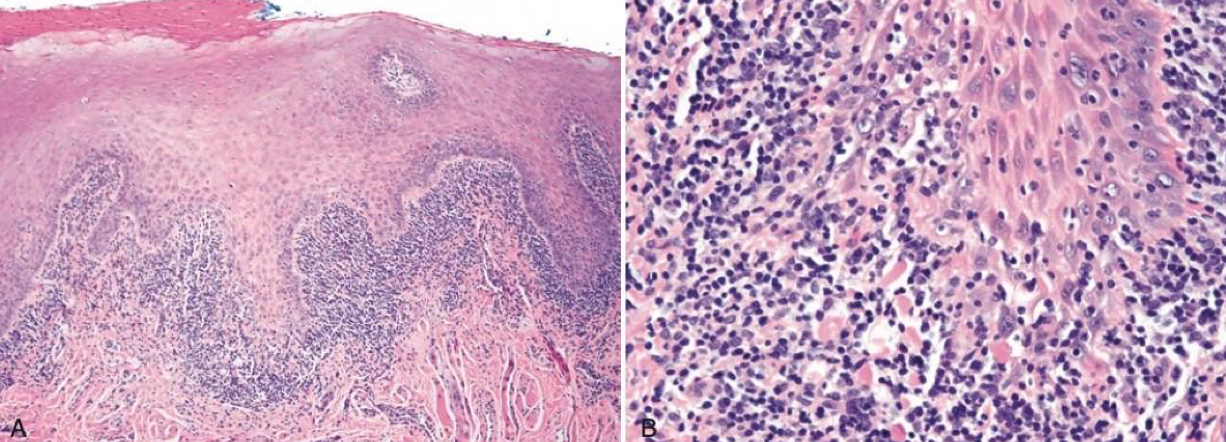
which autoimmune/immune-mediated/allergic lesion:
1% to 2% of middle-aged adults
2–3 : 1 female predominance
Idiopathic, medication-induced; hep C virus oral manifestations
T-cell destruction of the basal cells
Clinical features:
Typically, bilateral and symmetrical
Reticular/keratotic: Wickham striae
Ulcerative
Erythematous/erosive
Contact lichenoid reactions to dental amalgams
Treatment: Topical and systemic steroids or steroid-sparing agents (but pt can’t be on them forever), Replacing amalgam restorations
Controversial malignant transformation potential 0.1-1% of cases
oral lichen planus
REU score
reticular, erythematous, ulcerative
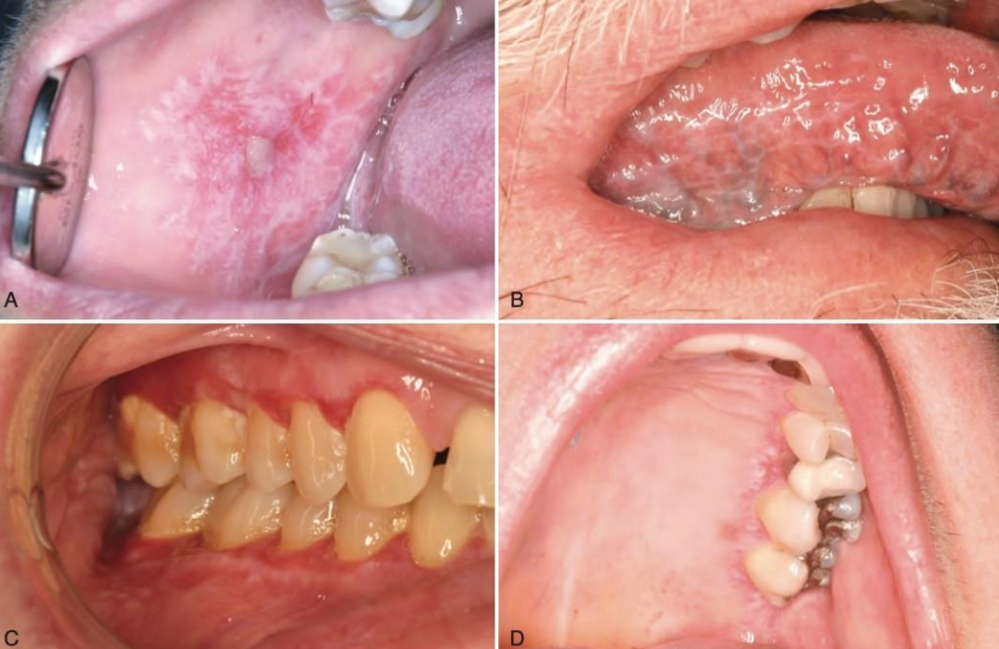
which autoimmune/immune-mediated/allergic lesion: A-ulcers D-desquamative gingivitis and reticulations around erythema
oral lichen planus
which autoimmune/immune-mediated/allergic lesion:
oral lichen planus
which autoimmune/immune-mediated/allergic lesion:
oral lichen planus
which autoimmune/immune-mediated/allergic lesion: T cell mediated basal cell destruction; blue band lymphocytes; stellate looking on edges bc keratin layer acanthosis
oral lichen planus
which autoimmune/immune-mediated/allergic lesion:
Autoimmune disease, unknown etiology
Affects multiple organs
SLE and DLE
Circulating antibodies in SLE:
ANA, anti-Smith, anti–double-stranded DNA, and anti ribonucleoprotein
20% and 45% of patients with DLE and SLE, respectively, have oral lesions
Oral lesions resemble oral lichen planus
Not always bilateral and symmetrical
Treatment as in OLP
lupus erythematosus
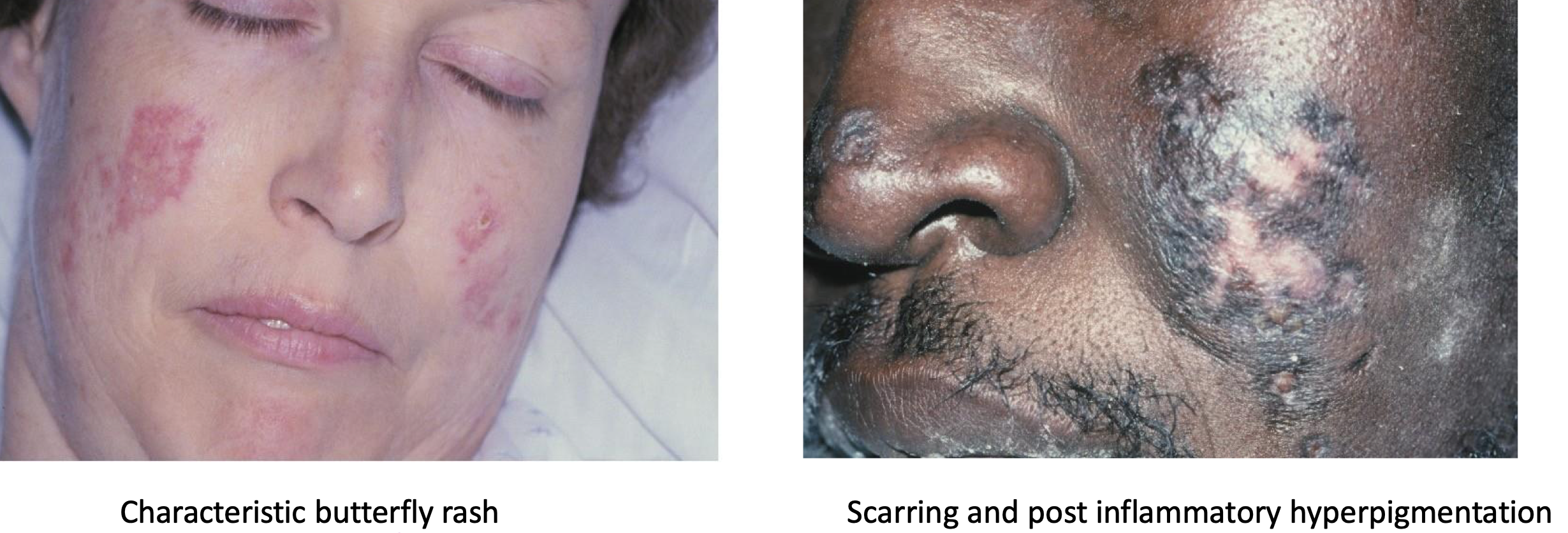
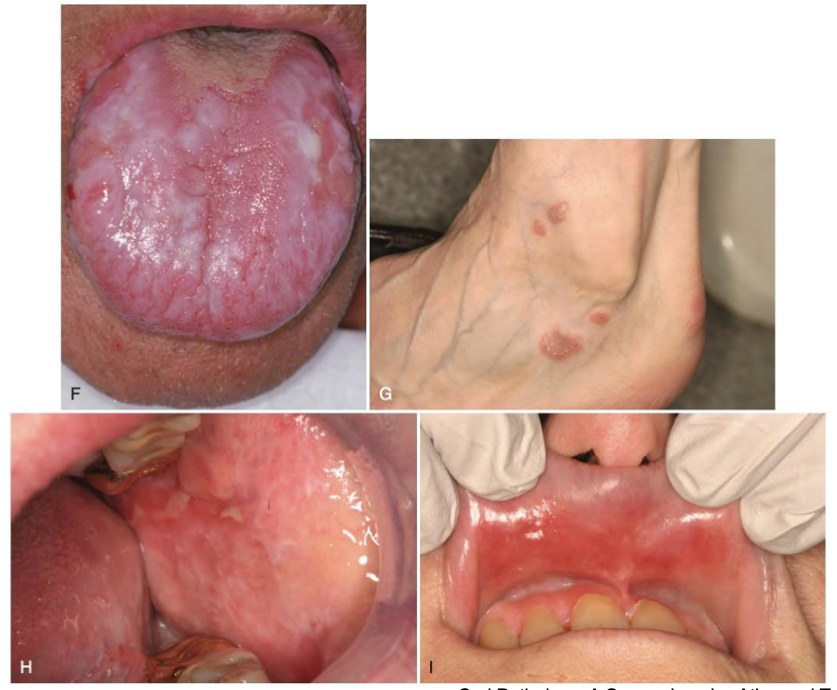
which autoimmune/immune-mediated/allergic lesion:
lupus erythematosus
which autoimmune/immune-mediated/allergic lesion: ulcer w raised border, erythema and striations surround it
lupus erythematosus
which autoimmune/immune-mediated/allergic lesion:
Complication following hematopoietic stem cell transplant for treatment of hematologic malignancies
Acute and chronic > 100 days
Mouth is commonly affected
Oral mucosal lesions essentially resemble OLP
Treated similarly to OLP
oral graft-vs-host disease
which autoimmune/immune-mediated/allergic lesion:
acute: ulcerative and erythematous changes diffusely, lip crusting
chronic: xerostomia, lichen planus-like features, SICCA syndrome-like features, trismus, mucoceles
oral graft-vs-host disease
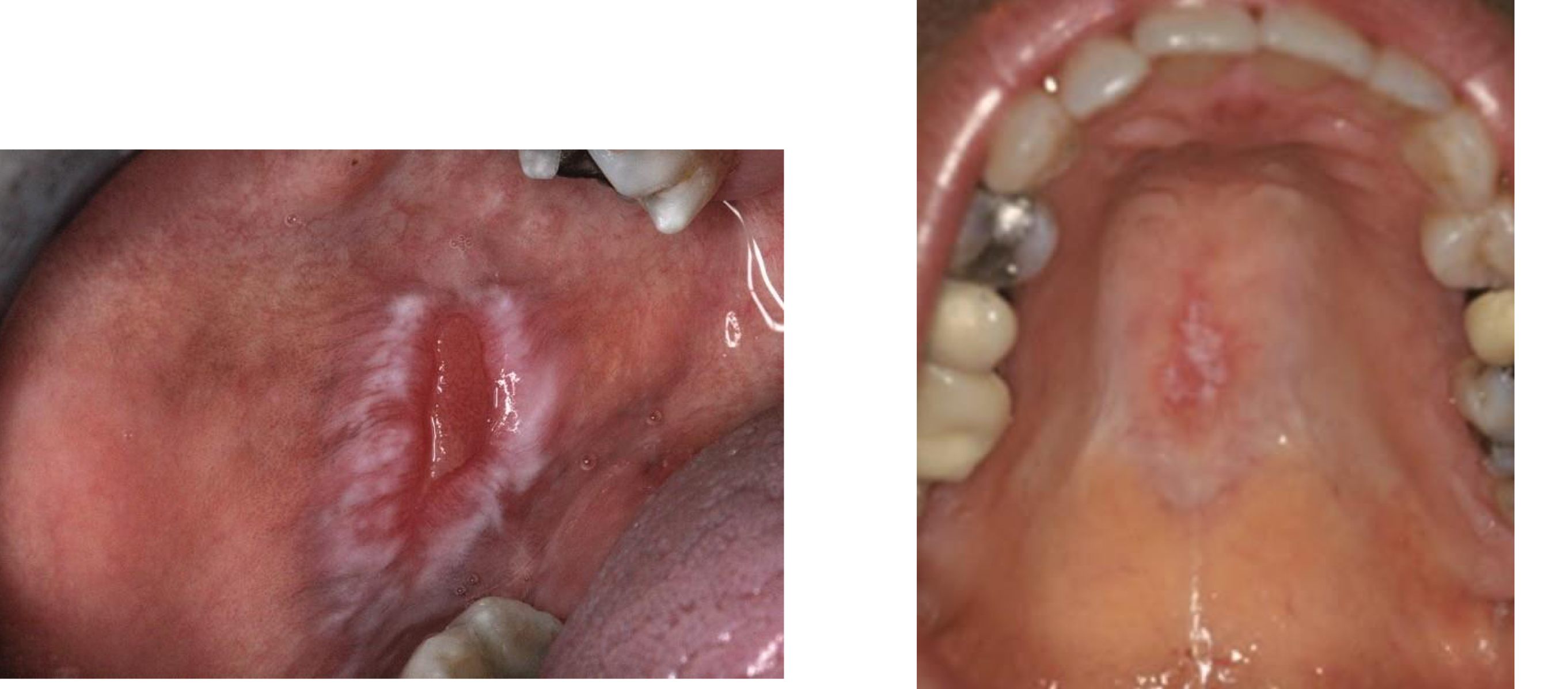
which autoimmune/immune-mediated/allergic lesion:
oral graft-vs-host disease
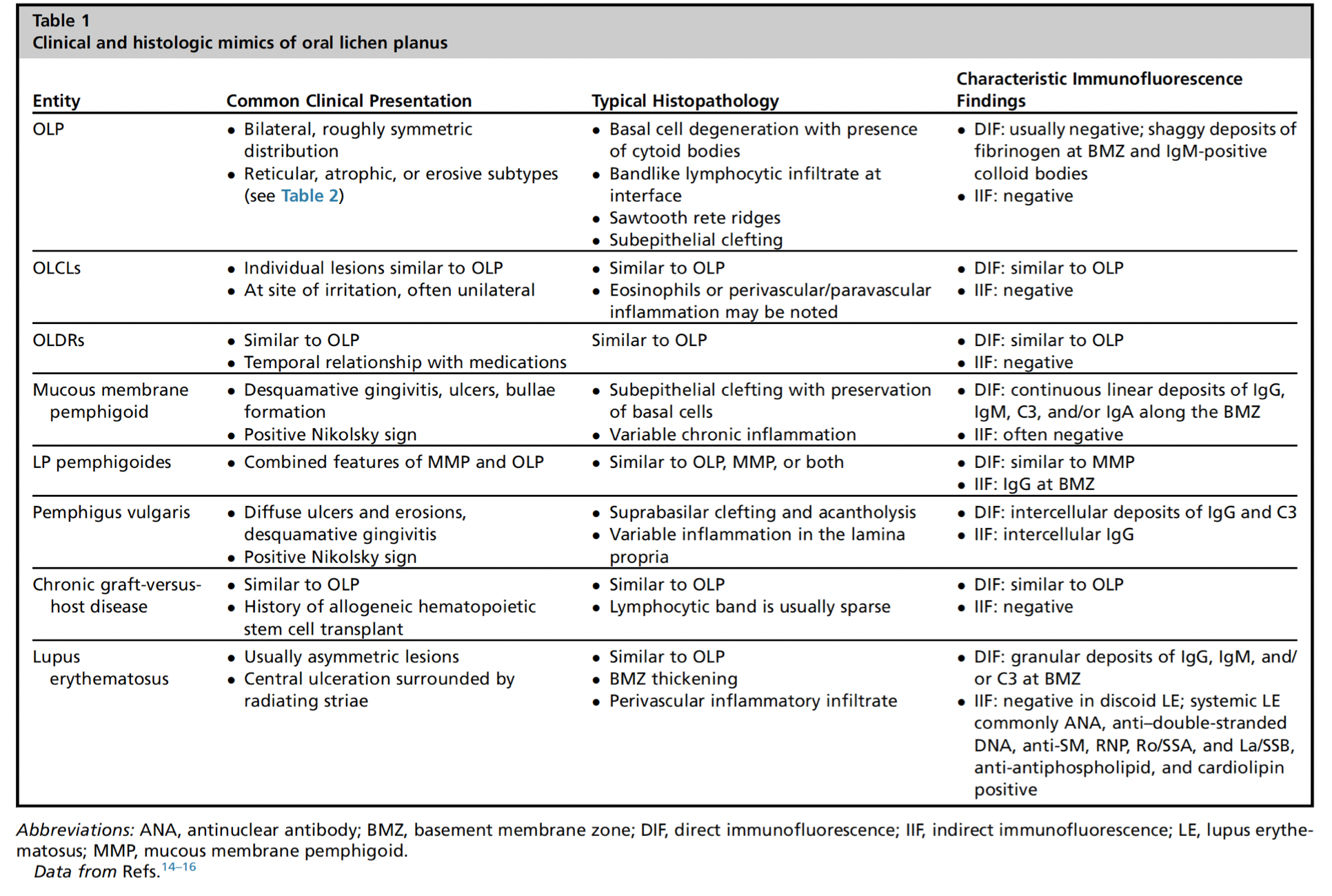
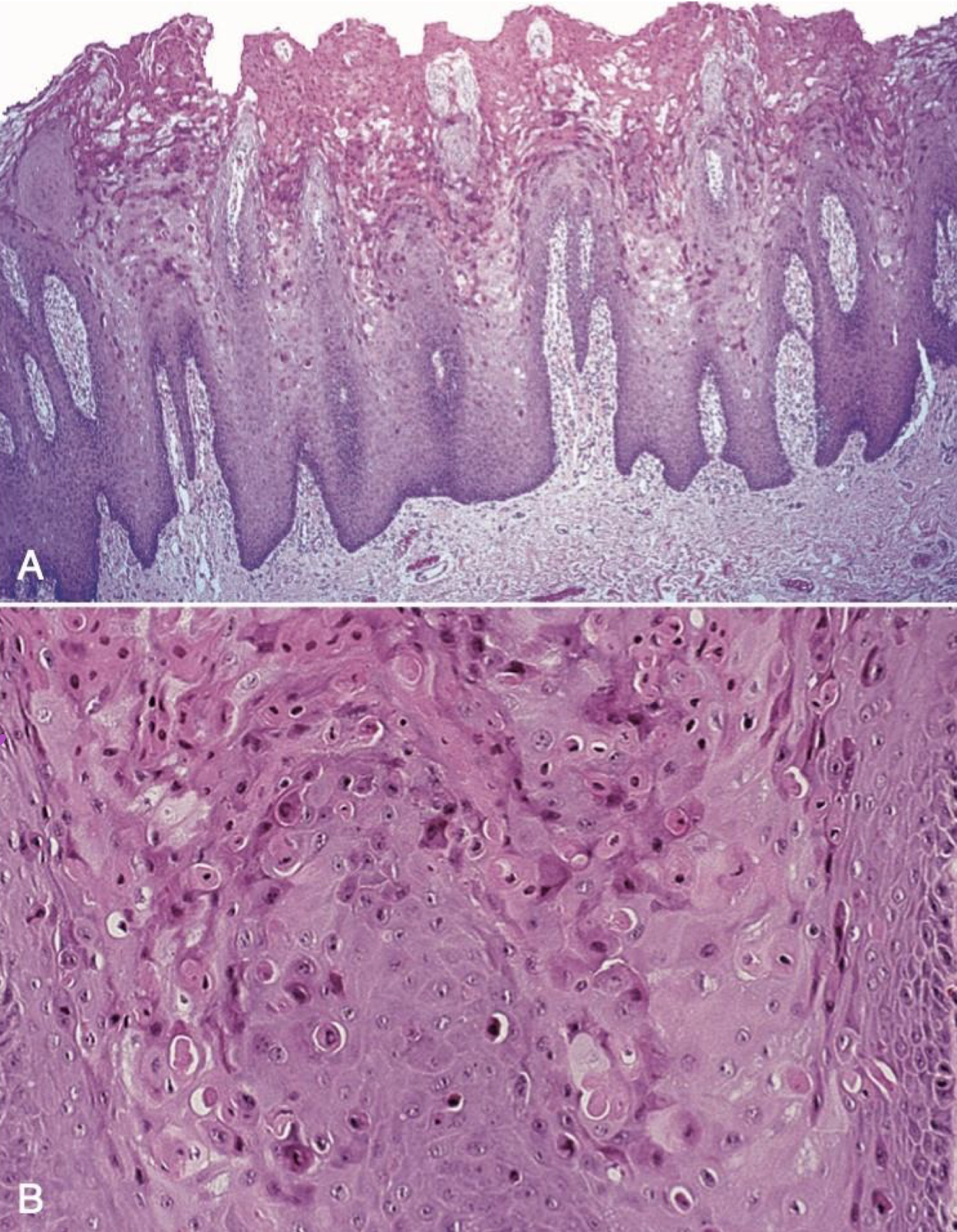
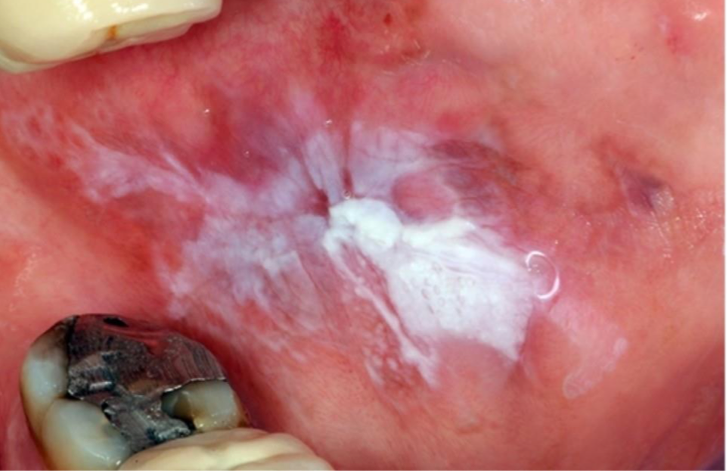
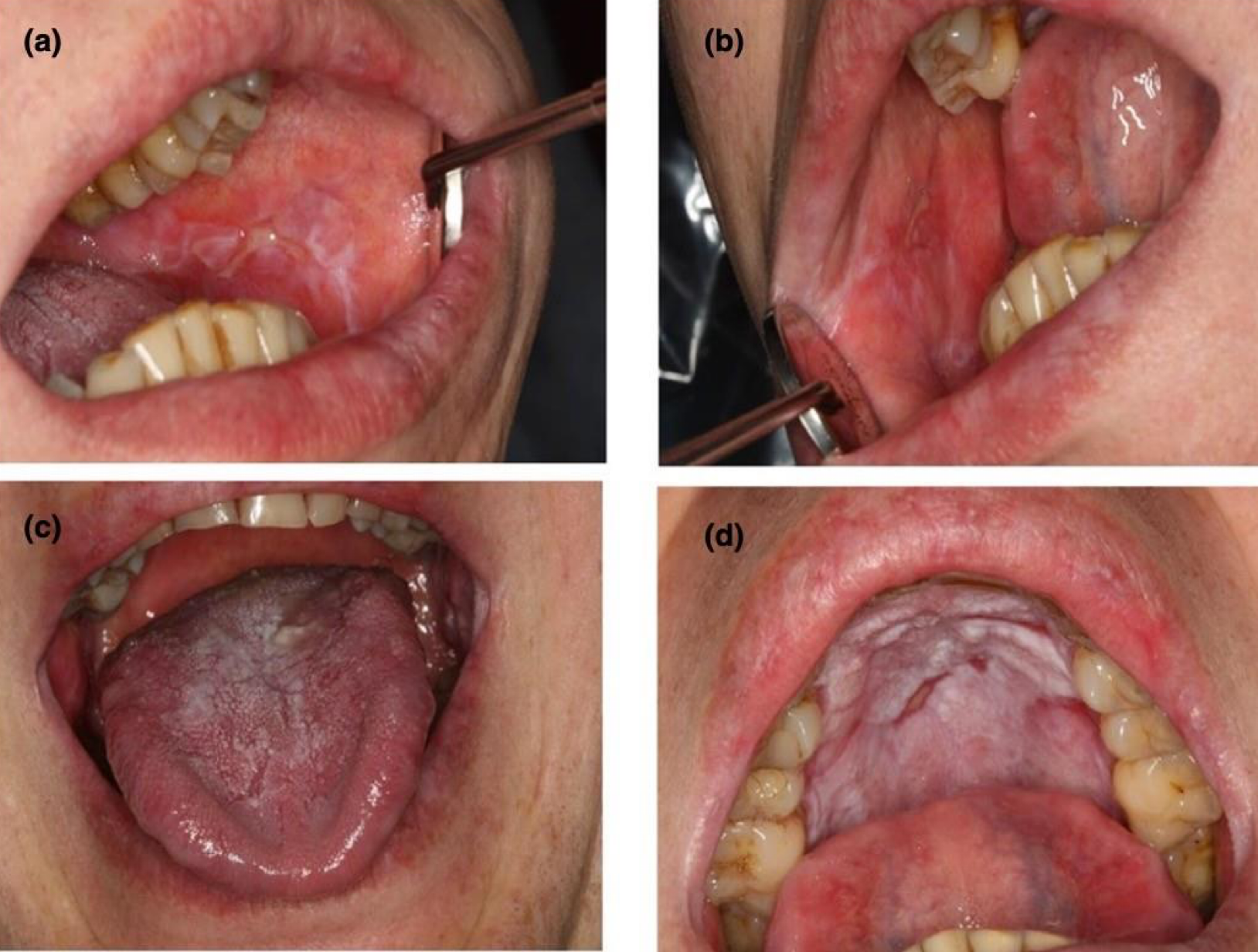
which neoplastic white lesion:
White plaque of questionable risk having excluded other known diseases or disorders that carry no increased risk for cancer
Highly associated with dysplasia and development of cancer
High risk sites: Ventral tongue, floor of mouth, buccal mucosa, soft palate, and gingiva
43% to 47% represent dysplasia, carcinoma-in-situ, or invasive SCC
Homogenous: 16% MT malignant transformation
Non-homogenous
Proliferative leukoplakia: 70-100% MT
oral leukoplakia
which neoplastic white lesion risk factors:
Smoking
Excessive alcohol consumption
H/o cancer and cancer therapy
Family h/o cancer
H/o autoimmune disorder or prolonged immunosuppression
Areca nut chewing
Older age
Human Papilloma Virus
oral leukoplakia
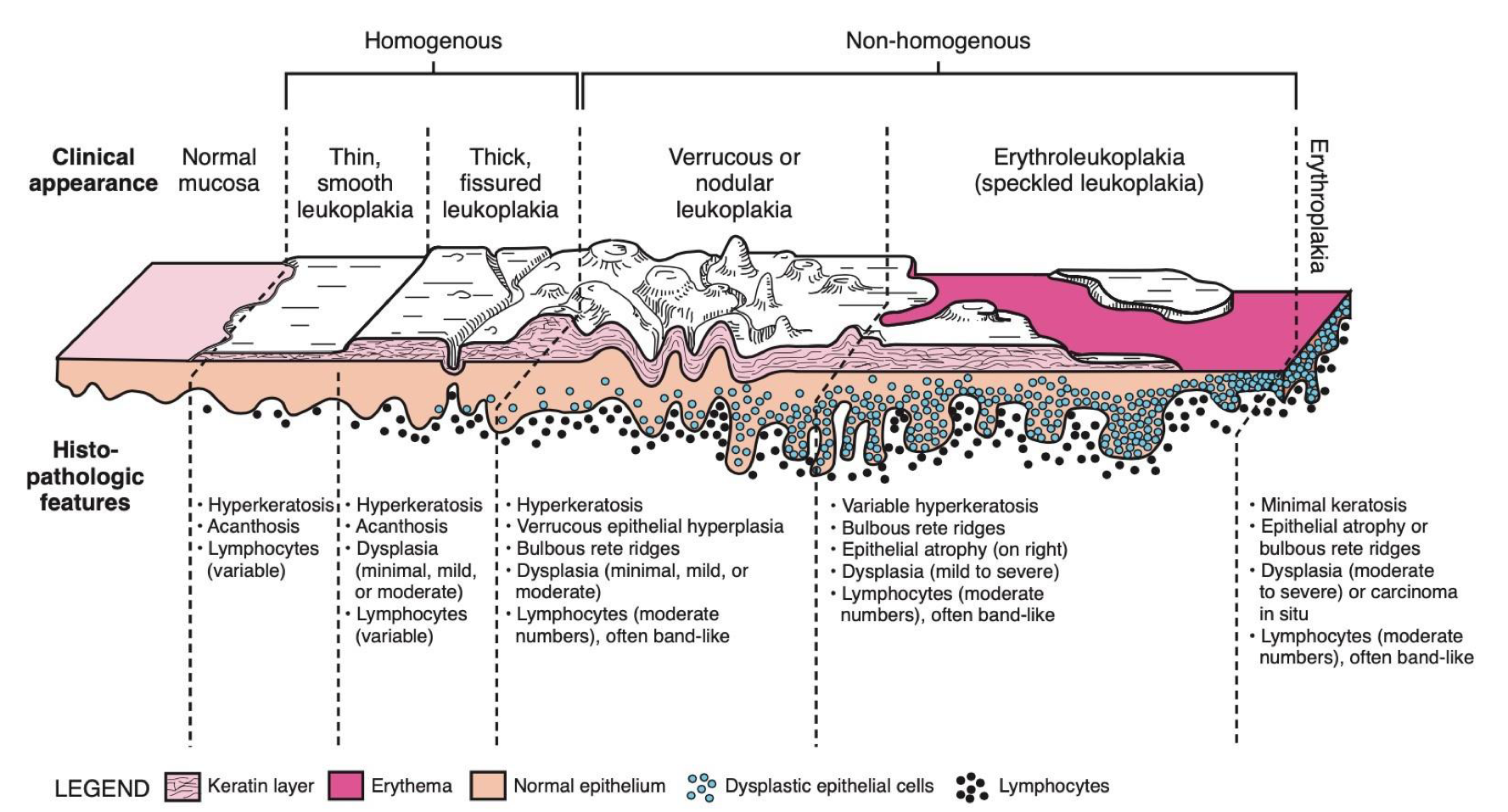
which neoplastic white lesion:
oral leukoplakia
which neoplastic white lesion:
25-27% of (BLANK) become/are dysplasia/SCC - show variable malignant transformation
homogenous 16%
proliferative leukoplakia 70-100%
oral leukoplakia
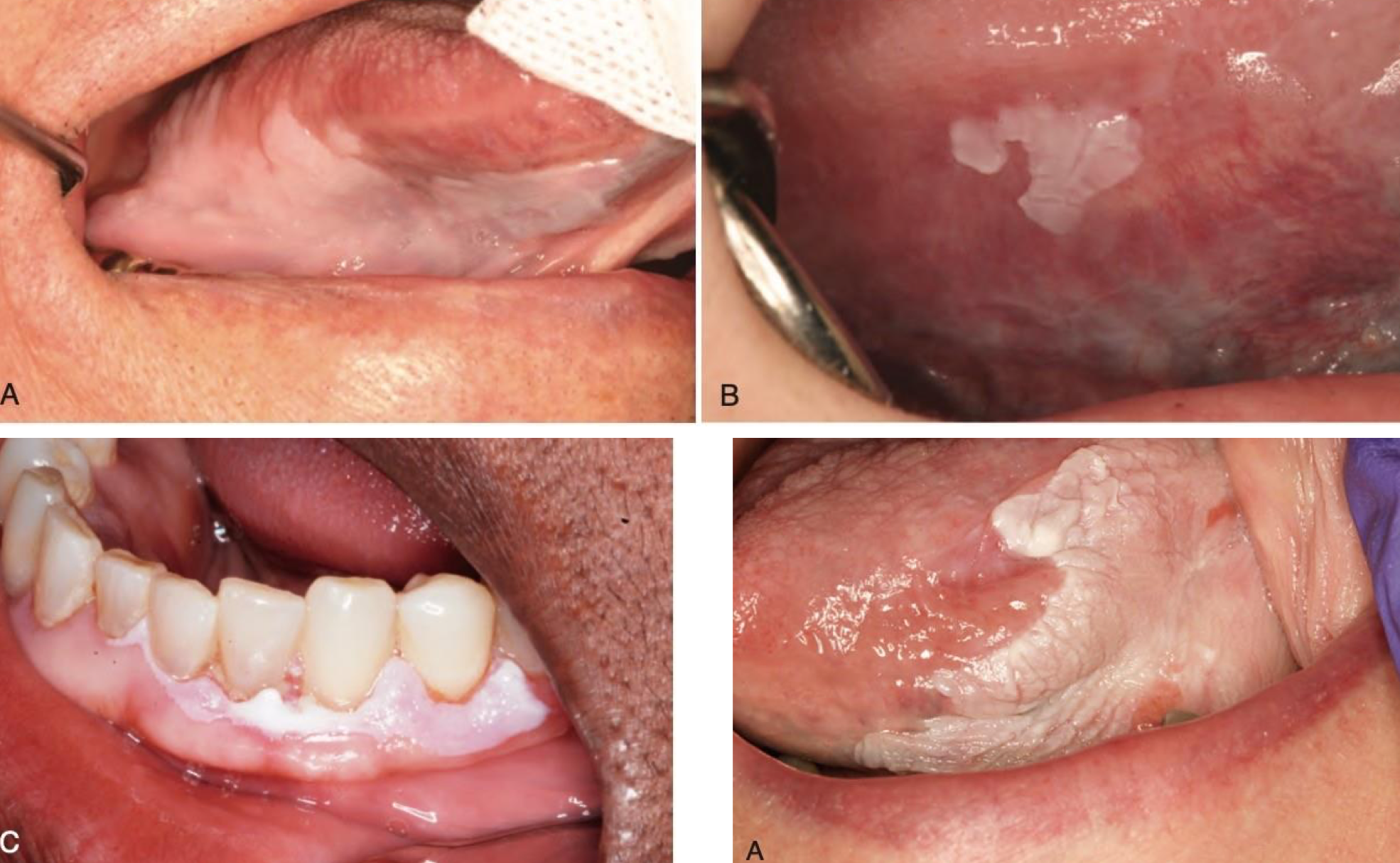
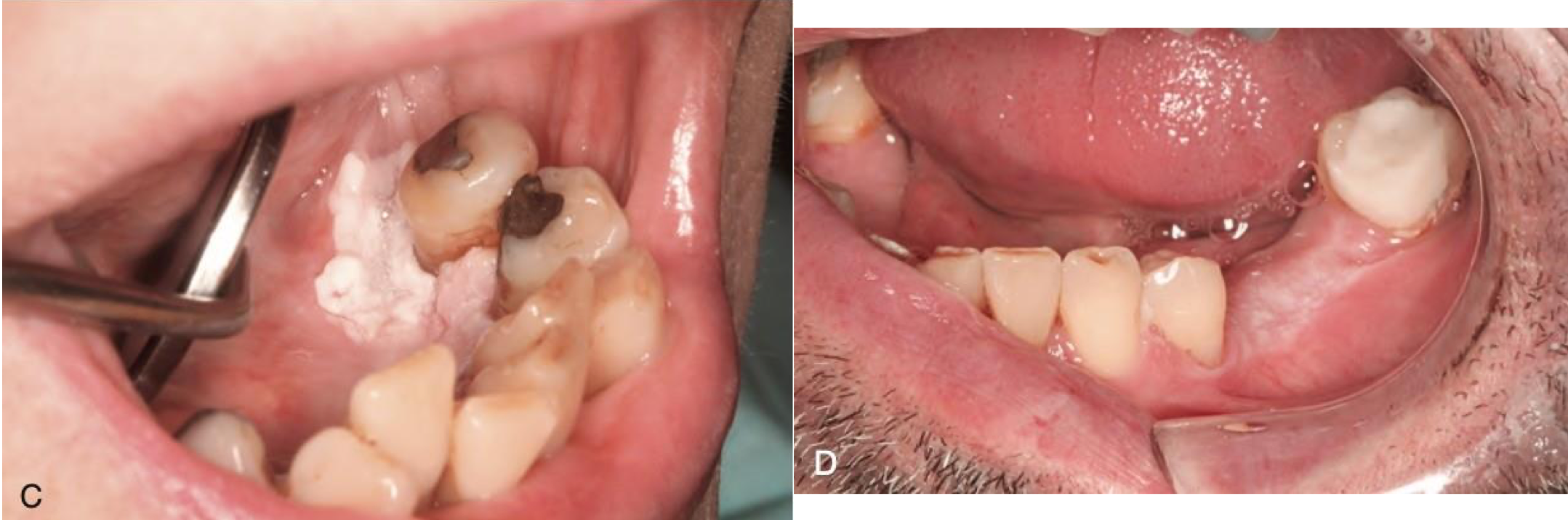
which neoplastic white lesion:
oral leukoplakia

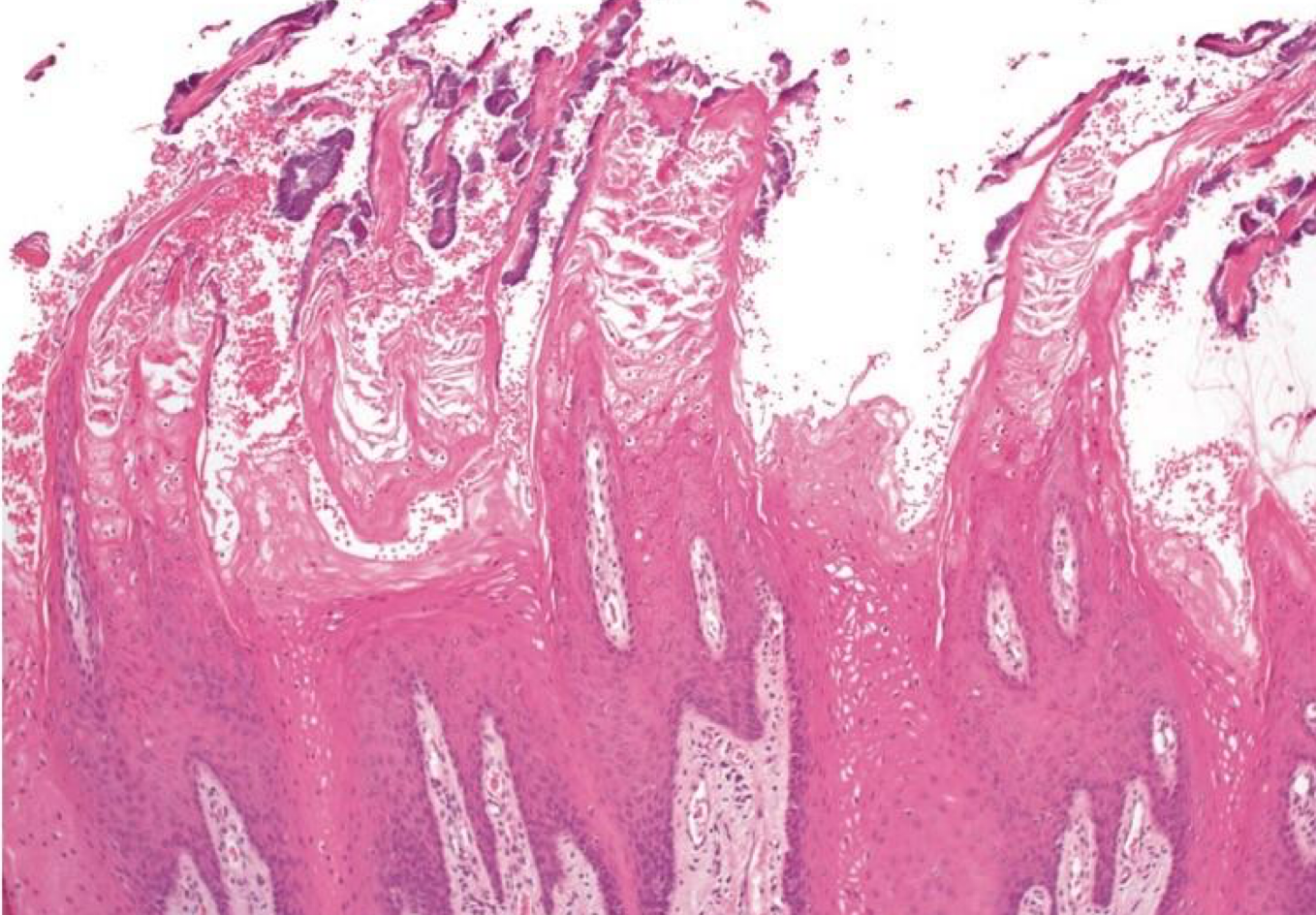
which neoplastic white lesion histological features of dysplasia
oral leukoplakia
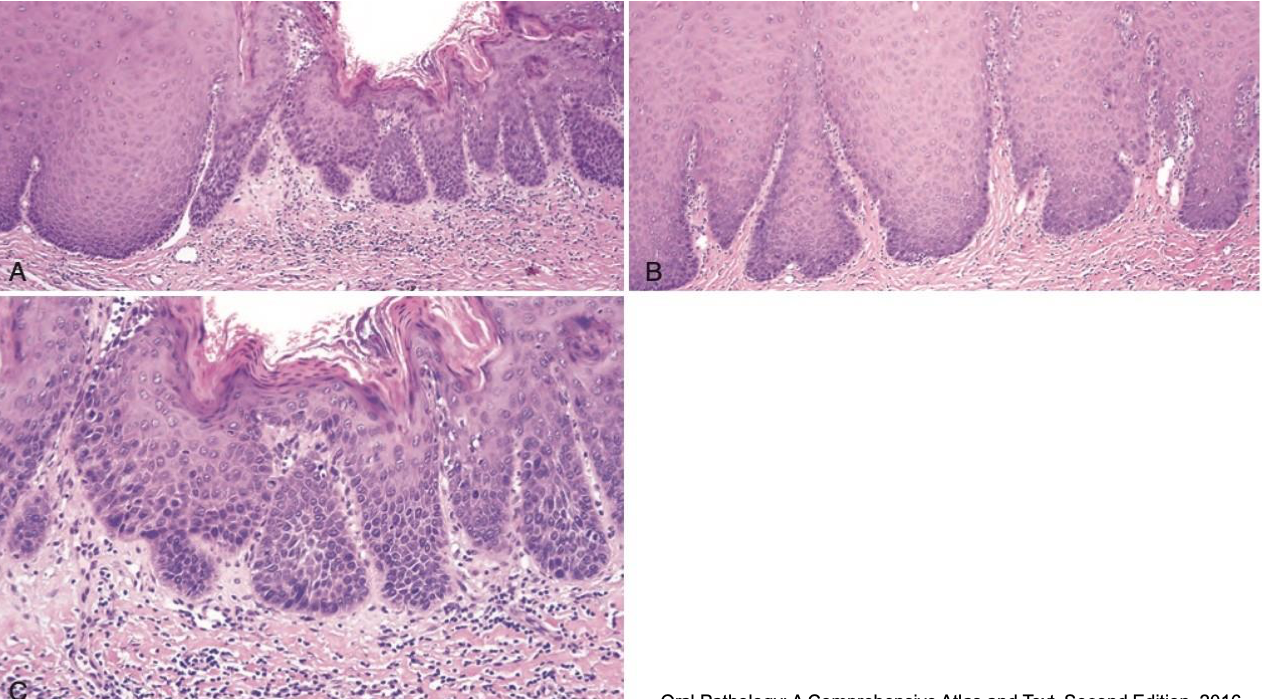
which neoplastic white lesion:
oral leukoplakia
which neoplastic white lesion:
oral leukoplakia
which neoplastic white lesion treatment:
Surgical excision of small lesions
Laser ablation
Novell off label use of topical chemotherapy: 5% imiquimod, TLR-4 activation
Monitoring
Clinical trial of immune checkpoint inhibitor (nivolumab) for proliferative leukoplakia
oral leukoplakia
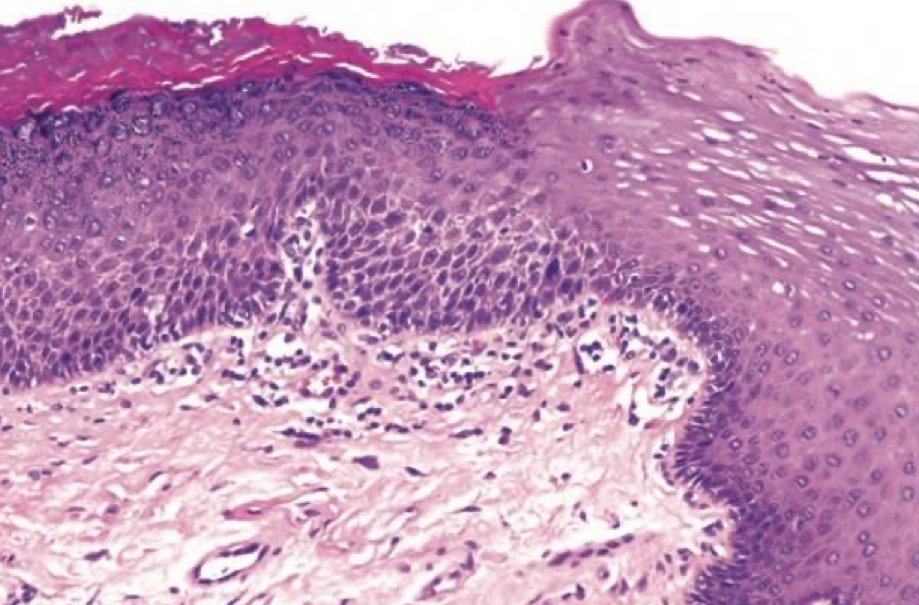
which neoplastic white lesion:
70% malignant transformation
mortality rate of 30-40%
Patients in their 6th decade (or older) and females (4x likely)
Unclear associated risks Gingiva, alveolar and palatal mucosa
?prognosis
proliferative oral leukoplakia
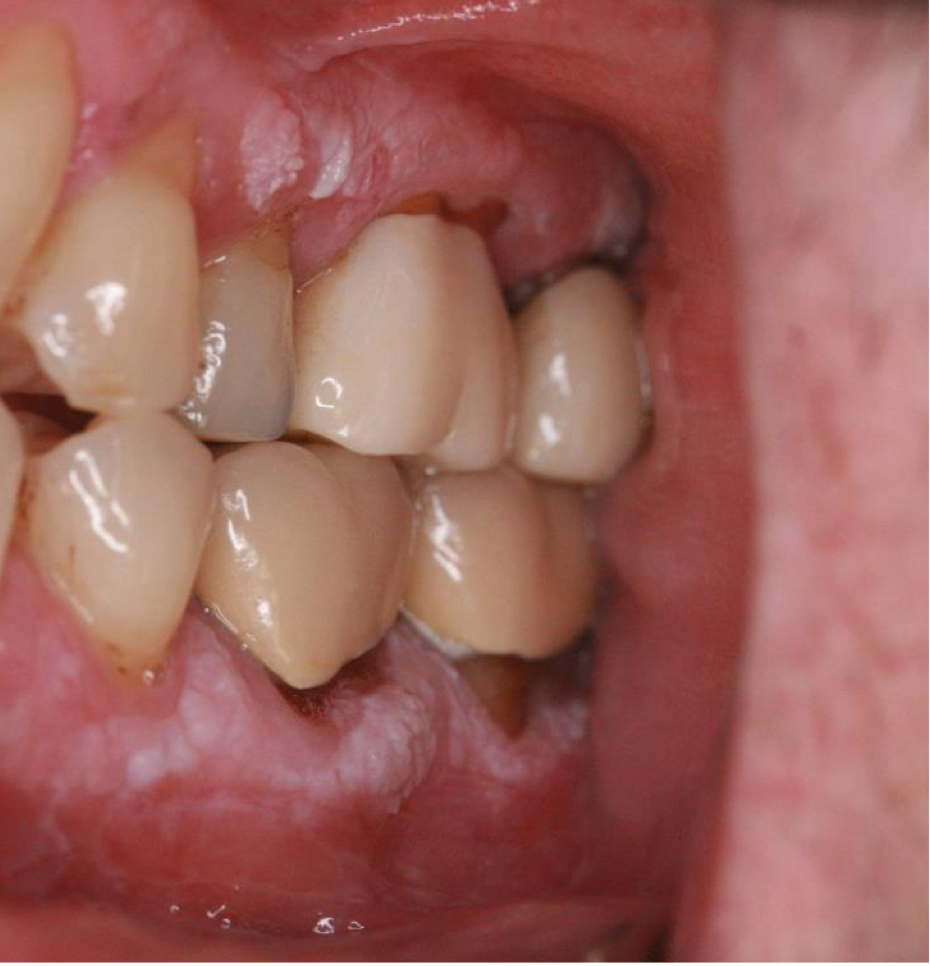
which neoplastic white lesion:
R: oral leukoplakia L: benign alveolar ridge keratosis
which neoplastic white lesion: OPMDs are clinical presentations that carry a risk of cancer development in the oral cavity, whether in a clinically definable precursor lesion or in clinically normal oral mucosa
WHO oral potentially malignant disorders (OPMD)

ranking of OPMD WHO 2017
which neoplastic white lesion:
High-risk, precancerous condition
Chronic, progressive scarring of the oral mucosa
Associated with betel quid chewing and related products
Commonly used in eastern and south-east Asia, and among immigrants from these countries
Estimated malignant transformation rate is 7%-13% (high) over variable periods of time
Oral submucous fibrosis (OSMF)
which neoplastic white lesion:
associated with arce nut, betel leaf, betel quid which has been classified as a Group 1 carcinogen by IARC
could be addictive
commercially available: simple betel quid, spices and other additives with or w/o tobacco
Oral submucous fibrosis (OSMF)
which neoplastic white lesion:
areca nut:
Increased collagen synthesis
Reduced collagenase activity
Inhibition of collagen phagocytosis
Collagen cross-linking with lysyl oxidase (LOX is a copper-dependent enzyme)
Oral submucous fibrosis (OSMF)
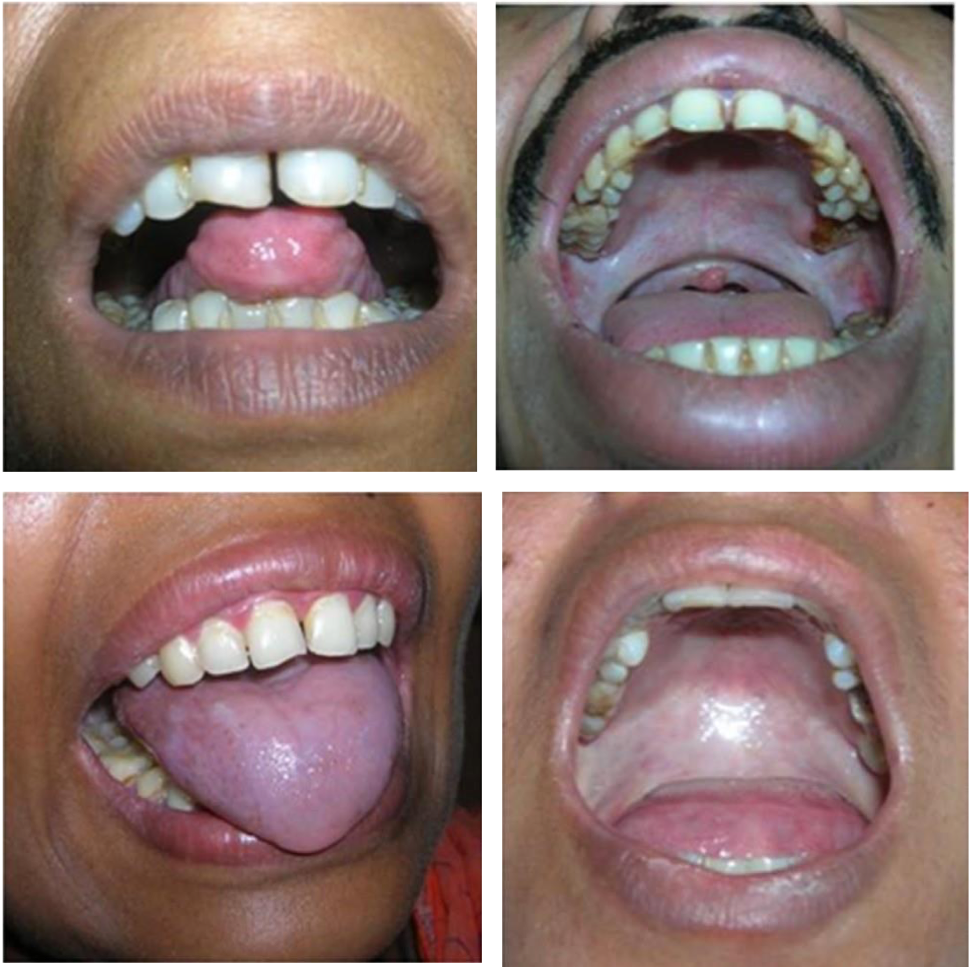
which neoplastic white lesion clinical features:
Mucosal blanching
Burning sensation (dry mouth)
Fibrous bands
Restriction in mouth opening
Shrunken and everted uvula
The tongue appears depapillated
could have precancerous mass but not the white lesion in question
Oral submucous fibrosis (OSMF)
which neoplastic white lesion:
90% of oral malignancies
Male predilection
High risk sites: Ventral tongue and floor of mouth
Clinical features: indurated mass, endo or exophytic ulcer w rolled borders; leukoplakia, erythroplakia
oral squamous cell carcinoma
which neoplastic white lesion risk factors and treatment:
Cigarette smoking
Excessive alcohol consumption
Areca nut chewing
H/o cancer and cancer therapy
H/o autoimmune disorder or prolonged immunosuppression
Family h/o cancer
Older age
Treatment: excision +/-chemo/RT
oral squamous cell carcinoma
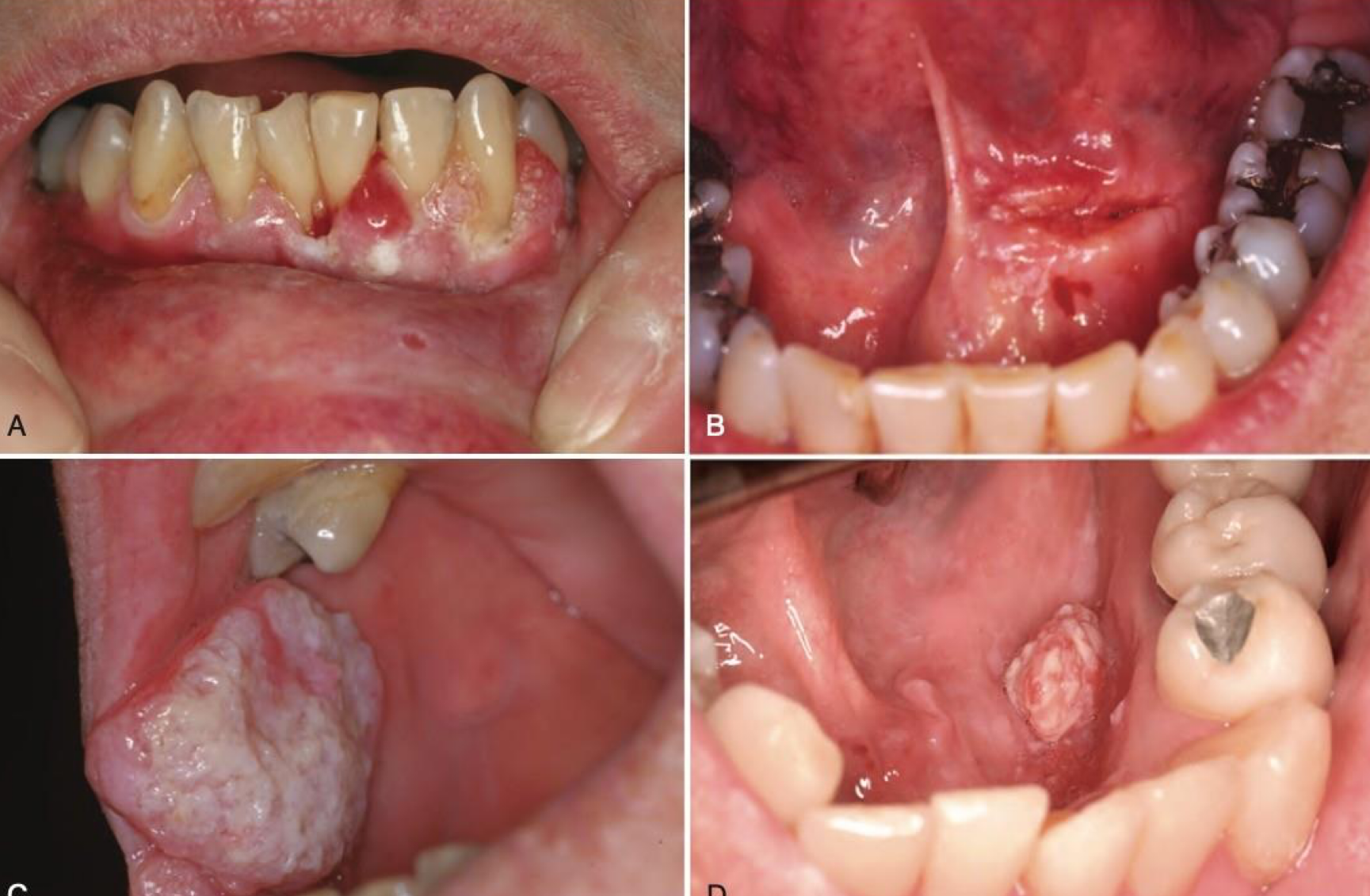
which neoplastic white lesion:
oral squamous cell carcinoma
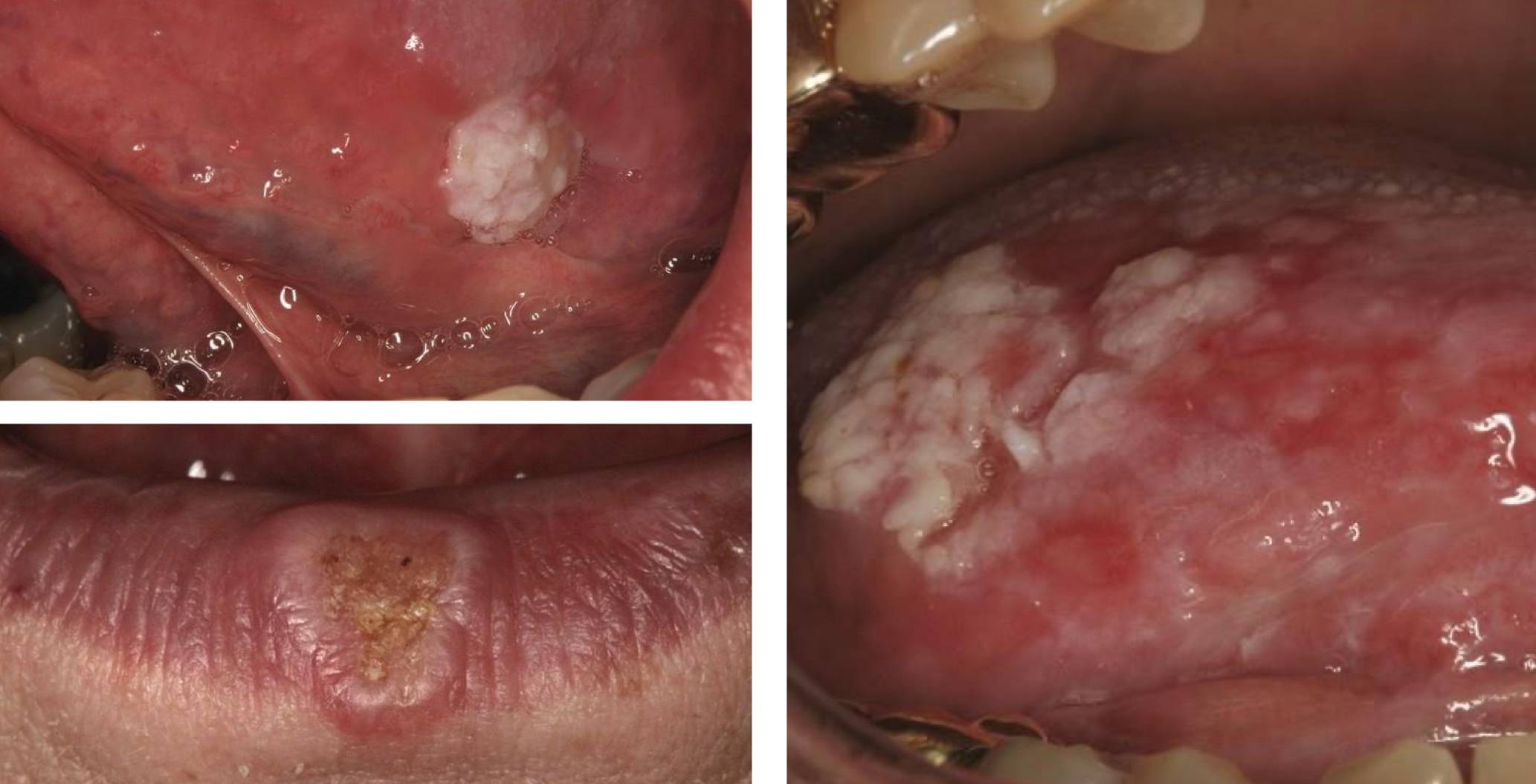
which neoplastic white lesion:
oral squamous cell carcinoma
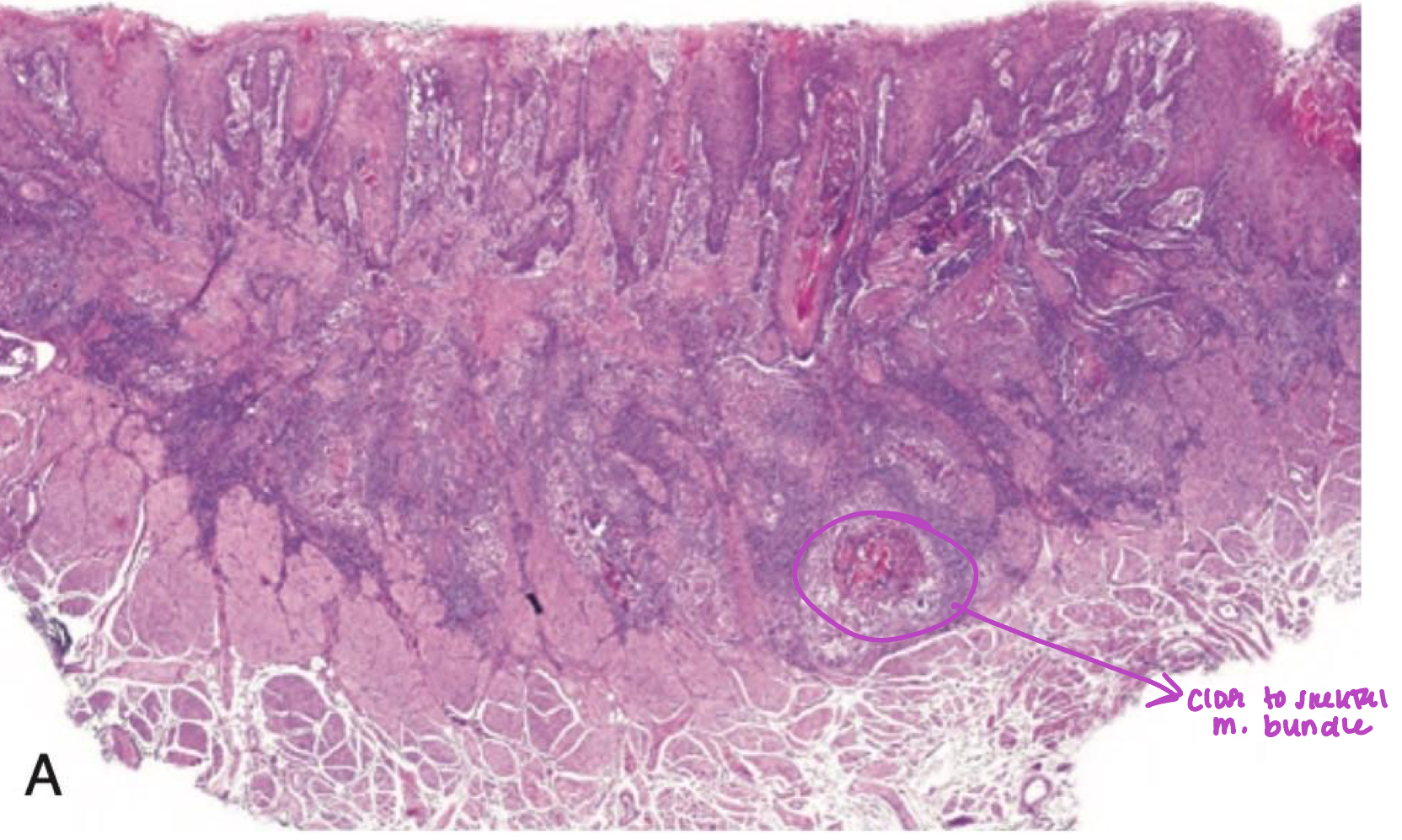
which neoplastic white lesion:
infiltration to underlying tissue → basement membrane broken
oral squamous cell carcinoma
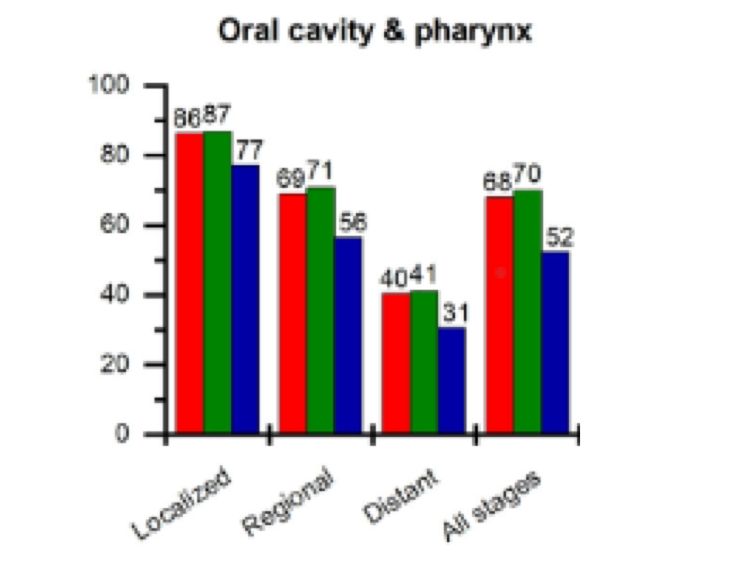
which neoplastic white lesion::
Five-year survival is:
83% with local disease
55% with loco-regional disease
32% with distant metastases
Long-term follow-up is highly importance
Second primary tumors occur in 7% to 33% of patients
oral squamous cell carcinoma