Chapter 10: Optics
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Physics
Geometric Optics
AP Physics 1: Algebra-Based
Barron's AP
Optics
Electromagnetic Waves
Electromagnetic Spectrum
Interference
Diffraction
Young’s Double-Slit Interference Experiment
fringes
Single-Slit Diffraction
Reflection and Refraction
angle of incidence
angle of reflection
angle of refraction
Law of Reflection
Law of Reflection
Dispersion of Light
Total Internal Reflection
Mirrors
Spherical Mirrors
Plane Mirror
Concave mirror
Convex mirror
Ray Tracing for Mirrorsv
Magnification
Converging lens
Diverging lens
AP Physics
University/Undergrad
Last updated 12:54 AM on 3/16/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
1
New cards
**Electromagnetic Waves**
Consist of time-varying electric and magnetic fields that oscillate perpendicular to each other and to the direction of propagation of the wave.
2
New cards
**the direction of polarization of the wave**
is the direction in which the wave’s electric field oscillates
3
New cards
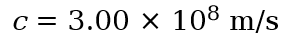
Through a vacuum, all electromagnetic waves travel at a fixed speed
4
New cards
**diffraction**
the alteration in the straight-line propagation of a wave when it encounters a barrier
5
New cards
**Single-Slit Diffraction**
A diffraction pattern will also form on the screen if the barrier contains only one slit.
6
New cards
**The angle of incidence**
angle that the incident beam makes with the normal
7
New cards
**The angle of reflection**
angle that the reflected beam makes with the normal.
8
New cards
**The angle of refraction**
angle that the transmitted beam makes with the normal
9
New cards
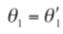
Law of Reflection
10
New cards
**Snell’s Law**
states when light enters a new medium (material) it changes speeds and may change directions
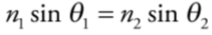
11
New cards
**Dispersion**
is when light travels through a material medium which is a variation in wave speed with frequency (or wavelength.
12
New cards
**Index of refraction**
which is n = c/v, should be accompanied by a statement of the frequency of the light used to measure v, since different frequencies have different speeds and different indices.
13
New cards
**total internal reflection (TIR)**
A phenomenon called ____________________________ which for angles of incidence that are greater than *θc,* there is no angle of refraction; the entire beam is reflected back into the original medium.
14
New cards
**Plane mirrors**
have light that’s reflected off of the object strikes the mirror and is reflected back to our eyes.
15
New cards
**Spherical Mirrors**
Mirror that’s curved in such a way that its surface forms part of a sphere.
16
New cards
**Center of curvature**
is the center of this imaginary sphere
17
New cards
**Radius of curvature,** ***R***
is the radius of the sphere
18
New cards
**Focus/ Focal point,** ***C***
it the halfway between the mirror and the center of curvature
19
New cards
**Axis**
is the intersection of the mirror’s optic (its axis of symmetry)
20
New cards
**Vertex,** ***V***
is the mirror itself
21
New cards
**Focal length,** ***f***
the distance from *V* to *F*, equal to one-half of the radius of curvature:
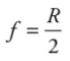
22
New cards
**Concave mirror**
a mirror whose reflective side is *caved in* toward the center of curvature
23
New cards
**Convex mirror**
which has a reflective side *curving away* from the center of curvature
24
New cards
**Ray tracing**
is the geometric approach to identify images formed by mirrors
25
New cards
**Mirror Equation**
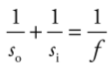
26
New cards
**Magnification Equation**
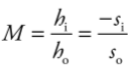
27
New cards
**Converging lens**
converges parallel paraxial rays of light to a focal point on the far side
28
New cards
**Diverging lens**
causes parallel paraxial rays of light to diverge away from a virtual focus, F, on the same side as the incident rays