Ap Psych Unit 1 Vocab
1/170
Earn XP
Description and Tags
hihihihihih its me Mello again! I hope this set really helps and also I highly recommend joining Mr. Sinn's discord server for extra psych help (You can find me there as MELLODOUGHHHHHH btw). Anyways thank you for using my Flashcards :))))
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
171 Terms
Evolutionary psychology
How natural selection, passing down genes, and behaviors, came from ancestors
Natural Selection
organisms who are the survivors of the fittest and passed on their traits to their offspring
Nature
Its about inherited genes that influences a person's psychological behavior

Nurture
The environment, like family relationships and cultures, shaping behaviors and human psychological development

Twin studies
Examine similarities and differences between identical and fraternal twins ti access the relative genes and environment
Adoption studies
Compare an adopted person’s behavior to both their biological and adoptive parents’ behavior.
Family studies
It focuses on research that examines how individuals grow when interacting within the family
Heredity
The intended characteristics that influences a person’s traits and genetics
Genetic Predisposition
The likelihood of developing a particular trait or condition due to genetics
Eugenics
Promoting selective breeding on humans to ‘improve the genetic quality’ for the desirable traits and rejecting the unsuitable traits.
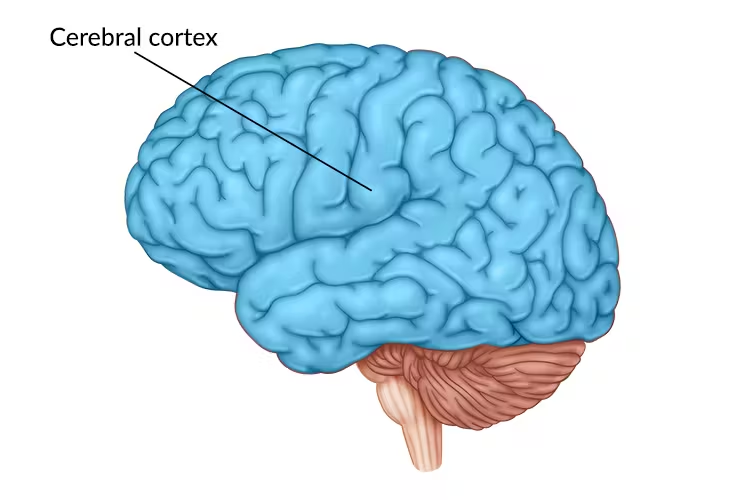
Cerebral Cortex
The outer layer of the brain that is made of gray matter. It’s responsible for higher cognitive functions and divided into two hemispheres and 4 lobes
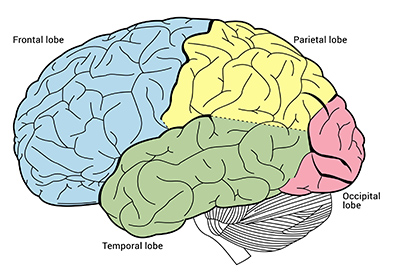
Lobes of the brain
The 4 divisions of that brain that includes the Frontal, Parietal, Temporal, and Occipital lobes
Association Areas
The regions of the cerebral cortex that are responsible for higher mental functions like learning and remembering
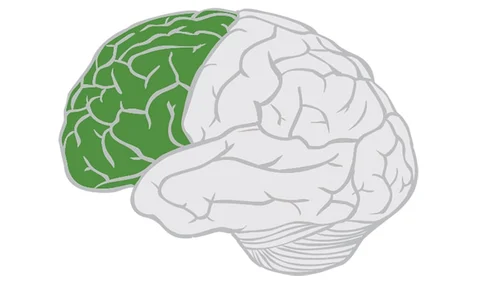
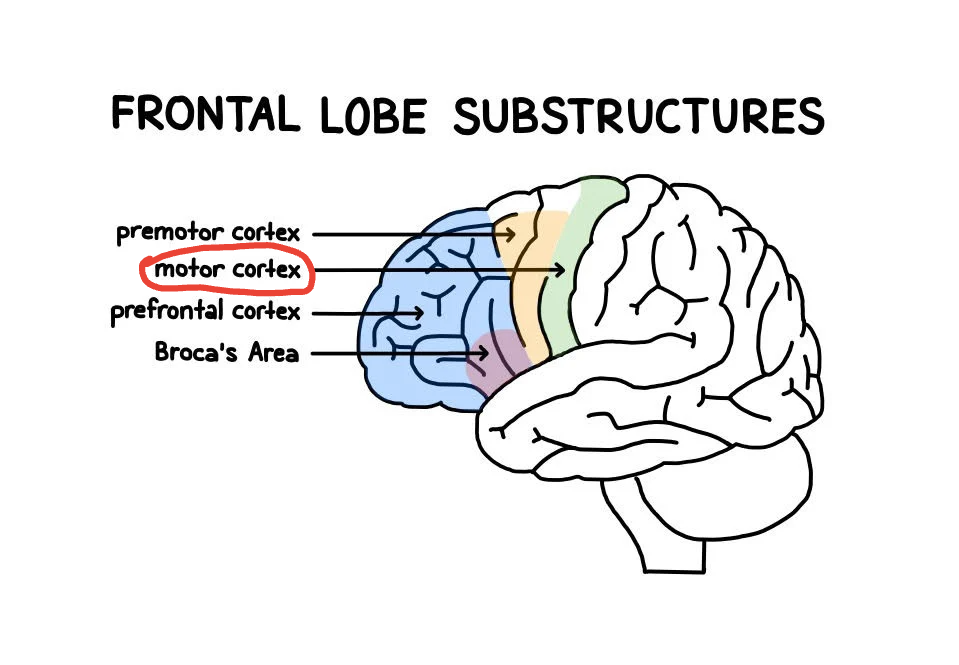
Frontal Lobe
Located behind the forehead. The main function for this is higher order thinking like problem solving and critical thinking.
Prefrontal Cortex
Located in front of the frontal lobe that specializes in memory, predictions, and judgement (MINOS PRIME REFERENCE RAHHHH)
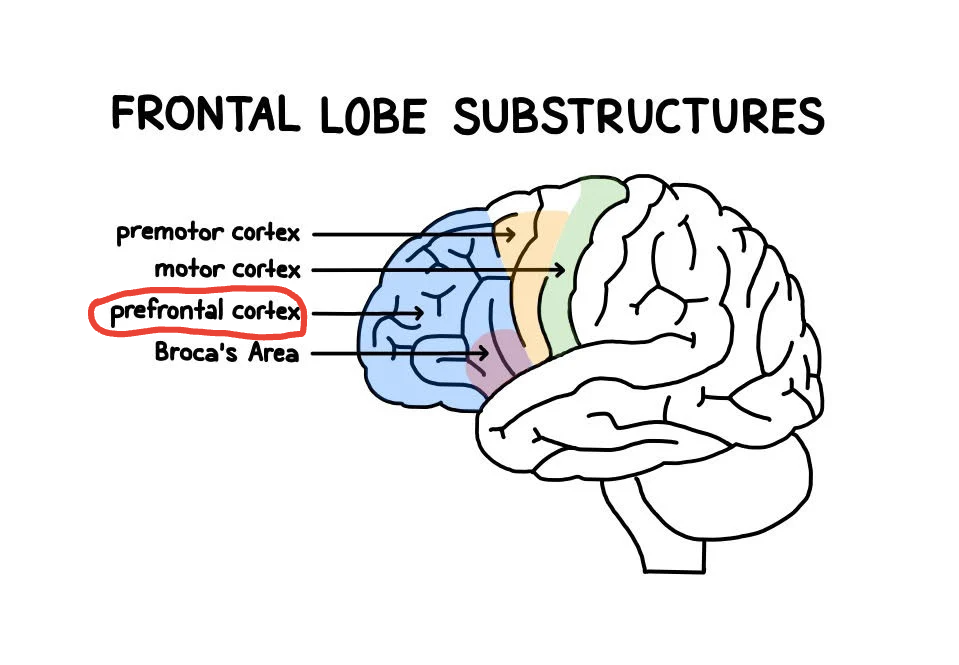
Motor Cortex
Located at the back of the frontal lobe which controls voluntary movement like walking or writing.
Executive Functioning
Cognitive processes that involves a person to plan, adapt and improvise in situations, and organize
Parietal Lobes
Located at the top of the head behind the frontal lobe. It’s responsible for receiving sensory information.
Somatosensory Cortex
Part of the Parietal lobe that processes sensory information that involves touch, temperature, pain, and pressure.
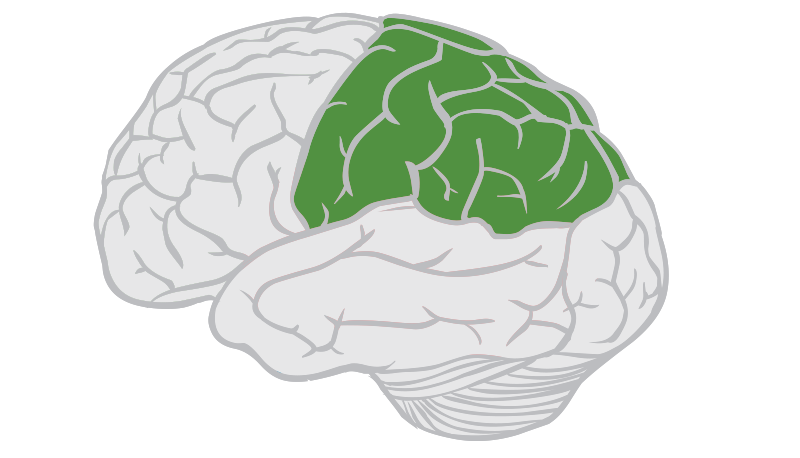
Occipital Lobes
Located in the back of the brain that is responsible for processing vision.
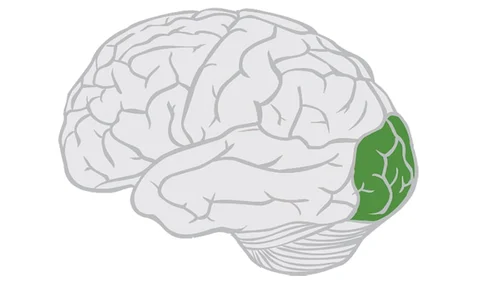
Temporal Lobes
responsible for hearing and mindful speech
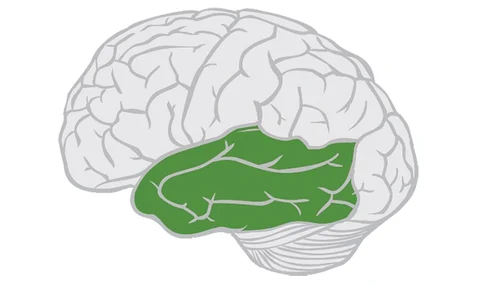
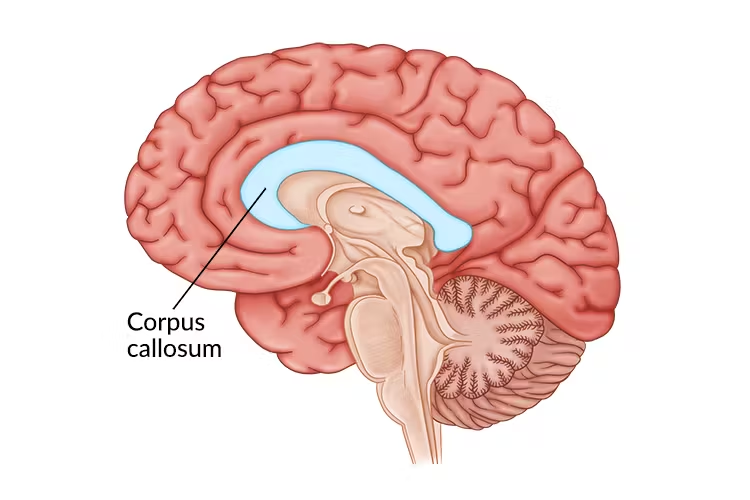
Corpus Callosum
A thick band of neural fibers that connects the left & right hemispheres of the brain to communicate with each other
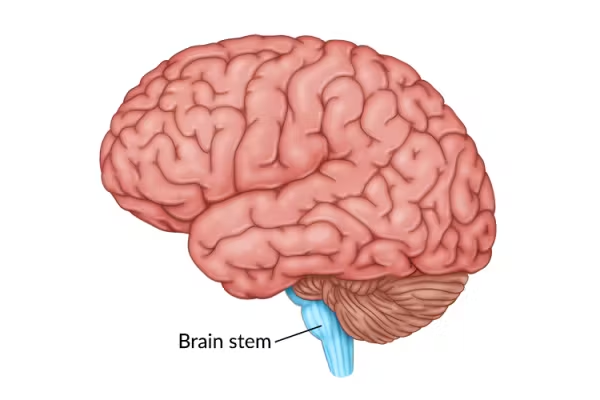
Brainstem
The oldest part of the brain and connects it to the spinal cord
Medulla
Part of the brain stem that controls autonomic functions like digestion, heart rate, and breathing without thinking about it
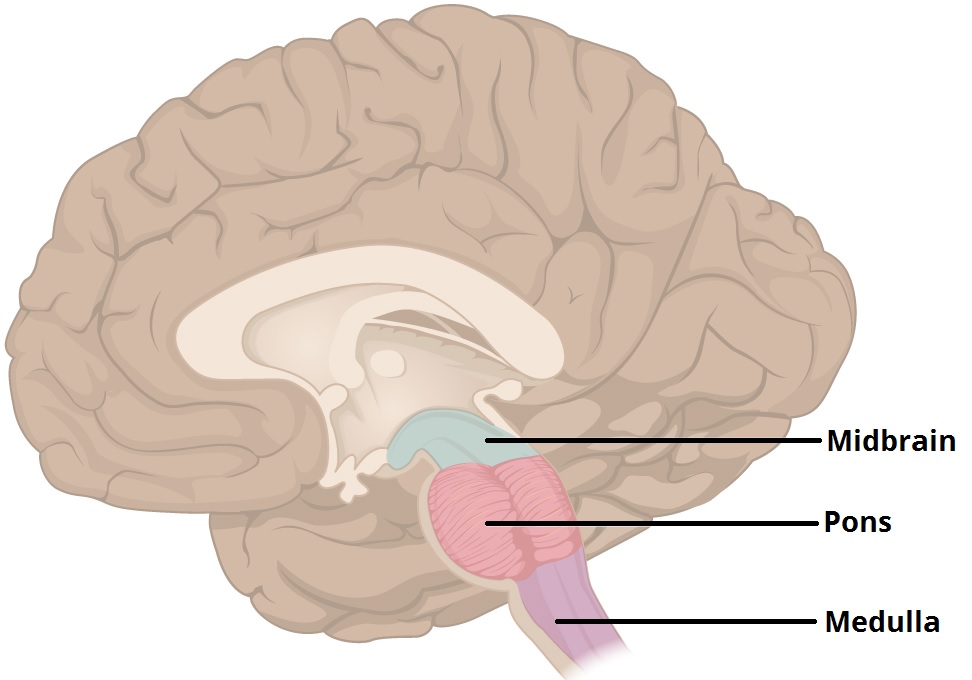
Reticular Activating System
Bundle of nerves in the brainstem. It controls the sleep-wake cycle and alertness.
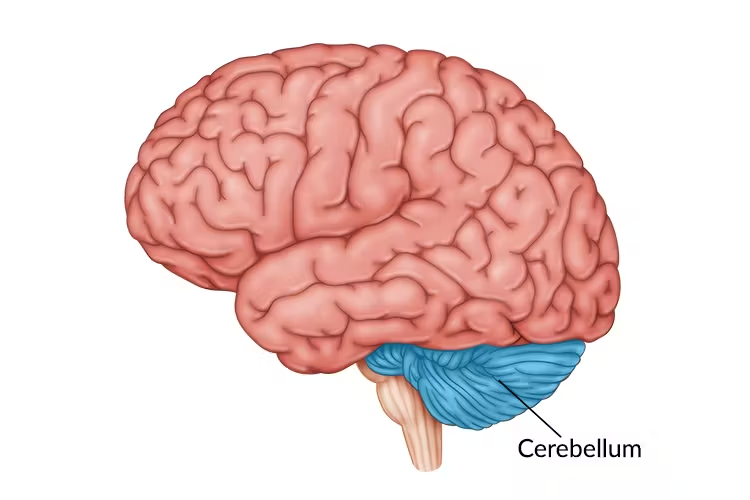
Cerebellum
Coordinates voluntary movement and balance
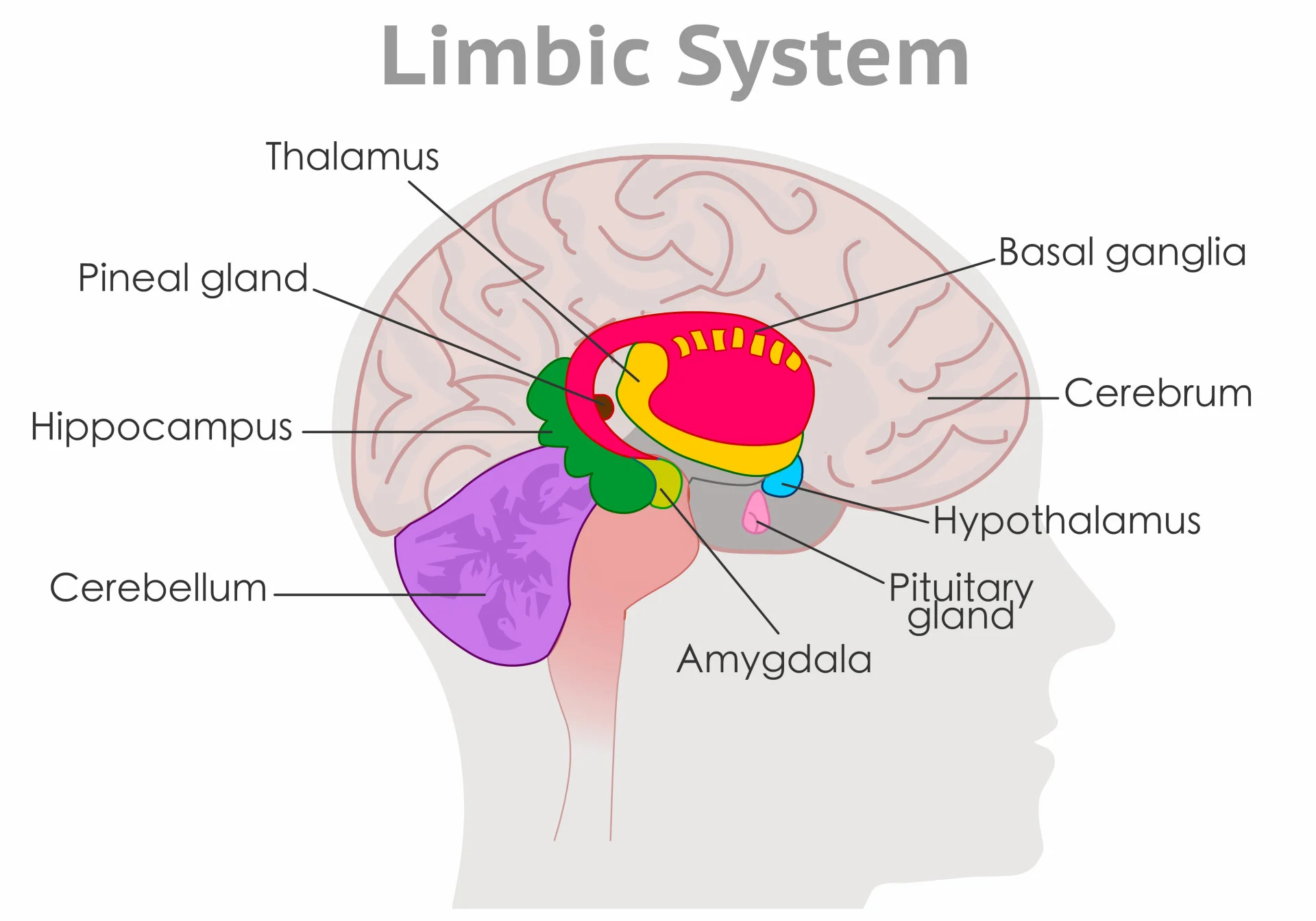
Limbic System
Includes the thalamus, hypothalamus, hippocampus and amygdala. It’s responsible for memory, emotion, learning, and motivation.
reward center
It’s responsible for what makes an individual feel satisfied and pleasure
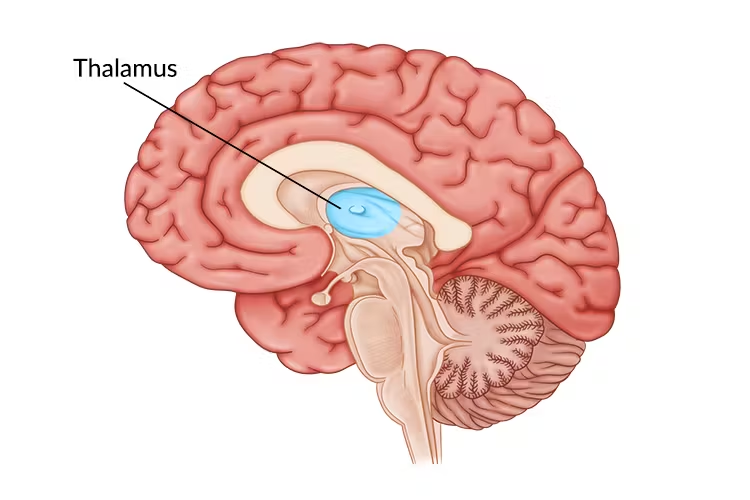
Thalamus
receives sensory information except smell and sends it to the right areas of the brain.
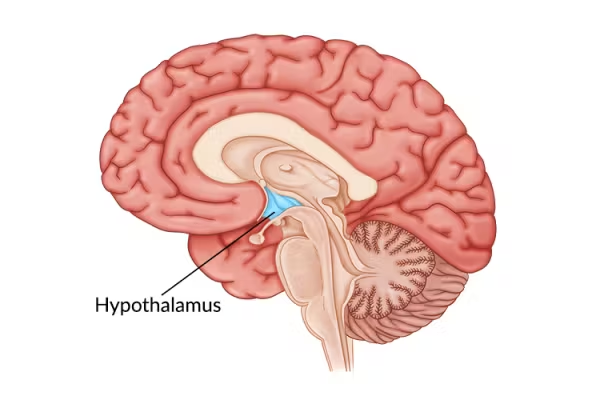
hypothalamus
part of the brain that maintains homeostasis, temperature, thirst and hunger, and sexual behavior
Pituitary Gland
Known as the master gland as it regulates the rest of the body’s glands and it’s controlled by the hypothalamus. Its responsible for regulating stress, growth, and reproduction.

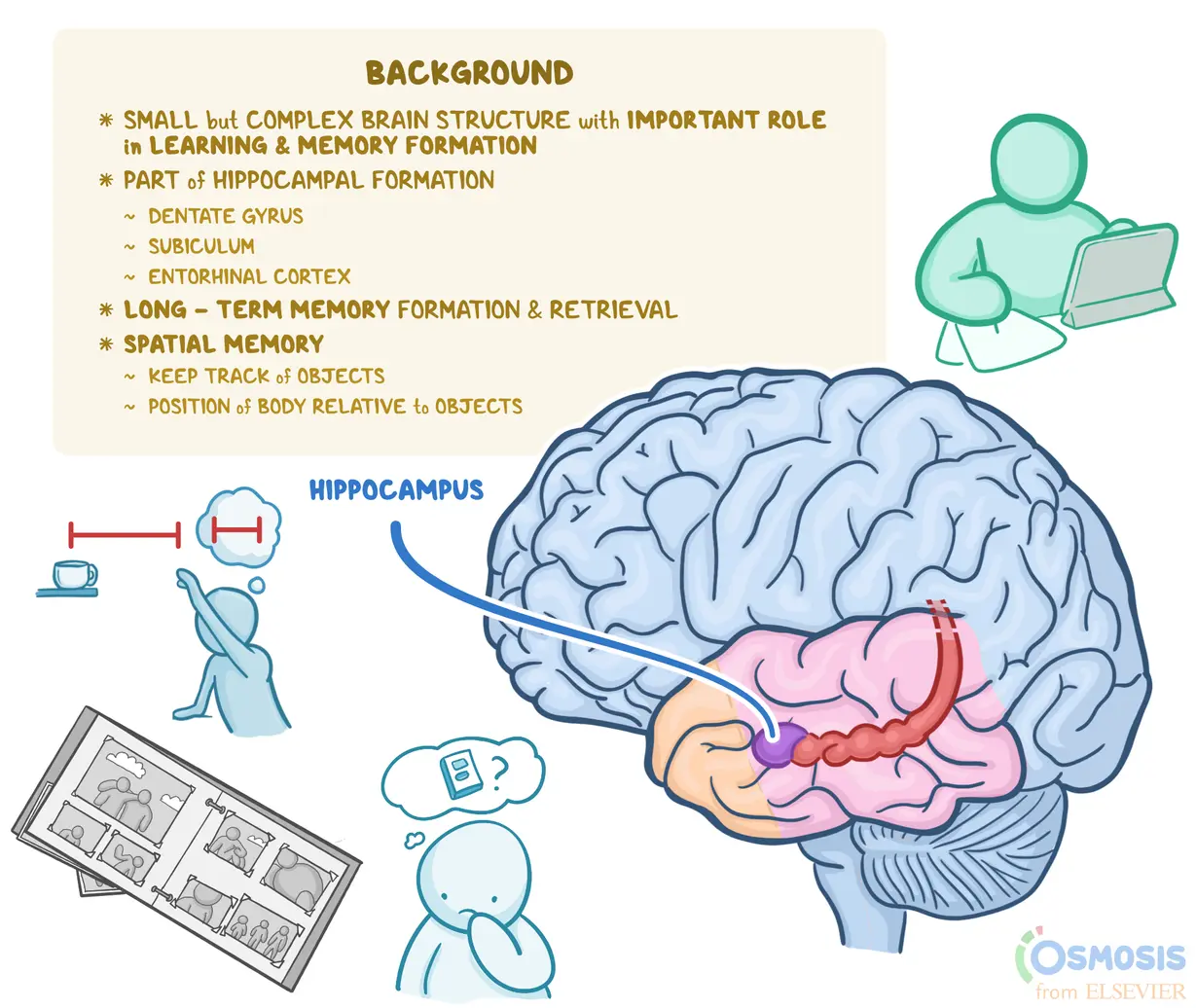
Hippocampus
responsible for forming long term memories and retrieving them.
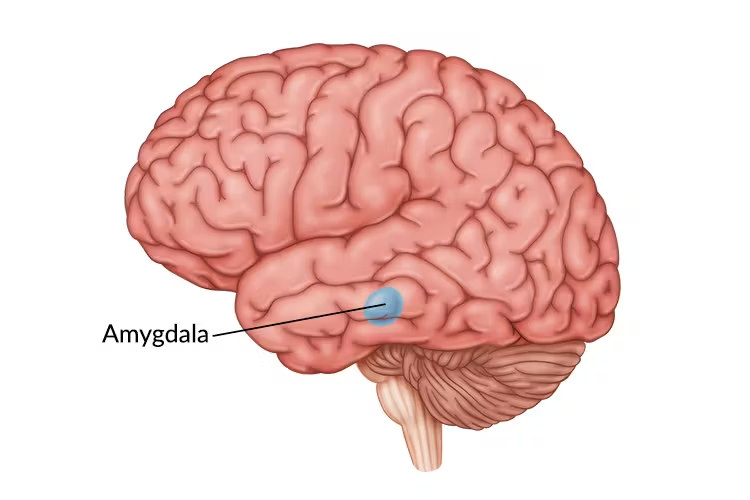
amygdala
triggers fear and survival instincts. Basically controls the body's emotions
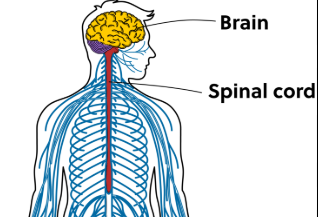
The Nervous System
A network of neurons connected to the brain and spinal cord that sends messages throughout the body.
Central Nervous System
It consists of the brain and spinal cord where information is sent
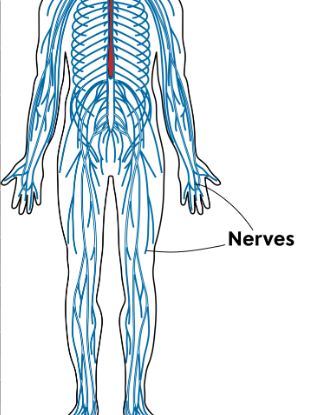
Peripheral Nervous System
It consists of nerves outside the brain and spinal cord. It connects the CNS to the body
Autonomic System
It’s important for maintaining the body’s non-voluntary functions like breathing or pumping blood
sympathetic nervous system
responsible for activating the ‘fight or flight’ response in terms of increased blood pressure and breathing

Parasympathetic Nervous System
Responsible for calming the body down by lowering blood pressure and breathing, helps digestion, and conserves energy

Somatic Nervous System
It allows the brain to communicate with the muscles that are involved with voluntary movement.
Neurons
Basic building blocks for the nervous system. They communicate using electrical impulses and chemical systems

Glial Cells
A type of glial cells that provide nutrition and protection for the neurons
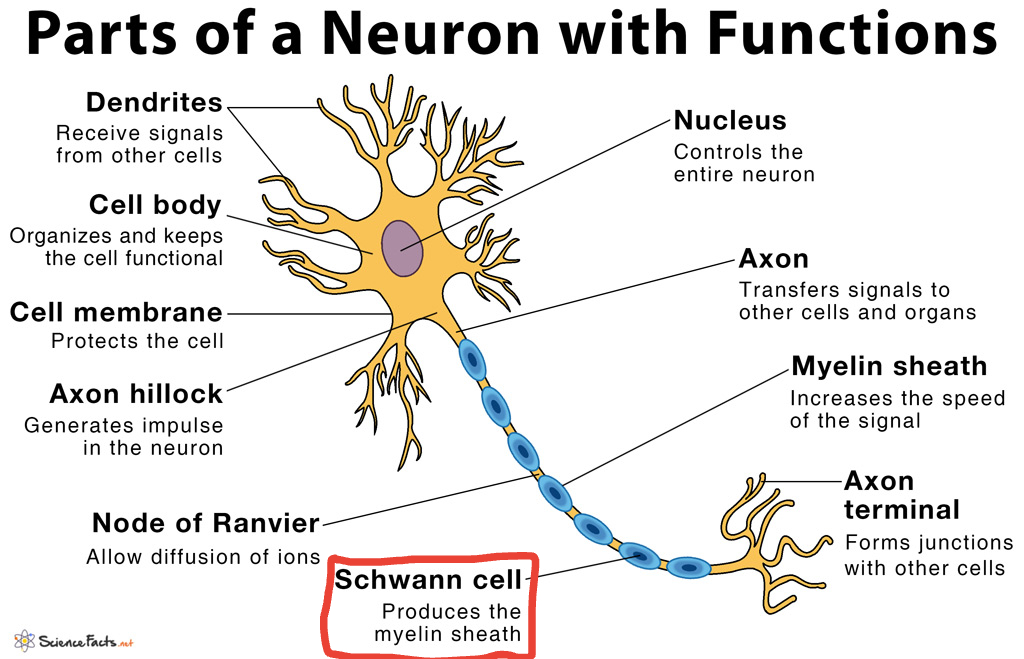
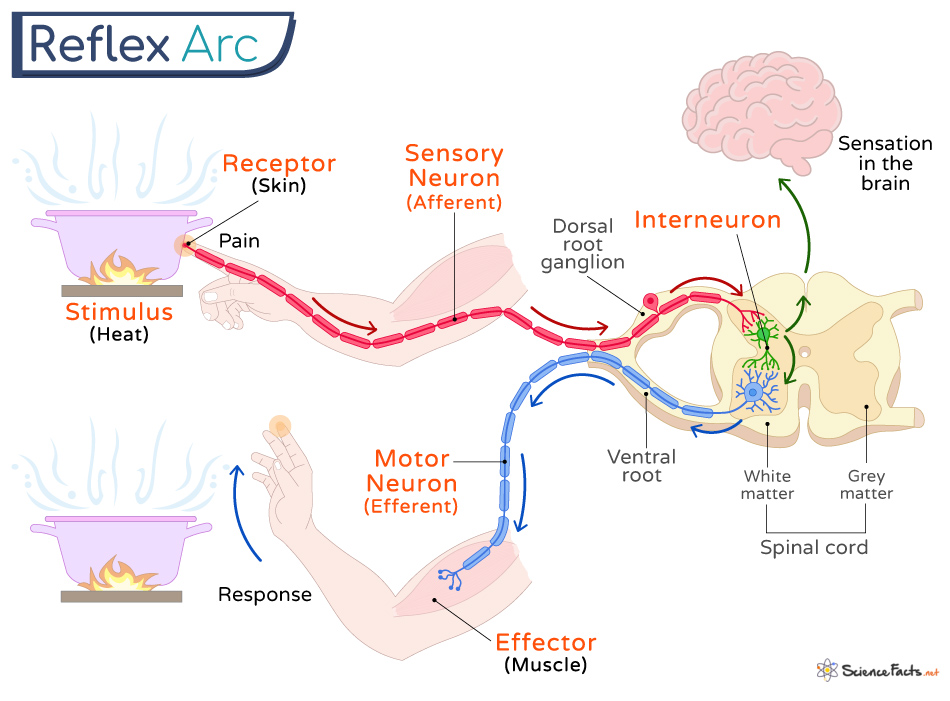
Motor neurons
Responsible for controlling muscle movement. They transmit signals FROM the brain and spinal cord to the muscles.
Sensory neurons
Carries messages relating to sensory input to the brain. The signals are transmitted TO the brain and spinal cord.
Interneurons
Neurons within the brain and spinal cord that connects sensory neurons to motor neurons
Reflex arc
It allows the body to react instantly to a stimuli without thinking.
Neural Transmission
Occurs when a neuron fires a signal to communicate
Threshold
The amount of stimulation needed to fire an action potential
Action Potential
Brief electrical pulses that travels along the axon
All-or-nothing principle
A neuron either sends an impulse or it does not.
depolarization
Positive sodium ions flood in the neuron and makes it positive
Refractory period
A resting pause, where neurons pump positively charged sodium ions back outside of the cell.
Resting potential
When a neuron does not have an action potential
Polarized charge
The state of a resting neuron; the outside of the membrane is positively charged while the inside of the membrane is negatively charged.
Reuptake
reabsorbtion of a neurotransmitter to recycle and use for future purposes
Multiple Selerosis ‘MS’
The loss of muscle control resulting from a deterioration of myelin sheath. The body’s immune system attacks the protective cover of the myelin. It can result in muscle weakness.
Myasthenia gravis ‘MG’
a chronic autoimmune disorder that affects the neuromuscular junction, where nerves communicate with muscles. It causes muscle weakness that worsens with activity.
Neurotransmitters
chemical messengers in the nervous system that sends messages between neurons
Excitatory Neurotransmitters
sends signals that stimulate the brain.
Inhibitory Neurotransmitters
Sends signals that calms the brain down.
Glutamate
the primary excitatory neurotransmitter in the CNS. It is involved in learning, memory, and adaptation
GABA
a neurotransmitter that acts as the primary inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system. It promotes relaxation and reduces anxiety
Dopamine
neurotransmitter that plays a role in regulating mood, reward, motivation, and movement
Serotonin
neurotransmitter that plays a vital role in regulating mood, sleep, appetite, and Stress
Endorphins
neurotransmitters produced by the brain that act as natural pain relievers and mood enhancers
Substance P
neurotransmitter involved in transmitting pain signals in the nervous system
Acetylcholine
neurotransmitter that plays an important role in the CNS and PNS. It is involved in various functions, including muscle contraction, memory, and learning.
Hormones
chemical messengers from the endocrine system that travel through the bloodstream
Ghrelin
hormone that increases hunger. Produced by the stomach and small intestines
Leptin
Hormone that balances energy by signalling the body’s full and decreases hunger
Melatonin
hormone that regulates the sleep-wake cycle
Adrenaline
hormone and neurotransmitter that is part of the fight or flight response when threatened. It’s usually released when the person is stressed, in danger, or has anxiety.
Norepinephrine
a neurotransmitter and a hormone in the body. It is involved in the body's 'fight or flight' response, regulating arousal, attention, and stress
Plasticity
The brain’s ability to adapt and repair even after it’s injured. It can formed new neurons and strengthened existing ones
Split Brain Research
studies people who got their corpus callosum removed which disconnects the two hemispheres of the brain.
Contralateral Hemispheric Organization
the phenomenon where each hemisphere of the brain controls the opposite side of the body

Hemispheric Specialization
explored through split brain research, refers to the concept that each hemisphere of the brain has specialized functions and abilities
Linguistic Processing
cognitive processing that involves in understanding and producing a language
Broca's Area
located in the left hemisphere of the brain, specifically in the frontal lobe, that is responsible for speech production and language processing
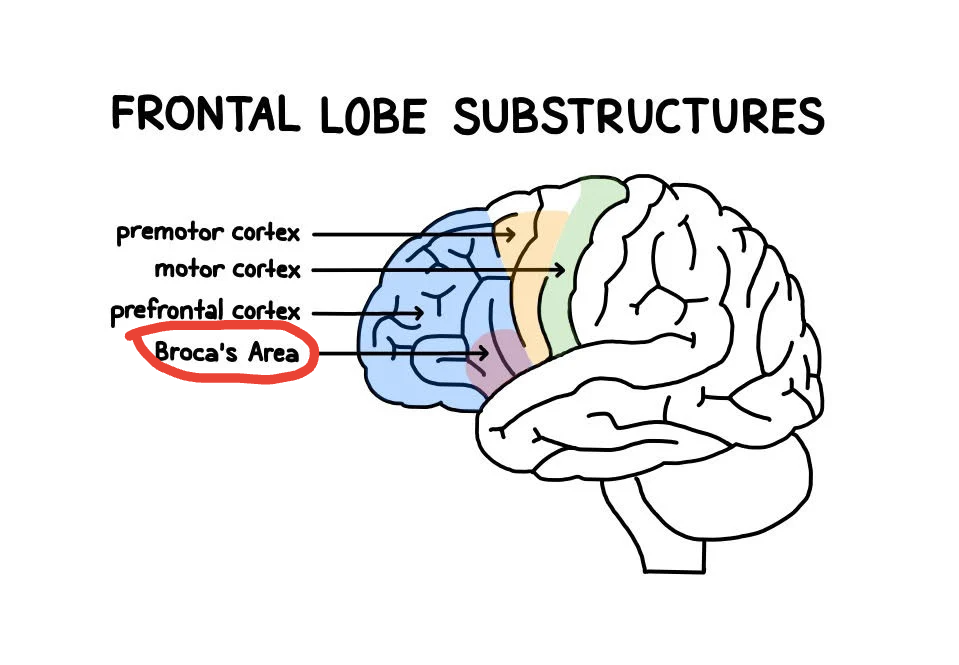
Broca's Aphasia
Damage to Broca's area in the left hemisphere of the brain, often resulting from stroke or brain injury. People who has this have trouble producing speech
Wernicke's Area
region located in the left hemisphere of the brain, specifically in the temporal lobe, that is involved in language comprehension and understanding spoken and written language
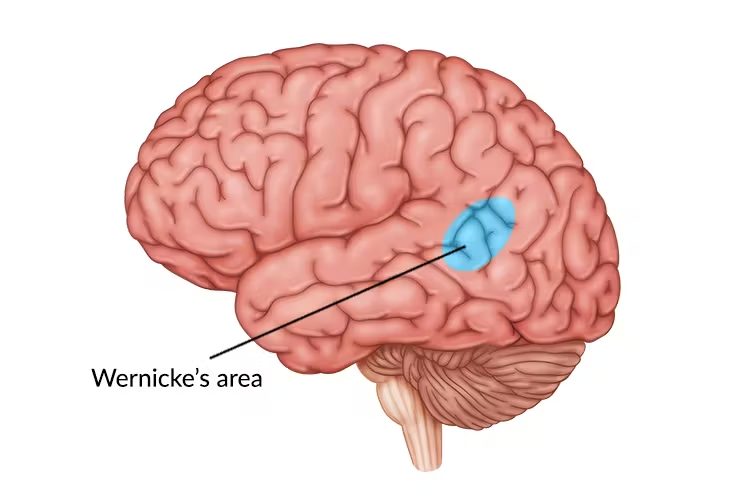
Wernicke's Aphasia
Damage to Wernicke's area in the left hemisphere of the brain, typically resulting from stroke or brain injury. A person may speak words that do not make sense and unable to understand what others are saying.
Electroencephalogram 'EEG'
non-invasive neuroimaging technique used to record the electrical activity of the brain
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging 'fMRI'
neuroimaging technique used to measure brain activity by detecting changes in blood flow and oxygen levels
Lesioning
a research technique where scientists purposely destroy specific areas of a test animals’ brain to study brain functions
Conciousness
refers to one’s awareness and the environment, along their thoughts and emotions
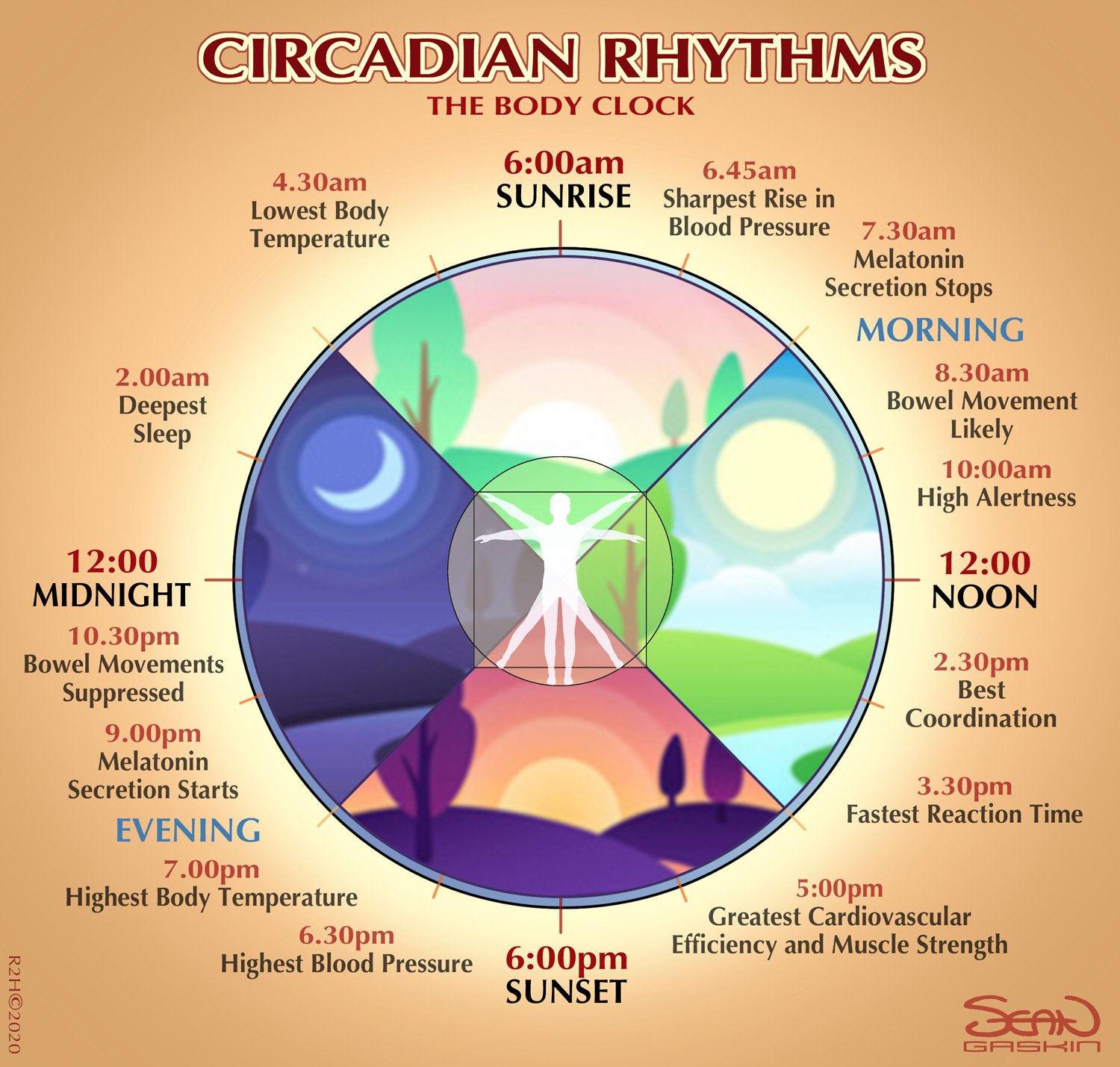
Circadian Rhythm
It regulates the sleep and wakefulness cycle. There are multiple factors that involves sleep patterns, hormone release, body temperature, and blood pressure
Jet Lag
A person’s internal clock feels out of sync with the current local time as they switch different timezones during travel.
Shift Work
Work schedules that requires working outside of daytime hours, which disrupts the circadian rhythm and therefore poses certain health risks
NREM Stage 1
light stage of sleep that lasts about 5-10 minutes, The body relaxes as the heart rate slows. Sensations are involved and Alpha brain waves are present
NREM Stage 2
Brain activity continues to slow where there are sleep spindles and K Complexes in the Theta waves which protects from waking up.
NREM Stage 3
The body enters one of the deepest stages of sleep that lasts 30 minutes. It is dominated by the Delta wave and the body releases growth hormones and repairs itself
REM (Rapid Eye Movement) Sleep
During this stage, external muscles become paralyzed. This stage is where dreams and nightmares are experienced as well as rapid eye movement occurs.
REM Rebound
The body sleeps more to make up for the hours it missed.
Activation-Synthesis (Dreams)
Suggests that dreams are the brain’s attempts to make sense of random neural activity, creating a narrative or story in a dream.
Consolidation Theory (Dreams)
Proposes that dreaming is part of the process when the brain reorganizes and therefore strengthens memory.
Insomnia
A condition of having trouble falling asleep caused by stress, pain, and horrible sleep schedules (cough cough OrlandoMCO if you see this cough cough)

Narcolepsy
A person struggles to sleep at night but uncontrollably sleep during the day
Sleep Apnea
Disorder where breathing repeatedly starts and stops during sleep, causing to snore and waking up a lot.
REM Sleep Behavior Disorder
Condition where a person may act out of their dreams during REM sleep.