Advanced Clinical Mycology
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
A bulldozer operator became ill while working on a new highway in the San Joaquin Valley. He developed chest pain, anorexia, headache and general malaise, and myalgia with fever. Chest x-ray showed pneumonic infiltrate and a single, well-defined nodule in the left lower lobe. His leukocyte count and sedimentation rate were slightly elevated. Although no fungus was seen in direct examination of a sputum specimen, processing included a culture on Sabouraud's dextrose agar with chloramphenicol and cycloheximide. Within 3 days at 28°C this culture produced moist, grayish growth, and a white aerial mycelium began to develop. If this fungus was the cause of infection, it was most probably:
Asperigillus fumigatus
Blastomyces dermatitidis
Coccidioides immitis
Cryptococcus neoformans
Histoplasma capsulatum
coccidioides immitis
The formation of arthroconidia is a characteristic important in the identification of all of the following, except:
Coccidioides
Geotrichum
Trichosporon
Sporothrix
Aureobasidium
Sporothrix
A blood agar plate inoculated with sputum from a patient with diabetes mellitus grew very few bacterial flora and a predominance of yeast. Given the following results what is the most likely identification of the yeast isolate?
Cornmeal Tween 80 Agar
Germ tube = NegPseudohyphae = Pos
Arthrospores = NegBlastoconidia = + (arranged as 'logs in a stream')
Chlamydospores = Neg
C. tropicalis
C. kefyr
Trichosporon beigelii
Geotrichum candidum
C. albicans
C. tropicalis
Chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis (CMCC) in children is associated with genetic defects in cellular immunity. Which of the following syndromes has been found to predispose to CMCC?
Flu
Hepatitis syndrome
DiGeorge's syndrome (with absence of thymus)
Bruton's hypogammaglobulinemia (humoral immunity deficiency)
Diarrhea syndrome
DiGeorge’s syndrome with absence of thymus
The microscopic identification of Pneumocystis jirovecii is based on the detection of:
Arthroconidia in subcutaneous tissue biopsies
Cysts and trophozoites in respiratory specimens
Yeasts in respiratory specimens
Tuberculate macroconidia in lung biopsies
Conidia in respiratory specimens
Cysts and trophozoites in respiratory specimens
In tissues infected with Histoplasma capsulatum:
The hyphae usually invade blood vessels
Encapsulated yeast cells are typical
Tuberculate macroconidia are typical
The fungus is usually intracellular
Fungal organisms are not detectable
the fungus is usually intracellular
For each numbered mycosis below, choose the lettered environment most commonly associated with an increased incidence of that infection.
histoplasmosis
sporotrichosis
Blastomycosis
coccidioidomycosis
cryptococcosis
Pigeon roosts
mississippi and ohio river basins
lower sonoran life zone
starling roosts
sphagnum moss
Histoplasmosis-starling roosts
sporotrichosis-sphagnum moss
blastomycosis- Mississippi and Ohio river basins
coccidioidomycosis- lower sonoran life zone
cryptococcosis- pigeon roosts
The incomplete statements below describe the appearance of growth of yeast or yeast-like fungi in morphology agar, such as rice agar or cornmeal agar with Tween 80, a finding helpful in the presumptive identification of these organisms. For each numbered description, select the most appropriate lettered species.
pseudohyphae, blastospores, and chlamydospores
pseudohyphae and blastospores only
blastospores only, without hyphae or pseudohyphae
true hyphae, arthrospores, and blastospores
True hyphae and arthrospores only
crytococus neoformans
trichosporon
candida tropicalis
candida albicans
geotrichum
Pseudohyphae, blastospores, and chlamydospores- candida albicans
pseudohyphae and blastospores only- candida tropicalis
blastospores only, without hyphae or pseudohyphae- cryptococcus neoformans
true hyphae, arthrospores, and blastospores-trichosporon
true hyphae and arthrospores only-geotrichum
A black pigment produced by colonies growing on bird seed agar is due to:
Urease
Phenol oxidase
Sucrose assimilation
Arthroconidia production
Glucose assimilation
Phenol oxidase
Which of the following is likely to be found in clinical specimens as normal microflora and as clinically significant isolates?
Aspergillus niger
Scopulariopsis
Penicillium notatum
Candida albicans
Fusarium
Candida albicans
For each incomplete statement, select the most appropriate lettered species.
the cause of white piedra
the cause of black piedra
the cause of tinea nigra
the cause of pityriasis (tinea) versicolor
a keratinophilic saprophyte
Trichosporon beijelii
malassezia furfur
trichophyton ajelloi
exophiala werneckii
piedraia hortae
the cause of white piedra-trichosporon beigelii
the cause of black piedra- piedraia hortae
The cause of tinea nigra- exophiala werneckii
The cause of pityriasis (tinea) versicolor- malassezia furfur
A keratinophilic saprophyte- trichophyton ajelloi
Although Candida albicans is the species most often found in clinical candidiasis, other species are more frequently isolated from Candida endocarditis. The more common etiologic agent of this syndrome is:
C. tropicalis
C. glabrata
C. pseudotropicalis
C. parapsilosis
C. famata
C. parapsilosis
Host conditions that are associated with an increased incidence of Candida albicans infections include all of the following, except:
Diabetes
Childhood viral infections
Prolonged antibiotic usage
Pregnancy
Use of immunosuppressive agents
childhood viral infections
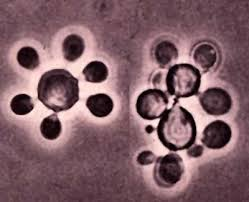
Identify the dimorphic fungus that typically has a tissue phase in which the large mother cells have one to a dozen narrow-necked buds and slow-growing mycelial form with intercalary chlamydoconidia and coiled hyphae.
Blastomyces dermatitidis
Coccidioides immitis
Histoplasma capsulatum
Paracoccidioides brasiliensis
Sporothrix schenckii
paracoccidioides brasiliensis
Observation of hyaline or dematiacious hyphae is an early clue in the identification of common, airborne fungi. Which of the following genera contains species found as dematiacious contaminants?
Alternaria
Penicillium
Paecilomyces
Fusarium
Scopulariopsis
alternaria
A fungus infecting only skin and nails typically produces in culture:
Spindle-shaped, hyaline, echinulate macroconidia and microconidia
Cylindrical or club-shaped, smooth thin-walled macroconidia and microconidia
Many microconidia in clusters or along the hyphae
Large, thin-walled, club-shaped conidia without microconidia
Racquet and spiral hyphae without conidia
Large, thin-walled, club-shaped conidia without microconidia
Broad, coenocytic hyphae found in tissue would be most typical of infection with:
Aspergillus
Blastomyces
Microsporum
Nocardia
Rhizopus
Rhizopus
Trichophyton rubrum and Trichophyton mentagrophytes may be differentiated by the:
Consistently different appearance of their colonies
Endothrix hair infection produced by T. rubrum
Fluorescence of hairs infected with T. rubrum
In vitro hair penetration by T. mentagrophytes
Production of urease by T. rubrum
in vitro hair penetration by T. mentagrophytes
Which of the following species of fungus is usually encapsulated and urease positive and typically produces mucoid, red colonies?
Crytococcus neoformans
Rhodotorula rubra
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Trichophyton rubrum
Trichosporon beigelii
Rhodotorula rubra
Five types of fungal structures are given below. Which of these is not produced by causative agents of chromomycosis?
a
b
c
d
e
A 69-year-old male patient who was a cigarette smoker visited the doctor's office complaining of a cough and congestion of the lungs. Routine cultures of early morning sputum (x3) for bacteria as well as for AFB revealed no pathogens. A fungal culture was also ordered that grew the following on Sabouraud dextrose agar after 3 days.
Hyphae = septate with dichotomous branching
Spores = produced by conidial heads with numerous conidia
Colonies = velvety or powdery, white then turning dark green to gray (reverse = white to tan)
Vesicle = holding phialides usually on upper two-thirds only
What is the most likely identification?
Aspergillus niger
Absidia spp.
Mucor spp.
Aspergillus fumigatus
Candida tropicalis
aspergillus fumigatus
The most useful finding for prompt, presumptive identification of C. albicans is its:
Failure to assimilate sucrose
"Feathering" on EMB
Production of chlamydoconidia
Production of germ tubes
Production of pseudohyphae
Production of germ tubes
A yeast-like fungus was isolated from sputum. No hyphae were produced in morphology agar. It was negative for nitrate assimilation and positive for inositol assimilation and produced urease at 37°C. These findings are typical of:
Candida krusei
Cryptococcus terreus
Cryptococcus neoformans
Trichosporon beigelii
Geotrichum candidum
cryptococcus neoformans
Select the most appropriate lettered specimen source for isolation of each numbered species.
cryptococcus neoformans
histoplasma capsulatum
pseudallescheria boydii
Aspergillus niger
trichophyton mentagrophytes
Chronic interdigital lesion of foot
otitis externa
cerebrospinal fluid
bone marrow
chronic draining sinus tract of foot
Cryptococcus neoformans- cerebrospinal fluid
histoplasma capsulatum- bone marrow
pseudallescheria boydii- chronic draining sinus tract of foot
aspergillus niger- otitis externa
trichophyton mentagrophytes- chronic interdigital lesion of foot
Large, one-celled, smooth to tuberculate macroconidia and smooth or echinulate microconidia are typical of mycelial phase growth of:
Bastomyces dermatitidis
Coccidioides immitis
Histoplasma capsulatum
Paracoccidioides brasiliensis
Sporothrix schenckii
Histoplasma capsulatum
Quesiton was weird
Fungi considered to be opportunistic pathogens include all of the following, except:
Absidia
Aspergillus
Coccidioides
Fusarium
Rhizopus
coccidioides
The location of the sporangiophores in relation to the rhizoids is the major clue in the differentiation of Rhizopus from:
Absidia
Circinella
Cunninghamella
Mucor
Syncephalastrum
Absidia
Which of the following types of Candida albicans infection is commonly acquired from an exogenous source?
Diaper rash
Neonatal thrush
Perianal infection
Urinary tract infection
Vulvovaginitis
Neonatal thrush
A rose gardener pricked himself with a contaminated thorn. A subcutaneous fungal infection characterized by the development of necrotic ulcers followed this direct inoculation of fungal spores into the skin. The causative fungus was cultured as a small yeast form at 36°C and as a mold at room temperature with delicate hyphae and conidia. This disease is:
Blastomycosis
Chromomycosis
Mycetoma
Sporotrichosis
Tinea
sporotrichosis
Weird again
Several children in a second-grade classroom developed tinea capitis. Under a Woods' lamp, their infected hairs showed green fluorescence. Cultures of these hairs grew fungi with aerial mycelia and terminal chlamydospores. These isolates were most probably:
Candida albicans
Epidermophyton floccosum
Microsporum audouinii
Microsporum gypseum
Trichophyton rubrum
Microsproum audouinii
All of the following statements correctly describe the yeast Rhodotorula rubra, except:
It has been isolated from dairy products, air, soil, and water
It is the most common fungal cause of diaper rash
It has been identified as a nosocomial pathogen
It has been found as a contaminant or commensal in specimens of urine, sputum, and feces
It has been found to cause endotoxic shock
It is the most common fungal cause of diaper rash. Rhodotorula are environmental organisms in the soil, air, foods, and some dairy products. Candida albicans is the primary fungal cause of diaper rash.
It is usually difficult or impossible to identify a fungal culture before it is mature. However, the presence of hyaline, septate hyphae, and a young conidiophore with a foot cell and a swollen vesicle are excellent clues to the identification of:
Scopulariopsis
Aspergillus
Paecilomyces
Penicillium
aspergillus
Which of the following stains greatly enhances the visibility of fungi by binding to the cell walls, causing the fungi to fluoresce blue-white or apple green?
Rhodamine-auramine
Warthin-Starry
Calcofluor white
Periodic acid-Schiff
Acridine orange
Calcofluor white
Conversion of the myelial phase to the tissue phase is especially important in differentiating certain dimorphic pathogens from saprophytes that resemble them. These "look-alike" pairs include:
Blastomyces and Chrysosporium
Coccidioides and Paracoccidioides
Histoplasma and Scopulariopsis
Trichosporon and Sporothrix
Fusarium and Coccidioides
blastomyces and chrysosporium
Which of the following fungi is most likely to be found as a common saprobe and as an agent of keratitis?
Exophiala
Phialophora
Fusarium
Wamgiella
b.Sporothrix
Fusarium
Zygomycetes are fast-growing, airborne saprobes. In clinical specimens they:
Are common as normal, human microflora
Are found only as contaminants
May be seen in a dimorphic tissue phase
May be found as a cause of rapidly fatal infection
May be found as a cause of tinea
May be found as a cause of rapidly fatal infection