Reproduction: Asexual and Sexual Processes Explained
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Reproduction
The ability to produce viable offspring
Asexual reproduction
A single parent produces genetically identical offspring - No Genetic Variation
Binary fission
Division of a single parent cell equally into 2 daughter cells
Budding
The unequal splitting of a parent cell or parent organism into two unequally sized offspring.
Fragmentation
A piece of an organism breaks away and is capable of becoming another genetically identical individual.
Regeneration
The replacement of lost body parts that is performed by the parent once the fragment breaks away.
Parthenogenesis
The development of an unfertilized egg into a new individual.
Sexual reproduction
Two parents contribute genetics to produce offspring that are genetically unique from each other and from the two parents.
Genetic Variation
Promotes genetic variation within a species.
Fertilization
One of the two events required in all sexual reproductive life cycles.
Types of asexual reproduction
1. Binary fission 2. Budding 3. Fragmentation 4. Parthenogenesis
Honeybees and parthenogenesis
In honeybees, parthenogenesis gives rise to only male bees which have half the chromosome number for the species.
Occurrence of binary fission
Occurs in bacteria and in some unicellular protists such as amoebas.
Occurrence of budding
Seen in yeast and in hydra.
Occurrence of fragmentation
Occurs in sponges, sea anemones, sea stars and in certain worm species.
Fertilization
The fusion of a sperm cell with an egg cell.
Zygote
A fertilized egg that possesses the diploid number of chromosomes (2n).
Gametes
The sex cells (sperm and egg) that possess the haploid number of chromosomes (n).
Meiosis
A cell division process that occurs in the gonads of animals to produce gametes.
Gonads
An animal's sex organs (testes and ovaries).
Homologous chromosomes
Chromosomes that are identical in size, shape, and the traits that they carry.
Tetrad
A pair of duplicated homologous chromosomes consisting of four chromatids.
Crossing over
The exchange of pieces of genetic material between two chromatids within a tetrad.
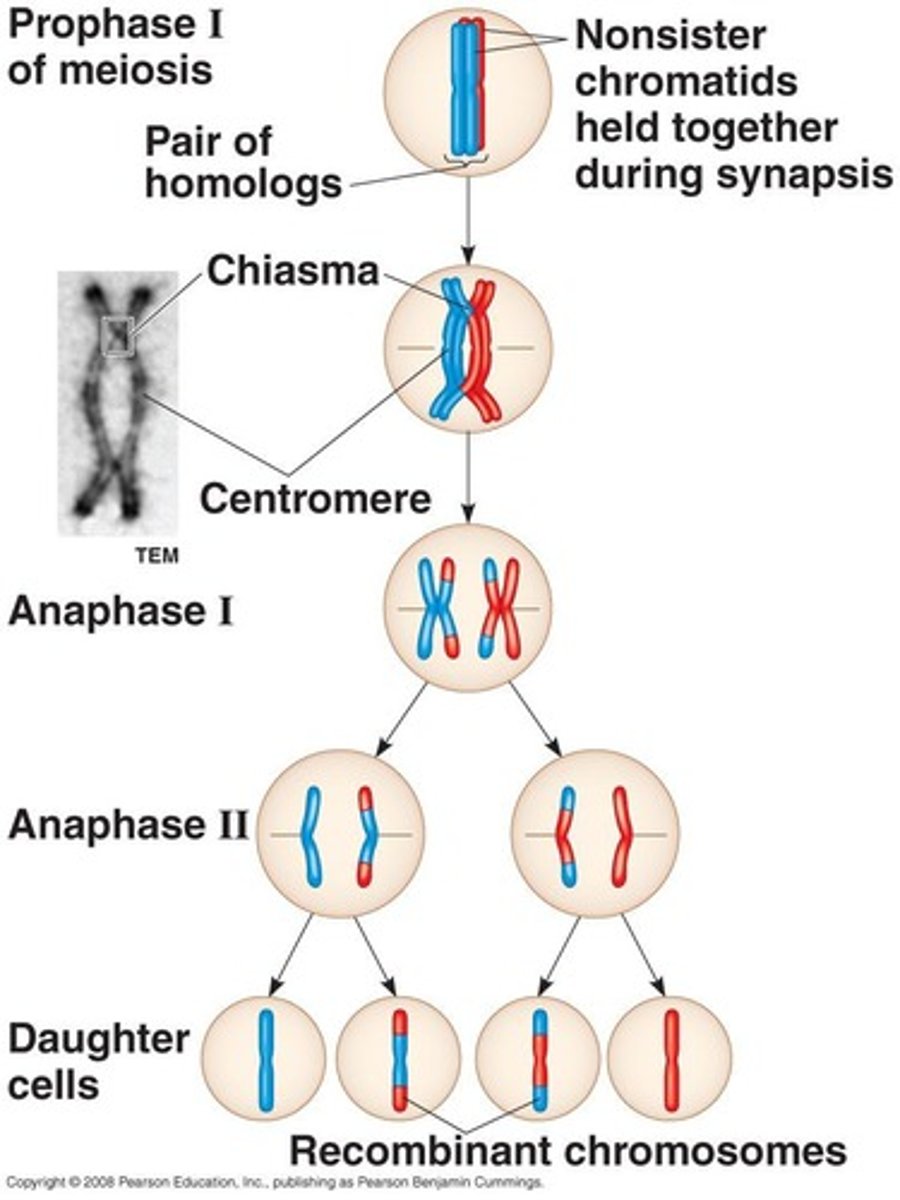
Chiasma
The point of crossover during crossing over.
Dyads
Duplicated chromosomes formed during Anaphase I.
Interkinesis
A brief period between Meiosis I and Meiosis II that replaces interphase and involves no cell growth or chromosomal duplication.
Gametogenesis
The production of gametes.
Spermatogenesis
The production of sperm in the testes, where one testis cell undergoing complete meiosis yields 4 genetically different sperm.
Oogenesis
The production of eggs (ova) in the ovaries, where one ovary cell undergoing complete meiosis yields 1 egg (ovum) and three nonviable polar bodies.
Polar bodies
Small cells produced during oogenesis that are much smaller in size than an ovum.
Independent Assortment
The process where tetrads line up independently during Metaphase I and are separated independently during Anaphase I.
Random fertilization
A source of genetic variation that occurs when any sperm can fertilize any egg.
Meiosis I
The reduction stage of meiosis where homologous chromosomes are separated.
Meiosis II
The division stage of meiosis where sister chromatids are separated.
Prophase I
The stage in Meiosis I where chromosomes become thick and visible, and tetrad formation occurs.
Metaphase I
The stage in Meiosis I where tetrads line up along the middle of the cell.
Anaphase I
The stage in Meiosis I where tetrads are separated into dyads.
Telophase I and Cytokinesis
The stage in Meiosis I where two haploid nuclei are formed, each with duplicated chromosomes.