Identifying EKGs
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
starts 7 min into the presentation
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
What is Premature Ventricular Contraction (PVC)?
early beat which originates from ventricles not SA node; ectopic beat
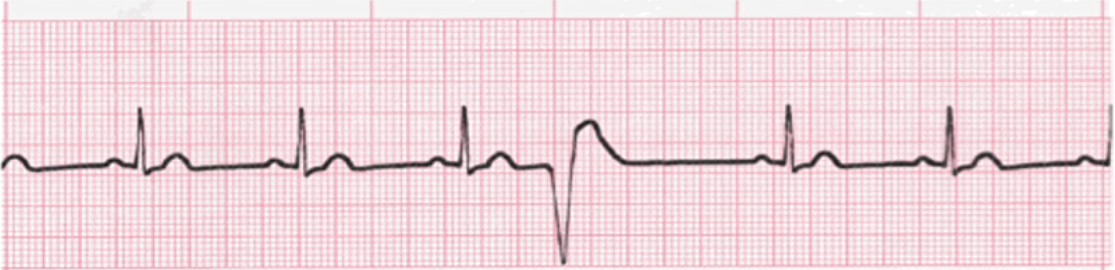
What does this EKG represent?
represents PVC
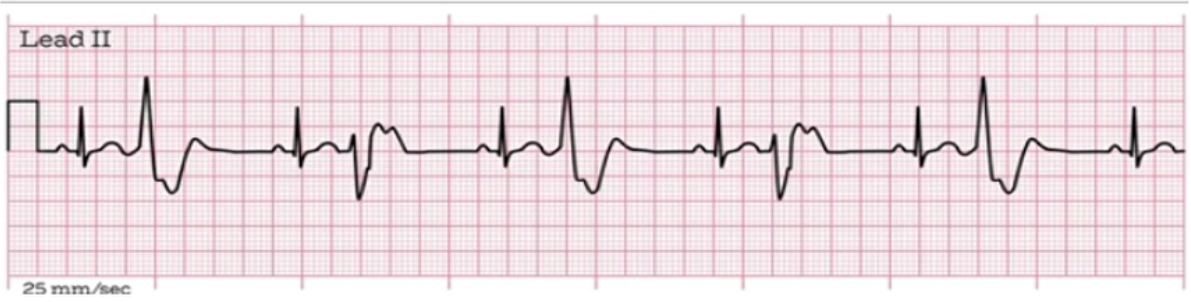
What does this EKG represent?
represents PVC bigeminy
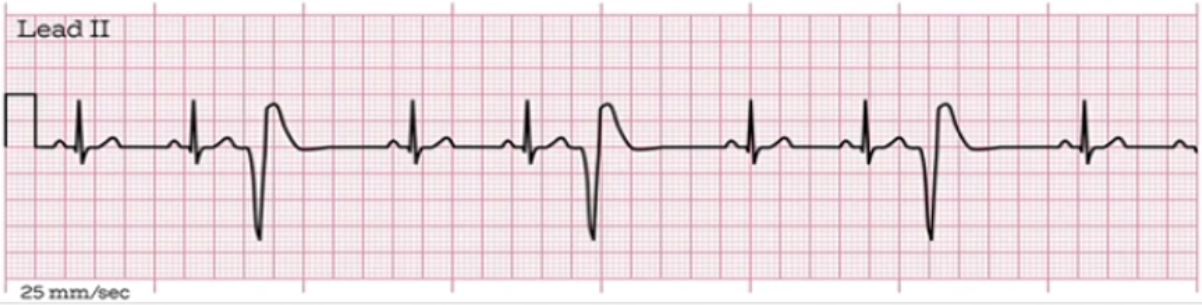
What does this EKG represent?
represents PVC trigeminy
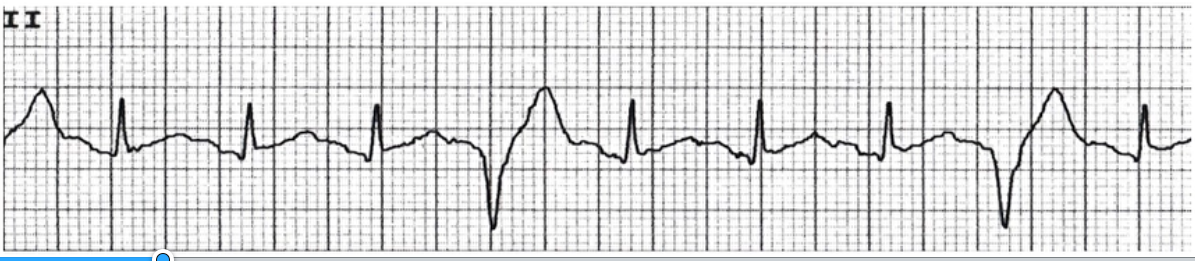
What does this EKG represent?
represents PVC quadrigeminy
What are the causes for PVC?
exercise, stress, too much caffeine, electrolyte imbalances, digoxin toxicity, hypoxia, MI, or most heart disease processes
What is the medical treatment for PVC?
treat underlying cause, such as eliminating caffeine, manage stress, correct electrolyte imbalance
What is “special” about Symptomatic PVCs?
they can be treated with beta blockers
How are Paced Rhythms represented?
via distinct pacing spikes
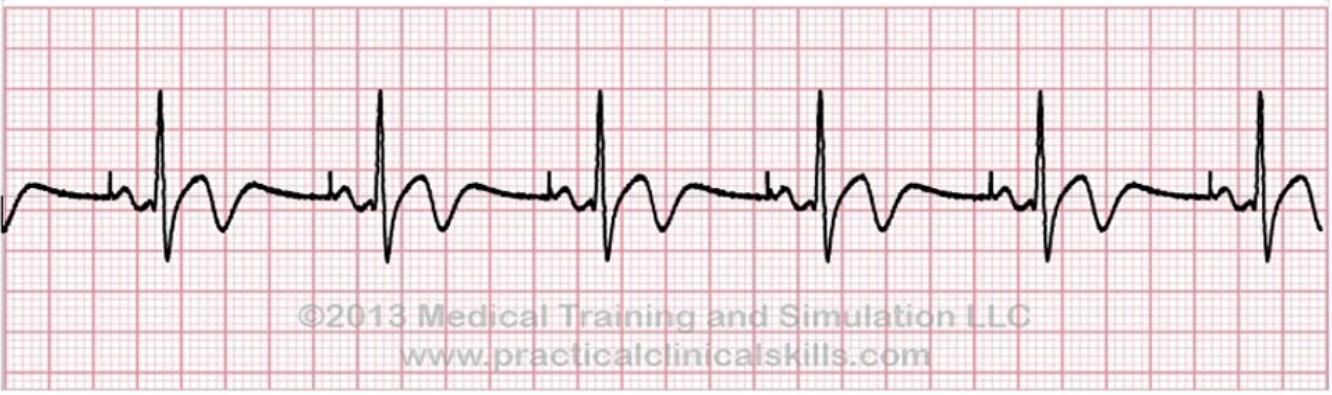
What does this EKG represent?
Paced Rhythm
What is the common demand for Paced Rhythm?
Demand Pacemakers; they send out electrical impulse when the heart rate falls below a preset rate
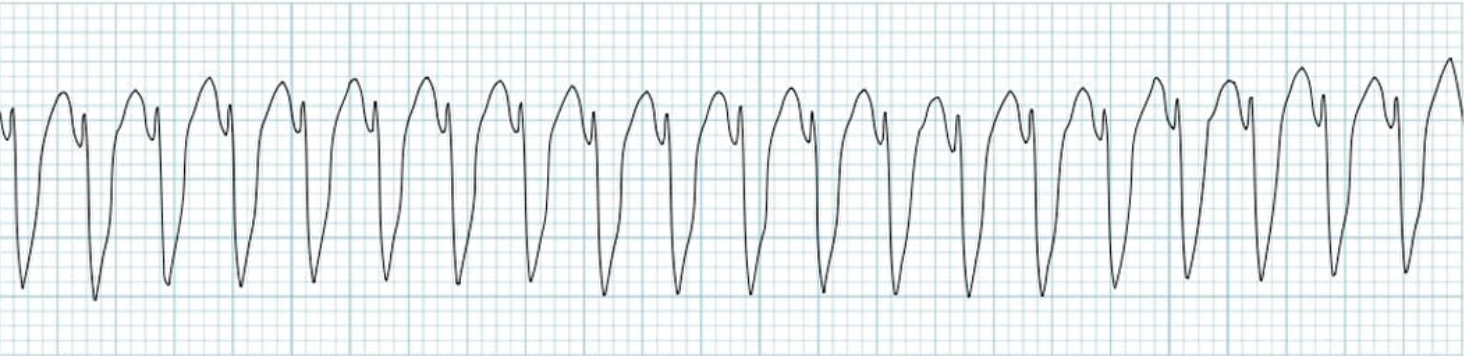
What does this EKG represent?
Ventricular Tachycardia
How can we identify Ventricular Tachycardia?
via wide QRS complexes, and we can’t really see and P waves / T waves due to the heart beating so quickly
What is Ventricular Tachycardia (VT)?
ventricles aren’t adequately pumping blood; LIFE THREATENING— SHOCKABLE RHYTHM
What are the causes for Ventricular Tachycardia?
ischemic heart disease, cardiomyopathy, congenital coronary artery abnormalities, cocaine and other drugs, digoxin toxicity, potassium imbalance
What are S/S of Ventricular Tachycardia?
patient might have dizziness, shortness of breath, chest pain, palpitations, or faint
What are some nursing interventions for Stable VT?
antiarrhythmic drugs such as sotalol or amiodarone. Carefully
monitor EKG, BP, and pulse
What are some nursing interventions for Unstable VT?
symptomatic patients are cardioverted, pulseless are defibrillated
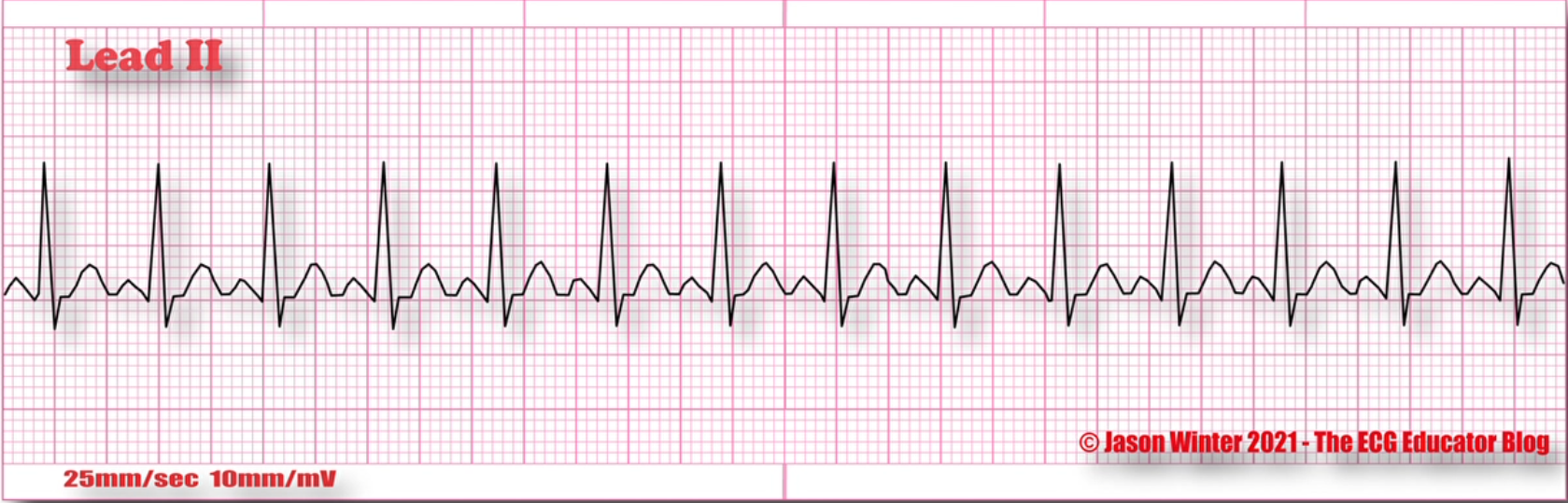
What does this EKG represent?
Sinus Tachycardia
What is Sinus Tachycardia?
rapid, regular rhythm originating in the SA node. It’s characterized by a heart rate about 100 BPM; Alarming above 150 BPM
What are the causes for Sinus Tachycardia?
exercise, anxiety, fever, shock, heart failure, excessive caffeine, drugs, and tobacco use
What is the medical treatment for Sinus Tachycardia?
vagal maneuvers, treating the underlying cause
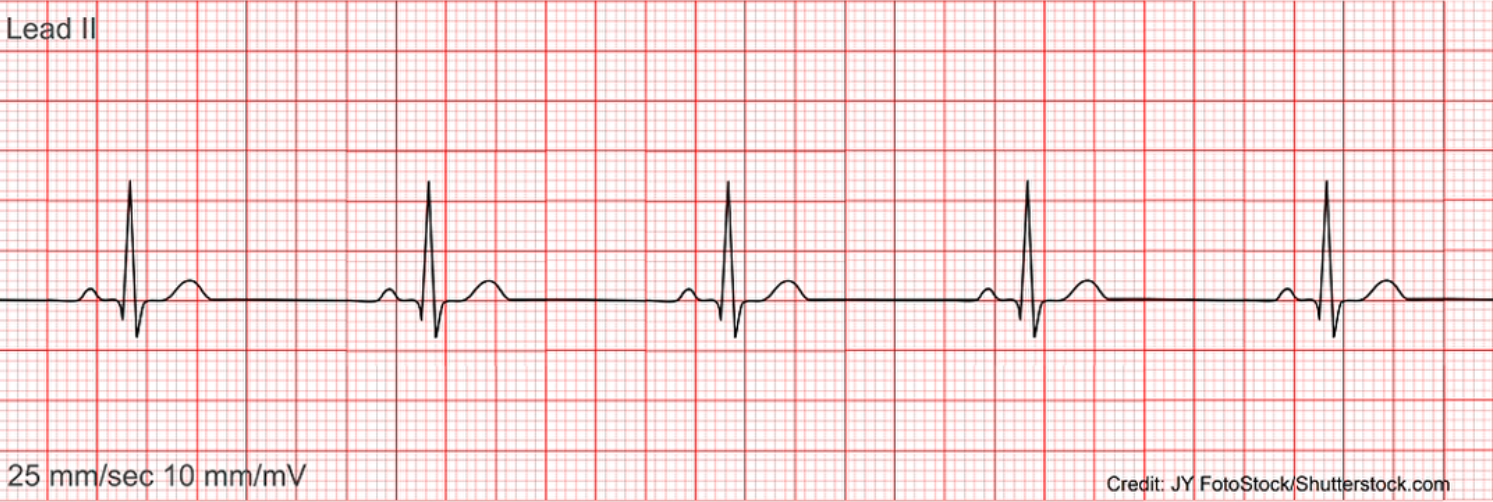
What does this EKG represent?
Sinus Bradycardia
What is Sinus Bradycardia?
slow rhythm that originates in the SA node. It is characterized by a heart rate less than 60 BPM
What are the causes for Sinus Bradycardia?
advancing age, inflammatory heart condition, hypothyroidism, myocardial infarction, normal resting rate for athletes, increased intracranial pressure, sinus node dysfunction, and medications (overdose of digoxin, beta blockers, and calcium channel blockers)
What is the medical treatment for Sinus Bradycardia?
treat underlying condition, atropine, or pacemaker
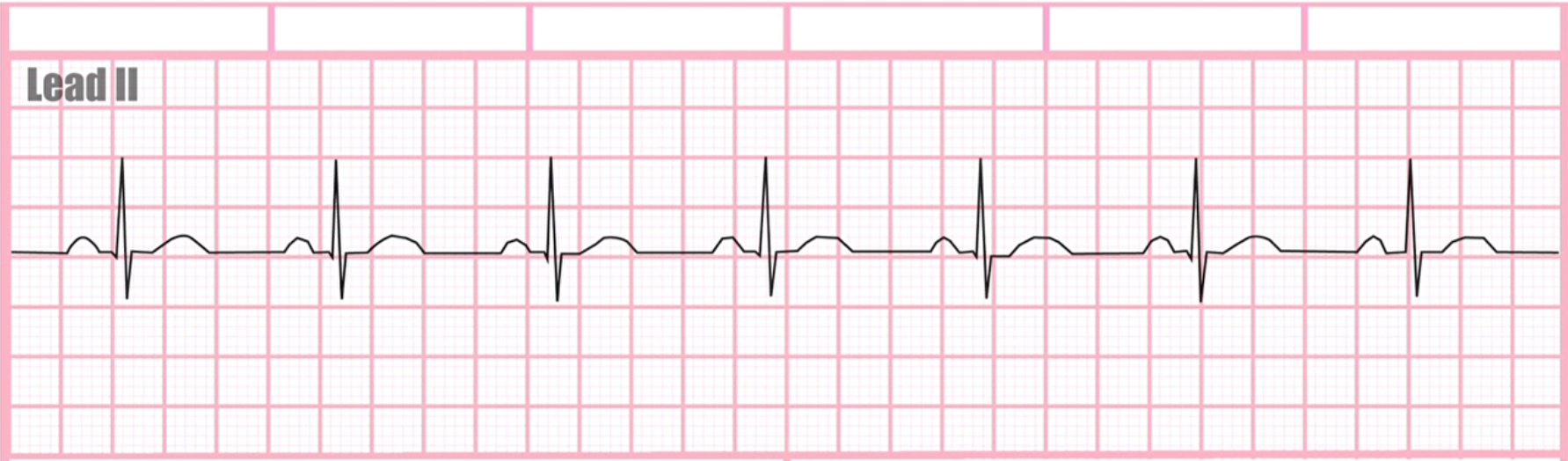
What does this EKG represent?
Sinus Rhythm
What is a Sinus Rhythm?
a regular rhythm with a rate of 60 - 100 BPM. There is a P wave before every QRS complex and a T wave after every QRS
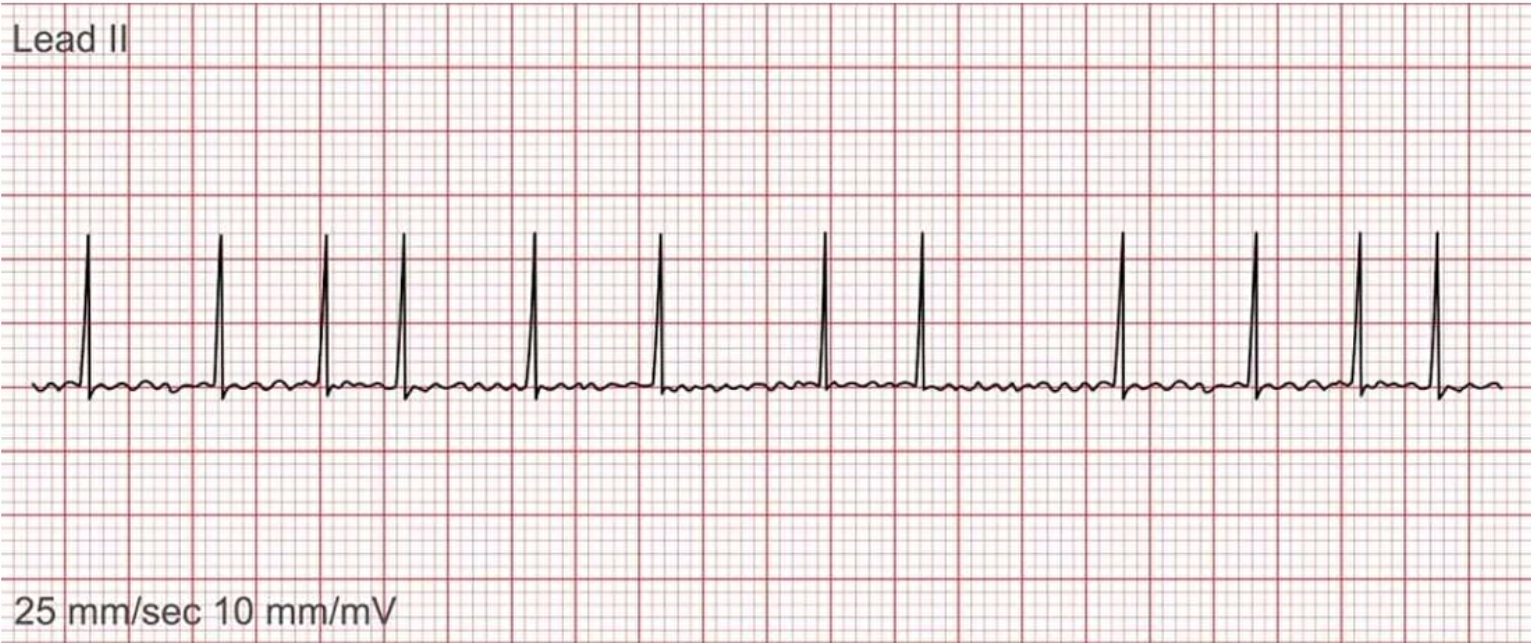
What does this EKG represent?
Atrial Fibrillation
What is Atrial Fibrillation characterized by?
wavy baseline, P waves irregular / absent - atria quivering with irregular QRS complexes
What are the causes of Atrial Fibillation?
advancing age, hypertension, alcohol consumption, diabetes, asthma, cardiomyopathy, MI, and cardiac surgery
What is the medical treatment for Atrial Fibrillation?
beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, digoxin, cardioversion, ablation, amiodarone
What do patients with Atrial Fibrillation have higher chance for?
clots, making them at risk for pulmonary embolus / stroke— likely need an anticoagulant

What does this EKG represent?
3rd Degree Heart Block (Complete Heart Block)
What is 3rd Degree Heart Block?
complete failure of the heart conduction system; the electrical signal from the atria isn’t making it to the ventricles— less QRS complexes
than P waves. No pattern or relationship noted between P waves to QRS.
“If your ps and qs don’t agree, then you have a 3rd degree”
What might the patient experience with 3rd Degree Heart Block?
hypotension, angina, and bradycardia; the HR is often 30 - 40 BPM
What is the medical treatment for 3rd Degree Heart Block?
atropine or pacemaker for irreversible heart blocks
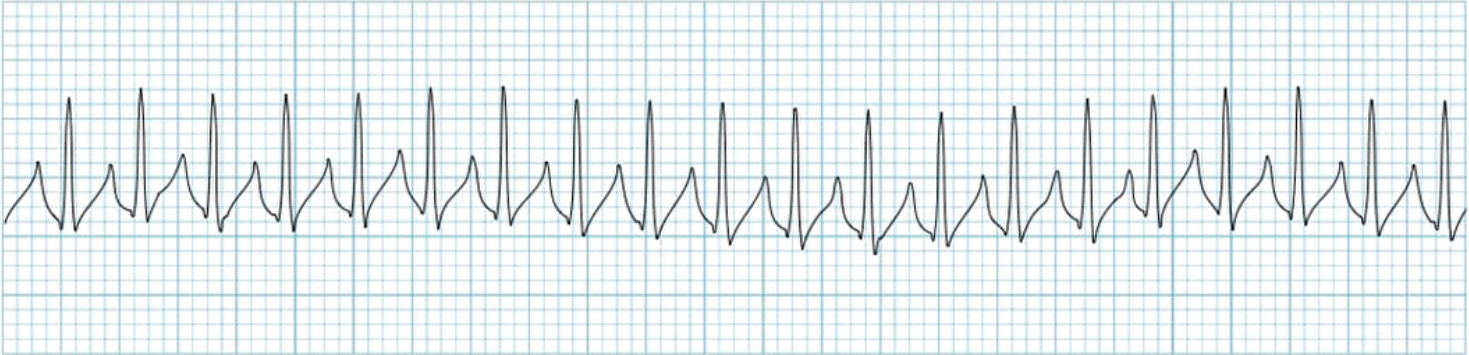
What does this EKG represent?
Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT)
What is SVT characterized by?
rate of 150 - 250 BPM. The P wave may be between, but is mostly hidden in the T wave.
What is the medical treatment for SVT?
vagal maneuvers (bearing down [valsalva maneuver] like having a BM / breathing thru a straw), adenosine, calcium channel blockers, or cardioversion
How does the cardioversion work regarding SVT?
involves delivering a synchronized electric shock to the heart using defibrillator pads or paddles. This is often done in a hospital setting under sedation
Why is the shock delivered on the R wave of the QRS complex for SVT?
if it lands on a T wave it could throw the patient into ventricular arrhythmia
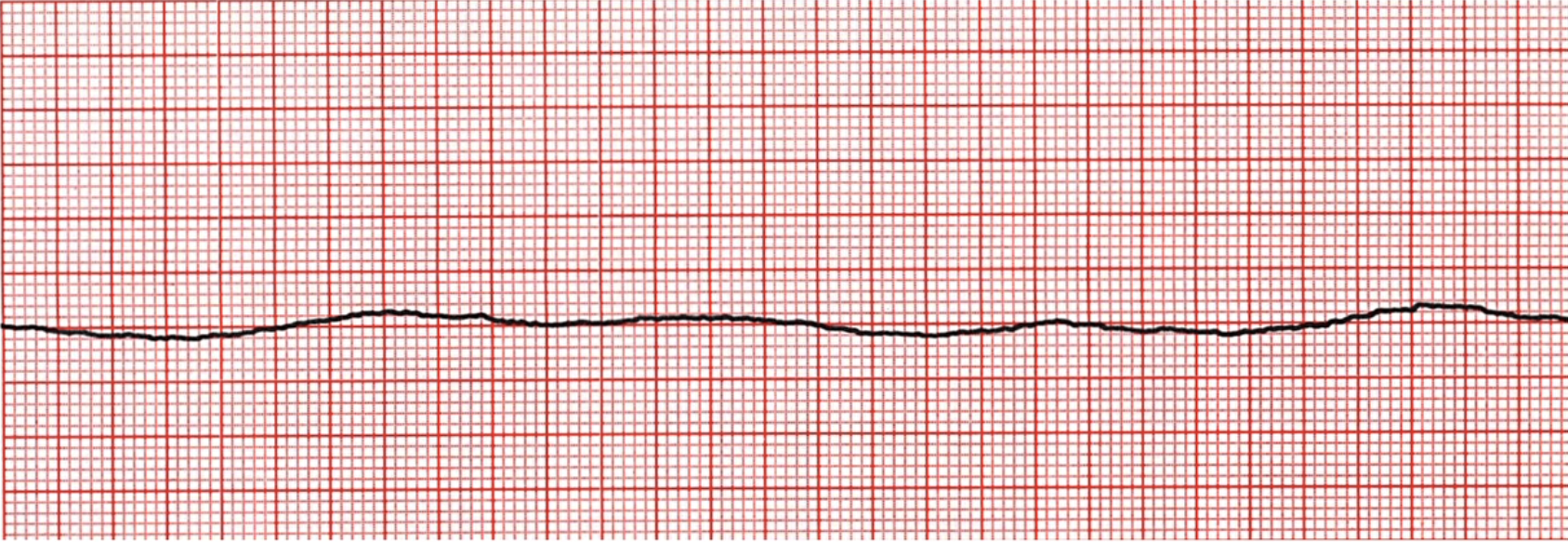
What does this EKG represent?
Asystole
What is Asystole?
the heart has no electrical activity and no pumping of the blood; looks like a flat line. This is LIFE THREATENING, and the heart needs to be restarted
What is the medical treatment for Asystole?
CPR and cardiac medications are given in hopes to restart the heart’s electrical activity and pump. DO NOT SHOCK THIS RHYTHM!
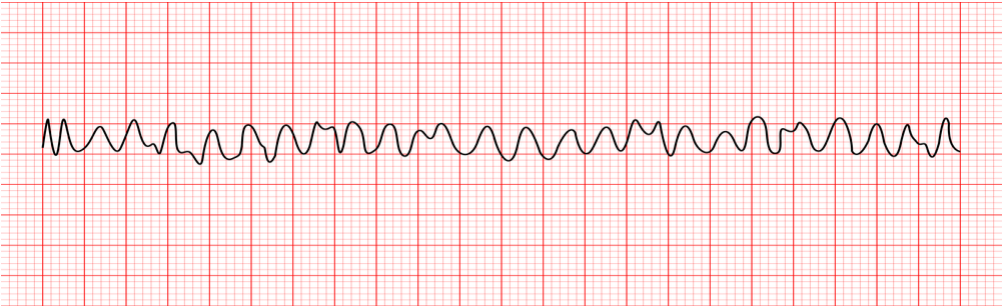
What does this EKG represent?
Ventricular Fibrillation
What is Ventricular Fibrillation?
quivering of the ventricles instead of coordinated forceful contraction. LIFE THREATENING— ALWAYS PULSELESS aka SHOCKABLE
What is Ventricular Fibrillation caused by?
CAD resulting in Myocardial Infarction (MI), untreated VT, previous MI, cardiomyopathy, illegal drugs
What is the medical treatment for Ventricular Fibrillation?
immediate defibrillation. Ideally within 15-20 seconds of onset and CPR
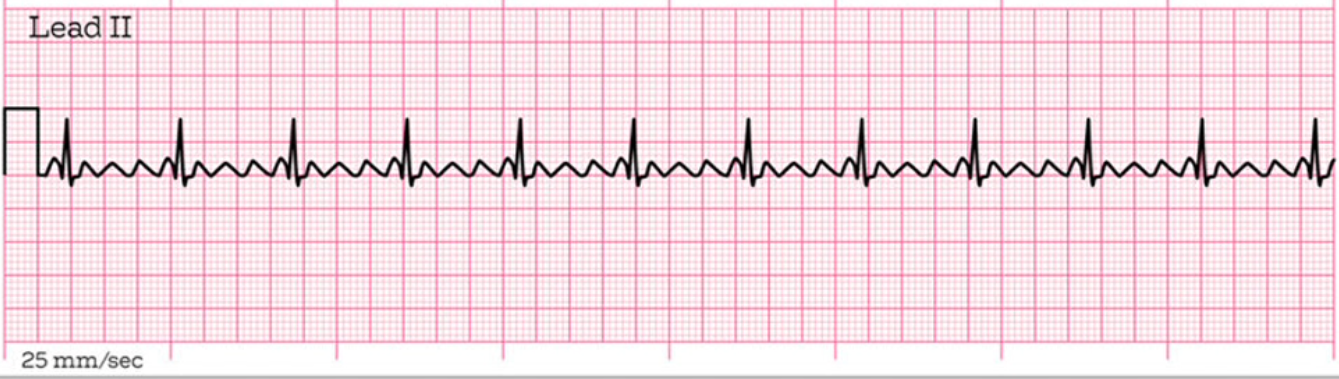
What does this EKG represent?
Atrial Flutter
What is Atrial Flutter?
multiple P waves for every QRS complex causes “flutter waves”. It’s treated similarly to Atrial Fibrillation.
often described as “sawtooth” pattern
What is the medical treatment for Atrial Flutter?
beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, digoxin, cardioversion, or ablation. Patient should be on anticoagulants to prevent thrombus
What is the medical treatment for Ventricular Tachycardia?
amiodarone, epipen if they have no pulse